Solubility and Efficiency of Rock Phosphate Fertilizers Partially Acidulated with Zeolite and Pillared Clay as Additives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phosphate Rocks and Additives
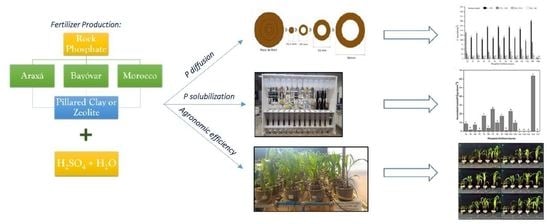
2.2. Fertilizer Production
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.4. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
2.5. Phosphorus Diffusion in Petri Dishes
2.6. Soil Columns P Solubilization
2.7. Plant Growth-Pot Experiment
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mineralogical and Structural Changes in Fertilizers
3.2. Phosphorus Diffusion
3.2.1. Changes in Soil pH by Phosphate Fertilizers
3.2.2. Available and Total P after Fertilizer Diffusion
3.3. Solubilization of Fertilizers in Soil Columns
3.3.1. Leaching Potential
3.3.2. Phosphorus Lability
3.4. Agronomic Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Treatments | Labile P | Moderately Labile P | Non-Labile P |
|---|---|---|---|
| mg Kg−1 | |||
| 0–1 cm | |||
| T1 | 709.6 a | 10618.3 b | 620.6 a |
| T2 | 555.2 c | 11779.9 a | 654.2 a |
| T3 | 647.9 b | 10206.3 b | 600.1 a |
| T4 | 588.6 c | 10268.8 b | 705.1 a |
| T5 | 609.3 b | 9797.2 c | 387.8 c |
| T6 | 479.8 d | 12343.4 a | 419.2 c |
| T7 | 583.3 c | 7776.2 c | 395.4 c |
| T8 | 390.4 e | 10360.9 b | 392.1 c |
| T9 | 624.7 b | 7840.0 c | 357.4 c |
| T10 | 520.6 d | 11000.6 b | 499.3 b |
| T11 | 567.0 c | 8171.4 c | 396.4 c |
| T12 | 329.3 f | 10381.0 b | 380.2 c |
| T13 | 140.5 h | 6152.8 d | 573.0 b |
| T14 | 191.0 g | 2773.1 e | 300.0 d |
| T15 | 213.6 g | 1523.4 f | 269.7 d |
| T16 | 638.8 b | 3548.3 e | 361.8 c |
| T17 | 21.9 i | 41.4 g | 197.9 d |
Appendix B
| Sources | Labile P (mg kg−1) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRTA | PiBIC | PoBIC | |||||||||||||
| 0–1 cm | 1–2 cm | 2–3 cm | 3–6 cm | 6–10 cm | 0–1 cm | 1–2 cm | 2–3 cm | 3–6 cm | 6–10 cm | 0–1 cm | 1–2 cm | 2–3 cm | 3–6 cm | 6–10 cm | |
| T1 | 220.7 a | 132.6 a | 139.5 b | 129.7 b | 89.6 d | 400.9 a | 74.2 b | 75.3 c | 80.2 a | 51.1 d | 88.6 a | 42.9 a | 16.8 a | 14.5 b | 10.6 a |
| T2 | 183.9 b | 108.0 b | 95.7 c | 93.3 c | 72.7 e | 322.3 c | 70.7 b | 61.6 d | 49.6 b | 39.3 e | 48.8 b | 30.0 b | 3.7 b | 17.6 a | 14.9 a |
| T3 | 190.6 b | 132.5 a | 151.4 b | 132.1 b | 107.1 b | 396.2 a | 81.0 a | 86.0 b | 76.6 a | 59.8 b | 61.0 a | 32.2 b | 20.1 a | 11.9 b | 14.5 a |
| T4 | 184.6 b | 111.6 b | 106.1 c | 98.6 c | 83.5 d | 336.5 b | 68.8 b | 66.5 d | 51.4 b | 42.1 e | 67.3 a | 31.3 b | 12.4 b | 13.4 b | 14.4 a |
| T5 | 208.1 a | 133.1 a | 154.8 b | 140.0 b | 123.8 a | 369.7 b | 79.5 a | 80.9 c | 77.5 a | 59.1 b | 61.1 a | 32.4 b | 19.7 a | 24.6 a | 19.6 a |
| T6 | 157.4 b | 106.4 b | 104.5 c | 98.6 c | 097.6 c | 269.8 d | 59.5 c | 62.6 d | 54.4 b | 50.7 d | 52.5 b | 25.9 b | 12.9 b | 18.4 a | 15.4 a |
| T7 | 207.0 a | 132.0 a | 137.0 b | 132.8 b | 113.1 b | 280.8 d | 72.2 b | 76.3 c | 76.1 a | 58.6 b | 95.4 a | 27.9 b | 7.7 b | 19.1 a | 13.8 a |
| T8 | 139.9 c | 88.6 c | 96.6 c | 98.3 c | 86.2 d | 156.4 e | 60.4 c | 61.0 d | 55.4 b | 48.1 d | 94.0 a | 18.5 c | 2.8 b | 14.2 b | 10.8 a |
| T9 | 245.7 a | 137.8 a | 143.1 b | 130.7 b | 112.5 b | 312.8 c | 74.4 b | 70.2 d | 67.8 a | 53.4 c | 66.0 a | 10.2 d | 26.4 a | 15.9 b | 11.0 a |
| T10 | 171.2 b | 83.0 c | 86.0 c | 89.7 c | 71.3 e | 296.6 c | 50.9 d | 50.0 e | 50.3 b | 35.7 f | 52.6 b | 5.0 d | 10.2 b | 21.0 a | 15.2 a |
| T11 | 217.0 a | 140.3 a | 186.6 a | 137.4 b | 119.8 a | 269.0 d | 72.1 b | 76.7 c | 74.1 a | 54.3 c | 80.9 a | 7.8 d | 16.4 a | 10.5 b | 14.2 a |
| T12 | 136.6 c | 88.3 c | 77.7 c | 92.3 c | 92.7 c | 120.8 f | 46.0 e | 38.0 f | 49.8 b | 41.1 e | 71.7 a | 7.0 d | 26.5 a | 18.7 a | 13.5 a |
