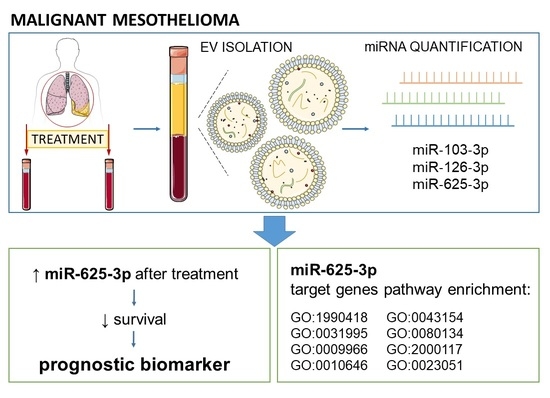
Extracellular Vesicle Enriched miR-625-3p Is Associated with Survival of Malignant Mesothelioma Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Isolation of Small EVs with Sucrose Cushion Ultracentrifugation (sUC)
2.3. Extraction of miRNA and Transcription to cDNA
2.4. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.5. Bioinformatic Analysis of miR-625-3p Targets
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Comparison of Serum EV-Enriched miRNA Expression at Diagnosis and after Treatment
3.3. Differentiation between MM Patients with Poor and Good Treatment Outcome Based on Serum EV-Enriched miRNA Expression
3.4. Survival Analysis
3.5. Bioinformatic Analysis of miR-625-3p Targets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kovac, V.; Zwitter, M.; Zagar, T. Improved survival after introduction of chemotherapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma in Slovenia: Population-based survey of 444 patients. Radiol. Oncol. 2012, 46, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapman, S.J.; Cookson, W.O.; Musk, A.W.; Lee, Y.C. Benign asbestos pleural diseases. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2003, 9, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lo Russo, G.; Tessari, A.; Capece, M.; Galli, G.; de Braud, F.; Garassino, M.C.; Palmieri, D. MicroRNAs for the diagnosis and management of malignant pleural mesothelioma: A literature review. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnen, G.; Gawrych, K.; Raiko, I.; Casjens, S.; Pesch, B.; Weber, D.G.; Taeger, D.; Lehnert, M.; Kollmeier, J.; Bauer, T.; et al. Calretinin as a blood-based biomarker for mesothelioma. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Damhuis, R.A.; Schroten, C.; Burgers, J.A. Population-based survival for malignant mesothelioma after introduction of novel chemotherapy. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helland, A.; Solberg, S.; Brustugun, O.T. Incidence and survival of malignant pleural mesothelioma in Norway: A population-based study of 1686 cases. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1858–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogelzang, N.J.; Rusthoven, J.J.; Symanowski, J.; Denham, C.; Kaukel, E.; Ruffie, P.; Gatzemeier, U.; Boyer, M.; Emri, S.; Manegold, C.; et al. Phase III study of pemetrexed in combination with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovac, V.; Zwitter, M.; Rajer, M.; Marin, A.; Debeljak, A.; Smrdel, U.; Vrankar, M. A phase II trial of low-dose gemcitabine in a prolonged infusion and cisplatin for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Anticancer Drugs 2012, 23, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.W.; Murray, N.; Anderson, H.; Rao, S.C.; Bishop, W. Outcomes with first-line platinum-based combination chemotherapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma: A review of practice in British Columbia. Lung Cancer 2009, 64, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ak, G.; Metintas, S.; Akarsu, M.; Metintas, M. The effectiveness and safety of platinum-based pemetrexed and platinum-based gemcitabine treatment in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gray, S.G.; Mutti, L. Immunotherapy for mesothelioma: A critical review of current clinical trials and future perspectives. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, S100–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gooijer, C.J.; Borm, F.J.; Scherpereel, A.; Baas, P. Immunotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cantini, L.; Hassan, R.; Sterman, D.H.; Aerts, J. Emerging treatments for malignant pleural mesothelioma: Where are we heading? Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baas, P.; Scherpereel, A.; Nowak, A.K.; Fujimoto, N.; Peters, S.; Tsao, A.S.; Mansfield, A.S.; Popat, S.; Jahan, T.; Antonia, S.