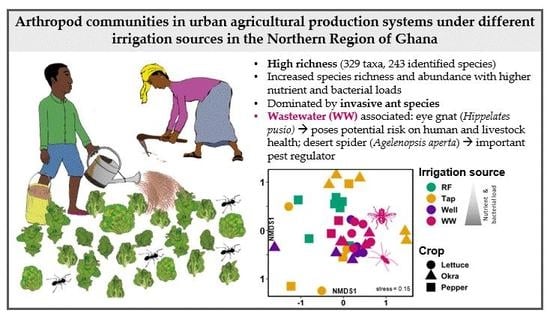
Arthropod Communities in Urban Agricultural Production Systems under Different Irrigation Sources in the Northern Region of Ghana
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Site Description
2.3. Arthropod Collection and Species Functions
2.4. Species Indices and Multivariate Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Arthropod Communities’ Structure
3.2. Effect of Farmers’ Management on Arthropod Species
4. Discussions
4.1. Richness and Function of Arthropod Species in the Context of UPA-Systems
4.2. Effects of Irrigation Sources on Arthropod Community Structure
4.3. Ecology of the Dominant Arthropod Species
4.4. Evaluation and Reliability of the Data
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watts, T.E. Beyond the Pleasure Garden: Urban Agriculture in Ancient Rome. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2018: Building Climate Resilience for Food Security and Nutrition; Food & Agriculture Organisation (FAO): Rome, Italy, 2018; ISBN 9251305714.
- World Bank. Poverty and Shared Prosperity 2018: Piecing Together the Poverty Puzzle; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/i9553en/i9553en.pdf (accessed on 16 August 2019).
- Bellwood-Howard, I.; Shakya, M.; Korbeogo, G.; Schlesinger, J. The role of backyard farms in two West African urban landscapes. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2018, 170, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.B.; Philpott, S.M.; Jha, S. The future of urban agriculture and biodiversity-ecosystem services: Challenges and next steps. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2015, 16, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, E.C.; Latty, T.; Webb, C.E.; Whitehouse, M.E.A.; Saunders, M.E. Engaging urban stakeholders in the sustainable management of arthropod pests. J. Pest. Sci. 2019, 92, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmerson, M.; Morales, M.B.; Oñate, J.J.; Batary, P.; Berendse, F.; Liira, J.; Aavik, T.; Guerrero, I.; Bommarco, R.; Eggers, S. How agricultural intensification affects biodiversity and ecosystem services. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2016, 55, 43–97. [Google Scholar]
- Lompo, D.J.-P.; Sangaré, S.A.K.; Compaoré, E.; Papoada Sedogo, M.; Predotova, M.; Schlecht, E.; Buerkert, A. Gaseous emissions of nitrogen and carbon from urban vegetable gardens in Bobo-Dioulasso, Burkina Faso. J. Plant. Nutr. Soil Sci. 2012, 175, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chambi, C.; Du, T.; Huang, C.; Wang, F.; Zhang, G.; Li, C.; Juma Kayeke, M. Effects of water immersion and soil moisture content on larval and pupal survival of Bactrocera minax (Diptera: Tephritidae). Insects 2019, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akpodiete, N.O.; Diabate, A.; Tripet, F. Effect of water source and feed regime on development and phenotypic quality in Anopheles gambiae (sl): Prospects for improved mass-rearing techniques towards release programmes. Parasit. Vectors 2019, 12, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okorogbona, A.O.M.; Denner, F.D.N.; Managa, L.R.; Khosa, T.B.; Maduwa, K.; Adebola, P.O.; Amoo, S.O.; Ngobeni, H.M.; Macevele, S. Water quality impacts on agricultural productivity and environment. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 27; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Githongo, M. Effect of sewage wastewater irrigation on soil biodiversity and heavy metals accumulation in soils and selected crops. J. Trop. Subtrop. Agro. 2010, 12, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenchly, K.; Dao, J.; Lompo, D.J.-P.; Buerkert, A. Effects of waste water irrigation on soil properties and soil fauna of spinach fields in a West African urban vegetable production system. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Clark, M.; Williams, D.R.; Kimmel, K.; Polasky, S.; Packer, C. Future threats to biodiversity and pathways to their prevention. Nature 2017, 546, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaertner, M.; Wilson, J.R.U.; Cadotte, M.W.; MacIvor, J.S.; Zenni, R.D.; Richardson, D.M. Non-native species in urban environments: Patterns, processes, impacts and challenges. Biol. Invasions 2017, 19, 3461–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabitsch, W.; Essl, F.; Schindler, S. The Rise of Non-native Vectors and Reservoirs of Human Diseases. In Impact of Biological Invasions on Ecosystem Services; Vilà, M., Hulme, P.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 263–275. ISBN 978-3-319-45119-0. [Google Scholar]
