Effects of Sublethal Doses of Methyl Benzoate on the Life History Traits and Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity of Aphis gossypii
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects and Reagents
2.2. Sublethal Effects of Methyl Benzoate on the Cotton Aphid F0 Generation
2.3. Transgenerational Effects of Methyl Benzoate on the Cotton Aphid F1 Generation
2.4. Preparation of Cotton Aphid Proteins
2.5. Determination of Acetylcholinesterase Activity
2.6. Molecular Docking Analysis of the Protein-Ligand
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
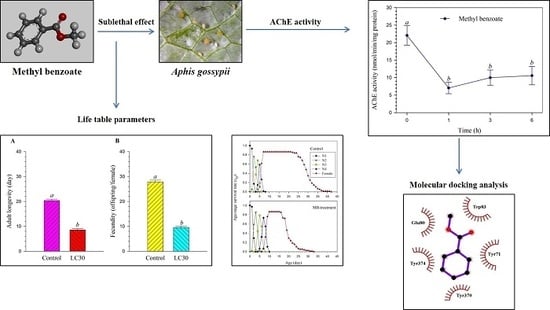
3.1. Sublethal Effects of Methyl Benzoate on the F0 Generation
3.2. Sublethal Effects of Methyl Benzoate on the F1 Generation
3.3. Transgenerational Effects of Methyl Benzoate on Population Parameters
3.4. Transgenerational Effects of Methyl Benzoate on Age-Stage Specific Rate of Survival and Fecundity
3.5. Effect of Methyl Benzoate on AChE Activity
3.6. Protein–Ligand Molecular Docking Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blackman, R.L.; Eastop, V.F. Aphids on the World’s Crops: An. Identification and Information Guide, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Carletto, J.; Martin, T.; Vanlerberghe-Masutti, F.; Brévault, T. Insecticide resistance traits differ among and within host races in Aphis gossypii. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.S.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Liang, P.Z.; Chen, X.W.; Gao, X.W. Identification of microRNAs and their response to the stress of plant allelochemicals in Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae). BMC Mol. Biol. 2017, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, R.B.; Parajulee, M.N. Potential cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii, population suppression by arthropod predators in upland cotton. Insect Sci. 2013, 20, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Pan, Y.; Xin, X.; Zheng, C.; Gao, X.; Xi, J.; Shang, Q. Cross-resistance pattern and basis of resistance in a thiamethoxam-resistant strain of Aphis gossypii Glover. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 138, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, J.; Cook, D.; Catchot, A.; Leonard, B.R.; Stewart, S.D.; Lorenz, G.; Kerns, D. Cotton aphid (Heteroptera: Aphididae) susceptibility to commercial and experimental insecticides in the southern United States. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, H.N.; An, J.J.; Park, S.E.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, G.H. Regional susceptibilities to 12 insecticides of melon and cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and a point mutation associated with imidacloprid resistance. Crop. Prot. 2014, 55, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Qi, H.; Yang, D.; Yuan, H.; Rui, C. Cycloxaprid: A novel cis-nitromethylene neonicotinoid insecticide to control imidacloprid-resistant cotton aphid (Aphis gossypii). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 132, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; Decourtye, A.; Delpuech, J.M. The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perveen, F.; Miyata, T. Effects of sublethal dose of chlorfluazuron on ovarian development and oogenesis in the common cutworm Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2000, 93, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desneux, N.; Wajnberg, E.; Fauvergue, X.; Privet, S.; Kaiser, L. Oviposition behaviour and patch-time allocation in two aphid parasitoids exposed to deltamethrin residues. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2004, 112, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ma, K.; Li, F.; Liang, P.; Liu, Y.; Guo, T.; Song, D.; Desneux, N.; Gao, X. Sublethal and transgenerational effects of sulfoxaflor on the biological traits of the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Desneux, N.; Sonoda, S.; Liang, P.; Han, P.; Gao, X.W. Sublethal and transgenerational effects of chlorantraniliprole on biological traits of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella L. Crop. Prot. 2013, 48, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.A.; Moscardini, V.F.; Da Costa Gontijo, P.; Carvalho, G.A.; De Oliveira, R.L.; De Oliveira, H.N. Sublethal and transgenerational effects of insecticides in developing Trichogramma galloi (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Biondi, A.; Desneux, N.; Gao, X.W. Assessment of physiological sublethal effects of imidacloprid on the mirid bug Apolygus lucorum (Meyer-Dü r). Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Lu, Y.; Xu, X.; Qian, X.; Wu, K.; Desneux, N. Lethal and sublethal effects of cycloxaprid, a novel cis-nitromethylene neonicotinoid insecticide, on the mirid bug Apolygus lucorum. J. Pest Sci. 2014, 87, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; You, M.; Atlıhan, R.; Smith, C.L.; Kavousi, A.; Özgökçe, M.S.; Güncan, A.; Tuan, S.J.; Fu, J.W.; Xu, Y.Y.; et al. Age-Stage, two-sex life table: An introduction to theory, data analysis, and application. Entomol. Gen. 2020, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, A. A floral fragrance methyl benzoate is an efficient green pesticide. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.I.; Naheed, N.; Abbaskhan, A.; Musharraf, S.G.; Siddiqui, H.; Atta-ur-Rahman. Phenolic and other constituents of fresh water fern Salvinia molesta. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, R. A structure-activity relationship for the estimation of rate constants for the gas-phase reactions of OH radicals with organic compounds. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 1987, 19, 799–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafiz, M.M.; Jhan, P.K.; Shim, J.K.; Lee, K.Y. Methyl benzoate exhibits insecticidal and repellent activities against Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius) (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafiz, M.M.; Hassan, E.; Shim, J.K.; Lee, K.Y. Insecticidal efficacy of three benzoate derivatives against Aphis gossypii and its predator Chrysoperla carnea. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 184, 109653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafiz, M.M.; Shim, J.K.; Hwang, H.S.; Bunch, H.; Lee, K.Y. Acaricidal effects of methyl benzoate against Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae) on common crop plants. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 2347–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafiz, M.M.; Hassan, E.; Shim, J.K.; Lee, K.Y. Lethal and sublethal effects of methyl benzoate on the predatory bug Nesidiocoris tenuis. Insects 2020, 11, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.J.; Cheng, W.X.; Ding, W.; Zhao, Z.M. The effect of the insecticide dichlorvos on esterase activity extracted from the psocids, Liposcelis bostrychophila and L. entomophila. J. Insect Sci. 2004, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weill, M.; Fort, P.; Berthomieu, A.; Dubois, M.P.; Pasteur, N.; Raymond, M. A novel acetylcholinesterase gene in mosquitoes codes for the insecticide target and is non–homologous to the ace gene Drosophila. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2002, 269, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Booth, L.H.; Wratten, S.D.; Kehrli, P. Effects of reduced rates of two insecticides on enzyme activity and mortality of an aphid and its lacewing predator. J. Econ. Entomol. 2007, 100, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harel, M.; Kryger, G.; Rosenberry, T.L.; Mallender, W.D.; Lewis, T.; Fletcher, R.J.; Guss, J.M.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L. Three-dimensional structures of Drosophila melanogaster acetylcholinesterase and of its complexes with two potent inhibitors. Protein Sci. 2000, 9, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Liu, H. Two new methods for the study of insect population ecology. Bull. Inst. Zool. Acad. Sin. 1985, 24, 225–240. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, H. Life-table analysis incorporating both sexes and variable development rates among individuals. Environ. Entomol. 1988, 17, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.; Su, H.Y. Age-stage, Two-sex life tables of Aphidius gifuensis (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and its host Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae) with mathematical proof of the relationship between female fecundity and the net reproductive rate. Environ. Entomol. 2006, 35, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.B.; Chi, H. Life tables of Bactrocera cucurbitae (Diptera: Tephritidae): With an invalidation of the jackknife technique. J. Appl. Entomol. 2013, 137, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H. TWOSEX-MSChart: A Computer Program for the Age-Stage, Two Sex Life Table Analysis; National Chung Hsing University: Taichung, Taiwan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R. An Introduction to the Bootstrap; Chapman and Hall/CRC: London, UK, 1994; p. 436. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.W.; Chi, H.; Smith, C.L. Linking demography and consumption of Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) fed on Solanum photeinocarpum (Solanales: Solanaceae): With a new method to project the uncertainty of population growth and consumption. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SAS Institute Inc. Base SAS 9.4 Procedures Guide, Statistical Procedures, 2nd ed.; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- SigmaPlot version 12.5. Systat Software, Inc., San Jose, California, USA. Available online: http://www.sigmaplot.co.uk/products/sigmaplot/sigmaplot-details.php (accessed on 2 September 2020).