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creaney, J.; Olsen, N.J.; Brims, F.; Dick, I.M.; Musk, A.W.; de Klerk, N.H.; Skates, S.J.; Robinson, B.W. Serum mesothelin for early detection of asbestos-induced cancer malignant mesothelioma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 2238–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hollevoet, K.; Reitsma, J.B.; Creaney, J.; Grigoriu, B.D.; Robinson, B.W.; Scherpereel, A.; Cristaudo, A.; Pass, H.I.; Nackaerts, K.; Rodriguez Portal, J.A.; et al. Serum mesothelin for diagnosing malignant pleural mesothelioma: An individual patient data meta-analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hollevoet, K.; van Cleemput, J.; Thimpont, J.; de Vuyst, P.; Bosquee, L.; Nackaerts, K.; Germonpre, P.; Vansteelandt, S.; Kishi, Y.; Delanghe, J.R.; et al. Serial measurements of mesothelioma serum biomarkers in asbestos-exposed individuals: A prospective longitudinal cohort study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillezeau, C.; van Gerwen, M.; Ramos, J.; Liu, B.; Flores, R.; Taioli, E. Biomarkers for malignant pleural mesothelioma: A meta-analysis. Carcinogenesis 2019, 40, 1320–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foddis, R.; Bonotti, A.; Landi, S.; Fallahi, P.; Guglielmi, G.; Cristaudo, A. Biomarkers in the prevention and follow-up of workers exposed to asbestos. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S360–S368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cristaudo, A.; Bonotti, A.; Guglielmi, G.; Fallahi, P.; Foddis, R. Serum mesothelin and other biomarkers: What have we learned in the last decade? J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, S353–S359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cavallari, I.; Urso, L.; Sharova, E.; Pasello, G.; Ciminale, V. Liquid biopsy in malignant pleural mesothelioma: State of the art, pitfalls, and perspectives. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cristaudo, A.; Foddis, R.; Bonotti, A.; Simonini, S.; Vivaldi, A.; Guglielmi, G.; Bruno, R.; Gemignani, F.; Landi, S. Two novel polymorphisms in 5′ flanking region of the mesothelin gene are associated with soluble mesothelin-related peptide (SMRP) levels. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2011, 26, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garritano, S.; de Santi, C.; Silvestri, R.; Melaiu, O.; Cipollini, M.; Barone, E.; Lucchi, M.; Barale, R.; Mutti, L.; Gemignani, F.; et al. A common polymorphism within MSLN affects miR-611 binding site and soluble mesothelin levels in healthy people. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 1662–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Santi, C.; Pucci, P.; Bonotti, A.; Melaiu, O.; Cipollini, M.; Silvestri, R.; Vymetalkova, V.; Barone, E.; Paolicchi, E.; Corrado, A.; et al. Mesothelin promoter variants are associated with increased soluble mesothelin-related peptide levels in asbestos-exposed individuals. Occup. Environ. Med. 2017, 74, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goricar, K.; Kovac, V.; Dodic-Fikfak, M.; Dolzan, V.; Franko, A. Evaluation of soluble mesothelin-related peptides and MSLN genetic variability in asbestos-related diseases. Radiol. Oncol. 2020, 54, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, L.; Zeng, R.; Wang, X.; Shen, C.; Lai, Y.; Wang, M.; Che, G. Prognostic significance of soluble mesothelin in malignant pleural mesothelioma: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 46425–46435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goricar, K.; Kovac, V.; Dolzan, V. Clinical-pharmacogenetic models for personalized cancer treatment: Application to malignant mesothelioma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmadzada, T.; Kao, S.; Reid, G.; Clarke, S.; Grau, G.E.; Hosseini-Beheshti, E. Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers in malignant pleural mesothelioma: A review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2020, 150, 102949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasetti, M.; Gaetani, S.; Monaco, F.; Neuzil, J.; Santarelli, L. Epigenetic regulation of miRNA expression in malignant mesothelioma: miRNAs as biomarkers of early diagnosis and therapy. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micolucci, L.; Akhtar, M.M.; Olivieri, F.; Rippo, M.R.; Procopio, A.D. Diagnostic value of microRNAs in asbestos exposure and malignant mesothelioma: Systematic review and qualitative meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 58606–58637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weber, D.G.; Johnen, G.; Bryk, O.; Jöckel, K.H.; Brüning, T. Identification of miRNA-103 in the cellular fraction of human peripheral blood as a potential biomarker for malignant mesothelioma—A pilot study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, D.G.; Casjens, S.; Johnen, G.; Bryk, O.; Raiko, I.; Pesch, B.; Kollmeier, J.; Bauer, T.T.; Brüning, T. Combination of MiR-103a-3p and mesothelin improves the biomarker performance of malignant mesothelioma diagnosis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cappellesso, R.; Nicolè, L.; Caroccia, B.; Guzzardo, V.; Ventura, L.; Fassan, M.; Fassina, A. Young investigator challenge: MicroRNA-21/MicroRNA-126 profiling as a novel tool for the diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma in pleural effusion cytology. Cancer Cytopathol. 