Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing for the Identification of Genetic Predictors of Radiation-Induced Late Skin Toxicity in Breast Cancer Patients: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
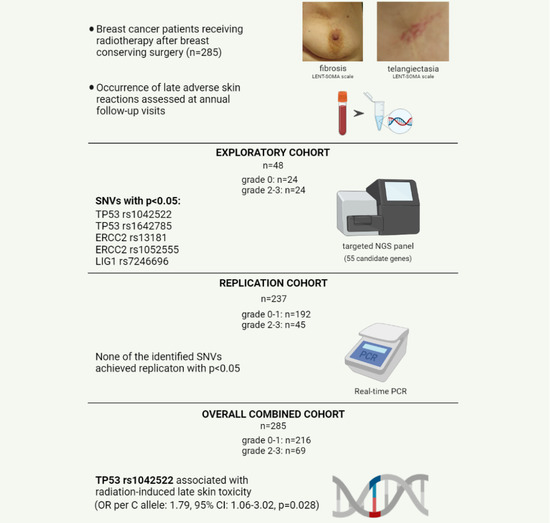
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting and Participants
2.2. DNA Extraction and Quality Control
2.3. NGS Library Preparation, Sequencing, and Data Analysis
2.4. Real-Time PCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients Characteristics
3.2. Identification of Candidate Variants by Targeted Gene Sequencing
3.3. Replication and Combined Cohort Analyses of SNVs Identified by Targeted NGS
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
Appendix A
| Pathway Function | Genes |
|---|---|
| Cell cycle | BAX, CDKN1A, CHEK1, CHEK2, ESPL1, RAD9A |
| DNA damage repair: BER | APEX1, APEX2, LIG3, OGG1, PNKP, XRCC1 |
| DNA damage repair: DR | MGMT |
| DNA damage repair: MMR | MLH1, MSH2, MSH3, MSH6, PMS2, SSBP1 |
| DNA damage repair: NER | ERCC1, ERCC2, ERCC3, ERCC4, ERCC5, ERCC6, ERCC8, LIG1, PCNA |
| DSB detection | MRE11A, NBN, RAD50 |
| DSB repair: HR | BRCA1, BRCA2, RAD51, RAD51C, XRCC2, XRCC3 |
| DSB repair: NHEJ | LIG4, PRKDC, XRCC4, XRCC5, XRCC6 |
| DSB signal transduction | ATM, ATR, TP53, TP53BP1 |
| Profibrotic and inflammatory cytokines | ACVRL1, IL12RB2, TGFB1, TNF-α, IL-6 |
| Reactive oxygen species pathway | GSTA1, GSTP1, NOS3, SOD2 |
References
- Darby, S.; McGale, P.; Correa, C.; Taylor, C.; Arriagada, R.; Clarke, M.; Cutter, D.; Davies, C.; Ewertz, M.; Godwin, J.; et al. Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: Meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet 2011, 378, 1707–1716. [Google Scholar]
- McGale, P.; Taylor, C.; Correa, C.; Cutter, D.; Duane, F.; Ewertz, M.; Gray, R.; Mannu, G.; Peto, R.; Whelan, T.; et al. Effect of radiotherapy after mastectomy and axillary surgery on 10-year recurrence and 20-year breast cancer mortality: Meta-analysis of individual patient data for 8135 women in 22 randomised trials. Lancet 2014, 383, 2127–2135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barnett, G.C.; West, C.M.; Dunning, A.M.; Elliott, R.M.; Coles, C.E.; Pharoah, P.D.; Burnet, N.G. Normal tissue reactions to radiotherapy: Towards tailoring treatment dose by genotype. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramseier, J.Y.; Ferreira, M.N.; Leventhal, J.S. Dermatologic toxicities associated with radiation therapy in women with breast cancer. Int. J. Womens Dermatol. 2020, 6, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straub, J.M.; New, J.; Hamilton, C.D.; Lominska, C.; Shnayder, Y.; Thomas, S.M. Radiation-induced fibrosis: Mechanisms and implications for therapy. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 1985–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batenburg, M.C.T.; Gregorowitsch, M.L.; Maarse, W.; Witkamp, A.; Young-Afat, D.A.; Braakenburg, A.; Doeksen, A.; van Dalen, T.; Sier, M.; Schoenmaeckers, E.J.P.; et al. Patient-reported cosmetic satisfaction and the long-term association with quality of life in irradiated breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 179, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lilla, C.; Ambrosone, C.B.; Kropp, S.; Helmbold, I.; Schmezer, P.; von Fournier, D.; Haase, W.; Sautter-Bihl, M.L.; Wenz, F.; Chang-Claude, J. Predictive factors for late normal tissue complications following radiotherapy for breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 106, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekrmandi, F.; Panzarella, T.; Dinniwell, R.E.; Helou, J.; Levin, W. Predictive factors for persistent and late radiation complications in breast cancer survivors. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 22, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuptsova, N.; Chang-Claude, J.; Kropp, S.; Helmbold, I.; Schmezer, P.; von Fournier, D.; Haase, W.; Sautter-Bihl, M.L.; Wenz, F.; Onel, K.; et al. Genetic predictors of long-term toxicities after radiation therapy for breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zschenker, O.; Raabe, A.; Boeckelmann, I.K.; Borstelmann, S.; Szymczak, S.; Wellek, S.; Rades, D.; Hoeller, U.; Ziegler, A.; Dikomey, E.; et al. Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in ATM, GSTP1, SOD2, TGFB1, XPD and XRCC1 with clinical and cellular radiosensitivity. Radiother. Oncol. 2010, 97, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, C.J.; Tanteles, G.A.; Barnett, G.C.; Burnet, N.G.; Chang-Claude, J.; Coles, C.E.; Davidson, S.; Dunning, A.M.; Mills, J.; Murray, R.J.; et al. A replicated association between polymorphisms near TNFα and risk for adverse reactions to radiotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falvo, E.; Strigari, L.; Citro, G.; Giordano, C.; Boboc, G.; Fabretti, F.; Bruzzaniti, V.; Bellesi, L.; Muti, P.; Blandino, G.; et al. SNPs in DNA repair or oxidative stress genes and late subcutaneous fibrosis in patients following single shot partial breast irradiation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 31, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seibold, P.; Behrens, S.; Schmezer, P.; Helmbold, I.; Barnett, G.; Coles, C.; Yarnold, J.; Talbot, C.J.; Imai, T.; Azria, D.; et al. XRCC1 Polymorphism Associated with Late Toxicity After Radiation Therapy in Breast Cancer Patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Lu, P.; Beeraka, N.M.; Sukocheva, O.A.; Madhunapantula, S.V.; Liu, J.; Sinelnikov, M.Y.; Nikolenko, V.N.; Bulygin, K.V.; Mikhaleva, L.M.; et al. Mitochondrial mutations and mitoepigenetics: Focus on regulation of oxidative stress-induced responses in breast cancers. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, S1044–579X(20)30203-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang-Claude, J.; Ambrosone, C.B.; Lilla, C.; Kropp, S.; Helmbold, I.; von Fournier, D.; Haase, W.; Sautter-Bihl, M.L.; Wenz, F.; Schmezer, P.; et al. Genetic polymorphisms in DNA repair and damage response genes and late normal tissue complications of radiotherapy for breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 1680–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quarmby, S.; Fakhoury, H.; Levine, E.; Barber, J.; Wylie, J.; Hajeer, A.H.; West, C.; Stewart, A.; Magee, B.; Kumar, S. Association of transforming growth factor beta-1 single nucleotide polymorphisms with radiation-induced damage to normal tissues in breast cancer patients. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2003, 79, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, G.C.; Coles, C.E.; Burnet, N.G.; Pharoah, P.D.; Wilkinson, J.; West, C.M.; Elliott, R.M.; Baynes, C.; Dunning, A.M. No association between SNPs regulating TGF-β1 secretion and late radiotherapy toxicity to the breast: Results from the RAPPER study. Radiother. Oncol. 2010, 97, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grossberg, A.J.; Lei, X.; Xu, T.; Shaitelman, S.F.; Hoffman, K.E.; Bloom, E.S.; Stauder, M.C.; Tereffe, W.; Schlembach, P.J.; Woodward, W.A.; et al. Association of Transforming Growth Factor β Polymorphism C-509T With Radiation-Induced Fibrosis Among Patients with Early-Stage Breast Cancer: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreassen, C.N.; Overgaard, J.; Alsner, J.; Overgaard, M.; Herskind, C.; Cesaretti, J.A.; Atencio, D.P.; Green, S.; Formenti, S.C.; Stock, R.G.; et al. ATM sequence variants and risk of radiation-induced subcutaneous fibrosis after postmastectomy radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 64, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.Y.; Fan, G.; Atencio, D.P.; Green, S.; Formenti, S.C.; Haffty, B.G.; Iyengar, P.; Bernstein, J.L.; Stock, R.G.; Cesaretti, J.A.; et al. Possession of ATM sequence variants as predictor for late normal tissue responses in breast cancer patients treated with radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 69, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanteles, G.A.; Murray, R.J.; Mills, J.; Barwell, J.; Chakraborti, P.; Chan, S.; Cheung, K.L.; Ennis, D.; Khurshid, N.; Lambert, K.; et al. Variation in telangiectasia predisposing genes is associated with overall radiation toxicity. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreassen, C.N.; Rosenstein, B.S.; Kerns, S.L.; Ostrer, H.; De Ruysscher, D.; Cesaretti, J.A.; Barnett, G.C.; Dunning, A.M.; Dorling, L.; West, C.M.L.; et al. International Radiogenomics Consortium (RgC). Individual patient data meta-analysis shows a significant association between the ATM rs1801516 SNP and toxicity after radiotherapy in 5456 breast and prostate cancer patients. Radiother. Oncol. 2016, 121, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terrazzino, S.; Cargnin, S.; Deantonio, L.; Pisani, C.; Masini, L.; Canonico, P.L.; Genazzani, A.A.; Krengli, M. Impact of ATM rs1801516 on late skin reactions of radiotherapy for breast cancer: Evidences from a cohort study and a trial sequential meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edvardsen, H.; Kristensen, V.N.; Grenaker Alnaes, G.I.; Bøhn, M.; Erikstein, B.; Helland, A.; Børresen-Dale, A.L.; Fosså, S.D. Germline glutathione S-transferase variants in breast cancer: Relation to diagnosis and cutaneous long-term adverse effects after two fractionation patterns of radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 67, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreassen, C.N.; Alsner, J.; Overgaard, M.; Overgaard, J. Prediction of normal tissue radiosensitivity from polymorphisms in candidate genes. Radiother. Oncol. 2003, 69, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavy, J.J.; Denekamp, J.; Letschert, J.; Littbrand, B.; Mornex, F.; Bernier, J.; Gonzales-Gonzales, D.; Horiot, J.C.; Bolla, M.; Bartelink, H. EORTC Late Effects Working Group. Late Effects toxicity scoring: The SOMA scale. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1995, 31, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmueller, K.E.; Pearce, C.L.; Pike, M.; Lander, E.S.; Hirschhorn, J.N. Meta-analysis of genetic association studies supports a contribution of common variants to susceptibility to common disease. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, P. Curses-winner’s and otherwise-in genetic epidemiology. Epidemiology 2008, 19, 649–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudkov, A.V.; Komarova, E.A. The role of p53 in determining sensitivity to radiotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, P.; Leu, J.I.; Della Pietra, A.C., 3rd; George, D.L.; Murphy, M. The codon 72 polymorphic variants of p53 have markedly different apoptotic potential. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pim, D.; Banks, L. p53 polymorphic variants at codon 72 exert different effects on cell cycle progression. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 108, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, M.; Sabapathy, K. Trp53-dependent DNA-repair is affected by the codon 72 polymorphism. Oncogene 2006, 25, 3489–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, X.L.; Popanda, O.; Ambrosone, C.B.; Kropp, S.; Helmbold, I.; von Fournier, D.; Haase, W.; Sautter-Bihl, M.L.; Wenz, F.; Schmezer, P.; et al. Association between TP53 and p21 genetic polymorphisms and acute side effects of radiotherapy in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2006, 97, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badie, C.; Dziwura, S.; Raffy, C.; Tsigani, T.; Alsbeih, G.; Moody, J.; Finnon, P.; Levine, E.; Scott, D.; Bouffler, S. Aberrant CDKN1A transcriptional response associates with abnormal sensitivity to radiation treatment. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 1845–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Rudolf, J.; Johnson, K.A.; McMahon, S.A.; Oke, M.; Carter, L.; McRobbie, A.M.; Brown, S.E.; Naismith, J.H.; White, M.F. Structure of the DNA repair helicase XPD. Cell 2008, 133, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satoh, M.S.; Jones, C.J.; Wood, R.D.; Lindahl, T. DNA excision-repair defect of xeroderma pigmentosum prevents removal of a class of oxygen free radical-induced base lesions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6335–6339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lunn, R.M.; Helzlsouer, K.J.; Parshad, R.; Umbach, D.M.; Harris, E.L.; Sanford, K.K.; Bell, D.A. XPD polymorphisms: Effects on DNA repair proficiency. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mangoni, M.; Bisanzi, S.; Carozzi, F.; Sani, C.; Biti, G.; Livi, L.; Barletta, E.; Costantini, A.S.; Gorini, G. Association between genetic polymorphisms in the XRCC1, XRCC3, XPD, GSTM1, GSTT1, MSH2, MLH1, MSH3, and MGMT genes and radiosensitivity in breast cancer patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomkinson, A.E.; Chen, L.; Dong, Z.; Leppard, J.B.; Levin, D.S.; Mackey, Z.B.; Motycka, T.A. Completion of base excision repair by mammalian DNA ligases. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 2001, 68, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.A.; Sivakumar, D.; Somvanshi, P. Cataloguing functionally relevant polymorphisms in gene DNA ligase I: A computational approach. 3 Biotech. 2011, 1, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Clinical Variable | All n (%) | Grade 0–1 n (%) | Grade ≥ 2 n (%) | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years (SD) | 60.8 (10.1) | 60.0 (10.0) | 63.2 (10.0) | 1.03 (1.00–1.06) | 0.023 |
