Quantification of EGFR-HER2 Heterodimers in HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer Cells Using Liquid-Phase Electron Microscopy
Abstract
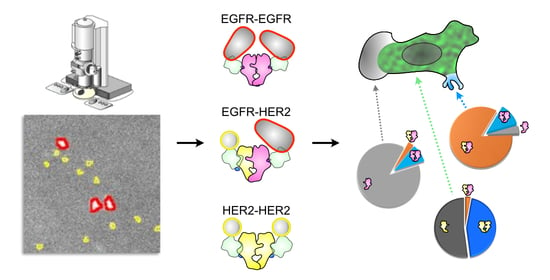
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mammalian Cell Culture
2.3. Coating of Microchips and Cell Culture Microscope Dishes
2.4. Cell Seeding on Microchips or Cell Culture Microscope Dishes
2.5. Dual Labeling of EGFR and HER2
2.6. Determination of the Labeling Efficiency for EGFR
2.7. Differential Interference Contrast and Fluorescence Microscopy
2.8. Graphene Enclosure of Microchips for Electron Microscopy
2.9. Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.10. Particle Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
2.12. Random Simulation
3. Results
3.1. Determination of the ρR of EGFR and HER2 in Functionally Distinct Subregions of the Plasma Membrane

3.2. Quantification of EGFR and HER2 in Heterodimeric, Homodimeric and Monomeric States
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, M.; Schwaederle, M.; Arguello, D.; Millis, S.Z.; Gatalica, Z.; Kurzrock, R. HER2 expression status in diverse cancers: Review of results from 37,992 patients. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Sun, Z. Spectrum of EGFR aberrations and potential clinical implications: Insights from integrative pan-cancer analysis. Cancer Commun. 2020, 40, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yarden, Y. The EGFR family and its ligands in human cancer. signalling mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Eur. J. Cancer 2001, 37 (Suppl. S4), 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkas-Kramarski, R.; Soussan, L.; Waterman, H.; Levkowitz, G.; Alroy, I.; Klapper, L.; Lavi, S.; Seger, R.; Ratzkin, B.J.; Sela, M.; et al. Diversification of Neu differentiation factor and epidermal growth factor signaling by combinatorial receptor interactions. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2452–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaito, A.; Kuwata, T.; Tokunaga, M.; Shitara, K.; Sato, R.; Akimoto, T.; Kinoshita, T. HER2 heterogeneity is a poor prognosticator for HER2-positive gastric cancer. World J. Clin. Cases 2019, 7, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger Filho, O.; Viale, G.; Stein, S.; Trippa, L.; Yardley, D.A.; Mayer, I.A.; Abramson, V.G.; Arteaga, C.L.; Spring, L.M.; Waks, A.G.; et al. Impact of HER2 heterogeneity on treatment response of early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer: Phase II neoadjuvant clinical trial of T-DM1 combined with pertuzumab. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2474–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onsum, M.D.; Geretti, E.; Paragas, V.; Kudla, A.J.; Moulis, S.P.; Luus, L.; Wickham, T.J.; McDonagh, C.F.; MacBeath, G.; Hendriks, B.S. Single-Cell Quantitative HER2 Measurement Identifies Heterogeneity and Distinct Subgroups within Traditionally Defined HER2-Positive Patients. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 1446–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Merritt, E.; Hu, X.; Cruz, A.; Jiang, C.; Sarkodie, H.; Zhou, Z.; Malhotra, J.; Riedlinger, G.M.; De, S. Non-Genetic Intra-Tumor Heterogeneity Is a Major Predictor of Phenotypic Heterogeneity and Ongoing Evolutionary Dynamics in Lung Tumors. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 2164–2174.e2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almendro, V.; Marusyk, A.; Polyak, K. Cellular Heterogeneity and Molecular Evolution in Cancer. Ann. Rev. Pathol. 2013, 8, 277–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heppner, G.H. Tumor Heterogeneity. Cancer Res. 1984, 44, 2259. [Google Scholar]