2016, 124, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weber, D.G.; Gawrych, K.; Casjens, S.; Brik, A.; Lehnert, M.; Taeger, D.; Pesch, B.; Kollmeier, J.; Bauer, T.T.; Johnen, G.; et al. Circulating miR-132-3p as a Candidate Diagnostic Biomarker for Malignant Mesothelioma. Dis. Markers 2017, 2017, 9280170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, M.; Grauslund, M.; Ravn, J.; Sørensen, J.B.; Andersen, C.B.; Santoni-Rugiu, E. Diagnostic potential of miR-126, miR-143, miR-145, and miR-652 in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 16, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santi, C.; Melaiu, O.; Bonotti, A.; Cascione, L.; di Leva, G.; Foddis, R.; Cristaudo, A.; Lucchi, M.; Mora, M.; Truini, A.; et al. Deregulation of miRNAs in malignant pleural mesothelioma is associated with prognosis and suggests an alteration of cell metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozzoni, P.; Ampollini, L.; Goldoni, M.; Alinovi, R.; Tiseo, M.; Gnetti, L.; Carbognani, P.; Rusca, M.; Mutti, A.; Percesepe, A.; et al. MicroRNA expression in malignant pleural mesothelioma and asbestosis: A pilot study. Dis. Markers 2017, 2017, 9645940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santarelli, L.; Gaetani, S.; Monaco, F.; Bracci, M.; Valentino, M.; Amati, M.; Rubini, C.; Sabbatini, A.; Pasquini, E.; Zanotta, N.; et al. Four-miRNA signature to identify asbestos-related lung malignancies. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santarelli, L.; Staffolani, S.; Strafella, E.; Nocchi, L.; Manzella, N.; Grossi, P.; Bracci, M.; Pignotti, E.; Alleva, R.; Borghi, B.; et al. Combined circulating epigenetic markers to improve mesothelin performance in the diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarelli, L.; Strafella, E.; Staffolani, S.; Amati, M.; Emanuelli, M.; Sartini, D.; Pozzi, V.; Carbonari, D.; Bracci, M.; Pignotti, E.; et al. Association of MiR-126 with soluble mesothelin-related peptides, a marker for malignant mesothelioma. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomasetti, M.; Staffolani, S.; Nocchi, L.; Neuzil, J.; Strafella, E.; Manzella, N.; Mariotti, L.; Bracci, M.; Valentino, M.; Amati, M.; et al. Clinical significance of circulating miR-126 quantification in malignant mesothelioma patients. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner, M.B.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Badrian, B.; Kao, S.C.; Creaney, J.; Edelman, J.J.; Armstrong, N.J.; Vallely, M.P.; Musk, A.W.; Robinson, B.W.; et al. Increased circulating miR-625-3p: A potential biomarker for patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kresoja-Rakic, J.; Szpechcinski, A.; Kirschner, M.B.; Ronner, M.; Minatel, B.; Martinez, V.D.; Lam, W.L.; Weder, W.; Stahel, R.; Früh, M.; et al. miR-625-3p and lncRNA GAS5 in liquid biopsies for predicting the outcome of malignant pleural mesothelioma patients treated with neo-adjuvant chemotherapy and surgery. Non-coding RNA 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karimi, N.; Cvjetkovic, A.; Jang, S.C.; Crescitelli, R.; Hosseinpour Feizi, M.A.; Nieuwland, R.; Lotvall, J.; Lasser, C. Detailed analysis of the plasma extracellular vesicle proteome after separation from lipoproteins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 2873–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaborowski, M.P.; Balaj, L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Lai, C.P. Extracellular vesicles: Composition, biological relevance, and methods of study. Bioscience 2015, 65, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Yang, F.; Zhu, X.; Lu, Y.; Xing, W. Rapid and efficient isolation and detection of extracellular vesicles from plasma for lung cancer diagnosis. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateescu, B.; Kowal, E.J.; van Balkom, B.W.; Bartel, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Buzas, E.I.; Buck, A.H.; de Candia, P.; Chow, F.W.; Das, S.; et al. Obstacles and opportunities in the functional analysis of extracellular vesicle RNA—An ISEV position paper. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1286095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, K.; Fang, C.; Yi, K.; Liu, X.; Qi, H.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The role of PTRF/Cavin1 as a biomarker in both glioma and serum exosomes. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1540–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, A.; Molins, L.; Marrades, R.M.; Moises, J.; Viñolas, N.; Morales, S.; Canals, J.; Castellano, J.J.; Ramírez, J.; Monzo, M. Exosome analysis in tumor-draining pulmonary vein identifies NSCLC patients with higher risk of relapse after curative surgery. Cancers 2019, 11, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, J.; Garcia, V.; Rodriguez, M.; Compte, M.; Cisneros, E.; Veguillas, P.; Garcia, J.M.; Dominguez, G.; Campos-Martin, Y.; Cuevas, J.; et al. Analysis of exosome release and its prognostic value in human colorectal cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2012, 51, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, M.H.; Caires, H.R.; Ābols, A.; Xavier, C.P.R.; Linē, A. Extracellular vesicles as a novel source of biomarkers in liquid biopsies for monitoring cancer progression and drug resistance. Drug Resist. Updates 2019, 47, 100647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.H.; Cerione, R.A.; Antonyak, M.A. Extracellular vesicles and their roles in cancer progression. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2174, 143–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiam, K.; Mayne, G.C.; Wang, T.; Watson, D.I.; Irvine, T.S.; Bright, T.; Smith, L.T.; Ball, I.A.; Bowen, J.M.; Keefe, D.M.; et al. Serum outperforms plasma in small extracellular vesicle microRNA biomarker studies of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 2570–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grange, C.; Brossa, A.; Bussolati, B. Extracellular vesicles and carried miRNAs in the progression of renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greening, D.W.; Ji, H.; Chen, M.; Robinson, B.W.; Dick, I.M.; Creaney, J.; Simpson, R.J. Secreted primary human malignant mesothelioma exosome signature reflects oncogenic cargo. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Creaney, J.; Dick, I.M.; Leon, J.S.; Robinson, B.W. A proteomic analysis of the malignant mesothelioma secretome using iTRAQ. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2017, 14, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munson, P.; Lam, Y.W.; Dragon, J.; MacPherson, M.; Shukla, A. Exosomes from asbestos-exposed cells modulate gene expression in mesothelial cells. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 4328–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalleri, T.; Angelici, L.; Favero, C.; Dioni, L.; Mensi, C.; Bareggi, C.; Palleschi, A.; Rimessi, A.; Consonni, D.; Bordini, L.; et al. Plasmatic extracellular vesicle microRNAs in malignant pleural mesothelioma and asbestos-exposed subjects suggest a 2-miRNA signature as potential biomarker of disease. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munson, P.B.; Hall, E.M.; Farina, N.H.; Pass, H.I.; Shukla, A. Exosomal miR-16-5p as a target for malignant mesothelioma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monaco, F.; Gaetani, S.; Alessandrini, F.; Tagliabracci, A.; Bracci, M.; Valentino, M.; Neuzil, J.; Amati, M.; Bovenzi, M.; Tomasetti, M.; et al. Exosomal transfer of miR-126 promotes the anti-tumour response in malignant mesothelioma: Role of miR-126 in cancer-stroma communication. Cancer Lett. 2019, 463, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcar, M.; Ferdin, J.; Sitar, S.; Tušek-Žnidarič, M.; Dolžan, V.; Plemenitaš, A.; Žagar, E.; Lenassi, M. Enrichment of plasma extracellular vesicles for reliable quantification of their size and concentration for biomarker discovery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondal, T.; Jensby Nielsen, S.; Baker, A.; Andreasen, D.; Mouritzen, P.; Wrang Teilum, M.; Dahlsveen, I.K. Assessing sample and miRNA profile quality in serum and plasma or other biofluids. Methods 2013, 59, S1–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donati, S.; Ciuffi, S.; Brandi, M.L. Human circulating miRNAs real-time qRT-PCR-based analysis: An Overview of endogenous reference genes used for data normalization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, J.; Wang, Q.; Gurvich, I.; Remotti, H.; Santella, R.M. Evaluating normalization approaches for the better identification of aberrant microRNAs associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatoma Res. 2016, 2, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Li, J.; Huang, K.Y.; Shrestha, S.; Hong, H.C.