Genetic Diversity of Soybeans (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) with Black Seed Coats and Green Cotyledons in Korean Germplasm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Growth Conditions of BLG Germplasms
2.2. DNA Extraction and Determination of Genotyping for Soybean Accessions
2.3. Basic Population Genetic Parameters, Population Structure, and Construction of a Core Subset Accession
2.4. Genotyping Assays for D1, D2, and PsbM
2.5. Phenotype Determination by High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.6. Genome Wide Association Study (GWAS) for Anthocyanin
2.7. Statistical Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure
3.2. Construction of Core Collection
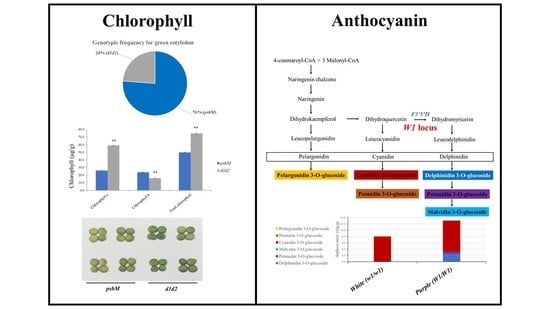
3.3. Frequency of the D1, D2, and PsbM Alleles and Their Relationship with the Chlorophyll Content in Cotyledon
3.4. GWAS for Anthocyanin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, K. Chemistry and nutritional value of soybean components. In Soybeans; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 25–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T. Science of Tofu, Chapter 2, Manufacture of Tofu; Food Journal Co. Ltd.: Kyoto, Japan, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Willcox, J.K.; Ash, S.L.; Catignani, G.L. Antioxidants and prevention of chronic disease. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2004, 44, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Chang, S.K. Antioxidant capacity of seed coat, dehulled bean, and whole black soybeans in relation to their distributions of total phenolics, phenolic acids, anthocyanins, and isoflavones. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8365–8373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, M.H.; Lee, S.S.; Jung, P.J.; Lee, M.H. Intake of fruits, vegetables, and soy foods in relation to breast cancer risk in Korean women: A case-control study. Nutr. Cancer 2007, 57, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, R.; Ohmori, R.; Kiyose, C.; Momiyama, Y.; Ohsuzu, F.; Kondo, K. Antioxidant activities of black and yellow soybeans against low density lipoprotein oxidation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4578–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, K.; Xu, B. A critical review on polyphenols and health benefits of black soybeans. Nutrients 2017, 9, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jhan, J.K.; Chung, Y.C.; Chen, G.H.; Chang, C.H.; Lu, Y.C.; Hsu, C.K. Anthocyanin contents in the seed coat of black soya bean and their anti-human tyrosinase activity and antioxidative activity. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2016, 38, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hymowitz, T.; Newell, C. Taxonomy, speciation, domestication, dissemination, germplasm resources, and variation in the genus Glycine. In Advances in Legume Science; Summerfield, R.J.B.A., Ed.; Royal Botanical Gardens: Richmond, UK, 1980; pp. 251–264. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzali, S.; Perata, P. Anthocyanins from Purple Tomatoes as Novel Antioxidants to Promote Human Health. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Masi, L.; Bontempo, P.; Rigano, D.; Stiuso, P.; Carafa, V.; Nebbioso, A.; Piacente, S.; Montoro, P.; Aversano, R.; D’Amelia, V.; et al. Comparative phytochemical characterization, genetic profile, and antiproliferative activity of polyphenol-rich extracts from pigmented tubers of different Solanum tuberosum varieties. Molecules 2020, 25, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Norberto, S.; Silva, S.; Meireles, M.; Faria, A.; Pintado, M.; Calhau, C. Blueberry anthocyanins in health promotion: A metabolic overview. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1518–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, T. Dietary anthocyanin-rich plants: Biochemical basis and recent progress in health benefits studies. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, S.J.; Tuteja, J.H.; Li, M.; Marek, L.F.; Shoemaker, R.C.; Vodkin, L.O. Features of a 103-kb gene-rich region in soybean include an inverted perfect repeat cluster of CHS genes comprising the I locus. Genome 2004, 47, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Todd, J.J.; Vodkin, L.O. Duplications that suppress and deletions that restore expression from a chalcone synthase multigene family. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kang, N.S.; Shin, S.O.; Shin, S.H.; Lim, S.G.; Suh, D.Y.; Baek, I.Y.; Park, K.Y.; Ha, T.J. Characterisation of anthocyanins in the black soybean (Glycine max L.) by HPLC-DAD-ESI/MS analysis. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choung, M.G.; Baek, I.Y.; Kang, S.T.; Han, W.Y.; Shin, D.C.; Moon, H.P.; Kang, K.H. Isolation and determination of anthocyanins in seed coats of black soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 5848–5851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendel, G. Versuche uber pflanzen-hybriden. Verh. Nat. Verein Brunn 1866, 4, 3–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.; Schellenberg, M.; Vicentini, F.; Matile, P. Gregor Mendel’s green and yellow pea seeds. Bot. Acta 1996, 109, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, O.E. Studies of inheritance in Pisum. II. The present state of knowledge of heredity and variation in peas. Proc. Am. Philos. Soc. 1917, 56, 487–588. [Google Scholar]
