Phylogenetic Analysis and Genetic Structure of Schlegel’s Japanese Gecko (Gekko japonicus) from China Based on Mitochondrial DNA Sequences
Abstract
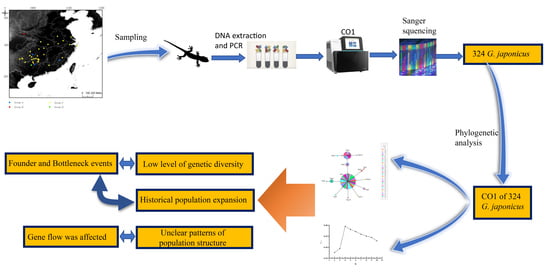
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.3. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analyses
2.4. Population Genetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sequence Information
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.3. Genetic Diversity, Genetic Structure and Historical Demography of G. japonicus Population
3.3.1. Genetic Diversity
3.3.2. Genetic Structure
3.3.3. Historical Demography
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rösler, H.; Bauer, A.M.; Heinicke, M.P.; Greenbaum, E.; Jackman, T.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Ziegler, T. Phylogeny, Taxonomy, and Zoogeography of the Genus Gekko Laurenti, 1768 with the Revalidation of G. reevesii Gray, 1831 (Sauria: Gekkonidae). Zootaxa 2011, 2989, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.-H.; Park, J.; Cheon, K.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, J.-K.; Park, D. Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Schlegel’s Japanese Gecko Gekko japonicus (Squamata: Gekkonidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2016, 27, 3684–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-I.; Park, I.-K.; Bae, S.-Y.; Fong, J.J.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Li, S.-R.; Ota, H.; Kim, J.-S.; Park, D. Prediction of Present and Future Distribution of the Schlegel’s Japanese Gecko (Gekko japonicus) Using MaxEnt Modeling. J. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 44, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Park, J.; Fong, J.J.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Li, S.-R.; Ota, H.; Min, S.-H.; Min, M.-S.; Park, D. Genetic Diversity and Inferred Dispersal History of the Schlegel’s Japanese Gecko (Gekko japonicus) in Northeast Asia Based on Population Genetic Analyses and Paleo-Species Distribution Modelling. Mitochondrial DNA A DNA Mapp. Seq. Anal. 2020, 31, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, S.; Beati, L.; Labruna, M.B.; Cáceres, A.G.; Mangold, A.J.; Guglielmone, A.A. Reassessment of the Taxonomic Status of Amblyomma cajennense (Fabricius, 1787) with the Description of Three New Species, Amblyomma tonelliae n. sp, Amblyomma interandinum n. sp. and Amblyomma patinoi n. sp., and Reinstatement of Amblyomma mixtum, and Amblyomma sculptum (Ixodida: Ixodidae). Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 252–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmer, K.R.; Kusche, H.; Lehtonen, T.K.; Meyer, A. Local Variation and Parallel Evolution: Morphological and Genetic Diversity across a Species Complex of Neotropical Crater Lake Cichlid Fishes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 1763–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Struck, T.H.; Feder, J.L.; Bendiksby, M.; Birkeland, S.; Cerca, J.; Gusarov, V.I.; Kistenich, S.; Larsson, K.-H.; Liow, L.H.; Nowak, M.D.; et al. Finding Evolutionary Processes Hidden in Cryptic Species. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Sousa-Paula, L.C.; Pessoa, F.A.C.; Otranto, D.; Dantas-Torres, F. Beyond Taxonomy: Species Complexes in New World Phlebotomine Sand Flies. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2021, 35, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fišer, C.; Robinson, C.T.; Malard, F. Cryptic Species as a Window into the Paradigm Shift of the Species Concept. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 613–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gill, B.A.; Kondratieff, B.C.; Casner, K.L.; Encalada, A.C.; Flecker, A.S.; Gannon, D.G.; Ghalambor, C.K.; Guayasamin, J.M.; Poff, N.L.; Simmons, M.P.; et al. Cryptic Species Diversity Reveals Biogeographic Support for the “mountain Passes Are Higher in the Tropics” Hypothesis. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2016, 283, 20160553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piganeau, G.; Gardner, M.; Eyre-Walker, A. A Broad Survey of Recombination in Animal Mitochondria. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 2319–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galtier, N.; Nabholz, B.; Glémin, S.; Hurst, G.D.D. Mitochondrial DNA as a Marker of Molecular Diversity: A Reappraisal. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 4541–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, T.R. Mitochondrial Gene Rearrangements: New Paradigm in the Evolutionary Biology and Systematics. Bioinformation 2008, 3, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solov’eva, E.N.; Poiarkov, N.A.; Dunaev, E.A.; Duĭsebaeva, T.N.; Bannikova, A.A. Molecular differentiation and taxonomy of the sunwatcher toadheaded agama species complex Phrynocephalus superspecies helioscopus (Pallas, 1771) (reptilia: Agamidae). Russ. J. Genet. 2011, 47, 842–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laopichienpong, N.; Muangmai, N.; Supikamolseni, A.; Twilprawat, P.; Chanhome, L.; Suntrarachun, S.; Peyachoknagul, S.; Srikulnath, K. Assessment of Snake DNA Barcodes Based on Mitochondrial COI and Cytb Genes Revealed Multiple Putative Cryptic Species in Thailand. Gene 2016, 594, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; deWaard, J.R. Biological Identifications through DNA Barcodes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanova, N.V.; Dewaard, J.R.; Hebert, P.D.N. An Inexpensive, Automation-Friendly Protocol for Recovering High-Quality DNA. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2006, 6, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Z.T.; Sonet, G.; Glaw, F.; Vences, M. First Large-Scale DNA Barcoding Assessment of Reptiles in the Biodiversity Hotspot of Madagascar, Based on Newly Designed COI Primers. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swindell, S.R.; Plasterer, T.N. SEQMAN. Contig Assembly. Methods Mol. Biol. 1997, 70, 75–89. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gintis, H. The Hitchhiker’s Guide to Altruism: Gene-Culture Coevolution, and the Internalization of Norms. J. Theor. Biol. 2003, 220, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New Methods for Selecting Partitioned Models of Evolution for Molecular and Morphological Phylogenetic Analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adeniran, A.A.; Hernández-Triana, L.M.; Ortega-Morales, A.I.; Garza-Hernández, J.A.; de la Cruz-Ramos, J.; Chan-Chable, R.J.; Vázquez-Marroquín, R.; Huerta-Jiménez, H.; Nikolova, N.I.; Fooks, A.R.; et al. Identification of Mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) from Mexico State, Mexico Using Morphology and COI DNA Barcoding. Acta Trop. 2021, 213, 105730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupanloup, I.; Schneider, S.; Excoffier, L. A Simulated Annealing Approach to Define the Genetic Structure of Populations. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 2571–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Yusoff, N.I.S.; Mat Jaafar, T.N.A.; Vilasri, V.; Mohd Nor, S.A.; Seah, Y.G.; Habib, A.; Wong, L.L.; Danish-Daniel, M.; Sung, Y.Y.; Mazlan, A.G.; et al. Genetic Diversity, Population Structure and Historical Demography of the Two-Spined Yellowtail Stargazer (Uranoscopus cognatus). