The Impact of Diabetes Education on Continuous Glucose Monitoring in SUS-Dependent Patients in a Northeastern Brazilian City
Abstract
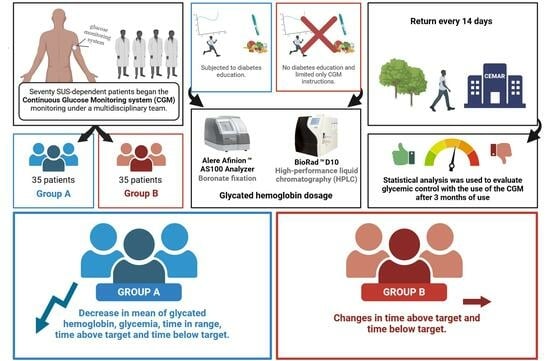
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Diabetes Education
2.2. Collection and Analysis of HbA1C
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Answers to the Questionnaire
3.2. Group A Patients
3.3. Group B Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtual Health Library. Available online: https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/26-6-dia-nacional-do-diabetes-4/ (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Guidoni, C.M.; Olivera, C.M.X.; Freitas, O.; Pereira, L.R.L. Diabetes care in the Brazilian National Health System: An analysis of the current model. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 45, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. Available online: https://www.ibge.gov.br/estatisticas/sociais/saude.html (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Malta, D.C.; Duncan, B.B.; Schmidt, M.I.; Machado, Í.E.; Silva, A.G.; Bernal, R.T.I.; Pereira, C.A.; Damacena, G.N.; Stopa, S.R.; Rosenfeld, L.G.; et al. Prevalência de diabetes mellitus determinada pela hemoglobina glicada na população adulta brasileira. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2019, 22, E190006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, A.D.; Harris-Hayes, M.; Schootman, M. Epidemiology of diabetes and diabetes-related complications. Phys. Ther. 2008, 88, 1254–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health. Available online: https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/assuntos/noticias/2021/dezembro/ministerio-da-saude-reajusta-valores-para-tratamento-de-hemodialise/ (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Secretary of State for Health. Available online: https://saude.se.gov.br/saude-orienta-sobre-como-prevenir-controlar-e-conviver-com-o-diabetes/ (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Silva, A.A.S.; Castro, A.A.; Bomfim, L.G.; Pitta, G.B.B. Amputation lower limb due to Diabetes Mellitus the states and regions of Brazil. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 2, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, R.; Wong, T.Y.; Sabanayagam, C. Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema and related vision loss. Eye Vis. 2015, 10, e11910413837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toscano, C.M.; Sugita, T.H.; Rosa, M.Q.M.; Pedrosa, H.C.; Rosa, R.D.S.; Bahia, L.R. Annual Direct Medical Costs of Diabetic Foot Disease in Brazil: A Cost of Illness Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakerveld, J.; Palmeira, A.L.; van Duinkerken, E.; Whitelock, V.; Peyrot, M.; Nouwen, A. Motivation: Key to a healthy lifestyle in people with diabetes? Current and emerging knowledge and applications. Diabetes Med. 2020, 37, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouwen, A.; Ford, T.; Balan, A.T.; Twisk, J.; Ruggiero, L.; White, D. Longitudinal motivational predictors of dietary self-care and diabetes control in adults with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. Health Psychol. 2011, 30, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigaki, C.; Kruse, R.L.; Mehr, D.; Sheldon, K.M.; Bin, G.; Moore, C.; Lemaster, J. Motivation and diabetes self-management. Chronic Illn. 2010, 6, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeri, C.; Pozzilli, P.; Leslie, D. Glucose control in diabetes. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2004, 20, S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, R.; Adelman, M.M.; Kirk, B.; Sambamoorthi, U. Relationship Among Diabetes Distress, Health Literacy, Diabetes Education, Patient-Provider Communication and Diabetes Self-Care. Am. J. Health Behav. 2022, 46, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibbad, R.G.; Ayello, E.A. Diabetes Education Linked to Improved Patient Outcomes and Healthcare System Change. Adv. Skin Wound Care 2023, 36, 566. [Google Scholar]
- FreeStyle Libre User Manual and Specifications. Available online: https://www.freestyle.abbott/pt-pt/tutoriais.html (accessed on 3 June 2023).
- JusBrasil. Freestyle Libre by SUS: How to Get it. Available online: https://www.jusbrasil.com.br/artigos/freestyle-libre-pelo-sus-como-obter/1984962759 (accessed on 6 February 2024).
- Diabetes Education Guidelines of the Brazilian Diabetes Society. Available online: https://diretriz.diabetes.org.br/ (accessed on 3 June 2023).
