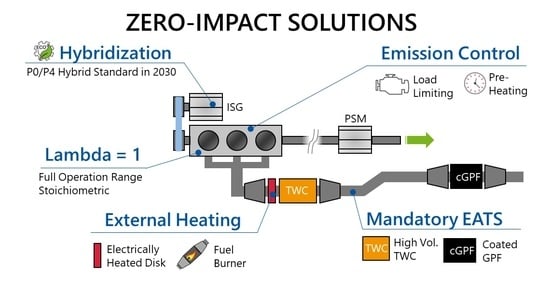
Achieving Zero-Impact Emissions with a Gasoline Passenger Car
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Modeling a Gasoline Passenger Car
2.1. Simulation Approach
2.1.1. Raw Emission Modeling
2.1.2. Exhaust Component Characterization
2.1.3. Three-Way Catalyst Modeling
2.2. Gasoline Passenger Car
2.2.1. Base Engine and Exhaust Aftertreatment
2.2.2. Vehicle Configuration for 2030+
3. Identifying Challenging Test Scenarios
3.1. Euro 7 Scenarios
3.2. Challenging Real-World Scenarios for Euro 7
3.3. Zero-Impact Emission Definition and Test Scenarios
4. Advanced Emission Control Technologies
4.1. Base Technologies for Future 2030+ Vehicles
4.2. Advanced Cold Emission Reduction
5. Results
5.1. Euro 7 Scenario
5.1.1. Electrical Heater Disk—EHD
5.1.2. Exhaust Gas Burner—ExB
5.2. Zero-Impact Emissions
5.2.1. Electrical Heater Disk—EHD
5.2.2. Exhaust Gas Burner—ExB
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Euro 7 Results for HC and CO


Appendix B. Cycle Profiles

References
- Reitz, R.D.; Ogawa, H.; Payri, R.; Fansler, T.; Kokjohn, S.; Moriyoshi, Y.; Agarwal, A.K.; Arcoumanis, D.; Assanis, D.; Bae, C.; et al. IJER editorial: The future of the internal combustion engine. Int. J. Engine Res. 2020, 21, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, R.J.; Ochieng, W.Y.; Quddus, M.A.; Noland, R.B.; Polak, J.W. Development of a vehicle emissions monitoring system. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Transp. 2005, 158, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontaras, G.; Zacharof, N.-G.; Ciuffo, B. Fuel consumption and CO2 emissions from passenger cars in Europe—Laboratory versus real-world emissions. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2017, 60, 97–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimaratos, A.; Toumasatos, Z.; Doulgeris, S.; Triantafyllopoulos, G.; Kontses, A.; Samaras, Z. Assessment of CO2 and NOx emissions of one diesel and one bi-fuel gasoline/CNG euro 6 vehicles during real-world driving and laboratory testing. Front. Mech. Eng. 2019, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonen, P.; Kalliokoski, J.; Karjalainen, P.; Rönkkö, T.; Timonen, H.; Saarikoski, S.; Aurela, M.; Bloss, M.; Triantafyllopoulos, G.; Kontses, A.; et al. Characterization of laboratory and real driving emissions of individual Euro 6 light-duty vehicles—Fresh particles and secondary aerosol formation. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claßen, J.; Krysmon, S.; Dorscheidt, F.; Sterlepper, S.; Pischinger, S. Real driving emission calibration—Review of current validation methods against the background of future emission legislation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toenges-Schuller, N.; Schneider, C.; Niederau, A.; Vogt, R.; Hausberger, S. Modelling the effect on air quality of Euro 6 emission factor scenarios. J. Earth Sci. Geotech. Eng. 2016, 6, 227–244. [Google Scholar]
- de Meij, A.; Astorga, C.; Thunis, P.; Crippa, M.; Guizzardi, D.; Pisoni, E.; Valverde, V.; Suarez-Bertoa, R.; Oreggioni, G.D.; Mahiques, O.; et al. Modelling the impact of the introduction of the EURO 6d-TEMP/6d regulation for light-duty vehicles on EU air quality. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, H.; Okada, M.; Yanai, K.; Kugata, M.; Hoshi, J. Exhaust emissions from gasoline vehicles after parking events evaluated by chassis dynamometer experiment and chemical kinetic model of three-way catalytic converter. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaras, Z.; Balazs, A.; Ehrly, M.; Kontses, A.; Dimaratos, A.; Kontses, D.; Aakko, P.; Ligterink, N.; Andersson, J.; Scarbarough, T.; et al. Preliminary findings on possible Euro 7 emission limits for passenger cars and LCVs. In Proceedings of the Online AGVES Meeting, Online, 8 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Samaras, Z.; Hausberger, S.; Mellios, G. Preliminary findings on possible Euro 7 emission limits for LD and HD vehicles. In Proceedings of the Online AGVES Meeting, Online, 27 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Raju, A.S.; Wallerstein, B.R.; Johnson, K.C. Achieving NOx and Greenhouse gas emissions goals in California’s Heavy-Duty transportation sector. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2021, 97, 102881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The California Low-Emission Vehicle Regulations: CARB. 2022.