| T13 | 72.4 d | 50.2 d | 55.4 d | 67.3 d | 76.0 e | 34.7 g | 35.4 f | 33.6 f | 39.8 c | 39.8 e | 33.3 b | 5.1 d | 20.1 a | 28.4 a | 12.2 a |
| T14 | 100.4 d | 39.0 d | 49.1 d | 63.9 d | 70.2 e | 51.3 g | 31.0 f | 36.1 f | 42.9 c | 39.5 e | 39.1 b | 5.3 d | 13.8 b | 17.4 a | 10.7 a |
| T15 | 134.2 c | 39.3 d | 49.1 d | 57.5 d | 67.0 e | 37.1 g | 31.0 f | 33.3 f | 39.5 c | 39.5 e | 42.1 b | 6.4 d | 11.5 b | 14.6 b | 12.9 a |
| T16 | 229.7 a | 130.5 a | 139.4 b | 157.4 a | 128.8 a | 361.2 b | 72.3 b | 94.0 a | 87.9 a | 63.5 a | 47.8 b | 9.6 d | 15.4 a | 26.4 a | 12.9 a |
| T17 | 0.7 e | 0.5 e | 0.2 e | 0.3 e | 0.4 f | 4.0 h | 3.7 g | 5.4 g | 6.0 d | 2.3 g | 17.0 b | 1.1 d | 8.1 b | 3.5 b | 2.7 b |
Appendix C
| Sources | Moderately Labile P (mg kg−1) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PiHid0.1 | PoHid0.1 | PHCl | |||||||||||||
| 0–1 cm | 1–2 cm | 2–3 cm | 3–6 cm | 6–10 cm | 0–1 cm | 1–2 cm | 2–3 cm | 3–6 cm | 6–10 cm | 0–1 cm | 1–2 cm | 2–3 cm | 3–6 cm | 6–10 cm | |
| T1 | 2227.6 b | 91.9 b | 92.8 a | 82.5 c | 66.8 e | 771.3 a | 22.0 c | 49.3 b | 36.9 b | 31.9 b | 7619.2 b | 3.0 a | 1.7 c | 1.5 b | 5.5 a |
| T2 | 1348.3 c | 89.6 b | 77.3 c | 69.5 e | 57.6 f | 302.1 c | 18.6 c | 36.0 c | 29.2 b | 23.2 c | 10129.4 a | 3.1 a | 1.3 d | 1.4 b | 3.5 a |
| T3 | 2690.5 a | 99.5 a | 100.8 a | 90.2 b | 78.5 c | 831.9 a | 10.2 d | 51.9 b | 38.9 b | 28.3 b | 6683.8 b | 3.6 a | 1.7 c | 1.7 b | 4.6 a |
| T4 | 914.8 d | 89.7 b | 87.1 b | 72.0 d | 63.5 e | 414.5 c | 4.8 d | 38.8 c | 27.5 b | 20.1 c | 8939.4 a | 2.9 a | 1.2 d | 1.5 b | 4.9 a |
| T5 | 1340.6 c | 99.8 a | 102.1 a | 91.7 b | 76.3 c | 518.5 b | 16.8 c | 49.4 b | 39.1 b | 22.0 c | 6879.2 b | 3.5 a | 1.8 c | 2.0 b | 5.2 a |
| T6 | 907.1 d | 90.7 b | 82.1 b | 73.3 d | 72.6 d | 264.8 c | 1.2 d | 35.2 c | 28.2 b | 21.6 c | 11171.3 a | 2.6 a | 1.5 c | 2.2 a | 4.5 a |
| T7 | 677.2 d | 99.9 a | 97.0 a | 87.2 b | 88.7 b | 308.5 c | 11.2 d | 42.7 c | 35.4 b | 22.6 c | 6790.4 b | 3.2 a | 1.8 c | 1.9 b | 1.6 b |
| T8 | 359.4 e | 87.0 b | 84.1 b | 77.2 d | 87.8 b | 292.3 c | 8.2 d | 37.3 c | 42.2 b | 22.8 c | 9709.0 a | 2.0 b | 1.7 c | 1.5 b | 1.0 b |
| T9 | 1049.0 d | 96.3 a | 104.6 a | 84.0 c | 88.6 b | 261.0 c | 53.2 a | 37.5 c | 31.0 b | 29.8 b | 6529.9 b | 1.8 b | 2.0 b | 2.9 a | 1.0 b |
| T10 | 850.0 d | 82.0 c | 78.3 c | 72.4 d | 74.1 d | 222.4 c | 37.8 b | 41.9 c | 26.7 b | 32.9 b | 9928.1 a | 0.7 c | 1.4 d | 1.7 b | 0.7 b |
| T11 | 307.0 e | 90.7 b | 97.0 a | 88.4 b | 90.7 b | 357.6 c | 58.7 a | 50.0 b | 31.3 b | 34.6 b | 7506.7 b | 1.2 c | 2.0 b | 2.0 b | 1.2 b |
| T12 | 186.6 e | 73.6 d | 75.2 c | 73.7 d | 79.0 c | 343.1 c | 35.7 b | 37.7 c | 30.2 b | 34.1 b | 9851.1 a | 0.7 c | 1.3 d | 1.4 b | 0.9 b |
| T13 | 66.2 f | 62.6 e | 64.2 d | 64.3 e | 77.8 c | 296.5 c | 38.9 b | 37.3 c | 31.9 b | 34.9 b | 5789.9 b | 1.7 b | 2.6 a | 2.8 a | 2.0 b |
| T14 | 57.6 f | 54.7 f | 61.7 d | 67.2 e | 77.1 c | 276.3 c | 33.8 b | 44.7 c | 29.4 b | 39.7 b | 2439.1 c | 2.1 b | 2.7 a | 2.9 a | 2.2 b |
| T15 | 45.5 f | 54.1 f | 59.8 d | 64.1 e | 72.9 d | 282.0 c | 29.5 b | 38.5 c | 35.0 b | 47.6 a | 1195.8 d | 1.9 b | 2.5 a | 2.7 a | 2.3 b |
| T16 | 2136.6 b | 97.3 a | 101.2 a | 99.4 a | 96.5 a | 511.7 b | 45.3 a | 72.3 a | 57.0 a | 49.7 a | 899.8 d | 1.8 b | 2.4 a | 2.6 a | 1.9 b |
| T17 | 12.4 f | 12.3 g | 10.3 e | 11.3 f | 10.6 g | 28.5 d | 0.3 d | 14.9 d | 2.6 c | 0.0 d | 0.5 e | 0.1 c | 0.1 e | 0.3 c | 0.3 b |
Appendix D
| Sources | Non-Labile P (mg kg−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Presidual | |||||
| 0–1 cm | 1–2 cm | 2–3 cm | 3–6 cm | 6–10 cm | |
| T1 | 620.6 a | 122.5 ns | 128.6 b | 138.8 a | 133.0 a |