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Smouse, P.E.; Quattro, J.M. Analysis of Molecular Variance Inferred from Metric Distances among DNA Haplotypes: Application to Human Mitochondrial DNA Restriction Data. Genetics 1992, 131, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, J.; Bryant, D. PopART: Full-Feature Software for Haplotype Network Construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, F. DNA Polymorphism in a Subdivided Population: The Expected Number of Segregating Sites in the Two-Subpopulation Model. Genetics 1989, 123, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.X. Statistical Tests of Neutrality of Mutations against Population Growth, Hitchhiking and Background Selection. Genetics 1997, 147, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.R.; Harpending, H. Population Growth Makes Waves in the Distribution of Pairwise Genetic Differences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1992, 9, 552–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harpending, H.C. Signature of Ancient Population Growth in a Low-Resolution Mitochondrial DNA Mismatch Distribution. Hum. Biol. 1994, 66, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Excoffier, L.; Lischer, H.E.L. Arlequin Suite Ver 3.5: A New Series of Programs to Perform Population Genetics Analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aungst, E.R.; Puente-Rolón, A.R.; Reynolds, R.G. Genetic Diversity in the US Ex Situ Populations of the Endangered Puerto Rican Boa, Chilabothrus inornatus. Zoo Biol. 2020, 39, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.-J.; Zhang, M.-L. Phylogeographical Structure Inferred from CpDNA Sequence Variation of Zygophyllum xanthoxylon across North-West China. J. Plant Res. 2015, 128, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajao, A.M.; Nneji, L.M.; Adeola, A.C.; Oladipo, S.O.; Ayoola, A.O.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Adeniyi, A.V.; Olademeji, Y.U. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of the Native Western African Honeybee (Apis mellifera Adansonii Latreille, 1804) in Nigeria Based on Mitochondrial COI Sequences. Zool. Anz. 2021, 293, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Wang, Q.; Chang, Q.; Ji, X.; Zhou, K. The Divergence of Two Independent Lineages of an Endemic Chinese Gecko, Gekko Swinhonis, Launched by the Qinling Orogenic Belt. Mol. Ecol. Mol. Ecol. 2010, 19, 2490–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Wang, Q. New Species Of Gekko (Squamata: Sauria: Gekkonidae) From China: Morphological And Molecular Evidence. Zootaxa 2008, 1778, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballenghien, M.; Faivre, N.; Galtier, N. Patterns of Cross-Contamination in a Multispecies Population Genomic Project: Detection, Quantification, Impact, and Solutions. BMC Biol. 2017, 15, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellegren, H.; Galtier, N. Determinants of Genetic Diversity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garza, J.C.; Williamson, E.G. Detection of Reduction in Population Size Using Data from Microsatellite Loci. Mol. Ecol. 2001, 10, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehouse, A.M.; Harley, E.H. Post-Bottleneck Genetic Diversity of Elephant Populations in South Africa, Revealed Using Microsatellite Analysis. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 10, 2139–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisely, S.M.; Buskirk, S.W.; Fleming, M.A.; McDonald, D.B.; Ostrander, E.A. Genetic Diversity and Fitness in Black-Footed Ferrets before and during a Bottleneck. J. Hered. 2002, 93, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ploshnitsa, A.; Goltsman, M.; Happ, G.; Macdonald, D.; Kennedy, L.; Volff, J. Historical and Modern Neutral Genetic Variability in Mednyi Arctic Foxes Passed through a Severe Bottleneck. J. Zool. 2013, 289, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbery, B.; Jones, D. Presence of Asian House Gecko Hemidactylus Frenatus across an Urban Gradient in Brisbane: Influence of Habitat and Potential for Impact on Native Gecko Species. In Pest or Guest: The Zoology of Overabundance; Lunney, D., Eby, P., Hutchings, P., Burgin, S., Eds.; Royal Zoological Society of New South Wales: Mosman, NSW, Australia, 2007; pp. 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, D.; González-Bernal, E.; Greenlees, M.; Shine, R. Interactions between Native and Invasive Gecko Lizards in Tropical Australia. Austral Ecol. 2012, 37, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werneck, F.P.; Leite, R.N.; Geurgas, S.R.; Rodrigues, M.T. Biogeographic History and Cryptic Diversity of Saxicolous Tropiduridae Lizards Endemic to the Semiarid Caatinga. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Excoffier, L.; Foll, M.; Petit, R.J. Genetic Consequences of Range Expansions. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Species | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. G. japonicus | 0.6 ± 0.2 | ||||||||||
| 2. AHAQ06 | 12.0–12.9 | - | |||||||||
| 3. G.wenxianensis | 21.7–23.5 | 23.6–24.1 | 1.0 ± 0.3 | ||||||||
| 4. G. chinensis | 31.7–33.3 | 28.3–31.0 | 25.4–28.7 | 3.4 ± 0.6 | |||||||
| 5. G. swinhonis | 30.0–34.4 | 27.2–31.6 | 29.2–32.8 | 25.1–30.0 | 9.1 ± 0.9 | ||||||
| 6. G. subpalmatus | 31.6–33.0 | 32.1–33.0 | 28.4–30.6 | 29.1–30.2 | 22.5–25.8 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | |||||
| 7. G.auriverrucosus | 30.2–31.4 | 30.5–31.3 | 31.5–32.7 | 30.2–33.0 | 24.0–27.2 | 24.5–26.2 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | ||||
| 8. G. hokouensis | 33.5–35.4 | 29.8–31.3 | 28.7–30.8 | 30.6–33.7 | 28.9–31.4 | 27.9–30.1 | 30.5–33.1 | 0.9 ± 0.3 | |||
| 9. G. scabridus | 31.4–35.2 | 33.8–36.2 | 26.8–30.7 | 24.1–29.3 | 23.2–29.5 | 25.3–29.0 | 27.3–31.7 | 29.2–33.0 | 4.3 ± 0.6 | ||
| 10. G.gecko | 36.2–38.6 | 35.1–35.8 | 35.4–37.3 | 36.4–38.5 | 34.2–37.8 | 42.0–44.9 | 39.1–40.7 | 37.0–40.8 | 35.3–38.5 | 2.1 ± 0.4 | |
| 11. G.kikuchii | 33.0–35.2 | 35.5 | 37.3–38.1 | 28.7–30.4 | 28.2–33.6 | 28.1–28.2 | 36.1–37.3 | 36.2–37.8 | 28.5–29.7 | 32.6–33.4 | - |
| Population | Number of Samples | Segregating Site (S) | Haplotypes | Haplotype Diversity (h) | Nucleotide Diversity (π) | Average Number of Difference (K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anqing, Anhui (AHAQ) | 11 | 2 | Hap1, 2, 3 | 0.473 | 0.00093 | 0.618 |
| Lin’an, Anhui (AHLA) | 1 | 0 | Hap1 | NA | NA | NA |
| Wuhu, Anhui (AHWH) | 12 | 2 | Hap1, 4 | 0.167 | 0.00050 | 0.333 |
| Yong’an, Fujian (FJYA) | 3 | 3 | Hap1, 5 | NA | NA | NA |
| Nanping, Fujian (FJNP) | 1 | 0 | Hap1 | NA | NA | NA |
| Guilin, Guangxi (GXGL) | 19 | 3 | Hap1, 5 | 0.105 | 0.00047 | 0.316 |
| Longsheng, Guangxi (GXLS) | 14 | 1 | Hap1, 6 | 0.264 | 0.00040 | 0.264 |
| Yongfu, Guangxi (GXYF) | 5 | 3 | Hap1, 5 | 0.400 | 0.00180 | 1.2 |
| Guiding, Guangzhou (GZGD) | 2 | 0 | Hap1 | NA | NA | NA |
| Libo, Guizhou (GZLB) | 3 | 0 | Hap1 | NA | NA | NA |
| Huaxi, Guizhou (GZHX) | 1 | 0 | Hap1 | NA | NA | NA |