- Armstead, I.; Donnison, I.; Aubry, S.; Harper, J.; Hörtensteiner, S.; James, C.; Mani, J.; Moffet, M.; Ougham, H.; Roberts, L.; et al. Cross-species identification of Mendel’s I locus. Science 2007, 315, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, Y.; Morita, R.; Nishimura, M.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kusaba, M. Mendel’s green cotyledon gene encodes a positive regulator of the chlorophyll degrading pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14169–14174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Croce, R.; Van Amerongen, H. Natural strategies for photosynthetic light harvesting. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckhardt, U.; Grimm, B.; Hortensteiner, S. Recent advances in chlorophyll biosynthesis and breakdown in higher plants. Plant Mol. Biol. 2004, 56, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortensteiner, S.; Krautler, B. Chlorophyll breakdown in higher plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1807, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, H.; Howarth, C.J. Five ways to stay green. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Owen, F.V. Inheritance studies in soybeans. II. Glabrousness, color of pubescence, time of maturity, and linkage relations. Genetics 1927, 12, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terao, H. Maternal inheritance in the soybean. Am. Nat. 1918, 52, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Li, C.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, Y.; Wu, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, G.; Kong, L.A.; et al. Concerted evolution of D1 and D2 to regulate chlorophyll degradation in soybean. Plant J. 2014, 77, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiamet, J.J.; Schwartz, E.; Pichersky, E.; Nooden, L.D. Characterization of cytoplasmic and nuclear mutations affecting chlorophyll and chlorophyll-binding proteins during senescence in soybean. Plant Physiol. 1991, 96, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohzuma, K.; Sato, Y.; Ito, H.; Okuzaki, A.; Watanabe, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Nakano, M.; Yamatani, H.; Masuda, Y.; Nagashima, Y.; et al. The non-Mendelian green cotyledon gene in soybean encodes a small subunit of photosystem II. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 2138–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirata, T.; Abe, J.; Shimamoto, Y. Genetic structure of the Japanese soybean population. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 1999, 46, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.D.; Yu, J.K.; Hwang, Y.H.; Blake, S.; So, Y.S.; Lee, G.J.; Nguyen, H.T.; Shannon, J.G. Genetic diversity of wild soybean (Glycine soja Sieb. and Zucc.) accessions from South Korea and other countries. Crop Sci. 2008, 48, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.D.; Vuong, T.D.; Moon, H.; Yu, J.K.; Nelson, R.L.; Nguyen, H.T.; Shannon, J.G. Genetic diversity and population structure of Korean and Chinese soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] accessions. Crop Sci. 2011, 51, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Nelson, R.L. Genetic diversity among soybean accessions from three countries measured by RAPDs. Crop Sci 2001, 41, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Wen, Z.; Fan, X.; Li, Y.; Guan, R.; Guo, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, D.; Qiu, L. Comparison of genetic diversity between Chinese and American soybean (Glycine max (L.)) accessions revealed by high-density SNPs. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.H.; Abe, J.; Gai, J.Y.; Shimamoto, Y. Diversity of chloroplast DNA SSRs in wild and cultivated soybeans: Evidence for multiple origins of cultivated soybean. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 105, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, O.H.; Brown, A.H. Plant genetic resources today: A critical appraisal. In Crop Genetic Resources; Holden, J.H.W., Williams, J.T., Eds.; Allen and Unwin: London, UK, 1984; pp. 249–257. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.S.; Cao, Y.S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, S.C.; Wang, L.F.; You, G.X.; Pang, B.S.; Li, L.H.; Jia, J.Z. Establishment of candidate core collections in Chinese common wheat germplasm. J. Plant Genet. Resour. 2003, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Diwan, N.; McIntosh, M.S.; Bauchan, G.R. Methods of developing a core collection of annual Medicago species. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1995, 90, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, C.C.; Anderson, W.F. Evaluation of a core collection to identify resistance to late leafspot in peanut. Crop Sci. 1995, 35, 1700–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, P.; Su, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, Q.; Sun, K. Microsatellite diversity, population structure, and core collection formation in melon germplasm. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 33, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Ro, N.Y.; Jeong, H.J.; Kwon, J.K.; Jo, J.; Ha, Y.; Jung, A.; Han, J.W.; Venkatesh, J.; Kang, B.C. Genetic diversity and population structure analysis to construct a core collection from a large Capsicum germplasm. BMC Genet. 2016, 17, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.C.; Zhang, H.I.; Cao, Y.S.; Qiu, Z.E.; Wei, X.H.; Tang, S.X.; Yu, P.; Wang, X. Studies on the sampling strategy for primary core collection of Chinese ingenious rice. Acta Agron. Sin. 2003, 29, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Guan, Y.; Guan, R.