Preparation of Stable Superhydrophobic Coatings on Wood Substrate Surfaces via Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine and Electroless Deposition Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Superhydrophobic Wood Surfaces
2.3. Characterizations
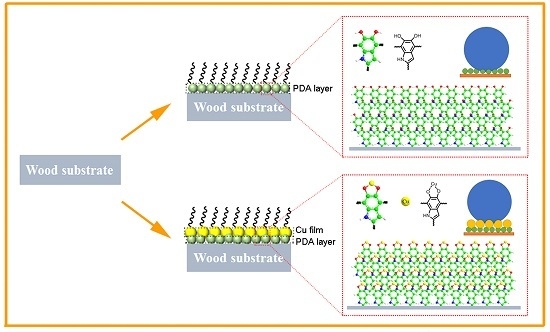
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation Process and Reaction Mechanism
3.2. Micromorphology and Chemical Component Analysis
3.3. Superhydrophobic Property and Stability
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zimmermann, J.; Reifler, F.A.; Fortunato, G.; Gerhardt, L.C.; Seeger, S. A simple, one-step approach to durable and robust superhydrophobic textiles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 3662–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstner, R.; Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C.; Walzel, P. Wetting and self-cleaning properties of artificial superhydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 2005, 21, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Yan, X.; Yao, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Jiang, L. The dry-style antifogging properties of mosquito compound eyes and artificial analogues prepared by soft lithography. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 2213–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Wong, T.S.; Alvarenga, J.; Kreder, M.J.; Adorno-Martinez, W.E.; Aizenberg, J. Liquid-infused nanostructured surfaces with extreme anti-ice and anti-frost performance. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6569–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Szunerits, S.; Xu, W.; Boukherroub, R. Preparation of superhydrophobic coatings on zinc as effective corrosion barriers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 1150–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guix, M.; Orozco, J.; García, M.; Gao, W.; Sattayasamitsathit, S.; Merkoçi, A.; Escarpa, A.; Wang, J. Superhydrophobic alkanethiol-coated microsubmarines for effective removal of oil. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4445–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Chu, S.; Lv, P.; Duan, H. Importance of hierarchical structures in wetting stability on submersed superhydrophobic surfaces. Langmuir 2012, 28, 9440–9450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassie, A.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed-Ziegler, I.; Tánczos, I.; Hórvölgyi, Z.; Agoston, B. Water-repellent acylated and silylated wood samples and their surface analytical characterization. Colloids Surf. A 2008, 319, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Tu, K.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Facile preparation of stable superhydrophobic coatings on wood surfaces using silica-polymer nanocomposites. BioResources 2015, 10, 2585–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, G.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Wang, C. Fabrication of superhydrophobic wood surface by a sol-gel process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 258, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Qing, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liang, J.; Luo, S. Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces on wood substrates via a one-step hydrothermal process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 330, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Shi, J.; Wang, C. Fabrication of superhydrophobic wood surfaces via a solution-immersion process. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 258, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Mao, Y.; Gupta, M.; Gleason, K.K.; Rutledge, G.C. Superhydrophobic fabrics produced by electrospinning and chemical vapor deposition. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 9742–9748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renneckar, S.; Zhou, Y. Nanoscale coatings on wood: Polyelectrolyte adsorption and layer-by-layer assembled film formation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Tang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Breedveld, V.; Hess, D.W. Creation of superhydrophobic wood surfaces by plasma etching and thin-film deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 281, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jia, S.; Qing, Y.; Luo, S.; Liu, M. A versatile and efficient method to fabricate durable superhydrophobic surfaces on wood, lignocellulosic fiber, glass, and metal substrates. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 14111–14121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, C.P.; Merkel, D.R.; Laursen, C.M.; Brinckmann, S.A.; Yakacki, C.M. Copper-coated liquid-crystalline elastomer via bioinspired polydopamine adhesion and electroless deposition. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 1912–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plana, D.; Campbell, A.I.; Patole, S.N.; Shul, G.; Dryfe, R.A. Kinetics of electroless deposition: The copper-dimethylamine borane system. Langmuir 2010, 26, 10334–10340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondin, G.; Wisser, F.M.; Leifert, A.; Mohamed-Noriega, N.; Grothe, J.; Dörfler, S.; Kaskel, S. Metal deposition by electroless plating on polydopamine functionalized micro-and nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 411, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, D.; Hu, W. Patterning of metal films on arbitrary substrates by using polydopamine as a uv-sensitive catalytic layer for electroless deposition. Langmuir 2016, 32, 5285–5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Song, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. High-performance and fully renewable soy protein isolate-based film from microcrystalline cellulose via bio-inspired poly(dopamine) surface modification. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 4354–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Lai, Y. A review on special wettability textiles: Theoretical models, fabrication technologies and multifunctional applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xia, C.; Dong, Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, J.; Shi, S.; Cai, L. Soy protein isolate-based films reinforced by surface modified cellulose nanocrystal. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 80, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shang, B.; Hu, X.; Peng, B.; Deng, Z. Temperature control of mussel-inspired chemistry toward hierarchical superhydrophobic surfaces for oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1600727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Flammability and physical-mechanical properties assessment of wood treated with furfuryl alcohol and nano-SiO2. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2015, 73, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavagione, H.J.; Martínez, G.; Gómez, M.A. Synthesis of poly(vinyl alcohol)/reduced graphite oxide nanocomposites with improved thermal and electrical properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 5027–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Chen, L.; Zhu, J.; Hu, Z. Polydopamine particles for next-generation multifunctional biocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 7578–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Dong, Y.; Yan, Y.; Qi, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Preparation of mechanical abrasion and corrosion resistant bulk highly hydrophobic material based on 3-d wood template. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 98248–98256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Baginska, M.; White, S.R.; Sottos, N.R. Core–shell polymeric microcapsules with superior thermal and solvent stability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 10952–10956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Tang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Tu, Q.; Weng, Y.; Shen, R.; Huang, N. Improved immobilization of biomolecules to quinone-rich polydopamine for efficient surface functionalization. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 106, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, F.; Ma, M.; Zang, D.; Gao, Z. One-step synthesis of unique silica particles for the fabrication of bionic and stably superhydrophobic coatings on wood surface. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Bai, N.; Xu, L.; Tan, C.; Li, Q. Fabrication of superhydrophobic wood surface with enhanced environmental adaptability through a solution-immersion process. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 277, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Surface free energy and dynamic wettability of differently machined poplar woods. BioResources 2014, 9, 3088–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, R.; Guenthner, A.J.; Meuler, A.J.; Tuteja, A.; Cohen, R.E.; McKinley, G.H.; Haddad, T.S.; Mabry, J.M. Superoleophobic surfaces through control of sprayed-on stochastic topography. Langmuir 2012, 28, 9834–9841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzaneh, M.; Kulinich, S.; Volat, C. Hydrophobicity of fluoroalkylsilane-and alkylsilane-grafted surfaces. Surf. Sci. 2004, 573, 379–390. [Google Scholar]






| Type of Liquid Reference | Surface Free Energy (mJ/m2) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| () | () | ||||
| Distilled Water | 72.8 | 21.8 | 51.0 | 25.5 | 25.5 |
| Diiodomethane | 50.8 | 50.8 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Preparation of Stable Superhydrophobic Coatings on Wood Substrate Surfaces via Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine and Electroless Deposition Methods. Polymers 2017, 9, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9060218
Wang K, Dong Y, Zhang W, Zhang S, Li J. Preparation of Stable Superhydrophobic Coatings on Wood Substrate Surfaces via Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine and Electroless Deposition Methods. Polymers. 2017; 9(6):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9060218
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kaili, Youming Dong, Wei Zhang, Shifeng Zhang, and Jianzhang Li. 2017. "Preparation of Stable Superhydrophobic Coatings on Wood Substrate Surfaces via Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine and Electroless Deposition Methods" Polymers 9, no. 6: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9060218
APA StyleWang, K., Dong, Y., Zhang, W., Zhang, S., & Li, J. (2017). Preparation of Stable Superhydrophobic Coatings on Wood Substrate Surfaces via Mussel-Inspired Polydopamine and Electroless Deposition Methods. Polymers, 9(6), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9060218