Time- and Dose-Dependent Effects of Ionizing Irradiation on the Membrane Expression of Hsp70 on Glioma Cells
Abstract
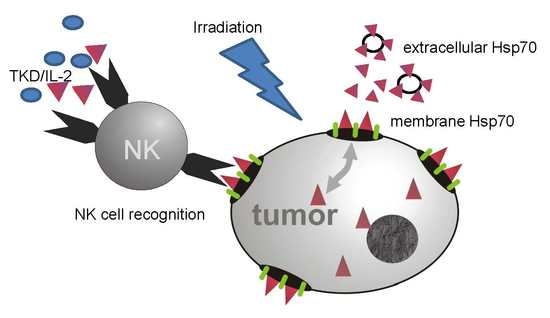
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Line and Culture Conditions
2.2. Irradiation
2.3. Flow Cytometry and Cell Cycle Analysis
2.4. Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
2.5. Hsp70 lipELISA
2.6. Europium Assay
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Membrane Hsp70 Expression Remains Stable During a Culture Period of 7 Days
3.2. Irradiation Induces an Increase in the Mhsp70 Density on Different Tumor Cell Lines
3.3. Irradiation-Induced Upregulation of mHsp70 Is Time-Dependent
3.4. Irradiation-Induced Effects on the mHsp70 Density Are Dose- and Time-Dependent
3.5. Irradiation-Induced Cell Cycle Arrest and Its Impact on the mHsp70 Density
3.6. Increased mHsp70 Expression Density Is Associated with an Increased Sensitivity to Lysis Mediated by TKD/IL-2-Activated NK Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. Combining radiotherapy and cancer immunotherapy: A paradigm shift. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasi, F.; Paolini, A.; Nano, R.; Di Liberto, R.; Capelli, E. Effects of single or combined treatments with radiation and chemotherapy on survival and danger signals expression in glioblastoma cell lines. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 453497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radons, J. The human Hsp70 family of chaperones: Where do we stand? Cell Stress Chaperones 2016, 21, 379–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Multhoff, G.; Hightower, L.E. Distinguishing integral and receptor-bound heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) on the cell surface by Hsp70-specific antibodies. Cell Stress Chaperones 2011, 16, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beere, H.M.; Wolf, B.B.; Cain, K.; Mosser, D.D.; Mahboubi, A.; Kuwana, T.; Tailor, P.; Morimoto, R.I.; Cohen, G.M.; Green, D.R. Heat-shock protein 70 inhibits apoptosis by preventing recruitment of procaspase-9 to the apaf-1 apoptosome. Nat.Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stokes, J., 3rd; Singh, U.P.; Scissum Gunn, K.; Acharya, A.; Manne, U.; Mishra, M. Targeting Hsp70: A possible therapy for cancer. Cancer Lett. 2016, 374, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Craig, E.A. The stress response: Changes in eukaryotic gene expression in response to environmental stress. Science 1985, 230, 800–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shevtsov, M.; Multhoff, G. Heat shock protein-peptide and hsp-based immunotherapies for the treatment of cancer. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radons, J.; Multhoff, G. Immunostimulatory functions of membrane-bound and exported heat shock protein 70. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2005, 11, 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Multhoff, G.; Pockley, A.G.; Schmid, T.E.; Schilling, D. The role of heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) in radiation-induced immunomodulation. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kokowski, K.; Stangl, S.; Seier, S.; Hildebrandt, M.; Vaupel, P.; Multhoff, G. Radiochemotherapy combined with NK cell transfer followed by second-line PD-1 inhibition in a patient with NSCLC stage IIIb inducing long-term tumor control: A case study. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2019, 195, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmid, T.E.; Multhoff, G. Radiation-induced stress proteins—The role of heat shock proteins (HSP) in anti-tumor responses. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 1765–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Multhoff, G. Heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70): Membrane location, export and immunological relevance. Methods 2007, 43, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuninger, S.; Ertl, J.; Knape, C.; Gunther, S.; Regel, I.; Rödel, F.; Gaipl, U.S.; Thorsteinsdottir, J.; Giannitrapani, L.; Dickinson, A.M.; et al. Quantitative analysis of liposomal Hsp70 in the blood of tumor patients using a novel lipHsp70 ELISA. J. Clin. Cell. Immunol. 2014, 5, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multhoff, G.; Mizzen, L.; Winchester, C.C.; Milner, C.M.; Wenk, S.; Eissner, G.; Kampinga, H.H.; Laumbacher, B.; Johnson, J. Heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) stimulates proliferation and cytolytic activity of natural killer cells. Exp. Hematol. 1999, 27, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastpar, R.; Gehrmann, M.; Bausero, M.A.; Asea, A.; Gross, C.; Schroeder, J.A.; Multhoff, G. Heat shock protein 70 surface-positive tumor exosomes stimulate migratory and cytolytic activity of natural killer cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 5238–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ireland, H.E.; Leoni, F.; Altaie, O.; Birch, C.S.; Coleman, R.C.; Hunter-Lavin, C.; Williams, J.H. Measuring the secretion of heat shock proteins from cells. Methods 2007, 43, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, V.L.; Rodriguez-Silva, M.; Frey, T.; Gehrmann, M.; Diaz, J.C.; Steinem, C.; Multhoff, G.; Arispe, N.; De Maio, A. Hsp70 translocates into the plasma membrane after stress and is released into the extracellular environment in a membrane-associated form that activates macrophages. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 4299–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hantschel, M.; Pfister, K.; Jordan, A.; Scholz, R.; Andreesen, R.; Schmitz, G.; Schmetzer, H.; Hiddemann, W.; Multhoff, G. Hsp70 plasma membrane expression on primary tumor biopsy material and bone marrow of leukaemic patients. Cell Stress Chaperones 2000, 5, 438–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murakami, N.; Kühnel, A.; Schmid, T.E.; Ilicic, K.; Stangl, S.; Braun, I.S.; Gehrmann, M.; Molls, M.; Itami, J.; Multhoff, G. Role of membrane Hsp70 in radiation sensitivity of tumor cells. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 10, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gehrmann, M.; Marienhagen, J.; Eichholtz-Wirth, H.; Fritz, E.; Ellwart, J.; Jäättelä, M.; Zilch, T.; Multhoff, G. Dual function of membrane-bound heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70), Bag-4, and Hsp40: Protection against radiation-induced effects and target structure for natural killer cells. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gehrmann, M.; Liebisch, G.; Schmitz, G.; Anderson, R.; Steinem, C.; DeMaio, A.; Pockley, A.G.; Multhoff, G. Tumor-specific Hsp70 plasma membrane localization is enabled by the glycosphingolipid Gb3. PONE. 2008, 3, e1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schilling, D.; Gehrmann, M.; Steinem, C.; De, M.A.; Pockley, A.G.; Abend, M.; Molls, M.; Multhoff, G. Binding of heat shock protein 70 to extracellular phosphatidylserine promotes killing of normoxic and hypoxic tumor cells. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 2467–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Multhoff, G.; Pfister, K.; Gehrmann, M.; Hantschel, M.; Gross, C.; Hafner, M.; Hiddemann, W. A 14-mer Hsp70 peptide stimulates natural killer (NK) cell activity. Cell Stress Chaperones 2001, 6, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stangl, S.; Wortmann, A.; Guertler, U.; Multhoff, G. Control of metastasized pancreatic carcinomas in scid/beige mice with human IL-2/TKD-activated NK cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 6270–6276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; Van Den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsteinsdottir, J.; Stangl, S.; Fu, P.; Guo, K.; Albrecht, V.; Eigenbrod, S.; Erl, J.; Gehrmann, M.; Tonn, J.-C.; Multhoff, G.; et al. Overexpression of cytosolic, plasma membrane bound and extracellular heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) in primary glioblastomas. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 135, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinjung, T.; Arndt, O.; Feldmann, H.J.; Bockmühl, U.; Gehrmann, M.; Zilch, T.; Pfister, K.; Schönberger, J.; Marienhagen, J.; Eilles, C.; et al. ; et al. Heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) membrane expression on head-and-neck cancer biopsy-a target for natural killer (NK) cells. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003, 57, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diller, K.R. Stress protein expression kinetics. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng 2006, 8, 403–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bausero, M.A.; Gastpar, R.; Multhoff, G.; Asea, A. Alternative mechanism by which IFN-y enhances tumor recognition: Active release of Hsp72. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2900–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paolini, A.; Pasi, F.; Facoetti, A.; Mazzini, G.; Corbella, F.; Di Liberto, R.; Nano, R. Cell death forms and Hsp70 expression in U87 cells after ionizing radiation and/or chemotherapy. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 3727–3731. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rylander, M.N.; Feng, Y.; Bass, J.; Diller, K.R. Thermally induced injury and heat-shock protein expression in cells and tissues. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 2005, 1066, 222–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pockley, A.G.; Henderson, B. Extracellular cell stress (heat shock) proteins-immune responses and disease: An overview. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20160522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, P. Interaction of heat shock proteins with peptides and antigen presenting cells: Chaperoning of the innate and adaptive immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 395–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Multhoff, G.; Botzler, C.; Wiesnet, M.; Muller, E.; Meier, T.; Wilmanns, W.; Issels, R.D. A stress-inducible 72-kDa heat-shock protein (Hsp72) is expressed on the surface of human tumor cells, but not on normal cells. Int. J. Cancer 1995, 61, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, C.; Koelch, W.; Arispe, N.; DeMaio, A.; Multhoff, G. Cell surface-bound Hsp70 mediates perforin-independent apoptosis by specific binding and uptake of granzyme B. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 17, 41173–41181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]















© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fellinger, H.; Stangl, S.; Hernandez Schnelzer, A.; Schwab, M.; Di Genio, T.; Pieper, M.; Werner, C.; Shevtsov, M.; Haller, B.; Multhoff, G. Time- and Dose-Dependent Effects of Ionizing Irradiation on the Membrane Expression of Hsp70 on Glioma Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040912
Fellinger H, Stangl S, Hernandez Schnelzer A, Schwab M, Di Genio T, Pieper M, Werner C, Shevtsov M, Haller B, Multhoff G. Time- and Dose-Dependent Effects of Ionizing Irradiation on the Membrane Expression of Hsp70 on Glioma Cells. Cells. 2020; 9(4):912. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040912
Chicago/Turabian StyleFellinger, Helena, Stefan Stangl, Alicia Hernandez Schnelzer, Melissa Schwab, Tommaso Di Genio, Marija Pieper, Caroline Werner, Maxim Shevtsov, Bernhard Haller, and Gabriele Multhoff. 2020. "Time- and Dose-Dependent Effects of Ionizing Irradiation on the Membrane Expression of Hsp70 on Glioma Cells" Cells 9, no. 4: 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040912
APA StyleFellinger, H., Stangl, S., Hernandez Schnelzer, A., Schwab, M., Di Genio, T., Pieper, M., Werner, C., Shevtsov, M., Haller, B., & Multhoff, G. (2020). Time- and Dose-Dependent Effects of Ionizing Irradiation on the Membrane Expression of Hsp70 on Glioma Cells. Cells, 9(4), 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040912