- McKinney, M.L. Urbanization as a major cause of biotic homogenization. Biol. Conserv. 2006, 127, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Bayo, F.; Wyckhuys, K.A.G. Worldwide decline of the entomofauna: A review of its drivers. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 232, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayerakwa, H.M. Urban households’ engagement in agriculture: Implications for household food security in Ghana’s medium sized cities. Geograph. Res. 2017, 55, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrier, M.-A.; Boyaud, C.; Lefebvre, R.; Asare, E. Final Technical Report: Hydrogeological Assessment Project of the Northern Regions of Ghana (HAP); INRS (Centre Eau, Terre et Environnement): Quebec City, QC, Canada, 2011; Available online: http://espace.inrs.ca/id/eprint/1646/1/R001325.pdf (accessed on 27 July 2020).
- Abdulai, A.-G.; Bawole, J.N.; Kojo Sakyi, E. Rethinking persistent poverty in Northern Ghana: The primacy of policy and politics over geography. Politics Policy 2018, 46, 233–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boateng, D.; Tia-Adjei, M.; Adams, E.A. Determinants of household water quality in the Tamale Metropolis, Ghana. JEES 2013, 3, 70–77. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, A.; Chiu, C.-H.; Jost, L. Unifying species diversity, phylogenetic diversity, functional diversity, and related similarity and differentiation measures through Hill numbers. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2014, 45, 297–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guevara, M.R.; Hartmann, D.; Mendoza, M. Diversity Measures for Complex Systems ‘Diverse’; R Package Version 0.1.5. 2017. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/diverse/diverse.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2020).
- Li, D. Diversity Through Hill Numbers ‘hillR’; R Package Version 0.5.0. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/hillR/hillR.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2020).
- Global Biodiversity Information Facility. Available online: www.gbif.org/what-is-gbif (accessed on 14 January 2020).
- Chao, A.; Wang, Y.T.; Jost, L. Entropy and the species accumulation curve: A novel entropy estimator via discovery rates of new species. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013, 4, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colwell, R.K. EstimateS, Version 9.1: Statistical Estimation of Species Richness and Shared Species from Samples: Software and User’s Guide. 2006. Available online: http://viceroy.eeb.uconn.edu/estimates (accessed on 1 February 2020).
- Tennekes, M.; Ellis, P. Package ‘Treemap’; R Package Version 2.4-2; R Development Core Team: Vienna, Austria. 2017. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/treemap/treemap.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2020).
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. Community Ecology Package; R Package Version 2.0-2. 2013. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/vegan.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2020).
- Laliberté, E.; Legendre, P.; Shipley, B.; Laliberté, M.E. Package ‘FD’—Measuring Functional Diversity (FD) from Multiple Traits, and other Tools for Functional Ecology; R Package Version 1.0-12. 2014. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/FD/FD.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2020).