| T2 | 654.2 a | 122.3 | 123.7 b | 142.7 a | 99.0 b |
| T3 | 600.0 a | 126.5 | 130.6 b | 146.4 a | 107.4 b |
| T4 | 705.1 a | 122.8 | 129.0 b | 127.2 b | 104.1 b |
| T5 | 387.7 c | 125.8 | 131.3 b | 148.5 a | 112.6 a |
| T6 | 419.1 c | 129.5 | 129.7 b | 137.6 a | 123.4 a |
| T7 | 395.3 c | 125.3 | 138.3 b | 149.9 a | 116.3 a |
| T8 | 392.1 c | 123.0 | 133.9 b | 142.5 a | 118.9 a |
| T9 | 357.4 c | 135.0 | 148.0 a | 149.4 a | 114.4 a |
| T10 | 499.3 b | 128.1 | 155.0 a | 129.7 b | 115.1 a |
| T11 | 396.4 c | 136.0 | 155.4 a | 141.3 a | 117.5 a |
| T12 | 380.1 c | 118.6 | 147.8 a | 138.1 a | 117.0 a |
| T13 | 572.9 b | 128.1 | 144.5 a | 149.4 a | 121.0 a |
| T14 | 300.0 d | 127.2 | 146.2 a | 141.1 a | 119.1 a |
| T15 | 269.7 d | 129.3 | 136.0 b | 138.3 a | 120.5 a |
| T16 | 361.7 c | 133.0 | 138.1 b | 149.4 a | 119.8 a |
| T17 | 94.8 d | 111.4 | 113.5 b | 109.8 c | 106.7 b |
Appendix E

References
- Lambers, H.; Plaxton, W.C. Phosphorus: Back to the roots. In Phosphorus Metabolism in Plants; Plaxton, W.C., Lambers, H., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, T.L.; Johnston, A.E. Phosphorus use efficiency and management in agriculture. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2015, 105, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Bai, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F. Phosphorus dynamics: From soil to plant. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- [USGS] United States Geological Survey. 2015 Minerals Yearbook: Phosphate Rock [Advance Release]. 2015. Available online: https://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/commodity/phosphate_rock/myb1-2015-phosp.pdf (accessed on 13 March 2019).
- Jarvie, H.P.; Sharpley, A.N.; Flaten, D.; Kleinman, P.J.A.; Jenkins, A.; Simmons, T. The pivotal role of phosphorus in a resilient water–energy–food security nexus. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 1049–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliari, P.H.; Strock, J.S.; Rosen, C.J. Changes in soil pH and extractable phosphorus following application of Turkey manure incinerator ash and triple superphosphate. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2010, 41, 1502–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, A.; Panhwar, Q.A.; Naher, U.A.; Rajput, S.; Hossain, E.; Shamshuddin, J. Influence of incubation period, temperature and different phosphate levels on phosphate adsorption in soil. Am. J. Agric. Biol. Sci. 2014, 9, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biswas, D.R.; Narayanasamy, G. Characterization of Partially Acidulated Phosphate Rocks. J. Indian Soc. Soil Sci. 1995, 43, 618–623. [Google Scholar]
- Cekinski, E. Fertilizantes Fosfatados [Phosphate fertilizers]. In Tecnologia de Produção de Fertilizantes [Fertilizer Production Technology]; Cekinski, E., Calmonovici, C.E., Bichara, J.M., Fabiani, M., Giulietti, M., Castro, M.L.M.M., Silveira, P.B.M., Pressionotti, Q.S.H.C., Guardani, R., Eds.; Instituto de Pesquisas Tecnológicas: São Paulo, Brazil, 1990; pp. 95–129. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Pickering, H.W.; Menzies, N.W.; Hunter, M.N. Zeolite/rock phosphate—A novel slow release phosphorus fertiliser for potted plant production. Sci. Hortic. 2002, 94, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-X.; Liao, Z.-W. Study on structural characteristics of pillared clay modified phosphate fertilizers and its increase efficiency mechanism. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2005, 6, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- [USDA-NRCS] United States Department of Agriculture—Natural Resources Conservation Service. Soil Survey Laboratory Methods Manual (SSIR 42), 4th ed.; USDA-NRCS: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Farkas, A.; Rozic, M.; Barbaric-Mikocevic, Z. Ammonium exchange in leakage waters of waste dumps using natural zeolite from the Krapina region, Croatia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 117, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, V.V.H.; Novais, R.F.; Dias, L.E.; Oliveira, J.A. Determinação e uso do fósforo remanescente [Determination and use of phosphorus remnants]. Soc. Bras. Ciênc. Solo Inf. Rep. 2000, 25, 27–33. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Mehra, O.P.; Jackson, M.L. Iron oxide removal from soils and clays by a dithionite-citrate system buffered with sodium bicarbonate. Clay Clay Miner. 1960, 7, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, S.; Deshpande, K. Alumina pillared montmorillonite: Characterization and catalysis of toluene benzylation and aniline ethylation. Appl. Catal. A-Gen. 2000, 193, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- [MAPA] Ministério da Agricultura Pecuária e Abastecimento—Brasil [Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock, and Supply—Brazil]. Manual de Métodos Analíticos Oficiais para Fertilizantes, Corretivos, Inoculantes, Substratos e Contaminantes [Official Analytical Methods Manual for Correctives, Inoculants, Substrates and Contaminants]; MAPA: Brasília, Brazil, 2007. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Degryse, F.; Mclaughlin, M.J. Phosphorus Diffusion from Fertilizer: Visualization, Chemical Measurements, and Modeling. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- [USDA-NRCS] United States Department of Agriculture—Natural Resources Conservation Service. Soil Taxonomy: A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys, 2nd ed.; Agriculture Handbook, 436; USDA-NRCS: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- [EMBRAPA] Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária [Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation]. Sistema Brasileiro de Classificação de Solos [Soil Classification System in Brazil], 3rd ed.; Embrapa Soils: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2013. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.R.; Sommers, L.E. Phosphorus. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Page, A.L., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 403–430. [Google Scholar]
- Hedley, M.J.; Stewart, J.W.B.; Chauhan, B.S. Changes in inorganic and organic soil phosphorus fractions induced by cultivation practices and by laboratory incubations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condron, L.M.; Goh, K.M.; Newman, R.H. Nature and distribution of soil phosphorus as revealed by a sequential extraction method followed by 31P nuclear magnetic resonance analysis. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1985, 36, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malavolta, E.; Vitti, G.C.; Oliveira, S.A. Avaliação do Estado Nutricional das Plantas: Principios E Aplicações [Assessment of the Nutritional Status of Plants: Principles and Applications], 2nd ed.; Potafos: Piracicaba, Brazil, 1997. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, E.B.; Cavalcanti, P.P.; Nogueira, D.A. ExpDes: Experimental Designs Package. R Package Version 1.1.2. 2013. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/ExpDes.pt/index.html (accessed on 6 October 2018).
- R Core Team. R: A language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2017; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 6 October 2018).