| BMI, mean (SD) | 25.0 (3.8) | 24.6 (3.8) | 26.2 (3.7) | 1.11 (1.03–1.19) | 0.006 |
| Breast diameter, cm (SD) | 12.2 (2.6) | 12.0 (2.6) | 12.7 (2.6) | 1.10 (1.00–1.22) | 0.054 |
| Breast CTV, cc (SD) | 394.2 (530.0) | 380.8 (586.5) | 438.3 (270.4) | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | 0.489 |
| Follow-up, years (SD) | 10.3 (4.0) | 10.0 (3.9) | 11.0 (4.2) | 1.06 (0.99–1.13) | 0.071 |
| Diabetes mellitus | |||||
| No | 267 (93.7) | 205 (94.9) | 62 (89.9) | 1 (reference) | |
| Yes | 18 (6.3) | 11 (5.1) | 7 (10.1) | 2.10 (0.78–5.66) | 0.140 |
| Hypertension | |||||
| No | 211 (74.0) | 155 (71.8) | 56 (81.2) | 1 (reference) | |
| Yes | 74 (26.0) | 61 (28.2) | 13 (18.8) | 0.60 (0.30–1.16) | 0.124 |
| Vascular disease | |||||
| No | 263 (92.3) | 200 (92.6) | 63 (91.3) | 1 (reference) | |
| Yes | 22 (7.7) | 16 (7.4) | 6 (8.7) | 1.19 (0.45–3.17) | 0.727 |
| Tabagism | |||||
| Never | 242 (84.9) | 181 (83.8) | 61 (88.4) | 1 (reference) | |
| Current or former | 43 (15.1) | 35 (16.2) | 8 (11.6) | 0.68 (0.30–1.54) | 0.354 |
| Alcohol | |||||
| No | 276 (96.8) | 209 (96.8) | 67 (97.1) | 1 (reference) | |
| Yes | 9 (3.2) | 7 (3.2) | 2 (2.9) | 0.89 (0.18–4.39) | 0.887 |
| Postsurgical complications | |||||
| None | 239 (83.9) | 176 (81.5) | 63 (91.3) | 1 (reference) | |
| Seromas and hematomas | 46 (16.1) | 40 (18.5) | 6 (8.7) | 0.42 (0.17–1.04) | 0.060 |
| Neoadjuvant CT | |||||
| No | 278 (97.5) | 210 (97.2) | 68 (98.6) | 1 (reference) | |
| Yes | 7 (2.5) | 6 (2.8) | 1 (1.4) | 0.51 (0.06–4.35) | 0.542 |
| Adjuvant treatments | |||||
| None | 40 (14.0) | 28 (13.0) | 12 (17.4) | 1 (reference) | |
| CT | 61 (21.4) | 48 (22.2) | 13 (18.8) | 0.63 (0.25–1.57) | 0.324 |
| HT | 131 (46.0) | 100 (46.3) | 31 (44.9) | 0.72 (0.33–1.59) | 0.420 |
| CT + HT | 53 (18.6) | 40 (18.5) | 13 (18.8) | 0.76 (0.30–1.90) | 0.556 |
| Radiation quality | |||||
| X-rays | 263 (92.3) | 199 (92.1) | 64 (92.8) | 1 (reference) | |
| γ-rays | 22 (7.7) | 17 (7.9) | 5 (7.2) | 0.91 (0.32–2.58) | 0.866 |
| Dose/fraction | |||||
| 2 Gy | 274 (96.1) | 208 (96.3) | 66 (95.7) | 1 (reference) | |
| 1,8 Gy | 11 (3.9) | 8 (3.7) | 3 (4.3) | 1.18 (0.30–4.58) | 0.809 |
| Boost dose/fraction | |||||
| 3 Gy | 72 (25.3) | 58 (26.9) | 14 (20.3) | 1 (reference) | |
| 1.5–2 Gy | 189 (66.3) | 139 (64.4) | 50 (72.5) | 1.49 (0.76–2.90) | 0.241 |
| No boost | 24 (8.4) | 19 (8.8) | 5 (7.2) | 1.09 (0.35–3.43) | 0.882 |
| Acute skin toxicity, RTOG grade | |||||
| 0–1 | 196 (68.8) | 151 (69.9) | 45 (65.2) | 1 (reference) | |
| ≥2 | 89 (31.2) | 65 (30.1) | 24 (34.8) | 1.24 (0.70–2.20) | 0.465 |
| Gene | Chr | SNP | BP | Region | Ref (Allele 1)/ Alt (Allele 2) | RAF Grade 0/ RAF Grade ≥ 2 | p-Value * | Risk Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP53 | 17 | rs1042522 | 7579472 | Exonic (p.Pro72Arg) | G/C | 0.40/0.15 | 0.011 | C |
| TP53 | 17 | rs1642785 | 7579801 | UTR5 | G/C | 0.40/0.15 | 0.011 | C |
| ERCC2 | 19 | rs13181 | 45854919 | Exonic (p.Lys751Gln) | G/T | 0.50/0.23 | 0.010 | T |