- Michels, M.J.; Coral, M.H.C.; Sakae, T.M.; Damas, T.B.; Furlanetto, L.M. Questionário de Atividades de Autocuidado com o Diabetes: Tradução, adaptação e avaliação das propriedades psicométricas. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 54, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. Population of the State of Sergipe in 2023. Available online: https://cidades.ibge.gov.br/brasil/se/pesquisa/53/49645?ano=2023 (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Baroni, I.; Caruso, R.; Dellafiore, F.; Ausili, D.; Barello, S.; Vangone, I.; Russo, S.; Magon, A.; Conte, G.; Guardamagna, L.; et al. Self-care and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM): A literature review in sex-related differences. Acta Bio-Med. 2022, 93, e2022277. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, M.L.; Preston, J.D.; Rashid, C.S.; Pearson, K.J.; Ham, J.N. Sex differences in type 2 diabetes: An opportunity for personalized medicine. Biol. Sex Differ. 2023, 14, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellary, S.; Kyrou, I.; Brown, J.E.; Bailey, C.J.A.J. Diabetes tipo 2 em idosos: Considerações clínicas e manejo.Opiniões sobre a natureza. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes. Lancet 1998, 352, 837–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.; Klein, B.E.K. Blood pressure control and diabetic retinopathy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 15, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, J.R.; Rayfield, E.J. An endocrine clinic’s perspective and experience with the Abbott Freestyle Libre Cgm. Endocr. Pract. 2018, 24, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolinder, J.; Antuna, R.; Geelhoed-Duijvestijn, P.; Kröger, J.; Weitgasser, R. Novel glucose-sensing technology and hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes: A multicentre, non-masked, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2254–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dover, A.R.; Stimson, R.H.; Zammitt, N.N.; Gibb, F.W. Flash glucose monitoring improves outcomes in a type 1 diabetes clinic. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2017, 11, 442–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haak, T.; Hanaire, H.; Ajjan, R.; Hermanns, N.; Riveline, J.P.; Rayman, G. Flash glucose-sensing technology as a replacement for blood glucose monitoring for the management of insulin-treated type 2 diabetes: A multicenter, open-label randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, I.B. Clinical review: Realistic expectations and practical use of continuous glucose monitoring for the endocrinologist. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 2232–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzner, K.; Greenwood, D.; Payne, H.; Thomson, J.; Vukovljak, L.; McCulloch, A.; Specker, J.E. An Assessment of Patient Education and Self-Management in Diabetes Disease Management—Two Case Studies. Popul. Health Manag. 2008, 11, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, M.E.; Cavanaugh, K.L.; Wolff, K.; Davis, D.; Gregory, R.P.; Shintani, A.; Rothman, R.L. The diabetes nutrition education study randomized controlled trial: A comparative effectiveness study of approaches to nutrition in diabetes self-management education. Patient Educ. Couns. 2016, 99, 1368–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colberg, S.R.; Sigal, R.J.; Yardley, J.E.; Riddell, M.C.; Dunstan, D.W.; Dempsey, P.C.; Horton, E.S.; Castorino, K.; Tate, D.F. Physical Activity/Exercise and Diabetes: A Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 2065–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, S.S.; Elenara, F.; Naomi, H.V. Riscos associados à mortalidade em pacientes atendidos em um programa de prevenção do pé diabético. Rev. Gaúcha. Enferm. 2018, 39, e20170230. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, M.B.; Karlan, V.J.; Hair, T.L. Effect of a Pharmacist-Managed Diabetes Care Program in a Free Medical Clinic. Am. J. Med. Qual. 2000, 15, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.A.; Lustman, P.J. The psychologist in diabetes care. Clin. Diabetes 1998, 16, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Bode, B.W.; Gross, T.M.; Thornton, K.R.; Mastrototaro, J.J. Continuous glucose monitoring used to adjust diabetes therapy improves glycosylated hemoglobin: A pilot study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1999, 46, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiffler, D.; Cullen, D.; Luna, G. Diabetes barriers and self-care management: The patient perspective. Clin. Nurs. Res. 2014, 23, 601–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulrehman, M.S.; With, W.; Jenkins, S.; Kossman, S.; Hunter, G.L. Exploring cultural influences of self-management of diabetes in coastal Kenya: An Ethnography. Glob. Qual. Nurs. Res. 2016, 3, 2333393616641825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adu, M.D.; Malabu, U.H.; Malau-Aduli, A.E.; Malau-Aduli, B.S. Enablers and barriers to effective diabetes self-management: A multi-national investigation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taleb, N.; Emami, A.; Suppere, C. Comparison of two continuous glucose monitoring systems, Dexcom G4 platinum and Medtronic paradigm Veo Enlite system, at rest and during exercise. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2016, 18, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, T.; Beck, R.W.; Bailey, R.; Ruedy, K.J.; Calhoun, P.; Peters, A.L.; Pop-Busui, R.; Philis-Tsimikas, A.; Bao, S.; Umpierrez, G.; et al. Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Treated With Basal Insulin: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 2262–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, R.W.; Riddlesworth, T.; Ruedy, K.; Ahmann, A.; Bergenstal, R.; Haller, S.; Kollman, C.; Kruger, D.; McGill, J.B.; Polonsky, W.; et al. Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Using Insulin Injections: The DIAMOND Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 317, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laffel, L.M.; Kanapka, L.G.; Beck, R.W.; Bergamo, K.; Clements, M.A.; Criego, A.; DeSalvo, D.J.; Goland, R.; Hood, K.; Liljenquist, D.; et al. Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adolescents and Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 323, 2388–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.T.; Li, I.C.; Lin, W.S.; Lin, G.M. Pros and cons of continuous glucose monitoring in the intensive care unit. World J. Clin. Cases 2021, 9, 8666–8670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Study Group. Prolonged nocturnal hypoglycemia is common during 12 months of continuous glucose monitoring in children and adults with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbay, M.A.L.; Rodacki, M.; Calliari, L.E. Time in range: A new parameter to evaluate blood glucose control in patients with diabetes. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelman, S.V.; Argento, N.B.; Pettus, J.; Hirsch, I.B. Clinical implications of real-time and intermittently scanned continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 2265–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberer, F.; Hajnsek, M.; Rumpler, M. Evaluation of subcutaneous glucose monitoring systems under routine environmental conditions in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dall, T.M.; Mann, S.E.; Zhang, Y. Distinguishing the economic costs associated with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Popul. Health Manag. 2009, 12, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pleus, S.; Schoemaker, M.; Morgenstern, K. Rate-of-change dependence of the performance of two CGM systems during induced glucose swings. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2015, 9, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pleus, S.; Kamecke, U.; Link, M.; Haug, C.; Freckmann, G. Flash glucose monitoring: Differences between intermittently scanned and continuously stored data. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2018, 12, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danne, T.; Nimri, R.; Battelino, T. International consensus on use of continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.C.; Brown, T.T.; Maruthur, N. Comparative effectiveness and safety of methods of insulin delivery and glucose monitoring for diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 157, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borges, L.P.; de Jesus, P.C.; de Souza, J.B.; Silva, D.M.R.R.; Moura, P.H.M.; Santos, R.S.; Barreto, M.d.S.; Guimarães, A.G.; da Mota Santana, L.A.; da Fonseca, D.L.M.; et al. The Impact of Diabetes Education on Continuous Glucose Monitoring in SUS-Dependent Patients in a Northeastern Brazilian City. Life 2024, 14, 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14030320
Borges LP, de Jesus PC, de Souza JB, Silva DMRR, Moura PHM, Santos RS, Barreto MdS, Guimarães AG, da Mota Santana LA, da Fonseca DLM, et al. The Impact of Diabetes Education on Continuous Glucose Monitoring in SUS-Dependent Patients in a Northeastern Brazilian City. Life. 2024; 14(3):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14030320
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorges, Lysandro Pinto, Pamela Chaves de Jesus, Jessiane Bispo de Souza, Deise Maria Rego Rodrigues Silva, Pedro Henrique Macedo Moura, Ronaldy Santana Santos, Marina dos Santos Barreto, Adriana Gibara Guimarães, Lucas Alves da Mota Santana, Dennyson Leandro Mathias da Fonseca, and et al. 2024. "The Impact of Diabetes Education on Continuous Glucose Monitoring in SUS-Dependent Patients in a Northeastern Brazilian City" Life 14, no. 3: 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14030320
APA StyleBorges, L. P., de Jesus, P. C., de Souza, J. B., Silva, D. M. R. R., Moura, P. H. M., Santos, R. S., Barreto, M. d. S., Guimarães, A. G., da Mota Santana, L. A., da Fonseca, D. L. M., Barreto, I. D. d. C., de Mello Silva, B., Oliveira, C. R. P., Rezende, K. F., Melo, N. H., Santos, E. F. d., Queiroz, C. L. M. d., Xavier, L. H. M., Cabral-Marques, O., & Silva, E. E. D. (2024). The Impact of Diabetes Education on Continuous Glucose Monitoring in SUS-Dependent Patients in a Northeastern Brazilian City. Life, 14(3), 320. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14030320