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Y.G.; Jin, C.N.; Yu, Y.; et al. miRTarBase 2020: Updates to the experimentally validated microRNA-target interaction database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D148–D154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warde-Farley, D.; Donaldson, S.L.; Comes, O.; Zuberi, K.; Badrawi, R.; Chao, P.; Franz, M.; Grouios, C.; Kazi, F.; Lopes, C.T.; et al. The GeneMANIA prediction server: Biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W214–W220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J.G. Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen, M.H.; Jensen, N.F.; Tarpgaard, L.S.; Qvortrup, C.; Rømer, M.U.; Stenvang, J.; Hansen, T.P.; Christensen, L.L.; Lindebjerg, J.; Hansen, F.; et al. High expression of microRNA-625-3p is associated with poor response to first-line oxaliplatin based treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2013, 7, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, M.H.; Lyskjær, I.; Jersie-Christensen, R.R.; Tarpgaard, L.S.; Primdal-Bengtson, B.; Nielsen, M.M.; Pedersen, J.S.; Hansen, T.P.; Hansen, F.; Olsen, J.V.; et al. miR-625-3p regulates oxaliplatin resistance by targeting MAP2K6-p38 signalling in human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okumura, T.; Shimada, Y.; Omura, T.; Hirano, K.; Nagata, T.; Tsukada, K. MicroRNA profiles to predict postoperative prognosis in patients with small cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 719–727. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Kong, D.; Xu, W. MicroRNA-625-3p promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of thyroid cancer cells by up-regulating astrocyte elevated gene 1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, K.; Pan, X.; Quan, J.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Lin, C.; Xu, J.; Xu, W.; Guan, X.; et al. miR-625-3p promotes migration and invasion and reduces apoptosis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 6475–6486. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Ma, R.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Li, D.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z. MiR-625-3p promotes cell migration and invasion via inhibition of SCAI in colorectal carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 27805–27815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Li, D.C.; Che, S.S.; Ma, K.; Wang, Y.J.; Xia, L.H.; Dai, X.M.; Zhang, G.T.; Shen, Y.; Jiao, W.J.; et al. The decreased expression of miR-625 predicts poor prognosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 9560–9564. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roth, C.; Stückrath, I.; Pantel, K.; Izbicki, J.R.; Tachezy, M.; Schwarzenbach, H. Low levels of cell-free circulating miR-361-3p and miR-625* as blood-based markers for discriminating malignant from benign lung tumors. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, X.; Qi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Long, H.; Yang, J. Decreased expression of microRNA-625 is associated with tumor metastasis and poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 108, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Lu, X.; Huang, P.; Gao, C.; Zhao, X.; Xing, T.; Li, G.; Bao, S.; Zheng, H. Expression of miR-652-3p and effect on apoptosis and drug sensitivity in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 5724686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.Z.; Lu, S.X.; Chen, G.G.; Li, L.Z.; Liu, L.L.; Yi, C.; Fu, J.; Hu, W.; Wen, J.M.; et al. miR-625 suppresses tumour migration and invasion by targeting IGF2BP1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2015, 34, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Fan, Y.; Fa, Z.; Xu, J.; Yu, H.; Li, P.; Gu, J. microRNA-625 inhibits tumorigenicity by suppressing proliferation, migration and invasion in malignant melanoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 13253–13263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Li, C.; Nie, H.; Lv, X.; Qu, Y.; Yu, B.; Su, L.