- Gowthaman, U.; Jayakanthan, M.; Sundar, D. Molecular docking studies of dithionitrobenzoic acid and its related compounds to protein disulfide isomerase: Computational screening of inhibitors to HIV-1 entry. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hevener, K.E.; Zhao, W.; Ball, D.M.; Babaoglu, K.; Qi, J.; White, S.W.; Lee, R.E. Validation of molecular docking programs for virtual screening against dihydropteroate synthase. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2009, 49, 444–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, F.E.; Cantrell, C.L.; Duke, S.O. Natural products in crop protection. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 4022–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajashekar, Y.; Tonsing, N.; Shantibala, T.; Manjunath, J.R. 2, 3-Dimethylmaleic anhydride (3, 4-Dimethyl-2, 5-furandione): A plant derived insecticidal molecule from Colocasia esculenta var. esculenta (L.) Schott. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, A. Commercially available natural benzyl esters and their synthetic analogs exhibit different toxicities against insect pests. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Gul, H.; Yousaf, H.K.; Xiu, W.; Qian, D.; Gao, X.; Tariq, K.; Han, P.; Desneux, N.; Song, D. Impact of low lethal concentrations of buprofezin on biological traits and expression profile of chitin synthase 1 gene (CHS1) in melon aphid, Aphis gossypii. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, H.B.; Li, J.H.; Liu, Y.Q.; Cui, L.; Lu, Y.H.; Xu, X.Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, K.M.; Desneux, N. Lethal, sublethal and transgenerational effects of the novel chiral neonicotinoid pesticide cycloxaprid on demographic and behavioral traits of Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Insect Sci. 2017, 24, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wu, D.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G.; Wu, K. Sublethal effects of imidacloprid on Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) under laboratory conditions. J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rix, R.R.; Ayyanath, M.M.; Christopher Cutler, G. Sublethal concentrations of imidacloprid increase reproduction, alter expression of detoxification genes, and prime Myzus persicae for subsequent stress. J. Pest Sci. 2016, 89, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sial, M.U.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, L.; Jiang, H. Evaluation of insecticides induced hormesis on the demographic parameters of Myzus persicae and expression changes of metabolic resistance detoxification genes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyanath, M.M.; Cutler, G.C.; Scott-Dupree, C.D.; Sibley, P.K. Transgenerational shifts in reproduction hormesis in green peach aphid exposed to low concentrations of imidacloprid. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, E.M.G.; de Moura, I.L.T.; Fadini, M.A.M.; Guedes, R.N.C. Beyond selectivity: Are behavioral avoidance and hormesis likely causes of pyrethroid-induced outbreaks of the southern red mite Oligonychus ilicis? Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, Y.; Wang, K.; Lin, F.; Li, Y.; Peng, X.; Piñero, J.C.; Chen, M. Sublethal effects of indoxacarb and beta-cypermethrin on Rhopalosiphum padi (Hemiptera: Aphididae) under laboratory conditions. Florida Entomol. 2016, 99, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, E.; Liao, X.; Yang, P.; Mao, K.; Zhang, X.; Shakeel, M.; Salim, A.M.A.; Wan, H.; Li, J. Sublethal effects of buprofezin on development and reproduction in the white-backed planthopper, Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhao, C.Q.; Zhang, Y.N.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Z.Y. Lethal and sublethal effects of sulfoxaflor on the small brown planthopper Laodelphax striatellus. J. Asia. Pac. Entomol. 