Discovery of a Novel MHC Class I Lineage in Teleost Fish which Shows Unprecedented Levels of Ectodomain Deterioration while Possessing an Impressive Cytoplasmic Tail Motif
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. The Structure and Function of Classical MHC-I
1.2. Classical and Nonclassical MHC-I Can Show Differences in Domain Organization
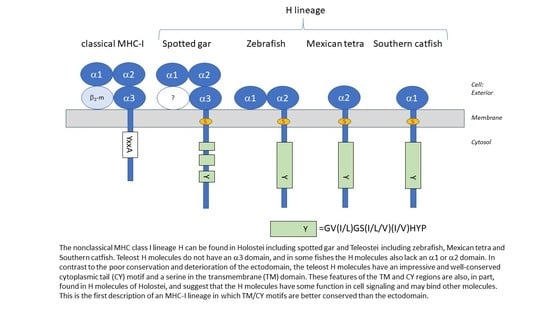
1.3. MHC-I in Teleost Fish and the Target of the Present Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datamining
2.2. Usage of the Word MHC-I
2.3. Experimental Analysis of Mexican Tetra HAA Transcript Sequences
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Synonymous Versus Non-Synonymous Nucleotide Substitution Rates
2.6. Expression Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Identification of H Lineage Sequences in Holostei and Teleostei
3.2. Genomic Positions of Detected H Lineage Genes Reveal Orthology
3.3. Intron-Exon Organization of H Lineage Genes and Losses of Ectodomain Exons
3.4. Deduced Amino Acid Sequences of Teleost H Lineage Molecules Reveal Deterioration of Ectodomains and the Possession of an Unusual Cytoplasmic Tail Motif
3.5. Nucleotide Sequences Encoding the Teleost H Lineage Cytoplasmic Tail Motif Indicate Purifying Selection
3.6. Expression Pattern
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bjorkman, P.J.; Saper, M.A.; Samraoui, B.; Bennett, W.S.; Strominger, J.L.; Wiley, D.C. Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2. Nature 1987, 329, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neefjes, J.; Jongsma, M.L.; Paul, P.; Bakke, O. Towards a systems understanding of MHC class I and MHC class II antigen presentation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madden, D.R. The three-dimensional structure of peptide-MHC complexes. Annu.Rev.Immunol. 1995, 13, 587–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rammensee, H.G. Chemistry of peptides associated with MHC class I and class II molecules. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1995, 7, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Okamura, K.; Yamaguchi, H.; Ototake, M.; Nakanishi, T.; Kurosawa, Y. Conservation and diversification of MHC class I and its related molecules in vertebrates. Immunol. Rev. 1999, 167, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, N.; Lin, C.; Gao, F.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; et al. MHC class I presentation and regulation by IFN in bony fish determined by molecular analysis of the class I locus in grass carp. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, N.; Qi, J.; Chen, R.; Dijkstra, J.M.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Xia, C. The Structure of the MHC Class I Molecule of Bony Fishes Provides Insights into the Conserved Nature of the Antigen-Presenting System. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 3668–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dijkstra, J.M.; Fischer, U.; Sawamoto, Y.; Ototake, M.; Nakanishi, T. Exogenous antigens and the stimulation of MHC class I restricted cell-mediated cytotoxicity: Possible strategies for fish vaccines. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2001, 11, 437–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Dijkstra, J.M. Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Genes and Disease Resistance in Fish. Cells 2019, 8, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, J.M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Grimholt, U. Conservation of sequence motifs suggests that the nonclassical MHC class I lineages CD1/PROCR and UT were established before the emergence of tetrapod species. Immunogenetics 2018, 70, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.L.; Nei, M. Evolution of the major histocompatibility complex: Independent origin of nonclassical class I genes in different groups of mammals. Mol. Bio. Evol. 1989, 6, 559–579. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, E.J.; Luoma, A.M. The adaptable major histocompatibility complex (MHC) fold: Structure and function of nonclassical and MHC class I-like molecules. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 529–561. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Araki, T.; Gejyo, F.; Takagaki, K.; Haupt, H.; Schwick, H.G.; Burgi, W.; Marti, T.; Schaller, J.; Rickli, E.; Brossmer, R.; et al. Complete amino acid sequence of human plasma Zn-alpha 2-glycoprotein and its homology to histocompatibility antigens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delker, S.L.; West, A.P., Jr.; McDermott, L.; Kennedy, M.W.; Bjorkman, P.J. Crystallographic studies of ligand binding by Zn-alpha2-glycoprotein. J. Struct. Biol. 2004, 148, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, L.M.; Chirino, A.J.; Bjorkman, P. Crystal structure of human ZAG, a fat-depleting factor related to MHC molecules. Science 1999, 283, 1914–1919. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fukudome, K.; Esmon, C.T. Identification, cloning, and regulation of a novel endothelial cell protein C/activated protein C receptor. J. Boil. Chem. 1994, 269, 26486–26491. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan Rao, L.V.; Esmon, C.T.; Pendurthi, U.R. Endothelial cell protein C receptor: A multiliganded and multifunctional receptor. Blood 2014, 124, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oganesyan, V.; Oganesyan, N.; Terzyan, S.; Qu, D.; Dauter, Z.; Esmon, N.L.; Esmon, C.T. The crystal structure of the endothelial protein C receptor and a bound phospholipid. J. Boil. Chem. 2002, 277, 24851–24854. [Google Scholar]
- Calabi, F.; Milstein, C. A novel family of human major histocompatibility complex-related genes not mapping to chromosome 6. Nature 1986, 323, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Castano, A.R.; Segelke, B.W.; Stura, E.A.; Peterson, P.A.; Wilson, I.A. Crystal structure of mouse CD1: An MHC-like fold with a large hydrophobic binding groove. Science 1997, 277, 339–345. [Google Scholar]
- Van Rhijn, I.; Godfrey, D.I.; Rossjohn, J.; Moody, D.B. Lipid and small-molecule display by CD1 and MR1. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Nomura, M.; Takihara, Y.; Yasunaga, T.; Shimada, K. Isolation and characterization of retinoic acid-inducible cDNA clones in F9 cells: A novel cDNA family encodes cell surface proteins sharing partial homology with MHC class I molecules. J. Biochem. 1996, 119, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Messina, L.; Reyburn, H.T.; Vales-Gomez, M. Human NKG2D-ligands: Cell biology strategies to ensure immune recognition. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasahara, M.; Yoshida, S. Immunogenetics of the NKG2D ligand gene family. Immunogenetics 2012, 64, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkstra, J.M.; Katagiri, T.; Hosomichi, K.; Yanagiya, K.; Inoko, H.; Ototake, M.; Aoki, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Shiina, T. A third broad lineage of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I in teleost fish; MHC class II linkage and processed genes. Immunogenetics 2007, 59, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimholt, U.; Hordvik, I.; Fosse, V.M.; Olsaker, I.; Endresen, C.; Lie, O. Molecular cloning of major histocompatibility complex class I cDNAs from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Immunogenetics 1993, 37, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Nakanishi, T.; Kurosawa, Y. Isolation of carp genes encoding major histocompatibility complex antigens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 6863–6867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruiswijk, C.P.; Hermsen, T.T.; Westphal, A.H.; Savelkoul, H.F.; Stet, R.J. A novel functional class I lineage in zebrafish (Danio rerio), carp (Cyprinus carpio), and large barbus (Barbus intermedius) showing an unusual conservation of the peptide binding domains. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 1936–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shum, B.P.; Rajalingam, R.; Magor, K.E.; Azumi, K.; Carr, W.H.; Dixon, B.; Stet, R.J.; Adkison, M.A.; Hedrick, R.P.; Parham, P. A divergent non-classical class I gene conserved in salmonids. Immunogenetics 1999, 49, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimholt, U.; Tsukamoto, K.; Azuma, T.; Leong, J.; Koop, B.F.; Dijkstra, J.M. A comprehensive analysis of teleost MHC class I sequences. BMC Evol. Boil. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, J.M.; Kiryu, I.; Yoshiura, Y.; Kumanovics, A.; Kohara, M.; Hayashi, N.; Ototake, M. Polymorphism of two very similar MHC class Ib loci in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Immunogenetics 2006, 58, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirscherl, H.; Yoder, J.A. Characterization of the Z lineage Major histocompatability complex class I genes in zebrafish. Immunogenetics 2013, 66, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aken, B.L.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Amode, M.R.; Bernsdorff, F.; Bhai, J.; Billis, K.; Carvalho-Silva, D.; Cummins, C.; Clapham, P.; et al. Ensembl 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D635–D642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamov, A.A.; Solovyev, V.V. Ab initio gene finding in Drosophila genomic DNA. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stothard, P. The sequence manipulation suite: JavaScript programs for analyzing and formatting protein and DNA sequences. BioTechniques 2000, 28, 1102–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, K. TMBASE—A database of membrane spanning protein segments. Biol.Chem. Hoppe-Seyel 1993, 374, 166. [Google Scholar]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Boil. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuckerkandl, E.; Pauling, L. Evolutionary divergence and convergence in proteins. In Evolving Genes and Proteins; Bryson, V., Vogel, H.J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1965; Volume 33, pp. 1870–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.T.; Taylor, W.R.; Thornton, J.M. The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1992, 8, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Boil. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korber, B. HIV Signature and Sequence Variation Analysis. In Computational Analysis of HIV Molecular Sequences; Rodrigo, A.G., Learn, G.H., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2000; pp. 55–72. [Google Scholar]
- Lien, S.; Koop, B.F.; Sandve, S.R.; Miller, J.R.; Kent, M.P.; Nome, T.; Hvidsten, T.R.; Leong, J.S.; Minkley, D.R.; Zimin, A.; et al. The Atlantic salmon genome provides insights into rediploidization. Nature 2016, 533, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rondeau, E.B.; Minkley, D.R.; Leong, J.S.; Messmer, A.M.; Jantzen, J.R.; von Schalburg, K.R.; Lemon, C.; Bird, N.H.; Koop, B.F. The genome and linkage map of the northern pike (Esox lucius): Conserved synteny revealed between the salmonid sister group and the Neoteleostei. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, J.; Bontrop, R.E.; Dawkins, R.L.; Erlich, H.A.; Gyllensten, U.B.; Heise, E.R.; Jones, P.P.; Parham, P.; Wakeland, E.K.; Watkins, D.I. Nomenclature for the major histocompatibility complexes of different species: A proposal. Immunogenetics 1990, 31, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Near, T.J.; Eytan, R.I.; Dornburg, A.; Kuhn, K.L.; Moore, J.A.; Davis, M.P.; Wainwright, P.C.; Friedman, M.; Smith, W.L. Resolution of ray-finned fish phylogeny and timing of diversification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13698–13703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kodama, M.; Brieuc, M.S.; Devlin, R.H.; Hard, J.J.; Naish, K.A. Comparative mapping between Coho Salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) and three other salmonids suggests a role for chromosomal rearrangements in the retention of duplicated regions following a whole genome duplication event. G3 (Bethesda) 2014, 4, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopp, T.P.; Woods, K.R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 3824–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, J. Vertebrates and the evolution of Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) class I and class II molecules. Verh.Dtsch.Zool.Ges. 1988, 81, 131–144. [Google Scholar]