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Ju, J.; et al. Down-regulated miR-625 suppresses invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting ILK. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2382–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Fang, T.; Liu, H.; Wang, S. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in cervical cancer by targeting miR-625-5p and AKT2. Panminerva Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, B. LINC00511 accelerated the process of gastric cancer by targeting miR-625-5p/NFIX axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bueno, R.; de Rienzo, A.; Dong, L.; Gordon, G.J.; Hercus, C.F.; Richards, W.G.; Jensen, R.V.; Anwar, A.; Maulik, G.; Chirieac, L.R.; et al. Second generation sequencing of the mesothelioma tumor genome. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyskjær, I.; Rasmussen, M.H.; Andersen, C.L. Putting a brake on stress signaling: miR-625-3p as a biomarker for choice of therapy in colorectal cancer. Epigenomics 2016, 8, 1449–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nymark, P.; Lindholm, P.M.; Korpela, M.V.; Lahti, L.; Ruosaari, S.; Kaski, S.; Hollmén, J.; Anttila, S.; Kinnula, V.L.; Knuutila, S. Gene expression profiles in asbestos-exposed epithelial and mesothelial lung cell lines. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamp, D.W.; Liu, G.; Cheresh, P.; Kim, S.J.; Mueller, A.; Lam, A.P.; Trejo, H.; Williams, D.; Tulasiram, S.; Baker, M.; et al. Asbestos-induced alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress response. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 49, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Okimoto, G.; Jube, S.; Napolitano, A.; Pass, H.I.; Laczko, R.; Demay, R.M.; Khan, G.; Tiirikainen, M.; Rinaudo, C.; et al. Continuous exposure to chrysotile asbestos can cause transformation of human mesothelial cells via HMGB1 and TNF-α signaling. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 1654–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borchert, S.; Suckrau, P.M.; Wessolly, M.; Mairinger, E.; Hegedus, B.; Hager, T.; Herold, T.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; Wohlschlaeger, J.; Aigner, C.; et al. Screening of pleural mesothelioma cell lines for kinase activity may identify new mechanisms of therapy resistance in patients receiving platin-based chemotherapy. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 2902985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.Q.; Dai, Y.Y.; Hsu, P.C.; Wang, H.; Cheng, L.; Yang, Y.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Xu, Z.D.; Liu, S.; Chan, G.; et al. Targeting YAP in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 2663–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasello, G.; Urso, L.; Mencoboni, M.; Grosso, F.; Ceresoli, G.L.; Lunardi, F.; Vuljan, S.E.; Bertorelle, R.; Sacchetto, V.; Ciminale, V.; et al. MDM2 and HIF1alpha expression levels in different histologic subtypes of malignant pleural mesothelioma: Correlation with pathological and clinical data. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 42053–42066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.; Oh, M.H.; Ji, S.Y.; Han, J.; Kim, T.J.; Eom, M.; Kwon, K.Y.; Ha, S.Y.; Choi, Y.D.; Lee, C.H.; et al. Practical utility of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding protein 3, glucose transporter 1, and epithelial membrane antigen for distinguishing malignant mesotheliomas from benign mesothelial proliferations. Pathol. Int. 2014, 64, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasetti, M.; Nocchi, L.; Staffolani, S.; Manzella, N.; Amati, M.; Goodwin, J.; Kluckova, K.; Nguyen, M.; Strafella, E.; Bajzikova, M.; et al. MicroRNA-126 suppresses mesothelioma malignancy by targeting IRS1 and interfering with the mitochondrial function. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 2109–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomasetti, M.; Monaco, F.; Manzella, N.; Rohlena, J.; Rohlenova, K.; Staffolani, S.; Gaetani, S.; Ciarapica, V.; Amati, M.; Bracci, M.; et al. MicroRNA-126 induces autophagy by altering cell metabolism in malignant mesothelioma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 36338–36352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weber, D.G.; Brik, A.; Casjens, S.; Burek, K.; Lehnert, M.; Pesch, B.; Taeger, D.; Brüning, T.; Johnen, G. Are circulating microRNAs suitable for the early detection of malignant mesothelioma? Results from a nested case-control study. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endzeliņš, E.; Berger, A.; Melne, V.; Bajo-Santos, C.; Soboļevska, K.; Ābols, A.; Rodriguez, M.; Šantare, D.; Rudņickiha, A.; Lietuvietis, V.; et al. Detection of circulating miRNAs: Comparative analysis of extracellular vesicle-incorporated miRNAs and cell-free miRNAs in whole plasma of prostate cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Cao, Y.; Kohler, J.; Lu, A.; Xu, S.; Wang, H. Unbiased RNA-Seq-driven identification and validation of reference genes for quantitative RT-PCR analyses of pooled cancer exosomes. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouin, K.; Peck, K.; Antes, T.; Johnson, J.L.; Li, C.; Vaturi, S.D.; Middleton, R.; de Couto, G.; Walravens, A.S.; Rodriguez-Borlado, L.; et al. A comprehensive method for identification of suitable reference genes in extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1347019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grimolizzi, F.; Monaco, F.; Leoni, F.; Bracci, M.; Staffolani, S.; Bersaglieri, C.; Gaetani, S.; Valentino, M.; Amati, M.; Rubini, C.; et al. Exosomal miR-126 as a circulating biomarker in non-small-cell lung cancer regulating cancer progression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, R.; Morrow, B.; Thomas, A.; Walsh, T.; Lee, M.K.; Gulsuner, S.; Gadiraju, M.; Panou, V.; Gao, S.; Mian, I.; et al. Inherited predisposition to malignant mesothelioma and overall survival following platinum chemotherapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 9008–9013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumann, F.; Flores, E.; Napolitano, A.; Kanodia, S.; Taioli, E.; Pass, H.; Yang, H.; Carbone, M. Mesothelioma patients with germline BAP1 mutations have 7-fold improved long-term survival. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carbone, M.; Adusumilli, P.S.; Alexander, H.R., Jr.; Baas, P.; Bardelli, F.; Bononi, A.; Bueno, R.; Felley-Bosco, E.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Jablons, D.; et al. Mesothelioma: Scientific clues for prevention, diagnosis, and therapy. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 402–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bracht, J.W.P.; Mayo-de-Las-Casas, C.; Berenguer, J.; Karachaliou, N.; Rosell, R. The present and future of liquid biopsies in non-small cell lung cancer: Combining four biosources for diagnosis, prognosis, prediction, and disease monitoring. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 20, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, G.J.; Goldkorn, A. Development and Application of liquid biopsies in metastatic prostate cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, E.; Falcon-Perez, J.M. Cell-derived extracellular vesicles as a platform to identify low-invasive disease biomarkers. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 15, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witwer, K.W.; Buzas, E.I.; Bemis, L.T.; Bora, A.; Lasser, C.; Lotvall, J.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; Piper, M.G.; Sivaraman, S.; Skog, J.; et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, G.; Johnson, T.G.; van Zandwijk, N. Manipulating microRNAs for the Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Past, Present and Future. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristic | Category/Unit | n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 10 (55.6) |
| Female | 8 (44.4) | |
| Age | Years, Median (25–75%) | 68.5 (59.8–72.5) |
| Stage | I | 4 (22.2) |
| II | 2 (11.1) | |
| III | 8 (44.4) | |
| IV | 3 (16.7) | |
| Peritoneal | 1 (5.6) | |
| Histological type | Epithelioid | 12 (66.7) |
| Biphasic | 3 (16.7) | |
| Sarcomatoid | 3 (16.7) | |
| ECOG performance status | 0 | 4 (22.2) |
| 1 | 8 (44.4) | |
| 2 | 6 (33.3) | |
