Quorum Sensing and Quorum Quenching in Agrobacterium: A “Go/No Go System”?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Ti Plasmid Transfer is Regulated by Quorum Sensing and Opines
3. TraM Acts as a Quorum Quenching Regulator of an Unusual Quorum Sensing System
4. Two Quorum Quenching Lactonases Modulating QS and Ti Plasmid Transfer
5. The Quorum Quenching Lactonases as Cogs to Sense Environmental Cues
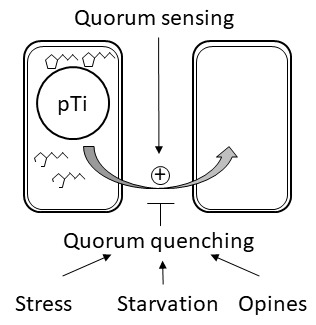
6. Quorum Sensing and Quorum Quenching as Two Parts of an Integrated Regulation Mechanism
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pitzschke, A.; Hirt, H. New insights into an old story: Agrobacterium-induced tumour formation in plants by plant transformation. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelvin, S.B. Traversing the Cell: Agrobacterium T-DNA’s journey to the host genome. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, B.; Citovsky, V. The roles of bacterial and host plant factors in Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2013, 57, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramoni, S.; Nathoo, N.; Klimov, E. Agrobacterium tumefaciens responses to plant-derived signaling molecules. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nester, E.W. Agrobacterium: Nature’s genetic engineer. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 5, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, P.J. The mosaic Type IV secretion systems. EcoSal Plus 2016, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelvin, S.B. Integration of Agrobacterium T-DNA into the plant genome. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2017, 51, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooms, G.; Hooykaas, P.J.; Moolenaar, G.; Schilperoort, R.A. Grown gall plant tumors of abnormal morphology, induced by Agrobacterium tumefaciens carrying mutated octopine Ti plasmids; analysis of T-DNA functions. Gene 1981, 14, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyoshi, D.E.; Morris, R.O.; Hinz, R.; Mischke, B.S.; Kosuge, T.; Garfinkel, D.J.; Gordon, M.P.; Nester, E.W. Cytokinin/auxin balance in crown gall tumors is regulated by specific loci in the T-DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ream, L.W.; Gordon, M.P.; Nester, E.W. Multiple mutations in the T region of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens tumor-inducing plasmid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 1660–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dessaux, Y.; Petit, A.; Farrand, S.K.; Murphy, P.M. Opine and opine-like molecules involved in plant-Rhizobiaceaea interactions. In The Rhizobiaceae; Spaink, H.P., Kondorosi, A., Hooykaas, P., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 173–197. ISBN 978-94-011-5060-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, J.; Vigouroux, A.; Planamente, S.; El Sahili, A.; Blin, P.; Aumont-Nicaise, M.; Dessaux, Y.; Moréra, S.; Faure, D. Agrobacterium uses a unique ligand-binding mode for trapping opines and acquiring a competitive advantage in the niche construction on plant host. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigouroux, A.; El Sahili, A.; Lang, J.; Aumont-Nicaise, M.; Dessaux, Y.; Faure, D.; Moréra, D. Structural basis for high specificity of octopine binding in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrand, S.K. Conjugal plasmids and their transfer. In The Rhizobiaceae; Spaink, H.P., Kondorosi, A., Hooykaas, P., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 199–233. ISBN 978-94-011-5060-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, J.; Faure, D. Functions and regulation of quorum-sensing in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, K.R.; Beck von Bodman, S.; Farrand, S.K. Conjugation factor of Agrobacterium tumefaciens regulates Ti plasmid transfer by autoinduction. Nature 1993, 362, 448–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Murphy, P.J.; Kerr, A.; Tate, M.E. Agrobacterium conjugation and gene regulation by N-acyl-l-homoserine lactones. Nature 1993, 362, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, J.G.; Kerr, A.; Petit, A.; Tempé, J. Conjugal transfer of nopaline and agropine Ti-plasmids–The role of agrocinopines. