RNA Interference Is Enhanced by Knockdown of Double-Stranded RNases in the Yellow Fever Mosquito Aedes aegypti
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DsRNase Expression Profiling and Phylogenetic Analyses
2.2. Knockdown of DsRNases by Feeding ShRNAs Expressed in Bacteria
2.3. Ex Vivo Degradation Assays
2.4. Co-Feeding of DsRNase and Reporter Gene ShRNA
2.5. Measurement of DsRNA Uptake and Degradation in the Mosquito Hemolymph
3. Results
3.1. Multiple DsRNases Are Found in Mosquitoes
3.2. Two DsRNases Are Expressed in the Gut of Larval Ae. Aegypti
3.3. Knockdown of DsRNases Reduces DsRNA Degradation in the Gut
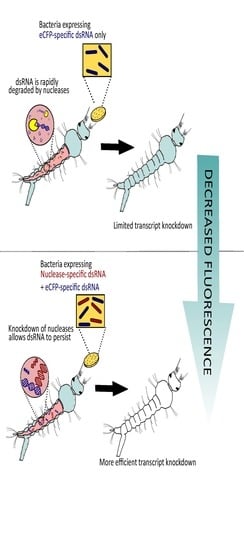
3.4. Co-Delivery of DsRNase ShRNA with a Target ShRNA Enhances RNAi Efficiency
3.5. DsRNA Enters the Hemolymph within Minutes of DsRNA Soaking
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joga, M.R.; Zotti, M.J.; Smagghe, G.; Christiaens, O. RNAi efficiency, systemic properties, and novel delivery methods for pest insect control: What we know so far. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heigwer, F.; Port, F.; Boutros, M. RNA Interference (RNAi) Screening in Drosophila. Genetics 2018, 208, 853–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuster, A.; Erasimus, H.; Fritah, S.; Nazarov, P.V.; van Dyck, E.; Niclou, S.P.; Golebiewska, A. RNAi/CRISPR screens: From a pool to a valid hit. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terenius, O.; Papanicolaou, A.; Garbutt, J.S.; Eleftherianos, I.; Huvenne, H.; Kanginakudru, S.; Albrechtsen, M.; An, C.; Aymeric, J.-L.; Barthel, A.; et al. RNA interference in Lepidoptera: An overview of successful and unsuccessful studies and implications for experimental design. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Khajuria, C.; Rangasamy, M.; Gandra, P.; Fitter, M.; Geng, C.; Woosely, A.; Hasler, J.; Schulenberg, G.; Worden, S.; et al. Long dsRNA but not siRNA initiates RNAi in western corn rootworm larvae and adults. J. Appl. Entomol. 2015, 139, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.G.; Michel, K.; Bartholomay, L.C.; Siegfried, B.D.; Hunter, W.B.; Smagghe, G.; Zhu, K.Y.; Douglas, A.E. Towards the elements of successful insect RNAi. J. Insect Physiol. 2013, 59, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, A.M.; Silver, K.; Zhang, J.; Park, Y.; Zhu, K.Y. Molecular mechanisms influencing efficiency of RNA interference in insects. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunte, N.; McGraw, E.; Bell, S.; Held, D.; Avila, L.-A. Prospects, challenges and current status of RNAi through insect feeding. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spit, J.; Philips, A.; Wynant, N.; Santos, D.; Plaetinck, G.; Vanden Broeck, J. Knockdown of nuclease activity in the gut enhances RNAi efficiency in the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata, but not in the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 81, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaens, O.; Swevers, L.; Smagghe, G. DsRNA degradation in the pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum) associated with lack of response in RNAi feeding and injection assay. Peptides 2014, 53, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.H.; Jing, X.; Luo, Y.; Douglas, A.E. Targeting symbiosis-related insect genes by RNAi in the pea aphid-Buchnera symbiosis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 95, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Swevers, L.; Iatrou, K.; Huvenne, H.; Smagghe, G. Bombyx mori DNA/RNA non-specific nuclease: Expression of isoforms in insect culture cells, subcellular localization and functional assays. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 1166–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, R.-B.; Li, H.-C.; Fan, Y.-J.; Hu, S.-R.; Christiaens, O.; Smagghe, G.; Miao, X.-X. A nuclease specific to lepidopteran insects suppresses RNAi. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 6011–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tayler, A.; Heschuk, D.; Giesbrecht, D.; Park, J.Y.; Whyard, S. Efficiency of RNA interference is improved by knockdown of dsRNA nucleases in tephritid fruit flies. Open Biol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pelletier, J.; Guidolin, A.; Syed, Z.; Cornel, A.J.; Leal, W.S. Knockdown of a mosquito odorant-binding protein involved in the sensitive detection of oviposition attractants. J. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 36, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Gort, T.; Boyle, D.L.; Clem, R.J. Effects of manipulating apoptosis on Sindbis virus infection of aedes aegypti mosquitoes. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 6546–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogel, K.J.; Brown, M.R.; Strand, M.R. Ovary ecdysteroidogenic hormone requires a receptor tyrosine kinase to activate egg formation in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5057–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Regna, K.; Harrison, R.M.; Heyse, S.A.; Chiles, T.C.; Michel, K.; Muskavitch, M.A.T. RNAi trigger delivery into anopheles gambiae pupae. JoVE J. Vis. Exp. 2016, e53738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgerton, E.B.; McCrea, A.R.; Berry, C.T.; Kwok, J.Y.; Thompson, L.K.; Watson, B.; Fuller, E.M.; Nolan, T.J.; Lok, J.B.; Povelones, M. Activation of mosquito immunity blocks the development of transmission-stage filarial nematodes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3711–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mysore, K.; Sun, L.; Tomchaney, M.; Sullivan, G.; Adams, H.; Piscoya, A.S.; Severson, D.W.; Syed, Z.; Duman-Scheel, M. siRNA-Mediated Silencing of doublesex during Female Development of the Dengue Vector Mosquito Aedes aegypti. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durant, A.C.; Donini, A. Evidence that Rh proteins in the anal papillae of the freshwater mosquito Aedes aegypti are involved in the regulation of acid-base balance in elevated salt and ammonia environments. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopez, S.B.G.; Guimarães-Ribeiro, V.; Rodriguez, J.V.G.; Dorand, F.A.P.S.; Salles, T.S.; Sá-Guimarães, T.E.; Alvarenga, E.S.L.; Melo, A.C.A.; Almeida, R.V.; Moreira, M.F. RNAi-based bioinsecticide for Aedes mosquito control. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, K.Y. Chitosan/double-stranded RNA nanoparticle-mediated RNA interference to silence chitin synthase genes through larval feeding in the African malaria mosquito (Anopheles gambiae). Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 19, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Debnath, N.; Cui, Y.; Unrine, J.; Palli, S.R. Chitosan, carbon quantum dot, and silica nanoparticle mediated dsRNA delivery for gene silencing in Aedes aegypti: A comparative analysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 19530–19535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyard, S.; Erdelyan, C.N.; Partridge, A.L.; Singh, A.D.; Beebe, N.W.; Capina, R. Silencing the buzz: A new approach to population suppression of mosquitoes by feeding larvae double-stranded RNAs. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hapairai, L.K.; Mysore, K.; Chen, Y.; Harper, E.I.; Scheel, M.P.; Lesnik, A.M.; Sun, L.; Severson, D.W.; Wei, N.; Duman-Scheel, M. Lure-and-Kill yeast interfering RNA larvicides targeting neural genes in the human disease vector mosquito Aedes aegypti. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taracena, M.L.; Hunt, C.M.; Benedict, M.Q.; Pennington, P.M.; Dotson, E.M. Downregulation of female doublesex expression by oral-mediated RNA interference reduces number and fitness of Anopheles gambiae adult females. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocco, D.A.; Garcia, A.S.G.; Scudeler, E.L.; dos Santos, D.C.; Nóbrega, R.H.; Paluzzi, J.-P.V. Glycoprotein hormone receptor knockdown leads to reduced reproductive success in male Aedes aegypti. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMeniman, C.J.; Corfas, R.A.; Matthews, B.J.; Ritchie, S.A.; Vosshall, L.B. Multimodal integration of carbon dioxide and other sensory cues drives mosquito attraction to humans. Cell 2014, 156, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Timmons, L.; Tabara, H.; Mello, C.C.; Fire, A.Z. Inducible systemic RNA silencing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 2972–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedhoff, P.; Gimadutdinow, O.; Pingoud, A. Identification of catalytically relevant amino acids of the extracellular Serratia marcescens endonuclease by alignment-guided mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 3280–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lutrat, C.; Giesbrecht, D.; Marois, E.; Whyard, S.; Baldet, T.; Bouyer, J. Sex sorting for pest control: It’s raining men! Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christophers, S.R. Aëdes Aegypti (L.) The Yellow Fever Mosquito: Its Life History, Bionomics and Structure; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1960; ISBN 978-0-521-04638-1. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, I.K.; Singh, S.; Mogilicherla, K.; Shukla, J.N.; Palli, S.R. Comparative analysis of double-stranded RNA degradation and processing in insects. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juliano, S.A.; Lounibos, L.P. Ecology of invasive mosquitoes: Effects on resident species and on human health. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 558–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asgari, S. Chapter Two - microRNAs as regulators of insect host–pathogen interactions and immunity. In Advances in Insect Physiology; Crop Protection; Smagghe, G., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; Volume 55, pp. 19–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bayer-Santos, E.; Marini, M.M.; da Silveira, J.F. Non-coding RNAs in host–pathogen interactions: Subversion of mammalian cell functions by protozoan parasites. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.S.; Koshio, S.; Kestemont, P. Recent advances of nucleotide nutrition research in aquaculture: A review. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 12, 1028–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysore, K.; Hapairai, L.K.; Wei, N.; Realey, J.S.; Scheel, N.D.; Severson, D.W.; Duman-Scheel, M. Preparation and use of a yeast shRNA delivery system for gene silencing in mosquito larvae. In Insect Genomics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 213–231. [Google Scholar]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giesbrecht, D.; Heschuk, D.; Wiens, I.; Boguski, D.; LaChance, P.; Whyard, S. RNA Interference Is Enhanced by Knockdown of Double-Stranded RNases in the Yellow Fever Mosquito Aedes aegypti. Insects 2020, 11, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11060327
Giesbrecht D, Heschuk D, Wiens I, Boguski D, LaChance P, Whyard S. RNA Interference Is Enhanced by Knockdown of Double-Stranded RNases in the Yellow Fever Mosquito Aedes aegypti. Insects. 2020; 11(6):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11060327
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiesbrecht, David, Daniel Heschuk, Ian Wiens, David Boguski, Parker LaChance, and Steve Whyard. 2020. "RNA Interference Is Enhanced by Knockdown of Double-Stranded RNases in the Yellow Fever Mosquito Aedes aegypti" Insects 11, no. 6: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11060327
APA StyleGiesbrecht, D., Heschuk, D., Wiens, I., Boguski, D., LaChance, P., & Whyard, S. (2020). RNA Interference Is Enhanced by Knockdown of Double-Stranded RNases in the Yellow Fever Mosquito Aedes aegypti. Insects, 11(6), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11060327