| Longli, Guizhou (GZLL) | 2 | 0 | Hap1 | NA | NA | NA |
| Wuhan, Hubei (HBWH) | 13 | 3 | Hap1, 4, 5 | 0.590 | 0.00197 | 1.308 |
| Hubeijing (HBJM) | 1 | 0 | Hap1 | NA | NA | NA |
| Chengbu, Hunan (HNCB) | 13 | 0 | Hap1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Changde, Hunan (HNCD) | 8 | 2 | Hap1, 7 | 0.250 | 0.00075 | 0.5 |
| Daoxian, Hunan (HNDX) | 19 | 4 | Hap1, 5, 6 | 0.556 | 0.00237 | 1.579 |
| Huaihua, Hunan (HNHH) | 15 | 3 | Hap1, 5 | 0.248 | 0.00112 | 0.743 |
| Huitong, Hunan (HNHT) | 16 | 2 | Hap1, 8, 9 | 0.542 | 0.00091 | 0.583 |
| Huayuan, Hunan (HNHY) | 16 | 3 | Hap1, 5 | 0.233 | 0.00105 | 0.7 |
| Shuangpai, Hunan (HNSP) | 4 | 4 | Hap1, 5, 10 | NA | NA | NA |
| Shaoyang, Hunan (HNSY) | 5 | 1 | Hap1, 11 | 0.400 | 0.00060 | 0.4 |
| Tongdao, Hunan (HNTD) | 6 | 2 | Hap1, 4 | 0.333 | 0.00100 | 0.667 |
| Xinkou, Hunan (HNXH) | 20 | 3 | Hap1, 5 | 0.521 | 0.00235 | 1.563 |
| Xinning, Hunan (HNXN) | 4 | 0 | Hap1 | NA | NA | NA |
| Yueyang, Hunan (HNYY) | 12 | 0 | Hap1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Yongzhou, Hunan (HNYZ) | 12 | 3 | Hap1, 4, 5 | 0.591 | 0.00232 | 1.545 |
| Zhuzhou, Hunan (HNZZ) | 7 | 4 | Hap1, 5, 6 | 0.524 | 0.00172 | 1.143 |
| Rugao, Jiangsu (JSRG) | 2 | 0 | Hap1 | NA | NA | NA |
| Longnan, Jiangxi (JXLN) | 24 | 6 | Hap1, 12 | 0.159 | 0.00144 | 0.957 |
| Yueyan Forestry, Qingtang, Yongzhou, Hunan (QTYY) | 5 | 3 | Hap1, 5 | 0.400 | 0.00188 | 1.200 |
| Yangxian, Shaanxi (SXYX) | 15 | 3 | Hap1, 5 | 0.533 | 0.00241 | 1.600 |
| Lingshutan, Yongzhou, Hunan (YZLST) | 12 | 2 | Hap1, 4 | 0.303 | 0.00091 | 0.606 |
| Hangzhou, Zhejiang (ZJHZ) | 8 | 5 | Hap1, 5, 13 | 0.464 | 0.00188 | 1.25 |
| Zhoushan, Zhejiang (ZJZS) | 11 | 4 | Hap1, 4, 14 | 0.564 | 0.00208 | 1.382 |
| Lishui, Zhejiang (ZJLS) | 1 | 0 | Hap1 | NA | NA | NA |
| Yangshuo, Guangxi (GXYS) | 1 | 0 | Hap1 | NA | NA | NA |
| Overall | 324 | 16 | 14 | 0.453 | 0.00176 | 1.171 |
| Source of Variations | Sum of Squares | Variance Components | Percentage of Variation | Fixation Indices | Significance Tests |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among groups | 47.762 | 0.57420 | 39.53 | FCT = 0.39527 | 0.00000 |
| Among populations within groups | 32.026 | 0.01214 | 0.84 | FSC = 0.01382 | 0.02639 |
| Within populations | 252.108 | 0.86635 | 59.64 | ||
| Total | 333.896 | 1.45269 | FST = 0.40362 | 0.03030 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, L.; Cai, F.; Chen, S.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, K.; Yan, J.; Li, P. Phylogenetic Analysis and Genetic Structure of Schlegel’s Japanese Gecko (Gekko japonicus) from China Based on Mitochondrial DNA Sequences. Genes 2023, 14, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010018
Xia L, Cai F, Chen S, Cai Y, Zhou K, Yan J, Li P. Phylogenetic Analysis and Genetic Structure of Schlegel’s Japanese Gecko (Gekko japonicus) from China Based on Mitochondrial DNA Sequences. Genes. 2023; 14(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Longjie, Fengna Cai, Shasha Chen, Yao Cai, Kaiya Zhou, Jie Yan, and Peng Li. 2023. "Phylogenetic Analysis and Genetic Structure of Schlegel’s Japanese Gecko (Gekko japonicus) from China Based on Mitochondrial DNA Sequences" Genes 14, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010018
APA StyleXia, L., Cai, F., Chen, S., Cai, Y., Zhou, K., Yan, J., & Li, P. (2023). Phylogenetic Analysis and Genetic Structure of Schlegel’s Japanese Gecko (Gekko japonicus) from China Based on Mitochondrial DNA Sequences. Genes, 14(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010018