- Lavorel, S.; Grigulis, K.; McIntyre, S.; Williams, N.S.G.; Garden, D.; Dorrough, J.; Berman, S.; Quétier, F.; Thébault, A.; Bonis, A. Assessing functional diversity in the field–methodology matters! Funct. Ecol. 2008, 22, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamito, S.; Furtado, R. Feeding diversity in macroinvertebrate communities: A contribution to estimate the ecological status in shallow waters. Ecol. Indic. 2009, 9, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeckel, B.; Baumann, K.-H. Vertical and lateral variations in coccolithophore community structure across the subtropical frontal zone in the South Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Micropaleontol. 2008, 67, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, C.L.; Aizen, M.A. Invasive mutualisms and the structure of plant–pollinator interactions in the temperate forests of north-west Patagonia, Argentina. J. Ecol. 2006, 94, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamito, S. Benthic ecology of semi-natural coastal lagoons, in the Ria Formosa (Southern Portugal), exposed to different water renewal regimes. In Marine Biodiversity; Martens, K., Queiroga, H., Cunha, M.R., Cunha, A., Moreira, M.H., Quintino, V., Rodrigues, A.M., Seroôdio, J., Warwick, R.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Dube, T.; DeNecker, L.; van Vuren, J.H.J.; Wepener, V.; Smit, N.J.; Brendonck, L. Spatial and temporal variation of invertebrate community structure in flood-controlled tropical floodplain wetlands. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2017, 32, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, S.A.; Karp, D.S.; DeClerck, F.; Kremen, C.; Naeem, S.; Palm, C.A. Functional traits in agriculture: Agrobiodiversity and ecosystem services. Trends Ecol. Evol. (Amst.) 2015, 30, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hallett, S.; Hoagland, L.; Toner, E.; Gradziel, T.M.; Mitchell, C.A.; Whipkey, A.L. Urban agriculture: Environmental, economic, and social perspectives. Hortic. Rev. 2016, 44, 65–120. [Google Scholar]
- Stenchly, K.; Hansen, M.V.; Stein, K.; Buerkert, A.; Loewenstein, W. Income Vulnerability of West African Farming Households to Losses in Pollination Services: A Case Study from Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rader, R.; Bartomeus, I.; Garibaldi, L.A.; Garratt, M.P.D.; Howlett, B.G.; Winfree, R.; Cunningham, S.A.; Mayfield, M.M.; Arthur, A.D.; Andersson, G.K.S. Non-bee insects are important contributors to global crop pollination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agyen-Sampong, M. Insect pests of sorghum heads and assessment of crop loss by the major pests. Ghana J. Agric. Sci. 1978, 11, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- N’Djolossè, K.; Atachi, P.; Gnanglè, C.P. Inventory of insects associated with shea trees (Vitellaria paradoxa) (Sapotaceae) in central and northern Benin. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2012, 32, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyerematen, R.; Owusu, E.H.; Acquah-Lamptey, D.; Anderson, R.S.; Ntiamoa-Baidu, Y. Species composition and diversity of insects of the Kogyae Strict Nature Reserve in Ghana. OJE 2014, 4, 1061–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergine, P.; Salerno, C.; Libutti, A.; Beneduce, L.; Gatta, G.; Berardi, G.; Pollice, A. Closing the water cycle in the agro-industrial sector by reusing treated wastewater for irrigation. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, M.J.; Rothman, J.A.; Jones, M.B.; McFrederick, Q.S.; Gan, J.; Trumble, J.T. Effects of contaminants of emerging concern on Myzus persicae (Sulzer, Hemiptera: Aphididae) biology and on their host plant. Capsicum Annuum. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd-Elwahed, M.S. Influence of long-term wastewater irrigation on soil quality and its spatial distribution. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2018, 63, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, J.; Lompo, D.J.-P.; Stenchly, K.; Haering, V.; Marschner, B.; Buerkert, A. Gypsum amendment to soil and plants affected by sodic alkaline industrial wastewater irrigation in urban agriculture of Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, E.R.; Carter, L.J.; McLaughlin, M.J. Bioaccumulation, uptake, and toxicity of carbamazepine in soil–plant systems. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evershed, R.P. Insect olfaction and molecular structure. In Handbook of Natural Pesticides; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Body, M.J.A.; Casas, J.; Christidès, J.