- Mattiello, E.M.; Resende Filho, I.D.P.; Barreto, M.S.; Soares, A.R.; Silva, I.R.; Vergütz, L.; Melo, L.C.A.; Soares, E.M.B. Soluble phosphate fertilizer production using acid effluent from metallurgical industry. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, W.O.; Hesterberg, D.; Mattiello, E.M.; Vergütz, L.; Barreto, M.S.C.; Silva, I.R.; Souza Filho, L.F.S. Increasing Soluble Phosphate Species by Treatment of Phosphate Rocks with Acidic Waste. J. Environ. Qual. 2016, 45, 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Dissolution mechanism of calcium apatites in acids: A review of literature. World J. Methodol. 2012, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesar, F.R.C.F. Eficiência Agronômica de Misturas no Mesmo Grânulo de Fosfatos Acidulados, Fosfatos Naturais e Enxofre Elementar [Efficiencies in Agronomics of Same Granule Mixtures in Acidulated Phosphates, Natural Phosphates, and Elementary Sulphurs]. Ph.D. Thesis, Luiz de Queiroz College of Agriculture—University of São Paulo, Piracicaba, Brazil, 2016. (In Portuguese). [Google Scholar]
- Hettiarachchi, G.M.; Lombi, E.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Chittleborough, D.; Self, P. Density changes around phosphorus granules and fluid bands in a Calcareous Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, W.L.; Frazier, A.W.; Stephenson, H.F. Identification of reaction products from phosphate fertilizers in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1962, 26, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo, D.; Degryse, F.; Mclaughlin, M.J. Fluid Fertilizers Improve Phosphorus Diffusion but not Lability in Andisols and Oxisols. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombi, E.; Mclaughlin, M.J.; Johnston, C.; Armstrong, R.D.; Holloway, R.E. Mobility, solubility and lability of fluid and granular forms of P fertiliser in calcareous and non-calcareous soils under laboratory conditions. Plant Soil 2004, 269, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombi, E.; Mclaughlin, M.J.; Johnston, C.; Armstrong, R.D.; Holloway, R.E. Mobility and lability of phosphorus from granular and fluid monoamonium phosphate differs in a calcareous soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2004, 68, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.C. Eficiência Agronômica de Fertilizantes Fosfatados Com Solubilidade Variada [Agronomic Efficiencies of Phosphate Fertilizers with Variable Solubility]. Ph.D. Thesis, Luiz de Queiroz College of Agriculture—University of São Paulo, Piracicaba, Brazil, 2013. (In Portuguese). [Google Scholar]
- Nascimento, C.A.C.; Pagliari, P.H.; Faria, L.A.; Vitti, G.C. Phosphorus mobility and behavior in soils treated with calcium, ammonium and magnesium phosphates. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2018, 82, 622–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerozi, B.S.; Fitzsimmons, K. The effect of pH on phosphorus availability and speciation in an aquaponics nutrient solution. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golden, D.C.; Stewart, R.B.; Tillman, R.W.; White, R.E. Partially acidulated reactive phosphate rock (PAPR) fertilizer and its reactions in soil—II. Mineralogy and morphology of the reaction products. Fertil. Res. 1991, 28, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.H. Reactions of surface applied superphosphate with soil II. Movement of the phosphorus and sulphur into the soil. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1971, 9, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesworth, W.; Van Straaten, P.; Smith, P.; Sadura, S. Solubility of apatite in clay and zeolite bearing systems: Application to agriculture. Appl. Clay Sci. 1987, 2, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, M.A.P. Influência do Silício Sobre a Difusão do Fósforo no Solo e na Eficiência Agronômica de Fertilizantes Fosfatados Granulados [Influence of Silicon on Phosphorus Diffusion in the Soil and on Agronomic Efficiency of Granulated Phosphate Fertilizers]. Master’s Thesis, Center of Nuclear Energy in Agriculture—University of São Paulo, Piracicaba, Brazil, 2016. (In Portuguese). [Google Scholar]
