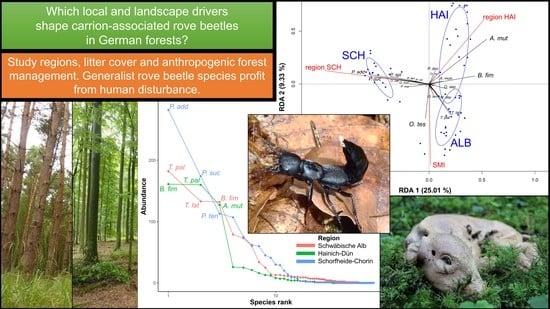
Local and Landscape Effects on Carrion-Associated Rove Beetle (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae) Communities in German Forests
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Which environmental parameters determine carrion-associated rove beetle abundance, diversity, and community composition?
- Which rove beetle species trapped on carrion are most affected by environmental drivers?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Exposure of Piglet Cadavers
2.3. Insect Sampling
2.4. Environmental Variables
2.5. Statistical Analyses
2.5.1. Data Exploration
2.5.2. Effects of Forest Management, Habitat Parameters, and Region on Rove Beetle Abundance and Diversity
“abundance” ~ ”SMI” + “pH” + “understory” + “shannon plants” + “region”;“richness” ~ ”SMI” + “pH” + “shannon plants” + “litter cover” + “deadwood cover” + “region”;“shannon” ~ ”SMI” + “pH” + “shannon plants” + “litter cover” + “silt content” + “region”.
2.5.3. Effects of Forest Management, Habitat Parameters, and Region on Rove Beetle Community Composition
2.5.4. Effects of Environmental Variables on Single Rove Beetle Species
2.5.5. Rank Abundance Curves
3. Results
3.1. Rove Beetles on Piglet Cadavers
3.2. Effects of Forest Management, Habitat Parameters, and Region on Rove Beetle Abundance and Diversity
3.3. Effects of Forest Management, Habitat Parameters, and Region on Rove Beetle Community Composition
3.4. Effects of Environmental Variables on Single Rove Beetle Species
4. Discussion
4.1. Local and Landscape Parameters Affecting Rove Beetle Abundance, Diversity, and Communities on Vertebrate Carrion
4.2. Impact on Forensic Entomological Assessments
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Statement
References
- Sala, O.E.; Chapin, F.S.; Armesto, J.J.; Berlow, E.; Bloomfield, J.; Dirzo, R.; Huber-Sanwald, E.; Huenneke, L.F.; Jackson, R.B.; Kinzig, A.; et al. Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100. Science 2000, 287, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newbold, T.; Hudson, L.N.; Hill, S.L.L.; Contu, S.; Lysenko, I.; Senior, R.A.; Börger, L.; Bennett, D.J.; Choimes, A.; Collen, B.; et al. Global effects of land use on local terrestrial biodiversity. Nature 2015, 520, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lange, M.; Türke, M.; Pašalić, E.; Boch, S.; Hessenmöller, D.; Müller, J.; Prati, D.; Socher, S.A.; Fischer, M.; Weisser, W.W.; et al. Effects of forest management on ground-dwelling beetles (Coleoptera; Carabidae, Staphylinidae) in Central Europe are mainly mediated by changes in forest structure. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2014, 329, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petermann, J.S.; Roberts, A.L.; Hemmerling, C.; Bajerski, F.; Pascual, J.; Overmann, J.; Weisser, W.W.; Ruess, L.; Gossner, M.M. Direct and indirect effects of forest management on tree-hole inhabiting aquatic organisms and their functional traits. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penone, C.; Allan, E.; Soliveres, S.; Felipe-Lucia, M.R.; Gossner, M.M.; Seibold, S.; Simons, N.K.; Schall, P.; van der Plas, F.; Manning, P.; et al. Specialisation and diversity of multiple trophic groups are promoted by different forest features. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossner, M.M.; Falck, K.; Weisser, W.W. Effects of management on ambrosia beetles and their antagonists in European beech forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 437, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Hoermann, C.; Weithmann, S.; Deißler, M.; Ayasse, M.; Steiger, S. Forest habitat parameters influence abundance and diversity of cadaver-visiting dung beetles in Central Europe. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 191722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- von Hoermann, C.; Jauch, D.; Kubotsch, C.; Reichel-Jung, K.; Steiger, S.; Ayasse, M. Effects of abiotic environmental factors and land use on the diversity of carrion-visiting silphid beetles (Coleoptera: Silphidae): A large scale carrion study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, O.; Irmler, U.; Klimaszewski, J. Biology of Rove Beetles (Staphylinidae): Life History, Evolution, Ecology and Distribution, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pohl, G.; Langor, D.; Klimaszewski, J.; Work, T.; Paquin, P. Rove beetles (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae) in northern Nearctic forests. Can. Entomol. 