| Asbestos exposure | Not exposed | 5 (27.8) |
| Exposed | 13 (72.2) | |
| Smoking | Non-smokers | 11 (61.1) |
| Smokers | 7 (38.9) | |
| CRP | mg/L, Median (25–75%) | 15.5 (2.8–46.5) |
| Chemotherapy | Gemcitabine + cisplatin | 12 (66.7) |
| Pemetrexed + cisplatin | 6 (33.3) | |
| PFS | Months, Median (25–75%) | 14.1 (7.2–20.2) |
| OS | Months, Median (25–75%) | 27.3 (12.5–29.4) |
| Follow-up time | Months, Median (25–75%) | 30.8 (23.4–30.8) |
| miRNA | At Diagnosis Relative Expression Median (25–75%) | After Treatment Relative Expression Median (25–75%) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All patients (n = 17) | miR-625-3p | 0.05 (0.01–0.13) | 0.07 (0.03–0.15) | 0.227 |
| miR-103a-3p | 0.40 (0.34–0.47) | 0.39 (0.32–0.48) | 0.981 | |
| miR-126-3p | 45.73 (38.30–74.96) | 68.05 (46.17–101.77) | 0.035 | |
| Poor outcome (n = 8) | miR-625-3p | 0.06 (0.02–0.13) | 0.11 (0.08–0.21) | 0.012 |
| miR-103a-3p | 0.39 (0.28–0.42) | 0.37 (0.28–0.48) | 0.889 | |
| miR-126-3p | 55.01 (038.03–72.06) | 78.81 (55.58–140.34) | 0.036 | |
| Good outcome (n = 9) | miR-625-3p | 0.04 (0.01–0.14) | 0.04 (0.01–0.05) | 0.173 |
| miR-103a-3p | 0.43 (0.34–0.50) | 0.40 (0.33–0.51) | 0.953 | |
| miR-126-3p | 44.46 (38.76–77.33) | 51.51 (37.69–94.09) | 0.374 |
| miRNA | Poor Outcome Median (25–75%) | Good Outcome Median (25–75%) | p | AUC (95% CI) | p | Cutoff | Sensitivity | Specificity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At diagnosis | miR-625-3p | 0.06 (0.02–0.13) | 0.05 (0.01–0.13) | 0.897 | 0.556 (0.273–0.838) | 0.700 | 0.01 | 0.333 | 0.875 |
| (n = 18) | miR-103a-3p | 0.39 (0.28–0.42) | 0.45 (0.36–0.54) | 0.146 | 0.681 (0.414–0.947) | 0.211 | 0.47 | 0.444 | 1.000 |
| miR-126-3p | 55.01 (38.03–72.06) | 45.09 (39.81–76.49) | 0.965 | 0.514 (0.221–0.807) | 0.923 | 46.28 | 0.667 | 0.925 | |
| Change (%) | miR-625-3p | 85.2 (25.8–565.9) | −17.5 (−82.8–150.6) | 0.036 | 0.806 (0.588–1.000) | 0.034 | 3.2 | 0.667 | 1.000 |
| (n = 17) | miR-103a-3p | 1.6 (-13.9–25.2) | −10.5 (−29.8–37.1) | 0.888 | 0.528 (0.242–0.814) | 0.847 | −16.7 | 0.333 | 0.875 |
| miR-126-3p | 16.1 (1.7–175.97) | 20.7 (−24.8–86.8) | 0.606 | 0.583 (0.297–0.869) | 0.564 | −8.7 | 0.333 | 1.000 |
| miRNA | PFS | OS | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <Cutoff Months, Median (25–75%) | >Cutoff Months, Median (25–75%) | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI)adj | Padj | <Cutoff Months, Median (25–75%) | >Cutoff Months, Median (25–75%) | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI)adj | Padj | |
| miR-625-3p | 19.4 (14.9–23.2) | 7.5 (6.4–14.7) | 3.92 (1.2–12.8) | 0.024 | 4.13 (1.25–13.65) | 0.020 | 49.1 (27.3–49.1) | 12.5 (9.1–28.3) | 5.45 (1.06–28.11) | 0.043 | 6.32 (1.18–33.99) | 0.032 |
| miR-103a-3p | 14.9 (5.8–17.1) | 14.1 (7.2–19.4) | 1.84 (0.52–6.56) | 0.348 | 1.76 (0.47–6.56) | 0.403 | 27.3 (5.8–49.1) | 25.7 (10.6–28.3) | 1.50 (0.30–7.37) | 0.621 | 1.35 (0.26–6.95) | 0.716 |
| miR-126-3p | 19.4 (14.9–23.2) | 8.5 (6.9–17.1) | 1.89 (0.53–6.76) | 0.327 | 2.90 (0.71–11.89) | 0.140 | 27.3 (27.3–27.3) | 25.7 (10.6–49.1) | 2.40 (0.29–19.60) | 0.416 | 7.77 (0.72–84.17) | 0.092 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goričar, K.; Holcar, M.; Mavec, N.; Kovač, V.; Lenassi, M.; Dolžan, V. Extracellular Vesicle Enriched miR-625-3p Is Associated with Survival of Malignant Mesothelioma Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11101014
Goričar K, Holcar M, Mavec N, Kovač V, Lenassi M, Dolžan V. Extracellular Vesicle Enriched miR-625-3p Is Associated with Survival of Malignant Mesothelioma Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(10):1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11101014
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoričar, Katja, Marija Holcar, Nina Mavec, Viljem Kovač, Metka Lenassi, and Vita Dolžan. 2021. "Extracellular Vesicle Enriched miR-625-3p Is Associated with Survival of Malignant Mesothelioma Patients" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 10: 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11101014
APA StyleGoričar, K., Holcar, M., Mavec, N., Kovač, V., Lenassi, M., & Dolžan, V. (2021). Extracellular Vesicle Enriched miR-625-3p Is Associated with Survival of Malignant Mesothelioma Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(10), 1014. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11101014