- Degryse, F.; Baird, R.; Da Silva, R.C.; Mclaughlin, M.J. Dissolution rate and agronomic effectiveness of struvite fertilizers – effect of soil pH, granulation and base excess. Plant Soil 2017, 410, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouldin, D.R.; Dement, J.D.; Sample, E.C. Interaction between dicalcium and monoammonium phosphates granulated together. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1960, 8, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbi, D.K.; Gilkes, R.J. The movement into soil of P from superphosphate grains and its availability to plants. Fertil. Res. 1987, 12, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatiboni, L.C.; Kaminski, J.; Rheinheimer, D.S.; Flores, J.P.C. Biodisponibilidade de formas de fósforo acumuladas em solo sob sistema plantio direto [Bioavailability of forms of phosphorus accumulated in soil under a direct planting system]. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2007, 31, 691–699. (In Potuguese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavinato, P.S.; Merlin, A.; Rosolem, C.A. Phosphorus fractions in Brazilian Cerrado soils as affected by tillage. Soil Tillage Res. 2009, 105, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiecher, T.; Rheinheimer, D.S.; Kaminski, J.; Calegari, A. Forms of inorganic phosphorus in soil under different long-term soil tillage systems and winter crops. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 2012, 36, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coelho, M.J.A.; Aguiar, A.C.F.; Sena, V.G.L.; Moura, E.G. Utilization and fate of phosphorus of different sources applied to cohesive soil of Amazonian periphery. Sci. Agric. 2017, 74, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shanableh, A.M.; Elsergany, M.M. Removal of phosphate from water using six Al-, Fe-, and Al-Fe-modified bentonite adsorbents. J. Environ. Sci. Health A 2013, 48, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolan, N.S. A critical review on the role of mycorrhizal fungi in the uptake of phosphorus by plants. Plant Soil 1991, 134, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltangheisi, A.; Moraes, M.T.; Cherubin, M.R.; Alvarez, D.O.; Souza, L.F.; Bieluczyk, W.; Navroski, D.; Teles, A.P.B.; Pavinato, P.S.; Martinelli, L.A.; et al. Forest conversion to pasture affects soil phosphorus dynamics and nutritional status in Brazilian Amazon. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 194, 104330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redel, Y.D.; Rubio, R.; Rouanet, J.L.; Borie, F. Phosphorus bioavailability affected by tillage and crop rotation on a Chilean volcanic derived Ultisol. Geoderma 2007, 139, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Pavinato, P.S.; Withers, P.J.A.; Teles, A.P.B.; Herrera, W.F.B. Legacy phosphorus and no tillage agriculture in tropical oxisols of the Brazilian savanna. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, A.P.B.; Rodrigues, M.; Herrera, W.F.B.; Soltangheisi, A.; Sartor, L.R.; Withers, P.J.A.; Pavinato, P.S. Do cover crops change the lability of phosphorus in a clayey subtropical soil under different phosphate fertilizers? Soil Use Manag. 