-P.; Giron, D. Underestimation of carbohydrates by sugar alcohols in classical anthrone-based colorimetric techniques compromises insect metabolic and energetic studies. bioRxiv 2018, 322123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blaum, N.; Seymour, C.; Rossmanith, E.; Schwager, M.; Jeltsch, F. Changes in arthropod diversity along a land use driven gradient of shrub cover in savanna rangelands: Identification of suitable indicators. Biodivers. Conserv. 2009, 18, 1187–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.L.; Demolin Leite, G.L.; de Souza Tavares, W.; Souza Silva, F.W.; Sampaio, R.A.; Azevedo, A.M.; Serrão, J.E.; Zanuncio, J.C. Diversity of arthropods on Acacia mangium (Fabaceae) and production of this plant with dehydrated sewage sludge in degraded area. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 191196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menta, C.; Remelli, S. Soil health and arthropods: From complex system to worthwhile investigation. Insects 2020, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bundschuh, M.; Hahn, T.; Gessner, M.O.; Schulz, R. Antibiotics as a chemical stressor affecting an aquatic decomposer–detritivore system. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardt, R.R.; Axtell, R.C. Flight of the Eye Gnat, Hippelates pallipes (Diptera: Chloropidae): Correlation with temperature, light, moisture and wind velocity. J. Med. Entomol. 1973, 10, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Otranto, D. Anaplasmosis. In Arthropod Borne Diseases; Marcondes, C.B., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 215–222. ISBN 978-3-319-13883-1. [Google Scholar]
- Machtinger, E.; Kaufman, P.E. Eye gnats, grass flies, eye flies, fruit flies Liohippelates spp. (Insecta: Diptera: Chloropidae). EDIS 2011, 2011, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Mitjà, O.; Asiedu, K.; Mabey, D. Yaws. Lancet 2013, 381, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agadzi, V.K.; Aboagye-Atta, Y.; Nelson, J.W.; Perine, P.L.; Hopkins, D.R. Resurgence of yaws in Ghana. Lancet 1983, 322, 389–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghinai, R.; El-Duah, P.; Chi, K.-H.; Pillay, A.; Solomon, A.W.; Bailey, R.L.; Agana, N.; Mabey, D.C.W.; Chen, C.-Y.; Adu-Sarkodie, Y. A cross-sectional study of ‘yaws’ in districts of Ghana which have previously undertaken azithromycin mass drug administration for trachoma control. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell-Sakyi, L.; Koney, E.B.M.; Dogbey, O.; Walker, A.R. Incidence and prevalence of tick-borne haemoparasites in domestic ruminants in Ghana. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 124, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghana Statistical Service. Types of Agricultural Activities by Region: 2010 by Indicators, Region. Available online: http://countrystat.org/home.aspx?c=GHA&ta=081POP010&tr=365 (accessed on 21 April 2020).
- Trager, J.C. A revision of the fire ants, Solenopsis geminata group (Hymenoptera: Formicidae: Myrmicinae). J. N. Y. Entomol. Soci. 1991, 99, 141–198. [Google Scholar]
- Wetterer, J.K. Worldwide spread of the pharaoh ant, Monomorium pharaonis (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecol. News 2010, 13, 115–129. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, W.M. The Ants of the Baltic Amber; BG Teubner: Leipzig, Germany, 1914. [Google Scholar]
- MacKay, W.P.; Mackay, E. The ants of New Mexico (Hymenoptera: Formicidae); Edwin Mellen Press: Lewiston, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 0773468846. [Google Scholar]
- Leong, C.-M.; Shiao, S.-F.; Guenard, B.S. Ants in the city, a preliminary checklist of Formicidae (Hymenoptera) in Macau, one of the most heavily urbanized regions of the world. Asian Myrmecol. 2017, 9, e009014. [Google Scholar]
- van den Noortgate, H.; Lagrain, B.; Wenseleers, T.; Martens, J.A. Analysis of cuticular lipids of the pharaoh ant (Monomorium pharaonis) and their selective adsorption on insecticidal zeolite powders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, H.C.; Arthofer, W.; Seifert, B.; Muster, C.; Steiner, F.M.; Schlick-Steiner, B.C. Light at the end of the tunnel: Integrative taxonomy delimits cryptic species in the Tetramorium caespitum complex (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Myrmecol. News 2017, 25, 95–129. [Google Scholar]
