A Numerical Study on Roughness-Induced Adhesion Enhancement in a Sphere with an Axisymmetric Sinusoidal Waviness Using Lennard–Jones Interaction Law
Abstract
:1. Introduction
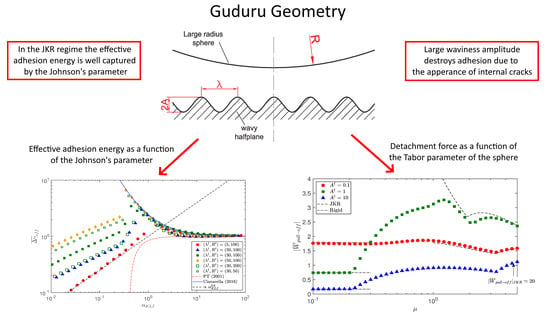
2. Guduru Contact Problem
JKR Theory
3. Numerical Solution
3.1. Axisymmetric BEM Formulation
3.2. Validation of the Numerical Results
4. Rigid Limit
5. Numerical Results
5.1. Effect of the Tabor Parameter
5.2. Hysteresis Cycle
5.3. Adhesion Map
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. BEM Formulation with Constant Pressure Discrete Elements
References
- Ciavarella, M.; Joe, J.; Papangelo, A.; Barber, J.R. The role of adhesion in contact mechanics. J. R. Soc. Interface 2019, 16, 20180738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tadmor, R.; Das, R.; Gulec, S.; Liu, J.; N’guessan, H.; Shah, M.; Wasnik, P.; Yadav, S.B. Solid–liquid work of adhesion. Langmuir 2017, 33, 3594–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakis, A.I.; Yastrebov, V.A.; Scheibert, J.; Nicola, L.; Dini, D.; Minfray, C.; Molinari, J.F. Modeling and simulation in tribology across scales: An overview. Tribol. Int. 2018, 125, 169–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorb, S.; Varenberg, M.; Peressadko, A.; Tuma, J. Biomimetic mushroom-shaped fibrillar adhesive microstructure. J. R. Soc. Interface 2007, 4, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skelton, S.; Bostwick, M.; O’Connor, K.; Konst, S.; Casey, S.; Lee, B.P. Biomimetic adhesive containing nanocomposite hydrogel with enhanced materials properties. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 3825–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Li, J.; Vlassak, J.J.; Suo, Z. Adhesion between highly stretchable materials. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.P.; Aksak, B.; Sitti, M. Gecko-inspired directional and controllable adhesion. Small 2009, 5, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papangelo, A.; Lovino, R.; Ciavarella, M. Electroadhesive sphere-flat contact problem: A comparison between DMT and full iterative finite element solutions. Tribol. Int. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahli, R.; Pallares, G.; Papangelo, A.; Ciavarella, M.; Ducottet, C.; Ponthus, N.; Scheibert, J. Shear-induced anisotropy in rough elastomer contact. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 122, 214301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papangelo, A.; Scheibert, J.; Sahli, R.; Pallares, G.; Ciavarella, M. Shear-induced contact area anisotropy explained by a fracture mechanics model. Phys. Rev. E 2019, 99, 053005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papangelo, A.; Ciavarella, M. On mixed-mode fracture mechanics models for contact area reduction under shear load in soft materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2019, 124, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciavarella, M.; Papangelo, A. On the Degree of Irreversibility of Friction in Sheared Soft Adhesive Contacts. Tribol. Lett. 2020, 68, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.N.J.; Tosatti, E. The effect of surface roughness on the adhesion of elastic solids. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 5597–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Violano, G.; Afferrante, L.; Papangelo, A.; Ciavarella, M. On stickiness of multiscale randomly rough surfaces. J. Adhes. 2019, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuller, K.N.G.; Tabor, D. The effect of surface roughness on the adhesion of elastic solids. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1975, 345, 327–342. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, G.A.D.; Briscoe, B.J. The effect of surface topography on the adhesion of elastic solids. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1977, 10, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guduru, P.R. Detachment of a rigid solid from an elastic wavy surface: Theory. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2007, 55, 445–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L.; Kendall, K.; Roberts, A. Surface energy and the contact of elastic solids. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1971, 324, 301–313. [Google Scholar]
- Guduru, P.R.; Bull, C. Detachment of a rigid solid from an elastic wavy surface: Experiments. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2007, 55, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesari, H.; Doll, J.C.; Pruitt, B.L.; Cai, W.; Lew, A.J. Role of surface roughness in hysteresis during adhesive elastic contact. Philos. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2010, 90, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kesari, H.; Lew, A.J. Effective macroscopic adhesive contact behavior induced by small surface roughness. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2011, 59, 2488–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, J.F.; Lee, S.; Guduru, P.R. Mechanics of axisymmetric wavy surface adhesion: JKR–DMT transition solution. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2009, 46, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradley, R.S. The cohesive force between solid surfaces and the surface energy of solids. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. J. Sci. 1932, 13, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavarella, M. On roughness-induced adhesion enhancement. J. Strain Anal. Eng. Des. 2016, 51, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rumpf, H. Particle Technology; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovich, Y.I.; Adler, J.J.; Ata, A.; Singh, R.K.; Moudgil, B.M. Adhesion between nanoscale rough surfaces: I. Role of asperity geometry. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 232, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovich, Y.I.; Adler, J.J.; Ata, A.; Singh, R.K.; Moudgil, B.M. Adhesion between nanoscale rough surfaces: II. Measurement and comparison with theory. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 232, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavarella, M. An upper bound to multiscale roughness-induced adhesion enhancement. Tribol. Int. 2016, 102, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, K.L. Contact Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, K.L. The adhesion of two elastic bodies with slightly wavy surfaces. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1995, 32, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.J. Numerical Analyses on the Adhesive Contact between a Sphere and a Longitudinal Wavy Surface. J. Adhes. 2014, 91, 381–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, S.; Dini, D. A numerical model for the deterministic analysis of adhesive rough contacts down to the nano-scale. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2014, 51, 2620–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rey, V.; Anciaux, G.; Molinari, J.F. Normal adhesive contact on rough surfaces: Efficient algorithm for FFT-based BEM resolution. Comput. Mech. 2017, 60, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Pohrt, R.; Popov, V.L. Adhesive Strength of Contacts of Rough Spheres. Front. Mech. Eng. 2019, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenwood, J.A. Adhesion of elastic spheres. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1997, 453, 1277–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.Q. Contact behavior of spherical elastic particles: A computational study of particle adhesion and deformations. Colloids Surfaces Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2000, 172, 175–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attard, P.; Parker, J.L. Deformation and adhesion of elastic bodies in contact. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 46, 7959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayfeh, A.H.; Balachandran, B. Applied Nonlinear Dynamics: Analytical, Computational, and Experimental Methods; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Maugis, D. Adhesion of spheres: The JKR-DMT transition using a Dugdale model. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1992, 150, 243–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastewka, L.; Robbins, M.O. Contact between rough surfaces and a criterion for macroscopic adhesion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3298–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciavarella, M. Universal features in “stickiness” criteria for soft adhesion with rough surfaces. Tribol. Int. 2020, 146, 106031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, R.; Gorb, S.; Jamar, V.; Flammang, P. Adhesion of echinoderm tube feet to rough surfaces. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 2555–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]















© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papangelo, A.; Ciavarella, M. A Numerical Study on Roughness-Induced Adhesion Enhancement in a Sphere with an Axisymmetric Sinusoidal Waviness Using Lennard–Jones Interaction Law. Lubricants 2020, 8, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants8090090
Papangelo A, Ciavarella M. A Numerical Study on Roughness-Induced Adhesion Enhancement in a Sphere with an Axisymmetric Sinusoidal Waviness Using Lennard–Jones Interaction Law. Lubricants. 2020; 8(9):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants8090090
Chicago/Turabian StylePapangelo, Antonio, and Michele Ciavarella. 2020. "A Numerical Study on Roughness-Induced Adhesion Enhancement in a Sphere with an Axisymmetric Sinusoidal Waviness Using Lennard–Jones Interaction Law" Lubricants 8, no. 9: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants8090090
APA StylePapangelo, A., & Ciavarella, M. (2020). A Numerical Study on Roughness-Induced Adhesion Enhancement in a Sphere with an Axisymmetric Sinusoidal Waviness Using Lennard–Jones Interaction Law. Lubricants, 8(9), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants8090090