2008, 140, 415–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magura, T.; Nagy, D.; Tóthmérész, B. Rove beetles respond heterogeneously to urbanization. J. Insect Conserv. 2013, 17, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bohac, J. Staphylinid beetles as bioindicators. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1999, 74, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansson, T.; Gibb, H.; Hjältén, J.; Pettersson, R.B.; Hilszczański, J.; Alinvi, O.; Ball, J.P.; Danell, K. The effects of substrate manipulations and forest management on predators of saproxylic beetles. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2007, 242, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, E.; Niederegger, S.; Beutel, R.G. Beetles and flies collected on pig carrion in an experimental setting in Thuringia and their forensic implications. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2011, 25, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekeirsschieter, J.; Frederick, C.; Verheggen, F.J.; Drugmand, D.; Haubruge, E. Diversity of forensic rove beetles (Coleoptera, Staphylinidae) associated with decaying pig carcass in a forest biotope. J. Forensic Sci. 2013, 58, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mądra, A.; Konwerski, S.; Matuszewski, S. Necrophilous Staphylininae (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae) as indicators of season of death and corpse relocation. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 242, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benbow, M.E.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Tarone, A.M. Carrion Ecology, Evolution, and Their Applications, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, K. Ökologie 1; Geocke & Evers: Krefeld, Germany, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Peschke, K.; Friedrich, P.; Franke, S.; Francke, W. Isopropyl (Z9)-hexadecenoate as a male attractant pheromone from the sternal gland of the rove beetle Aleochara curtula (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae). Chemoecology 1999, 9, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farwig, N.; Brandl, R.; Siemann, S.; Wiener, F.; Müller, J. Decomposition rate of carrion is dependent on composition not abundance of the assemblages of insect scavengers. Oecologia 2014, 175, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, U.; León-Cortés, J.L.; Morón-Ríos, A. Response of rove beetles (Staphylinidae) to various habitat types and change in Southern Mexico. J. Insect Conserv. 2009, 13, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, E.; Castro, C.; Garcia, M.D.; Serrano, A.R.M.; Gamarra, P.; Outerelo, R. Staphylinid forensic communities from Lisbon with new records for Portugal (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae). Boln. Asoc. Esp. Ent. 2010, 34, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Villet, M.H. African carrion ecosystems and their insect communities in relation to forensic entomology. Pest. Technol. 2011, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Buse, A.; Good, E.G. The effects of conifer forest design and management on abundance and diversity of rove beetles (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae): Implications for conservation. Biol. Conserv. 1992, 64, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmain, G.; Bouget, C.; Müller, J.; Horak, J.; Gossner, M.M.; Lachat, T.; Isacsson, G. Can rove beetles (Staphylinidae) be excluded in studies focusing on saproxylic beetles in central European beech forests? Bull. Entomol. Res. 2015, 105, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marquez, J. Ecological patterns in necrophilous Staphylinidae (Insecta: Coleoptera) from Tlayacapan, Morelos, México. Acta Zool. Mex. 2003, 89, 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Matuszewski, S. Estimating the preappearance interval from temperature in Creophilus maxillosus L. (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae). J. Forensic Sci. 2012, 57, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frątczak-Łagiewska, K.; Grzywacz, A.; Matuszewski, S. Development and validation of forensically useful growth models for Central European population of Creophilus maxillosus L. (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae). Int. J. Legal Med. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matuszewski, S.; Bajerlein, D.; Konwerski, S.; Szpila, K. An initial study of insect succession and carrion decomposition in various forest habitats of Central Europe. Forensic Sci. Int. 2008, 180, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszewski, S.; Szafałowicz, M.; Jarmusz, M. Insects colonising carcasses in open and forest habitats of Central Europe: Search for indicators of corpse relocation. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 231, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Bossdorf, O.; Gockel, S.; Hänsel, F.; Hemp, A.; Hessenmöller, D.; Korte, G.; Nieschulze, J.; Pfeiffer, S.; Prati, D.; et al. Implementing large-scale and long-term functional biodiversity research: The Biodiversity Exploratories. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2010, 11, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schall, P.; Ammer, C. How to quantify forest management intensity in Central European forests. Eur. J. For. Res. 2013, 132, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assing, V.; Schülke, M. Freude-Harde-Lohse-Klausnitzer-Die Käfer Mitteleuropas. Band 4 Staphylinidae I, 2nd ed.; Spektrum Akademischer Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Palm, T. Svensk Insektfauna. 9, Skalbaggar. Coleoptera. Kortvingar: Fam. Staphylinidae H. 6, Underfam. Aleocharinae (Atheta); Entomologiska Föringen: Stockholm, Sweden, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Freude, H.; Harde, K.W.; Lohse, G.A. Die Käfer Mitteleuropas. Bd. 5 Staphylinidae II (Hypocyphtinae und Aleocharinae) Pselaphidae; Freude, H., Harde, K.W., Lohse, G.A., Eds.; Geocke & Evers: Krefeld, Germany, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Schülke, M.; Smetana, A. Staphylinidae. In Catalogue of Palaearctic Coleoptera. Volume 2. Hydrophiloidea—Staphylinoidea, 1st ed.; Lobl, I., Lobl, D., Eds.; Brill: Boston, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Irmler, U.; Görlich, S. What do rove beetles (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae) indicate for site conditions? Faun. Ökol. Mitt. 2007, 8, 439–455. [Google Scholar]
- Nagy, D.D.; Magura, T.; Debnár, Z.; Horváth, R.; Tóthmérész, B. Shift of rove beetle assemblages in reforestations: Does nativity matter? J. Insect Conserv. 2015, 19, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Topp, W.; Kappes, H.; Kulfan, J.; Zach, P. Litter-dwelling beetles in primeval forests of Central Europe: Does deadwood matter? J. Insect Conserv. 2006, 10, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package; R Package Version 2.5-6; 2019; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 21 November 2020).
- Morris, E.K.; Caruso, T.; Buscot, F.; Fischer, M.; Hancock, C.; Maier, T.S.; Meiners, T.; Müller, C.; Obermaier, E.; Prati, D.; et al. Choosing and using diversity indices: Insights for ecological applications from the German Biodiversity Exploratories. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 3514–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Elphick, C.S. A protocol for data exploration to avoid common statistical problems. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Walker, N.; Saveliev, A.A.; Smith, G.M. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S, 4th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lenth, R. Emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, aka Least-Squares Means; R Package Version 1.4.3.01; 2019; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=emmeans (accessed on 21 November 2020).
- Hartig, F. DHARMa: Residual Diagnostics for Hierarchical (Multi-Level/Mixed) Regression Models; R Package Version 0.2.6; 2019; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=DHARMa (accessed on 21 November 2020).
- Lüdecke, D. sjPlot: Data Visualization for Statistics in Social Science; R Package Version 2.8.4; 2020; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=sjPlot (accessed on 21 November 2020).
- Oksanen, J. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Communities in R: Vegan Tutorial; R Package Version 1.7; 2013; pp. 1–43. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/275524120_Multivariate_analysis_of_ecological_communities_in_R_vegan_tutorial_R_package_version_17 (accessed on 21 November 2020).