- Buocikova, V.; Rios-Mondragon, I.; Pilalis, E.; Chatziioannou, A.; Miklikova, S.; Mego, M.; Pajuste, K.; Rucins, M.; Yamani, N.E.; Longhin, E.M.; et al. Epigenetics in Breast Cancer Therapy—New Strategies and Future Nanomedicine Perspectives. Cancers 2020, 12, 3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Peng, Y.; Gao, A.; Du, C.; Herman, J.G. Epigenetic heterogeneity in cancer. Biomarker Res. 2019, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lajoie, P.; Partridge, E.A.; Guay, G.; Goetz, J.G.; Pawling, J.; Lagana, A.; Joshi, B.; Dennis, J.W.; Nabi, I.R. Plasma membrane domain organization regulates EGFR signaling in tumor cells. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 179, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hommelgaard, A.M.; Lerdrup, M.; van Deurs, B. Association with membrane protrusions makes ErbB2 an internalization-resistant receptor. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 1557–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeong, J.; Kim, W.; Kim, L.K.; VanHouten, J.; Wysolmerski, J.J. HER2 signaling regulates HER2 localization and membrane retention. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174849. [Google Scholar]
- Peckys, D.B.; Korf, U.; de Jonge, N. Local variations of HER2 dimerization in breast cancer cells discovered by correlative fluorescence and liquid electron microscopy. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, I.; Reichelt, M.; Shao, L.; Akita, R.W.; Koeppen, H.; Rangell, L.; Schaefer, G.; Mellman, I.; Sliwkowski, M.X. High cell-surface density of HER2 deforms cell membranes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casaletto, J.B.; McClatchey, A.I. Spatial regulation of receptor tyrosine kinases in development and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckys, D.B.; Quint, C.; Jonge, N. Determining the Efficiency of Single Molecule Quantum Dot Labeling of HER2 in Breast Cancer Cells. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 7948–7955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endres, N.; Das, R.; Smith, A.; Arkhipov, A.; Kovacs, E.; Huang, Y.; Pelton, J.; Shan, Y.; Shaw, D.; Wemmer, D.; et al. Conformational Coupling across the Plasma Membrane in Activation of the EGF Receptor. Cell 2013, 152, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- King, C.; Raicu, V.; Hristova, K. Understanding the FRET Signatures of Interacting Membrane Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 5291–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgert, A.; Letschert, S.; Doose, S.; Sauer, M. Artifacts in single-molecule localization microscopy. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 144, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapino, A.; Goia, M.; Recupero, D.; Marchio, C. Current Challenges for HER2 Testing in Diagnostic Pathology: State of the Art and Controversial Issues. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kent, S.P.; Ryan, K.H.; Siegel, A.L. Steric hindrance as a factor in the reaction of labeled antibody with cell surface antigenic determinants. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1978, 26, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deka, C.; Lehnert, B.E.; Lehnert, N.M.; Jones, G.M.; Sklar, L.A.; Steinkamp, J.A. Analysis of fluorescence lifetime and quenching of FITC-conjugated antibodies on cells by phase-sensitive flow cytometry. Cytometry 1996, 25, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, Á.; Szendi-Szatmári, T.; Ujlaky-Nagy, L.; Rádi, I.; Vereb, G.; Szöllősi, J.; Nagy, P. The Effect of Fluorophore Conjugation on Antibody Affinity and the Photophysical Properties of Dyes. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, V.S.; Srinivas, K.; Sujini, G.N.; Kumar, G.N.S. Protein-Protein Interaction Detection: Methods and Analysis. Int. J. Proteom. 2014, 2014, 147648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Ottersen, O.P. Immunogold cytochemistry in neuroscience. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, A.; Cheng, J.; Hirakawa, M.; Furukawa, K.; Kusunoki, S.; Fujimoto, T. Gangliosides GM1 and GM3 in the Living Cell Membrane Form Clusters Susceptible to Cholesterol Depletion and Chilling. Mol. Biol. Cell 2007, 18, 2112–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiala, G.J.; Kaschek, D.; Blumenthal, B.; Reth, M.; Timmer, J.; Schamel, W.W. Pre-clustering of the B cell antigen receptor demonstrated by mathematically extended electron microscopy. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinberg, F.; Peckys, D.B.; de Jonge, N. EGFR expression in HER2-driven breast cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Bhamidimarri, S.P.; Brending, N.; Colin-York, H.; Collinson, L.; De Jonge, N.; De Pablo, P.; Debroye, E.; Eggeling, C.; Franck, C. The 2018 correlative microscopy techniques roadmap. J. Phys. D 2018, 51, 443001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holliday, D.L.; Speirs, V. Choosing the right cell line for breast cancer research. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robertson, K.W.; Reeves, J.R.; Smith, G.; Keith, W.N.; Ozanne, B.W.; Cooke, T.G.; Stanton, P.D. Quantitative estimation of epidermal growth factor receptor and c-erbB-2 in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 3823–3830. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blach, P.; Keskin, S.; de Jonge, N. Graphene Enclosure of Chemically Fixed Mammalian Cells for Liquid-Phase Electron Microscopy. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 163, e61458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Thapa, N.; Sun, Y.; Anderson, R.A. A kinase-independent role for EGF receptor in autophagy initiation. Cell 2015, 160, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herr, P.; Boström, J.; Rullman, E.; Rudd, S.G.; Vesterlund, M.; Lehtiö, J.; Helleday, T.; Maddalo, G.; Altun, M. Cell cycle profiling reveals protein oscillation, phosphorylation, and localization dynamics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2020, 19, 608–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heins, A.-L.; Johanson, T.; Han, S.; Lundin, L.; Carlquist, M.; Gernaey, K.V.; Sørensen, S.J.; Eliasson Lantz, A. Quantitative flow cytometry to understand population heterogeneity in response to changes in substrate availability in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae chemostats. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoyan, D.; Stoyan, H. Estimating pair correlation functions of planar cluster processes. Biometric. J. 1996, 38, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyan, D.; Stoyan, H. Fractals, Random Shapes, and Point Fields: Methods of Geometrical Statistics; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Fiksel, T. Edge-corrected density estimators for points processes. Statistics 1988, 19, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyan, D.; Bertram, U.; Wendrock, H. Estimation variances for estimators of product densities and pair correlation functions of planar points processes. Ann. Inst. Statist. Math. 1993, 45, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alansary, D.; Peckys, D.B.; Niemeyer, B.A.; de Jonge, N. Detecting single ORAI1 proteins within the plasma membrane reveals higher order channel complexes. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arkhipov, A.; Shan, Y.; Kim, E.T.; Dror, R.O.; Shaw, D.E. Her2 activation mechanism reflects evolutionary preservation of asymmetric ectodomain dimers in the human EGFR family. eLife 2013, 2, e00708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, S.; Saini, S. Phenotypic Heterogeneity in Tumor Progression, and Its Possible Role in the Onset of Cancer. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, e604528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckys, D.B.; Korf, U.; Wiemann, S.; de Jonge, N. Liquid-phase electron microscopy of molecular drug response in breast cancer cells reveals irresponsive cell subpopulations related to lack of HER2 homodimers. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 28, 3193–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckys, D.B.; de Jonge, N. Studying the Stoichiometry of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Intact Cells using Correlative Microscopy. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 103, e53186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Björkelund, H.; Gedda, L.; Barta, P.; Malmqvist, M.; Andersson, K. Gefitinib induces epidermal growth factor receptor dimers which alters the interaction characteristics with 125I-EGF. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peckys, D.B.; Baudoin, J.P.; Eder, M.; Werner, U.; de Jonge, N. Epidermal growth factor receptor subunit locations determined in hydrated cells with environmental scanning electron microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Wang, Y.; Cai, M.; Pan, Y.; Xu, H.; Jiang, J.; Ji, H.; Wang, H. Mechanistic insights into EGFR membrane clustering revealed by super-resolution imaging. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 2511–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarnuczak, A.F.; Najgebauer, H.; Barzine, M.; Kundu, D.J.; Ghavidel, F.; Perez-Riverol, Y.; Papatheodorou, I.; Brazma, A.; Vizcaíno, J.A. An integrated landscape of protein expression in human cancer. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigal, A.; Milo, R.; Cohen, A.; Geva-Zatorsky, N.; Klein, Y.; Liron, Y.; Rosenfeld, N.; Danon, T.; Perzov, N.; Alon, U. Variability and memory of protein levels in human cells. Nature 2006, 444, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger Filho, O.; Viale, G.; Trippa, L.; Li, T.; Yardley, D.A.; Mayer, I.A.; Abramson, V.G.; Arteaga, C.L.; Spring, L.; Waks, A.G.; et al. HER2 heterogeneity as a predictor of response to neoadjuvant T-DM1 plus pertuzumab: Results from a prospective clinical trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horii, R.; Nitta, H.; Nojima, M.; Maruyama, R.; Ueno, T.; Ito, Y.; Ohno, S.; Banks, P.; Kanda, H.; Akiyama, F. Predictive significance of HER2 intratumoral heterogeneity, determined by simultaneous gene and protein analysis, for resistance to trastuzumab-based treatments for HER2-positive breast cancer. Virchows Archiv 2021, 479, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahavi, D.; Weiner, L. Monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy. Antibodies 2020, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, V.A.; Balthasar, J.P. Understanding inter-individual variability in monoclonal antibody disposition. Antibodies 2019, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ternant, D.; Azzopardi, N.; Raoul, W.; Bejan-Angoulvant, T.; Paintaud, G. Influence of antigen mass on the pharmacokinetics of therapeutic antibodies in humans. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 58, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriki, T.; Maruyama, H.; Maruyama, I.N. Activation of preformed EGF receptor dimers by ligand-induced rotation of the transmembrane domain. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 311, 1011–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.-H.; Maruyama, I.N. All EGF(ErbB) receptors have preformed homo- and heterodimeric structures in living cells. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 3207–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin-Fernandez, M.L.; Clarke, D.T.; Roberts, S.K.; Zanetti-Domingues, L.C.; Gervasio, F.L. Structure and Dynamics of the EGF Receptor as Revealed by Experiments and Simulations and Its Relevance to Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cells 2019, 8, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arkhipov, A.; Shan, Y.; Das, R.; Endres, N.F.; Eastwood, M.P.; Wemmer, D.E.; Kuriyan, J.; Shaw, D.E. Architecture and membrane interactions of the EGF receptor. Cell 2013, 152, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Macdonald-Obermann, J.; Westfall, C.; Piwnica-Worms, D.; Pike, L.J. Quantitation of the effect of ErbB2 on epidermal growth factor receptor binding and dimerization. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 31116–31125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peckys, D.B.; Hirsch, D.; Gaiser, T.; de Jonge, N. Visualisation of HER2 homodimers in single cells from HER2 overexpressing primary formalin fixed paraffin embedded tumour tissue. Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appert-Collin, A.; Hubert, P.; Crémel, G.; Bennasroune, A. Role of ErbB Receptors in Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Cappuzzo, F. Predictive value of EGFR and HER2 overexpression in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2009, 28 (Suppl. S1), 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, D.; Liu, C.Y.; Shen, D.; Fan, S.; Su, X.; Ye, P.; Gavine, P.R.; Yin, X. Assessment and prognostic analysis of EGFR, HER2, and HER3 protein expression in surgically resected gastric adenocarcinomas. Onco. Targets Ther. 2015, 8, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- DiGiovanna, M.P.; Stern, D.F.; Edgerton, S.M.; Whalen, S.G.; Moore, D.; Thor, A.D. Relationship of epidermal growth factor receptor expression to ErbB-2 signaling activity and prognosis in breast cancer patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Ballman, K.; Vassilakopoulou, M.; Dueck, A.; Reinholz, M.; Tenner, K.; Gralow, J.; Hudis, C.; Davidson, N.; Fountzilas, G. EGFR expression is associated with decreased benefit from trastuzumab in the NCCTG N9831 (Alliance) trial. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1065–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Worthylake, R.; Opresko, L.K.; Wiley, H.S. ErbB-2 Amplification Inhibits Down-regulation and Induces Constitutive Activation of Both ErbB-2 and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 8865–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, S.P.; Hastings, J.F.; Han, J.Z.R.; Croucher, D.R. The Under-Appreciated Promiscuity of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Family. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, T.; Farnie, G.; Bundred, N.J.; Anderson, N.G. The Mitogenic Action of Insulin-like Growth Factor I in Normal Human Mammary Epithelial Cells Requires the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rinne, S.S.; Xu, T.; Dahlsson Leitao, C.; Ståhl, S.; Löfblom, J.; Orlova, A.; Tolmachev, V.; Vorobyeva, A. Influence of Residualizing Properties of the Radiolabel on Radionuclide Molecular Imaging of HER3 Using Affibody Molecules. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burstein, H.J.; Sun, Y.; Dirix, L.Y.; Jiang, Z.; Paridaens, R.; Tan, A.R.; Awada, A.; Ranade, A.; Jiao, S.; Schwartz, G. Neratinib, an irreversible ErbB receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced ErbB2-positive breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol 2010, 28, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Liu, H.; Pearson, T.; Iwase, T.; Fuson, J.; Lalani, A.S.; Eli, L.D.; Diala, I.; Tripathy, D.; Lim, B. PI3K and MAPK Pathways as Targets for Combination with the Pan-HER Irreversible Inhibitor Neratinib in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer and TNBC by Kinome RNAi Screening. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Weihua, Z. Rethink of EGFR in Cancer With Its Kinase Independent Function on Board. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söderberg, O.; Leuchowius, K.-J.; Gullberg, M.; Jarvius, M.; Weibrecht, I.; Larsson, L.-G.; Landegren, U. Characterizing proteins and their interactions in cells and tissues using the in situ proximity ligation assay. Methods 2008, 45, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocanu, M.-M.; Váradi, T.; Szöllősi, J.; Nagy, P. Comparative analysis of fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) and proximity ligation assay (PLA). Proteomics 2011, 11, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Type | Images | Receptor | n | ρR | Homo | Hetero | Mono | CV | CV of ρR Ratios (HER2/EGFR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSM | 102 | HER2 | 78,425 | 340 | 0.45 | 0.03 | 0.52 | 0.5 | 0.8 |
| EGFR | 2636 | 22 | 0.11 | 0.42 | 0.47 | 0.8 | |||
| LMPs | 64 | HER2 | 178,003 | 1124 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.14 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| EGFR | 6065 | 70 | 0.12 | 0.84 | 0.04 | 0.7 | |||
| Lamellipodia | 31 | HER2 | 18,710 | 255 | 0.23 | 0.00 | 0.77 | 0.3 | 0.7 |
| EGFR | 662 | 13 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.88 | 0.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peckys, D.B.; Gaa, D.; de Jonge, N. Quantification of EGFR-HER2 Heterodimers in HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer Cells Using Liquid-Phase Electron Microscopy. Cells 2021, 10, 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113244
Peckys DB, Gaa D, de Jonge N. Quantification of EGFR-HER2 Heterodimers in HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer Cells Using Liquid-Phase Electron Microscopy. Cells. 2021; 10(11):3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113244
Chicago/Turabian StylePeckys, Diana B., Daniel Gaa, and Niels de Jonge. 2021. "Quantification of EGFR-HER2 Heterodimers in HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer Cells Using Liquid-Phase Electron Microscopy" Cells 10, no. 11: 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113244
APA StylePeckys, D. B., Gaa, D., & de Jonge, N. (2021). Quantification of EGFR-HER2 Heterodimers in HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancer Cells Using Liquid-Phase Electron Microscopy. Cells, 10(11), 3244. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10113244