- Grimholt, U.; Drablos, F.; Jorgensen, S.M.; Hoyheim, B.; Stet, R.J. The major histocompatibility class I locus in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.): Polymorphism, linkage analysis and protein modelling. Immunogenetics 2002, 54, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, K.; Dijkstra, J.M.; Xia, C.; Denda, I.; Ototake, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Nakanishi, T. Classical MHC class I genes composed of highly divergent sequence lineages share a single locus in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, G.; Lizee, G.; Reinicke, A.T.; Seipp, R.P.; Omilusik, K.D.; Jefferies, W.A. MHC class I endosomal and lysosomal trafficking coincides with exogenous antigen loading in dendritic cells. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizee, G.; Basha, G.; Jefferies, W.A. Tails of wonder: Endocytic-sorting motifs key for exogenous antigen presentation. Trends Immunol. 2005, 26, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashman, J.B.; Miller, J. A role for the transmembrane domain in the trimerization of the MHC class II-associated invariant chain. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 2704–2712. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dijkstra, J.M.; Yamaguchi, T. Ancient features of the MHC class II presentation pathway, and a model for the possible origin of MHC molecules. Immunogenetics 2019, 71, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottwick, C.; He, X.; Hofmann, A.; Vesper, N.; Reth, M.; Yang, J. A symmetric geometry oftransmembrane domains inside the B cell antigen receptor complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 13468–13473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Tissue\Gene | Sasa-HAA | Eslu-HAA | Dare-HAA | Leoc-HAA | Sasa-UBA | Sasa-UDA | Sasa-LDA | Sasa-ZBAa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gills | 9.48 | 1.57 | 3.50 | 0.95 | 253.57 | 5.65 | 3.36 | 43.46 |
| Kidney * | 11.49 | 1.79 | 4.11 | 3.55 | 66.97 | 4.05 | 4.17 | 9.42 |
| Intestine/gut ** | 16.47 | 1.90 | 4.41 | 11.09 | 361.72 | 4.27 | 1.86 | 18.57 |
| Ovary | 56.84 | 2.66 | 8.65 | 1.35 | 1.25 | 4.29 | 6.08 | 0.11 |
| Testis | 10.49 | 1.54 | 3.18 | 2.07 | 60.84 | 6.31 | 1.14 | 2.70 |
| Spleen | 9.62 | n/a | n/a | n/a | 260.43 | 6.63 | 2.72 | 19.47 |
| Heart | 2.85 | n/a | n/a | n/a | 16.79 | 1.35 | 1.24 | 8.11 |
| Brain | 5.61 | n/a | n/a | n/a | 17.65 | 1.75 | 0.30 | 3.34 |
| Nose | 2.40 | n/a | n/a | n/a | 60.70 | 5.44 | 2.02 | 8.61 |
| Liver | 0.94 | n/a | n/a | n/a | 12.92 | 0.78 | 1.23 | 4.30 |
| Skin | 0.17 | n/a | n/a | n/a | 4.84 | 6.31 | 0.09 | 0.08 |
| Eye | 1.77 | n/a | n/a | n/a | 11.75 | 0.79 | 0.15 | 2.76 |
| Query Length (bp) | 741 | 741 | 693 | 1056 | 1068 | 1068 | 1080 | 1128 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grimholt, U.; Tsukamoto, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Dijkstra, J.M. Discovery of a Novel MHC Class I Lineage in Teleost Fish which Shows Unprecedented Levels of Ectodomain Deterioration while Possessing an Impressive Cytoplasmic Tail Motif. Cells 2019, 8, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091056
Grimholt U, Tsukamoto K, Hashimoto K, Dijkstra JM. Discovery of a Novel MHC Class I Lineage in Teleost Fish which Shows Unprecedented Levels of Ectodomain Deterioration while Possessing an Impressive Cytoplasmic Tail Motif. Cells. 2019; 8(9):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091056
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrimholt, Unni, Kentaro Tsukamoto, Keiichiro Hashimoto, and Johannes M. Dijkstra. 2019. "Discovery of a Novel MHC Class I Lineage in Teleost Fish which Shows Unprecedented Levels of Ectodomain Deterioration while Possessing an Impressive Cytoplasmic Tail Motif" Cells 8, no. 9: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091056
APA StyleGrimholt, U., Tsukamoto, K., Hashimoto, K., & Dijkstra, J. M. (2019). Discovery of a Novel MHC Class I Lineage in Teleost Fish which Shows Unprecedented Levels of Ectodomain Deterioration while Possessing an Impressive Cytoplasmic Tail Motif. Cells, 8(9), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8091056