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1982, 186, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sahili, A.; Li, S.Z.; Lang, J.; Virus, C.; Planamente, S.; Ahmar, M.; Guimaraes, B.G.; Aumont-Nicaise, M.; Vigouroux, A.; Soulère, L.; et al. A pyranose-2-phosphate motif is responsible for both antibiotic import and quorum-sensing regulation in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck von Bodman, S.; Hayman, G.T.; Farrand, S.K. Opine catabolism and conjugal transfer of the nopaline Ti plasmid pTiC58 are coordinately regulated by a single repressor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayman, G.T.; Beck Von Bodman, S.; Kim, H.; Jiang, P.; Farrand, S.K. Genetic analysis of the agrocinopine catabolic region of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid pTiC58, which encodes genes required for opine and agrocin 84 transport. J. Bacteriol. 1993, 175, 5575–5584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.Q.; Farrand, S.K. Signal-dependent DNA binding and functional domains of the quorum-sensing activator TraR as identified by repressor activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9009–9014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piper, K.R.; Beck von Bodman, S.; Hwang, I.; Farrand, S.K. Hierarchical gene regulatory systems arising from fortuitous gene associations: Controlling quorum sensing by the opine regulon in Agrobacterium. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 32, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.; Li, P.L.; Zhang, L.; Piper, K.R.; Cook, D.M.; Tate, M.E.; Farrand, S.K. TraI, a LuxI homologue, is responsible for production of conjugation factor, the Ti plasmid N-acylhomoserine lactone autoinducer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 4639–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.L.; Everhart, D.M.; Farrand, S.K. Genetic and sequence analysis of the pTiC58 trb locus, encoding a mating-pair formation system related to members of the type IV secretion family. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 6164–6172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cook, D.M.; Li, P.L.; Ruchaud, F.; Padden, S.; Farrand, S.K. Ti plasmid conjugation is independent of vir: Reconstitution of the tra functions from pTiC58 as a binary system. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrand, S.K.; Hwang, I.; Cook, D.M. The tra region of the nopaline-type Ti plasmid is a chimera with elements related to the transfer systems of RSF1010, RP4, and F. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 4233–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuqua, W.C.; Winans, S.C. A LuxR-LuxI type regulatory system activates Agrobacterium Ti plasmid conjugal transfer in the presence of a plant tumor metabolite. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 2796–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alt-Mörbe, J.; Stryker, J.L.; Fuqua, C.; Li, P.L.; Farrand, S.K.; Winans, S.C. The conjugal transfer system of Agrobacterium tumefaciens octopine-type Ti plasmids is closely related to the transfer system of an IncP plasmid and distantly related to Ti plasmid vir genes. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 4248–4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, S.; Khan, S.R.; Farrand, S.K. Induction and loss of Ti plasmid conjugative competence in response to the acyl-homoserine lactone quorum-sensing signal. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 4398–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.; Cook, D.M.; Farrand, S.K. A new regulatory element modulates homoserine lactone-mediated autoinduction of Ti plasmid conjugal transfer. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuqua, C.; Burbea, M.; Winans, S.C. Activity of the Agrobacterium Ti plasmid conjugal transfer regulator TraR is inhibited by the product of the traM gene. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.; Smyth, A.J.; Luo, Z.Q.; Farrand, S.K. Modulating quorum sensing by antiactivation: TraM interacts with TraR to inhibit activation of Ti plasmid conjugal transfer genes. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 34, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandclément, C.; Tannières, M.; Moréra, S.; Dessaux, Y.; Faure, D. Quorum quenching: Role in nature and applied developments. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 86–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlier, A.; Uroz, S.; Smadja, B.; Fray, R.; Latour, X.; Dessaux, Y.; Faure, D. The Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens harbors an attM-paralogous gene, aiiB, also encoding N-acyl homoserine lactonase activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4989–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Thomas, P.W.; Momb, J.; Hoang, Q.Q.; Petsko, G.A.; Ringe, D.; Fast, W. Structure and specificity of a quorum-quenching lactonase (AiiB) from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 11789–11799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haudecoeur, E.; Tannières, M.; Cirou, A.; Raffoux, A.; Dessaux, Y.; Faure, D. Different regulation and roles of lactonases AiiB and AttM in Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.B.; Wang, L.H.; Zhang, L.H. Genetic control of quorum-sensing signal turnover in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4638–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.H. Quorum quenching and proactive host defense. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 8, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlier, A.; Chevrot, R.; Dessaux, Y.; Faure, D. The assimilation of gamma-butyrolactone in Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 interferes with the accumulation of the N-acyl-homoserine lactone signal. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2004, 17, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, Y.; Tsai, C.S.; Cho, H.; Winans, S.C. Reconstitution of the biochemical activities of the AttJ repressor and the AttK, AttL, and AttM catabolic enzymes of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 3674–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.R.; Farrand, S.K. The BlcC (AttM) lactonase of Agrobacterium tumefaciens does not quench the quorum-sensing system that regulates Ti plasmid conjugative transfer. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, H.B.; Wang, L.H.; Zhang, L.H. Succinic semialdehyde couples stress response to quorum-sensing signal decay in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 62, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, R.; Matthysse, A.G.; Becher, D.; Biran, D.; Yura, T.; Hecker, M.; Ron, E.Z. Proteome analysis of plant-induced proteins of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2003, 44, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrot, R.; Rosen, R.; Haudecoeur, E.; Cirou, A.; Shelp, B.J.; Ron, E.; Faure, D. GABA controls the level of quorum-sensing signal in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7460–7464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.C.; Haudecoeur, E.; Faure, D.; Kerr, K.F.; Nester, E.W. Comparative transcriptome analysis of Agrobacterium tumefaciens in response to plant signal salicylic acid, indole-3-acetic acid and gamma-amino butyric acid reveals signalling cross-talk and Agrobacterium–plant co-evolution. Cell Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2339–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, J.; Gonzalez-Mula, A.; Taconnat, L.; Clement, G.; Faure, D. The plant GABA signaling downregulates horizontal transfer of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens virulence plasmid. New Phytol. 2016, 210, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelp, B.J.; Bozzo, G.G.; Trobacher, C.P.; Zarei, A.; Deyman, K.L.; Brikis, C.J. Hypothesis/review: Contribution of putrescine to 4-aminobutyrate (GABA) production in response to abiotic stress. Plant Sci. 2012, 193–194, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancucci, M.; Mattioli, R.; Forlani, G.; Funck, D.; Costantino, P.; Trovato, M. Role of proline and GABA in sexual reproduction of angiosperms. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, M.; Ezura, H. How and why does tomato accumulate a large amount of GABA in the fruit? Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, S.A.; Tyerman, S.D.; Gilliham, M.; Xu, B. γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) signalling in plants. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 1577–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholz, S.S.; Reichelt, M.; Mekonnen, D.W.; Ludewig, F.; Mithöfer, A. Insect herbivory-elicited GABA accumulation in plants is a wound-induced, direct, systemic, and jasmonate-independent defense response. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haudecoeur, E.; Planamente, S.; Cirou, A.; Tannières, M.; Shelp, B.J.; Moréra, S.; Faure, D. Proline antagonizes GABA-induced quenching of quorum-sensing in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14587–14592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planamente, S.; Vigouroux, A.; Mondy, S.; Nicaise, M.; Faure, D.; Moréra, S. A conserved mechanism of GABA binding and antagonism is revealed by structure-function analysis of the periplasmic binding protein Atu2422 in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 30294–30303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.H. The quormone degradation system of Agrobacterium tumefaciens is regulated by starvation signal and stress alarmone (p)ppGpp. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 52, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauryliuk, V.; Atkinson, G.C.; Murakami, K.S.; Tenson, T.; Gerdes, K. Recent functional insights into the role of (p)ppGpp in bacterial physiology. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinchen, W.; Bange, G. The magic dance of the alarmones (p)ppGpp. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 101, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brohn, F.; Tchen, T.T. A single transaminase for 1,4-diaminobutane and 4-aminobutyrate in a Pseudomonas species. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1971, 45, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dover, S.; Halpern, Y.S. Utilization of γ-aminobutyric acid as the sole carbon and nitrogen source by Escherichia coli K-12 mutants. J. Bacteriol. 1972, 109, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakano, Y.; Tokunaga, H.; Kitaoka, S. Two omega-amino acid transaminases from Bacillus cereus. J. Biochem. 1977, 81, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilms, I.; Voss, B.; Hess, W.R.; Leichert, L.I.; Narberhaus, F. Small RNA-mediated control of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens GABA binding protein. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 80, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Rockett, K.S.; Kørner, C.J.; Pajerowska-Mukhtar, K.M. Salicylic acid signalling: New insights and prospects at a quarter-century milestone. Essays Biochem. 2015, 58, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodner, B.; Hinkle, G.; Gattung, S.; Miller, N.; Blanchard, M.; Qurollo, B.; Goldman, B.S.; Cao, Y.; Askenazi, M.; Halling, C.; et al. Genome sequence of the plant pathogen and biotechnology agent Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58. Science 2001, 294, 2323–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, D.W.; Setubal, J.C.; Kaul, R.; Monks, D.E.; Kitajima, J.P.; Okura, V.K.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, L.; Wood, G.E.; Almeida, N.F., Jr.; et al. The genome of the natural genetic engineer Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58. Science 2001, 294, 2317–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, J.; Planamente, S.; Mondy, S.; Dessaux, Y.; Moréra, S.; Faure, D. Concerted transfer of the virulence Ti plasmid and companion At plasmid in the Agrobacterium tumefaciens-induced plant tumour. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 90, 1178–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grohmann, E.; Christie, P.J.; Waksman, G.; Backert, S. Type IV secretion in Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 2018, 107, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tannières, M.; Lang, J.; Barnier, C.; Shykoff, J.A.; Faure, D. Quorum-quenching limits quorum-sensing exploitation by signal-negative invaders. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, C.E.; Finan, T.M. Quorum quenching in Agrobacterium tumefaciens: Chance or necessity? J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 1123–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haudecoeur, E.; Faure, D. A fine control of quorum-sensing communication in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2010, 3, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, J.; Faure, D. Plant GABA: Proline ratio modulates dissemination of the virulence Ti plasmid within the Agrobacterium tumefaciens hosted population. Plant Signal. Behav. 2016, 11, e1178440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Pinto, U.M.; Winans, S.C. Transsexuality in the rhizosphere: Quorum sensing reversibly converts Agrobacterium tumefaciens from phenotypically female to male. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 3375–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobzhansky, T. Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution. Am. Biol. Teach. 1973, 35, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dessaux, Y.; Faure, D. Quorum Sensing and Quorum Quenching in Agrobacterium: A “Go/No Go System”? Genes 2018, 9, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9040210
Dessaux Y, Faure D. Quorum Sensing and Quorum Quenching in Agrobacterium: A “Go/No Go System”? Genes. 2018; 9(4):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9040210
Chicago/Turabian StyleDessaux, Yves, and Denis Faure. 2018. "Quorum Sensing and Quorum Quenching in Agrobacterium: A “Go/No Go System”?" Genes 9, no. 4: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9040210
APA StyleDessaux, Y., & Faure, D. (2018). Quorum Sensing and Quorum Quenching in Agrobacterium: A “Go/No Go System”? Genes, 9(4), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9040210