- Legendre, P.; Gallagher, E.D. Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia 2001, 129, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER V6: User Manual-Tutorial; Plymouth Marine Laboratory: Plymouth, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kindt, R.; Coe, R. Tree Diversity Analysis: A Manual and Software for Common Statistical Methods for Ecological and Biodiversity Studies; World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF): Nairobi, Kenya, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chisté, M.N.; Mody, K.; Gossner, M.M.; Simons, N.K.; Köhler, G.; Weisser, W.W.; Blüthgen, N. Losers, winners, and opportunists: How grassland land-use intensity affects orthopteran communities. Ecosphere 2016, 7, e01545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibold, S.; Gossner, M.M.; Simons, N.K.; Blüthgen, N.; Müller, J.; Ambarlı, D.; Ammer, C.; Bauhus, J.; Fischer, M.; Habel, J.C.; et al. Arthropod decline in grasslands and forests is associated with landscape-level drivers. Nature 2019, 574, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimaszewski, J.; Langor, D.W.; Work, T.T.; Hammond, J.H.E.; Savard, K. Smaller and more numerous harvesting gaps emulate natural forest disturbances: A biodiversity test case using rove beetles (Coleoptera, Staphylinidae). Divers. Distrib. 2008, 14, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, P.S.; Evans, M.J. Insect biodiversity meets ecosystem function: Differential effects of habitat and insects on carrion decomposition. Ecol. Entomol. 2017, 42, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, G.R.; Langor, D.W.; Spence, J.R. Rove beetles and ground beetles (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae, Carabidae) as indicators of harvest and regeneration practices in western Canadian foothills forests. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 137, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leidinger, J.; Seibold, S.; Weisser, W.W.; Lange, M.; Schall, P.; Türke, M.; Gossner, M.M. Effects of forest management on herbivorous insects in temperate Europe. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2019, 437, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluhm, C.; Scheu, S.; Maraun, M. Oribatid mite communities on the bark of dead wood vary with log type, surrounding forest and regional factors. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 89, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gossner, M.M.; Fonseca, C.R.; Pašalić, E.; Türke, M.; Lange, M.; Weisser, W.W. Limitations to the use of arthropods as temperate forests indicators. Biodivers. Conserv. 2014, 23, 945–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Wende, B.; Strobl, C.; Eugster, M.; Gallenberger, I.; Floren, A.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Linsenmair, K.E.; Weisser, W.W.; Gossner, M.M. Forest management and regional tree composition drive the host preference of saproxylic beetle communities. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 52, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnold, J.M.; Greiser, G.; Kampmann, S.; Martin, I. Status und Entwicklung ausgewählter Wildtierarten in Deutschland: Jahresbericht 2014; Deutscher Jagdverband: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Horion, A. Faunistik der Mitteleuropäischen Käfer. Band X: Staphylinidae. 2. Teil Paederinae—Staphylininae; Verlagsdruckerei PH. C. W. Schmidt: Neustadt a.d. Aisch, Germany, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Horion, A. Faunistik der Mitteleuropäischen Käfer. Band XI: Staphylinidae. 3. Teil Habrocerinae—Aleocharinae (ohne Subtribus Athetae); Verlagsdruckerei PH. C. W. Schmidt: Neustadt a.d. Aisch, Germany, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Horion, A. Faunistik der Mitteleuropäischen Käfer. Band IX: Staphylinidae. 