- Eichlseder, H.; Hausberger, S.; Sturm, P. The zero impact combustion engine—A vision? In Proceedings of the 32nd International AVL Conference “Engine & Environment”, Graz, Austria, 25–29 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Eichlseder, H.; Hausberger, S.; Beidl, C.; Steinhaus, T. Zero impact—Objective and significance for vehicle powertrains and air quality. In Internationaler Motorenkongress 2021; Liebl, J., Beidl, C., Maus, W., Eds.; MORGAN KAUFMANN: Burlington, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 437–451. ISBN 978-3-658-35587-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hausberger, S.; Urner, U.; Toenges-Schuller, N.; Stadlhofer, W.; Schneider, C. Zero-Impact Vehicle Emissions—Final Report; FVV e.V.: Frankfurt, Germany.
- Maurer, R.; Kossioris, T.; Hausberger, S.; Toenges-Schuller, N.; Sterlepper, S.; Günther, M.; Pischinger, S. How to define and achieve zero-impact emissions in road transport? Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2023, 12, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, H.; Fischer, R. Zero-impact mobility. Emissions and lifecycle CO2: No longer a conflict? In Proceedings of the 32nd International AVL Conference “Engine & Environment”, Graz, Austria, 25–29 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Maurer, R.; Yadla, S.K.; Balazs, A.; Thewes, M.; Walter, V.; Uhlmann, T. Designing zero impact emission vehicle concepts. In Experten-Forum Powertrain: Ladungswechsel und Emissionierung 2020; Liebl, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 75–116. ISBN 978-3-662-63523-0. [Google Scholar]
- García-Contreras, R.; Soriano, J.A.; Fernández-Yáñez, P.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, L.; Mata, C.; Gómez, A.; Armas, O.; Cárdenas, M.D. Impact of regulated pollutant emissions of Euro 6d-Temp light-duty diesel vehicles under real driving conditions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 124927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntziachristos, L.; Papadimitriou, G.; Ligterink, N.; Hausberger, S. Implications of diesel emissions control failures to emission factors and road transport NOx evolution. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 141, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharof, N.; Tietge, U.; Franco, V.; Mock, P. Type approval and real-world CO2 and NOx emissions from EU light commercial vehicles. Energy Policy 2016, 97, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Yin, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; He, C.; Liang, J.; He, D.; Yin, H.; He, K. Assessing Heavy-Duty Vehicles (HDVs) on-road NOx emission in China from On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) remote report data. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 846, 157209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, J.; Xu, P.; Zhang, Y. Moving towards sustainability: Road grades and on-road emissions of heavy-duty vehicles—A case study. Sustainability 2015, 7, 12644–12671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papetti, V.; Dimopoulos Eggenschwiler, P.; Emmanouil, V.; Koltsakis, G. Analysis of TWC characteristics in a Euro6 gasoline light duty vehicle. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Engines & Vehicles; SAE Technical Paper Series; Warrendale, PA, USA, 15–19 September 2019; SAE International400 Commonwealth Drive: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, D. New Generation Gasoline Particulate Filters for Uncatalyzed Applications and Lowest Particulate Emissions. In Proceedings of the 12th International VERT FORUM, eConference. 24 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Association for Emissions Control by Catalyst. Gasoline Particle Filter: How Can the GPF Cut Emissions of Ultrafine Particles from Gasoline Engines? 2017. Available online: https://www.aecc.eu/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/2017-AECC-technical-summary-on-GPF-final.pdf (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Maus, W.; Brück, R.; Konieczny, R.; Scheeder, A. Electrically heated catalyst for thermal management in modern vehicle applications. MTZ Worldw. 2010, 71, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Tian, G.; Sorniotti, A.; Karci, A.E.; Di Palo, R. Review of thermal management of catalytic converters to decrease engine emissions during cold start and warm up. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 147, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucchi, M.; Medda, M.; Paltrinieri, S.; Rossi, V.; Rulli, F.; Tonelli, R. Active heating devices to reduce cold start emissions in sport cars. In Proceedings of the 43rd International Vienna Motor Symposium, Vienna, Austria, 27–29 April 2022; p. 32, ISBN 978-3-9504969-1-8. [Google Scholar]