| ERCC2 | 19 | rs1052555 | 45855524 | Exonic (p.Asp711Asp) | A/G | 0.44/0.17 | 0.007 | G |
| LIG1 | 19 | rs7246696 | 48673212 | Intronic | C/T | 0.56/0.31 | 0.023 | T |
| SNP | Cohort | Genotype Count | Crude OR (95%CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR * (95%CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controls 11/12/22 | Cases 11/12/22 | ||||||
| TP53 rs1042522 | Exploratory | 3/13/8 | 0/7/17 | 4.70 (1.51–14.6) | 0.007 | 4.23 (1.25–14.4) | 0.021 |
| Replication | 7/74/111 | 2/11/32 | 1.52 (0.82–2-83) | 0.186 | 1.27 (0.68–2.39) | 0.456 | |
| Combined | 10/87/119 | 2/18/49 | 1.79 (1.06–3.02) | 0.028 | 1.54 (0.90–2.63) | 0.111 | |
| ERCC2 rs13181 | Exploratory | 5/14/5 | 0/11/13 | 4.78 (1.56–14.7) | 0.006 | 4.14 (1.27–13.4) | 0.018 |
| Replication | 24/83/85 | 10/22/13 | 0.60 (0.38–0.96) | 0.031 | 0.61 (0.38–0.97) | 0.036 | |
| Combined | 29/97/90 | 10/33/26 | 0.90 (0.61–1.33) | 0.595 | 0.90 (0.60–1.4) | 0.598 | |
| ERCC2 rs1052555 | Exploratory | 4/13/7 | 0/8/16 | 4.75 (1.57–14.4) | 0.006 | 4.09 (1.30–12.9) | 0.016 |
| Replication | 22/81/89 | 9/20/16 | 0.67 (0.42–1.07) | 0.093 | 0.64 (0.40–1.03) | 0.064 | |
| Combined | 26/94/96 | 9/28/32 | 1.02 (0.68–1.52) | 0.922 | 0.98 (0.65–1.46) | 0.916 | |
| LIG1 rs7246696 | Exploratory | 8/11/5 | 2/11/11 | 2.81 (1.16–6.82) | 0.022 | 2.72 (1.09–6.80) | 0.032 |
| Replication | 27/81/84 | 10/17/18 | 0.80 (0.51–1.24) | 0.316 | 0.81 (0.51–1.28) | 0.365 | |
| Combined | 35/92/89 | 12/28/29 | 0.99 (0.68–1.45) | 0.971 | 1.00 (0.68–1.47) | 0.993 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cargnin, S.; Barizzone, N.; Basagni, C.; Pisani, C.; Ferrara, E.; Masini, L.; D’Alfonso, S.; Krengli, M.; Terrazzino, S. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing for the Identification of Genetic Predictors of Radiation-Induced Late Skin Toxicity in Breast Cancer Patients: A Preliminary Study. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11100967
Cargnin S, Barizzone N, Basagni C, Pisani C, Ferrara E, Masini L, D’Alfonso S, Krengli M, Terrazzino S. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing for the Identification of Genetic Predictors of Radiation-Induced Late Skin Toxicity in Breast Cancer Patients: A Preliminary Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(10):967. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11100967
Chicago/Turabian StyleCargnin, Sarah, Nadia Barizzone, Chiara Basagni, Carla Pisani, Eleonora Ferrara, Laura Masini, Sandra D’Alfonso, Marco Krengli, and Salvatore Terrazzino. 2021. "Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing for the Identification of Genetic Predictors of Radiation-Induced Late Skin Toxicity in Breast Cancer Patients: A Preliminary Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 10: 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11100967
APA StyleCargnin, S., Barizzone, N., Basagni, C., Pisani, C., Ferrara, E., Masini, L., D’Alfonso, S., Krengli, M., & Terrazzino, S. (2021). Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing for the Identification of Genetic Predictors of Radiation-Induced Late Skin Toxicity in Breast Cancer Patients: A Preliminary Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(10), 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11100967