1. Teil Micropeplinae—Euaesthetinae; Kommissionsverlag Buchdruckerei Aug. Feyel: Überlingen, Germany, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- von Hoermann, C.; Ruther, J.; Ayasse, M. The attraction of virgin female hide beetles (Dermestes maculatus) to cadavers by a combination of decomposition odour and male sex pheromones. Front. Zool. 2012, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mądra-Bielewicz, A.; Frątczak-Łagiewska, K.; Matuszewski, S. Sex- and size-related patterns of carrion visitation in Necrodes littoralis (Coleoptera: Silphidae) and Creophilus maxillosus (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae). J. Forensic Sci. 2017, 62, 1229–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Negative Binomial GLM: Response Variable “Abundance” | ||||
| Covariates | Estimate (ED) | Standard Error | F | p |
| SMI index | 0.446 (↑) | 0.128 | 14.85 | <0.001 |
| Mineral soil pH | 0.271 (↑) | 0.135 | 5.20 | 0.026 |
| Understory proportion | −0.449 (↓) | 0.155 | 8.94 | 0.004 |
| Shannon plants | 0.225 | 0.14 | 2.86 | 0.096 |
| Region | 12.92 | <0.001 | ||
| ALB–HAI: 0.0622 ALB–SCH: −1.7871 ↓ HAI–SCH: −1.8493 ↓ | ALB–HAI: 0.241 ALB–SCH: 0.443 HAI–SCH: 0.393 | ALB–HAI: 0.964 ALB–SCH: <0.001 HAI–SCH: <0.001 | ||
| Negative Binomial GLM: Response Variable “Species Richness” | ||||
| Covariates | Estimate (ED) | Standard Error | F | p |
| SMI index | 0.127 | 0.078 | 2.32 | 0.133 |
| Mineral soil pH | 0.33 (↑) | 0.075 | 17.21 | <0.001 |
| Shannon plants | 0.136 | 0.083 | 2.45 | 0.123 |
| Litter cover | 0.257 (↑) | 0.082 | 8.61 | 0.005 |
| Deadwood cover | 0.1 | 0.065 | 2.06 | 0.157 |
| Region | ALB–HAI: 0.478 ↑ ALB–SCH: −0.641 ↓ HAI–SCH: −1.119 ↓ | ALB–HAI: 0.124 ALB–SCH: 0.222 HAI–SCH: 0.224 | 14.98 | <0.001 ALB–HAI: <0.001 ALB–SCH: 0.011 HAI–SCH: <0.001 |
| Gaussian GLM: Response Variable “Shannon Diversity” | ||||
| Covariates | Estimate (ED) | Standard Error | F | p |
| SMI index | 0.092 | 0.049 | 3.43 | 0.069 |
| Mineral soil pH | 0.171 (↑) | 0.052 | 11.55 | 0.001 |
| Shannon plants | 0.089 | 0.053 | 2.86 | 0.097 |
| Litter cover | 0.219 (↑) | 0.057 | 15.7 | <0.001 |
| Silt content | −0.129 | 0.071 | 3.13 | 0.082 |
| Region | ALB–HAI: 0.309 ↑ ALB–SCH: −0.1 HAI–SCH: −0.408 | ALB–HAI: 0.091 ALB–SCH: 0.197 HAI–SCH: 0.208 | 6.71 | 0.002 ALB–HAI: 0.002 ALB–SCH: 0.868 HAI–SCH: 0.121 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weithmann, S.; Kuppler, J.; Degasperi, G.; Steiger, S.; Ayasse, M.; von Hoermann, C. Local and Landscape Effects on Carrion-Associated Rove Beetle (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae) Communities in German Forests. Insects 2020, 11, 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11120828
Weithmann S, Kuppler J, Degasperi G, Steiger S, Ayasse M, von Hoermann C. Local and Landscape Effects on Carrion-Associated Rove Beetle (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae) Communities in German Forests. Insects. 2020; 11(12):828. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11120828
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeithmann, Sandra, Jonas Kuppler, Gregor Degasperi, Sandra Steiger, Manfred Ayasse, and Christian von Hoermann. 2020. "Local and Landscape Effects on Carrion-Associated Rove Beetle (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae) Communities in German Forests" Insects 11, no. 12: 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11120828
APA StyleWeithmann, S., Kuppler, J., Degasperi, G., Steiger, S., Ayasse, M., & von Hoermann, C. (2020). Local and Landscape Effects on Carrion-Associated Rove Beetle (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae) Communities in German Forests. Insects, 11(12), 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11120828