2016, 19, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, H.K.; Shan, T.; Chen, X.; Ma, K.; Shi, X.; Desneux, N.; Biondi, A.; Gao, X. Impact of the secondary plant metabolite cucurbitacin B on the demographical traits of the melon aphid, Aphis gossypii. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, P.W.; Sears, T.A. Action of methyl hydroxybenzoate on nervous conduction. Nature 1961, 192, 668–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opdyke, D.L.J. (Ed.) Monographs on Fragrance Raw Materials; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979; p. 537. [Google Scholar]
- Senthil Nathan, S.; Young Choi, M.; Yul Seo, H.; Hoon Paik, C.; Kalaivani, K.; Duk Kim, J. Effect of azadirachtin on acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity and histology of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 70, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Developmental Time (Days) of F1 Progeny | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biological Parameters | Control | Methyl Benzoate (LC30) | p | ||
| N | Mean ± SE a,b | N | Mean ± SE a,b | ||
| First instar (d) | 68 | 2.10 ± 0.05a | 67 | 2.31 ± 0.06b | 0.0108 |
| Second instar (d) | 66 | 1.55 ± 0.06a | 65 | 2.14 ± 0.06b | <0.0001 |
| Third instar (d) | 66 | 1.41 ± 0.06a | 65 | 2.15 ± 0.07b | <0.0001 |
| Fourth instar (d) | 65 | 1.14 ± 0.04a | 65 | 2.05 ± 0.06b | <0.0001 |
| Pre-adult (d) | 65 | 6.17 ± 0.08a | 65 | 8.68 ± 0.09b | <0.0001 |
| Pre-adult survival rate (sa) | 75 | 0.87 ± 0.039a | 75 | 0.87 ± 0.039a | 1.000 |
| Adult longevity (d) | 65 | 23.94 ± 0.45a | 65 | 12.0 ± 0.43b | <0.0001 |
| Total longevity (d) | 75 | 26.51 ± 1.14a | 75 | 18.21 ± 0.82b | <0.0001 |
| APRP (d) | 65 | 0.08 ± 0.04a | 65 | 0.65 ± 0.14b | <0.0001 |
| TPRP (d) | 65 | 6.25 ± 0.08a | 65 | 9.32 ± 0.16b | <0.0001 |
| Reproductive days (d) | 65 | 18.55 ± 0.31a | 65 | 8.69 ± 0.2b | <0.0001 |
| Fecundity (offspring/individual) | 65 | 35.2 ± 0.45a | 65 | 13.49 ± 0.26b | <0.0001 |
| Population Parameter a | Bootstrap (Mean ± SE b,c) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | MB (LC30) | ||
| r (d−1) | 0.2752 ± 0.0069a | 0.1793 ± 0.0048b | <0.0001 |
| λ (d−1) | 1.3169 ± 0.0092a | 1.1964 ± 0.0058b | <0.0001 |
| R0 (offspring/individual) | 30.51 ± 1.43a | 11.69 ± 0.57b | <0.0001 |
| T (d) | 12.42 ± 0.23a | 13.71 ± 0.24b | <0.0001 |
| GRR (offspring/individual) | 44.83 ± 1.63a | 21.92 ± 1.51b | <0.0001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mostafiz, M.M.; Alam, M.B.; Chi, H.; Hassan, E.; Shim, J.-K.; Lee, K.-Y. Effects of Sublethal Doses of Methyl Benzoate on the Life History Traits and Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity of Aphis gossypii. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091313
Mostafiz MM, Alam MB, Chi H, Hassan E, Shim J-K, Lee K-Y. Effects of Sublethal Doses of Methyl Benzoate on the Life History Traits and Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity of Aphis gossypii. Agronomy. 2020; 10(9):1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091313
Chicago/Turabian StyleMostafiz, Md Munir, Md Badrul Alam, Hsin Chi, Errol Hassan, Jae-Kyoung Shim, and Kyeong-Yeoll Lee. 2020. "Effects of Sublethal Doses of Methyl Benzoate on the Life History Traits and Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity of Aphis gossypii" Agronomy 10, no. 9: 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091313
APA StyleMostafiz, M. M., Alam, M. B., Chi, H., Hassan, E., Shim, J. -K., & Lee, K. -Y. (2020). Effects of Sublethal Doses of Methyl Benzoate on the Life History Traits and Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity of Aphis gossypii. Agronomy, 10(9), 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10091313