2017, 33, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khasawneh, F.E.; Doll, E.C. The use of phosphate rock for direct application to soils. Adv. Agron. 1978, 30, 159–206. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, S.H.; Menon, R.G. Factors affecting the agronomic effectiveness of phosphate rock for direct application. Fertil. Res. 1995, 41, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, S.S.S.; Brown, M.W.; Boyes, M.K.; Upsdell, M.P. Extractable phosphorus to predict agronomic effectiveness of ground and unground phosphate rocks. Fertil. Res. 1992, 32, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, N.; Meurer, E.J. Eficiência agronômica de fosfatos naturais. In Simpósio Sobre Fósforo na Agricultura Brasileira; Potafos/Anda: Piracicaba, Brazil, 2003; CD-ROM. [Google Scholar]
- Beura, K.; Padbhushan, R.; Pradhan, A.K.; Mandal, N. Partial acidulation of phosphate rock for enhanced phosphorus availability in alluvial soils of Bihar. J. Nat. Appl. Sci. 2016, 8, 1393–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.H.; Prochnow, L.I.; Tu, S.; Snyder, C.S. Agronomic and environmental aspects of phosphate fertilizers varying in source and solubility: An update review. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2011, 89, 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, L.L.; Chien, S.H.; Mokwunye, A.U. Agronomic Value of Unacidulated and Partially Acidulated Phosphate Rocks Indigenous to the Tropics. Adv. Agron. 1986, 40, 89–140. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, D.; Sale, P.W.; Johnson, D. Agronomic effectiveness of a partially acidulated reactive phosphate rock fertiliser. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1997, 37, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Bennoah, E.; Zapata, F.; Fardeau, J.C. Comparison of greenhouse and 32P isotopic laboratory methods for evaluating the agronomic effectiveness of natural and modified rock phosphates in some acid soils of Ghana. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2002, 63, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.; Herrera, J. Field evaluation of partially acidulated phosphate rocks in a Ferralsol from Cuba. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2002, 63, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizane, A.; Rehamnia, R. Study of some parameters to obtain the P2O5 water- soluble from partially acidulated phosphate rocks (PAPRs) by sulfuric acid. Phosphorus Res. Bull. 2012, 27, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nkebiwe, P.M.; Weinmann, M.; Bar-Tal, A.; Müller, T. Fertilizer placement to improve crop nutrient acquisition and yield: A review and meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2016, 196, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Rock Phosphate | Phosphorus (P2O5) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | PCA 2% (1:100; w/v) | H2O | |||||||||
| % | |||||||||||
| Araxá (ARP) | 29.9 | 5.7 | 0.03 | ||||||||
| Bayovar (BRP) | 28.9 | 14.8 | 0.02 | ||||||||
| Morocco (MRP) | 30.0 | 9.0 | 0.08 | ||||||||
| Additives | SiO2 | Al2O3 | K2O | Fe2O3 | MgO | TiO2 | Na2O | CEC | MPAC 3 | ||
| % | mmolc kg−1 | mg kg−1 | |||||||||
| Pillared clay | 35.7 | 23.7 | 0.2 | 6.6 | 4.0 | 0.5 | 0.04 | 676 1 | 5527 | ||
| Zeolite | 51.3 | 14.6 | 1.5 | 1.9 | 3.3 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 1450 2 | 31 | ||
| Fertilizers | Treatment | Phosphorus Level (P2O5) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | H2O | NAC + H2O | PCA 2% | ||
| % | |||||
| ARP + PILC + 50% acidulation | 1 | 20.1 | 2.6 | 7.6 | 5.5 |
| ARP + PILC + 25% acidulation | 2 | 23.3 | 1.4 | 5.0 | 4.7 |