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Dong, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. Establishment of Chinese soybean Glycine max core collections with agronomic traits and SSR markers. Euphytica 2006, 151, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Gao, J.; Du, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Pang, X. Identifying the genetic diversity, genetic structure and a core collection of Ziziphus jujuba Mill. var. jujuba accessions using microsatellite markers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Mei, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhu, J.; Gong, P. Sampling a core collection of island cotton (Gossypium barbadense L.) based on the genotypic values of fiber traits. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2006, 53, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhu, J.; Xu, H.M. Methods of constructing core collections by stepwise clustering with three sampling strategies based on the genotypic values of crops. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2000, 101, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.B.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.L. Genetic diversity and structure of core collection of winter mushroom (Flammulina velutipes) developed by genomic SSR markers. Hereditas 2018, 155, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hymowitz, T. The history of the soybean. In Soybeans: Chemistry, Production, Processing, and Utilization; Johnson, L.A., White, P.J., Galloway, R., Eds.; AOCS Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 2008; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Agrobiodiversity Center. Available online: http://genebank.rda.go.kr/ (accessed on 15 December 2020).
- Baek, I.Y.; Kang, S.T.; Shin, D.C.; Choung, M.G.; Han, W.Y.; Kwack, Y.H.; Moon, H.P. A new black soybean variety with green cotyledon, early maturity and large seed size “Cheongjakong”. Korean J. Breed Sci. 2001, 33, 240–241. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Choi, M.S.; Kim, H.T.; Yun, H.T.; Lee, B.; Chung, Y.S.; Kim, R.W.; Choi, H.K. Soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merrill]: Importance as a crop and pedigree reconstruction of Korean varieties. Plant Breed Biotech. 2015, 3, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fehr, W.R.; Caviness, C.E.; Burmood, D.T.; Pennington, J.S. Stage of development descriptions for soybeans, Glycine Max (L.) Merrill1. Crop Sci. 1971, 11, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.; Doyle, J.L. Genomic plant DNA preparation from fresh tissue-CTAB method. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Akond, M.; Liu, S.; Schoener, L.; Anderson, J.A.; Kantartzi, S.K.; Meksem, K.; Song, Q.; Wang, D.; Wen, Z.; Lightfoot, D.A.; et al. A SNP-based genetic linkage map of soybean using the SoySNP6K Illumina Infinium BeadChip genotyping array. J. Plant Genome Sci. 2013, 1, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Hyten, D.L.; Jia, G.; Quigley, C.V.; Fickus, E.W.; Nelson, R.L.; Cregan, P.B. Development and evaluation of SoySNP50K, a high-density genotyping array for soybean. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, K.; Muse, S.V. PowerMarker: An integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinform 2005, 21, 2128–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Sharma, D.; Tiwari, A.; Jaiswal, J.P.; Singh, N.K.; Sood, S. Genotyping-by-sequencing analysis for determining population structure of finger millet germplasm of diverse origins. Plant Genome 2016, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Wen, W.; Daniel, D. Documentation for Structure Software, version 2; University of Chicago: Chicago, IL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Jeong, S.C.; Kang, S.T.; Moon, J.K.; Kim, N. GenoCore: A simple and fast algorithm for core subset selection from large genotype datasets. PLoS ONE 2018, 12, e0181420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bradbury, P.J.; Zhang, Z.; Kroon, D.E.; Casstevens, T.M.; Ramdoss, Y.; Buckler, E.S. TASSEL: Software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinform 2007, 23, 2633–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ersoz, E.; Lai, C.Q.; Todhunter, R.J.; Tiwari, H.K.; Gore, M.A.; Bradbury, P.J.; Yu, J.; Arnett, D.K.; Ordovas, J.M.; et al. Mixed linear model approach adapted for genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Pressoir, G.; Briggs, W.H.; Bi, I.V.; Yamasaki, M.; Doebley, J.F.; McMullen, M.D.; Gaut, B.S.; Nielsen, D.M.; Holland, J.B.; et al. A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, N.; Kim, K.S.; Jeong, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, S.K.; Lee, J.S.; Jeong, S.C.; Kang, S.T.; Ha, B.K.; Kim, D.Y.; et al. Korean soybean core collection: Genotypic and phenotypic diversity population structure and genome-wide association study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, D.; Cheng, H.; Yin, Z.; Cui, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, H.; Yu, D. Identification of single nucleotide polymorphisms and haplotypes associated with yield and yield components in soybean (Glycine max) landraces across multiple environments. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 124, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.S.; Lee, J.; Kim, C.Y.; Kang, J.H.; Cho, E.G.; Baek, H.J. DNA profiling and genetic diversity of Korean soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) landraces by SSR markers. Euphytica 2009, 165, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Smulders, M.J.; Chang, R.Z.; Qiu, L.J. Genetic diversity and association mapping in a collection of selected Chinese soybean accessions based on SSR marker analysis. Conserv. Genet. 2011, 12, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gou, Z.; Lyu, J.; Li, W.; Yu, Y.; Shu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Y.; et al. Resequencing 302 wild and cultivated accessions identifies genes related to domestication and improvement in soybean. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Hintum, T.J.; Brown, A.H.; Spillane, C. Core Collections of Plant Genetic Resources; IPGRI Technical Bulletin No. 3; International Plant Genetic Resources Institute: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, J.D.; Palmer, R.G. Variability of thirteen isozyme loci in the USDA soybean germplasm collections. Crop Sci. 1995, 35, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, J.; Xu, D.; Suzuki, Y.; Kanazawa, A.; Shimamoto, Y. Soybean germplasm pools in Asia revealed by nuclear SSRs. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, M.S. Nutrition and cancer: A review of the evidence for an anti-cancer diet. Nutr. J. 2004, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.T.; Tsao, H.W.; Chen, Y.Y.; Cheng, S.W.; Hsu, Y.C. A study on the photodynamic properties of chlorophyll derivatives using human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2007, 6, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Seo, M.; Moon, J.; Yun, H.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S.; Hwang, Y.; Lee, S.; Choung, M. Introduction of stay green mutant for the development of black seed coat and green cotyledon soybean variety. Korean J. Crop Sci. 2010, 55, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Gillman, J.D.; Tetlow, A.; Lee, J.D.; Shannon, J.G.; Bilyeu, K. Loss-of-function mutations affecting a specific Glycine max R2R3 MYB transcription factor result in brown hilum and brown seed coats. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.; Liu, Z.; Hong, H.; Ma, Y.; Tian, L.; Li, X.; Li, Y.H.; Guan, R.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, L.J. Identification and validation of loci governing seed coat color by combining association mapping and bulk segregation analysis in soybean. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, K.; Yang, D.; Yamanaka, N.; Watanabe, S.; Harada, K.; Takahashi, R. A single-base deletion in soybean flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase gene is associated with gray pubescence color. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 50, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuteja, J.H.; Clough, S.J.; Chan, W.C.; Vodkin, L.O. Tissue-specific gene silencing mediated by a naturally occurring chalcone synthase gene cluster in Glycine max. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 819–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zabala, G.; Vodkin, L.O. A rearrangement resulting in small tandem repeats in the F3′5′ H gene of white flower genotypes is associated with the soybean W1 locus. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, S113–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Lee, C.Y.; Jeong, M.G.; Xu, J.L.; Choi, Y.; Jung, H.W.; Choi, H.K. Dissecting seed pigmentation-associated genomic loci and genes by employing dual approaches of reference-based and k-mer-based GWAS with 438 Glycine accessions. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovinich, N.; Saleem, A.; Arnason, J.T.; Miki, B. Combined analysis of transcriptome and metabolite data reveals extensive differences between black and brown nearly-isogenic soybean (Glycine max) seed coats enabling the identification of pigment isogenes. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jo, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Cho, H.; Choi, H.J.; Son, C.K.; Bae, J.S.; Bilyeu, K.; Song, J.T.; Lee, J.-D. Genetic Diversity of Soybeans (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) with Black Seed Coats and Green Cotyledons in Korean Germplasm. Agronomy 2021, 11, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11030581
Jo H, Lee JY, Cho H, Choi HJ, Son CK, Bae JS, Bilyeu K, Song JT, Lee J-D. Genetic Diversity of Soybeans (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) with Black Seed Coats and Green Cotyledons in Korean Germplasm. Agronomy. 2021; 11(3):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11030581
Chicago/Turabian StyleJo, Hyun, Ji Yun Lee, Hyeontae Cho, Hong Jib Choi, Chang Ki Son, Jeong Suk Bae, Kristin Bilyeu, Jong Tae Song, and Jeong-Dong Lee. 2021. "Genetic Diversity of Soybeans (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) with Black Seed Coats and Green Cotyledons in Korean Germplasm" Agronomy 11, no. 3: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11030581
APA StyleJo, H., Lee, J. Y., Cho, H., Choi, H. J., Son, C. K., Bae, J. S., Bilyeu, K., Song, J. T., & Lee, J. -D. (2021). Genetic Diversity of Soybeans (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) with Black Seed Coats and Green Cotyledons in Korean Germplasm. Agronomy, 11(3), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11030581