- Vilwanathan Velmurugan, D.; McKelvey, T.; Olsson, J.-O. Data-driven near-optimal on-line control for an electrically heated catalyst-equipped gasoline engine. SAE Int. J. Engines 2023, 16, 03-16-03-0019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgarten, H.; Scharf, J.; Thewes, M.; Uhlmann, T.; Balazs, A.; Böhmer, M. Simulation-Based Development Methodology for Future Emission Legislation. In Proceedings of the 37th Internationales Wiener Motorensymposium, Vienna, Austria, 28–29 April 2016; pp. 209–231, ISBN 9783186799128. [Google Scholar]
- Böhmer, M. Marius Böhmer. Simulation of Exhaust Emissions for Hybrid Vehicles Considering Real Driving Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- DiGiulio, C.D.; Pihl, J.A.; Parks, J.E., II; Amiridis, M.D.; Toops, T.J. Passive-ammonia Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR): Understanding NH3 formation over close-coupled Three Way Catalysts (TWC). Catal. Today 2014, 231, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekman, S.K. Review of nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions from motor vehicles. SAE Int. J. Fuels Lubr. 2020, 13, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J. An evaluation of the conversion of gasoline and natural gas spark ignition engines to ammonia/hydrogen operation from the perspective of laminar flame speed. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2023, 145, 012302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The International Council on Clean Transportation. Driving Resistances of Light-Duty Vehicles in Europe: Present Situation, Trends and Scenarios for 2025; The International Council on Clean Transportation: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlmann, T.; Alt, N.; Thewes, M.; Lückmann, D.; Balazs, A.; Maurer, R.; Sahr, C.; Kürten, C.; Vosshall, T.; Müller, A. Hybrid BEV—A one platform solution for future passenger cars. In 30. Aachen Colloquium Sustainable Mobility; RWTH Aachen University: Aachen, Germany, 2021; ISBN 978-3-00-068207-0. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlmann, T.; Alt, N.; Lückmann, D.; Balazs, A.; Zwar, P.; Müller, A.; Thewes, M.; Frese, J. xHEV Konzept zur Erreichung der CO2-Ziele in 2030. In Proceedings of the 42nd International Vienna Motor Symposium, Vienna, Austria, 29–30 April 2021; ISBN 9783950496901. [Google Scholar]
- Proposal for a Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council on Type-Approval of Motor Vehicles and Engines and of Systems, Components and Separate Technical Units Intended for Such Vehicles, with Respect to Their Emissions and Battery Durability (Euro 7) and Repealing Regulations (EC) No 715/2007 and (EC) No 595/2009. 2022. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A52022PC0586 (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Meng, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J. Investigation of in-cylinder combustion deterioration of diesel engines in plateau regions. Fuel 2022, 324, 124824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kexel, J.; Müller, J.; Günther, M.; Pischinger, S.; Sens, M. HyFlex-ICE Intermediate Report; FVV e.V.: Frankfurt, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Maurer, R.; Kossioris, T.; Sterlepper, S.; Günther, M.; Bunar, F. Zero-Impact Tailpipe Emissions: Final Report, Project no. 1412; FVV eV: Frankfurt, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hausberger, S.; Urner, U.; Toenges-Schuller, N.; Stadlhofer, W.; Schneider, C. Zero-Impact Vehicle Emissions— Interim Report 15.12.2020 t; FVV e.V.: Frankfurt, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kossioris, T.; Maurer, R. Zero-Impact Tailpipe Emissions—Test Cycles, Mendeley Data, V1. Available online: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/z4kdp3k6dp/1 (accessed on 4 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; McNabola, A.; Misstear, B.; Pilla, F.; Alam, M.S. Assessing the impact of vehicle speed limits and fleet composition on air quality near a school. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, M.C.; Farias, T.L.; Rouphail, N.M. Effect of roundabout operations on pollutant emissions. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2006, 11, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, M.C.; Farias, T.L.; Rouphail, N.M. Impact of speed control traffic signals on pollutant emissions. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2005, 10, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, M.C.; Frey, H.C.; Rouphail, N.M.; Zhai, H.; Pelkmans, L. Assessing methods for comparing emissions from gasoline and diesel light-duty vehicles based on microscale measurements. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2009, 14, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proposal for a Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council Amending Regulation (EU) 2019/631. 2021. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/en/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A52021PC0556 (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Zhu, G.; Liu, J.; Fu, J.; Xu, Z.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, H. Experimental study on combustion and emission characteristics of turbocharged gasoline direct injection (GDI) engine under cold start New European Driving Cycle (NEDC). Fuel 2018, 215, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, G.; Subramanian, S. Experimental investigation of cold start emission using dynamic catalytic converter with pre-catalyst and hot air injector on a multi cylinder spark ignition engine; SAE Technical Paper Series. In Proceedings of the International Powertrains, Fuels & Lubricants Meeting, Beijing, China, 8 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf, A.A.; Inambao, F.L. Effect of cold start emissions from gasoline-fueled engines of light-duty vehicles at low and high ambient temperatures: Recent trends. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2019, 14, 100417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, F.; Steinhuber, T.; Grußmann, E.; Rusche, U. Concept studies for electrically heated catalysts. MTZ Worldw. 2021, 82, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, J.; Hirth, P.; Brück, R.; Kruse, C. Electrically heated catalyst for future USA and european legislation; SAE Technical Paper Series. In Proceedings of the International Congress & Exposition, Atlanta, Ga, USA, 1 February 1996; p. 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Öser, P.; Mueller, E.; Härtel, G.; Schürfeld, A. Novel emission technologies with emphasis on catalyst cold start improvements status report on VW-Pierburg Burner/Catalyst systems. SAE Trans. 1994, 103, 183–196. [Google Scholar]
- Canè, S.; Brunelli, L.; Gallian, S.; Perazzo, A.; Brusa, A.; Cavina, N. Performance assessment of a predictive pre-heating strategy for a hybrid electric vehicle equipped with an electrically heated catalyst. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 219, 119341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brück, R.K.K. Innovative catalyst system to achieve EU7 legislation for electrified powertrains. In Proceedings of the 43rd International Vienna Motor Symposium, Vienna, Austria, 27–29 April 2022; ISBN 978-3-9504969-1-8. [Google Scholar]
- Jean, E.; Capirchia, M.; Herbers, C. Electrically heated catalyst for Euro7 hybrid vehicles. In Proceedings of the 43rd International Vienna Motor Symposium, Vienna, Austria, 27–29 April 2022; ISBN 978-3-9504969-1-8. [Google Scholar]
- Werblinski, T.; Christgen, W.; Traversa, P.; Schroeder, C. Valve train system for P0 und P1 hybrid powertrains. In Proceedings of the 30 Aachen Colloquium Sustainable Mobility, Aachen, Germany, 4–6 October 2021; pp. 1301–1324, ISBN 978-3-00-068207-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcutts, M.; Wolk, B.; Yang, X.; Wang, R. Electrified deceleration cylinder cutoff engine control benefits and strategies; SAE Technical Paper Series. In Proceedings of the SAE WCX Digital Summit, Online, 6 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
















| Euro 6 Gasoline | Euro 7 CLOVE A 2021 [11] | Euro 7 EC Draft 2022 [21] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOX | mg/km | 60 | 30 | 60 |
| CO | mg/km | 1000 | 300 | 500 |
| HC * | mg/km | 100 | 70 | 100 |
| PN ** | 1/km | 6 × 1011 | 1 × 1011 | 6 × 1011 |
| PM | mg/km | 4.5 | - | 4.5 |
| N2O | mg/km | - | 10 | - |
| NH3 | mg/km | - | 5 | 20 |
| Reference distance / km | - | 16 | 10 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maurer, R.; Kossioris, T.; Sterlepper, S.; Günther, M.; Pischinger, S. Achieving Zero-Impact Emissions with a Gasoline Passenger Car. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020313
Maurer R, Kossioris T, Sterlepper S, Günther M, Pischinger S. Achieving Zero-Impact Emissions with a Gasoline Passenger Car. Atmosphere. 2023; 14(2):313. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020313
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaurer, Robert, Theodoros Kossioris, Stefan Sterlepper, Marco Günther, and Stefan Pischinger. 2023. "Achieving Zero-Impact Emissions with a Gasoline Passenger Car" Atmosphere 14, no. 2: 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020313
APA StyleMaurer, R., Kossioris, T., Sterlepper, S., Günther, M., & Pischinger, S. (2023). Achieving Zero-Impact Emissions with a Gasoline Passenger Car. Atmosphere, 14(2), 313. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos14020313