| ARP + Zeo + 50% acidulation | 3 | 20.3 | 2.1 | 9.2 | 5.6 |
| ARP + Zeo + 25% acidulation | 4 | 23.5 | 1.4 | 5.0 | 4.8 |
| BRP + PILC + 50% acidulation | 5 | 21.7 | 3.3 | 6.9 | 8.1 |
| BRP + PILC + 25% acidulation | 6 | 23.6 | 1.3 | 4.6 | 8.4 |
| BRP + Zeo + 50% acidulation | 7 | 21.2 | 6.3 | 8.0 | 11.0 |
| BRP + Zeo + 25% acidulation | 8 | 23.7 | 1.7 | 3.9 | 6.2 |
| MRP + PILC + 50% acidulation | 9 | 21.6 | 3.6 | 6.4 | 8.9 |
| MRP + PILC + 25% acidulation | 10 | 23.7 | 1.1 | 3.6 | 7.8 |
| MRP + Zeo + 50% acidulation | 11 | 22.0 | 6.1 | 6.1 | 9.6 |
| MRP + Zeo + 25% acidulation | 12 | 24.0 | 2.2 | 3.2 | 7.4 |
| Granulometry | CBD | Oxalate | MPAC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay | Silt | Sand | Fed | Ald | Feox | Alox | |||
| g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | ||||||||
| 75 | 37 | 888 | 5.13 | 0.99 | 0.31 | 1.39 | 157 | ||
| pH | P resin | S | H + Al | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | K+ | BS | CEC | V |
| CaCl2 | mg dm−3 | mmolc dm−3 | % | ||||||
| 5.2 | 4 | 142 | 12 | 21 | 6 | 1.7 | 28.7 | 40.7 | 71 |
| Granulometry | CBD | Oxalate | MPAC | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clay | Silt | Sand | Fed | Ald | Feox | Alox | |||||||
| g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | ||||||||||||
| 180 | 90 | 730 | 9.11 | 1.99 | 0.27 | 1.41 | 295 | ||||||
| pH | OM | P resin | Al3+ | H + Al | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | K+ | BS | CEC | m | V | ||
| CaCl2 | g dm−3 | mg dm−3 | mmolc dm−3 | % | |||||||||
| 5.1 | 3 | <3 | <2 | 11 | 9 | 3 | <0.9 | 12.1 | 23.1 | 14 | 52 | ||
| Treatments | Dry Matter (g) | Accumulated P (mg pot−1) | RAE (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoot | Root | Shoot | Root | ||
| T1 | 7.8 d | 4.5 b | 3.7 c | 2.6 c | 56.9 |
| T2 | 4.1 e | 3.0 c | 2.1 c | 1.5 c | 26.8 |
| T3 | 5.8 e | 5.6 b | 3.2 c | 4.5 b | 40.7 |
| T4 | 4.4 e | 3.7 c | 2.4 c | 2.1 c | 29.3 |
| T5 | 11.8 b | 6.8 a | 6.4 b | 3.6 b | 89.4 |
| T6 | 5.7 e | 4.7 b | 2.8 c | 2.3 c | 39.8 |
| T7 | 10.0 c | 7.0 a | 4.8 b | 6.5 a | 74.8 |
| T8 | 5.9 e | 4.8 b | 3.2 c | 2.2 c | 41.5 |
| T9 | 10.2 c | 7.8 a | 5.9 b | 4.8 b | 76.4 |
| T10 | 4.9 e | 3.7 c | 2.7 c | 1.9 c | 33.3 |
| T11 | 11.3 b | 7.2 a | 4.9 b | 4.2 b | 85.4 |
| T12 | 5.0 e | 4.1 c | 2.6 c | 1.6 c | 34.1 |
| T13 | 0.9 f | 0.9 d | 0.5 d | 0.4 d | 0.8 |
| T14 | 5.3 e | 3.9 c | 3.0 c | 1.8 c | 36.6 |
| T15 | 2.1 f | 2.1 d | 1.2 d | 0.9 d | 10.6 |
| T16 | 13.1 a | 5.8 b | 14.3 a | 3.9 b | 100.0 |
| T17 | 0.8 f | 0.6 d | 0.3 d | 0.1 d | -- |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teles, A.P.B.; Rodrigues, M.; Pavinato, P.S. Solubility and Efficiency of Rock Phosphate Fertilizers Partially Acidulated with Zeolite and Pillared Clay as Additives. Agronomy 2020, 10, 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10070918
Teles APB, Rodrigues M, Pavinato PS. Solubility and Efficiency of Rock Phosphate Fertilizers Partially Acidulated with Zeolite and Pillared Clay as Additives. Agronomy. 2020; 10(7):918. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10070918
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeles, Ana Paula Bettoni, Marcos Rodrigues, and Paulo Sergio Pavinato. 2020. "Solubility and Efficiency of Rock Phosphate Fertilizers Partially Acidulated with Zeolite and Pillared Clay as Additives" Agronomy 10, no. 7: 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10070918
APA StyleTeles, A. P. B., Rodrigues, M., & Pavinato, P. S. (2020). Solubility and Efficiency of Rock Phosphate Fertilizers Partially Acidulated with Zeolite and Pillared Clay as Additives. Agronomy, 10(7), 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10070918