- Cordonnier, M.; Gibert, C.; Bellec, A.; Kaufmann, B.; Escarguel, G. Multi-scale impacts of urbanization on species distribution within the genus Tetramorium. Landsc. Ecol. 2019, 34, 1937–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katayama, N.; Suzuki, N. Bodyguard effects for aphids of Aphis craccivora Koch (Homoptera: Aphididae) as related to the activity of two ant species, Tetramorium caespitum Linnaeus (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) and Lasius niger L. (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2003, 38, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pommeresche, R.; Løes, A.-K.; Torp, T. Effects of animal manure application on springtails (Collembola) in perennial ley. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 110, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utami, A.I.; Utami, S.N.H.; Indarti, S. Influence of Cow and Chicken Manure on Soil Fauna Abundance and N Uptake by Rice in Conversion from Conventional to Organic Farming System. In Proceeding of the 1st International Conference on Tropical Agriculture; Isnansetyo, A., Nuringtyas, T.R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 23–39. ISBN 978-3-319-60362-9. [Google Scholar]
- Akamatsu, F.; Hideshige, T.; Okino, T. Food source of riparian spiders analyzed by using stable isotope ratios. Ecol. Res. 2004, 19, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Ramos, P.A.; Mezquida, E.T.; Acebes, P. Ants indirectly reduce the reproductive performance of a leafless shrub by benefiting aphids through predator deterrence. Plant Ecol. 2020, 221, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, E.A.; de Fellowes, M. Urbanisation alters ecological interactions: Ant mutualists increase and specialist insect predators decrease on an urban gradient. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borcard, D.; Gillet, F.; Legendre, P. Canonical ordination. In Numerical Ecology with R; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 203–297. [Google Scholar]
- Fok, E.J.; Petersen, J.D.; Nault, B.A. Relationships between insect predator populations and their prey, Thrips tabaci, in onion fields grown in large-scale and small-scale cropping systems. Biocontrol. Sci. 2014, 59, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koricheva, J.; Hayes, D. The relative importance of plant intraspecific diversity in structuring arthropod communities: A meta-analysis. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 1704–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, J.-K.; Jeong, J.-C.; Lee, J.-H. Effects of pitfall trap size and sampling duration on collection of ground beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) in temperate forests. Entomol. Res. 2019, 49, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.F.; Phillips, B.B.; Doyle, T.; Pell, J.K.; Redhead, J.W.; Savage, J.; Woodcock, B.A.; Bullock, J.M.; Osborne, J.L. Mass-flowering crops have a greater impact than semi-natural habitat on crop pollinators and pollen deposition. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 35, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Irrigation | EC (µS cm−1) | C/N | P (g kg−1) | pH | E. coli (MPN 100 mL−1) | Enterococcus spp. (MPN 100 mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfed | 68.84 ± 33.75 a | 10.14 ± 1.50 a | 75.38 ± 77.98 a | 6.37 ± 0.70 ab | - | - |
| Tap | 129.01 ± 135.69 ab | 11.94 ± 2.80 ab | 73.25 ± 43.69 a | 5.92 ± 0.81 a | 4.23 | 3.71 |
| Well | 225.95 ± 98.52 ab | 12.73 ± 2.97 ab | 210.82 ± 101.90 ab | 6.67 ± 0.13 ab | 3.63 | 3.04 |
| WW | 280.83 ± 187.20 b | 13.71 ± 2.75 b | 94.64 ± 36.90 b | 6.70 ± 0.99 b | 6.57 | 5.83 |
| Location | Abundance | Species Richness | Exponential Shannon Index | Inverse Simpson’s Index | Berger–Parker Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfed | 101 | 15 | 5.6 | 3.3 | 1.9 |
| Tap | 125 | 11 | 5.2 | 4.1 | 2.7 |
| Well | 78 | 13 | 6.9 | 5.7 | 3.3 |
| WW | 73 | 9 | 5.8 | 5.2 | 3.2 |
| Location | Total Abundance | Species Richness | Exponential Shannon Index | Inverse Simpson’s Index | Inverse Berger–Parker Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfed | 2105 | 90 | 19 | 9.36 | 3.89 |
| Tap | 3888 | 113 | 12 | 5.65 | 2.16 |
| Well | 2131 | 85 | 18 | 6.11 | 2.38 |
| WW | 6102 | 136 | 11 | 4.11 | 2.00 |
| Functional Richness | Functional Evenness | Functional Dispersion | CWM Carnivore | CWM Decomposers | CWM Herbivore | CWM Omnivore | CWM Pollinators | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locations | ||||||||
| Rainfed | 4.71 ± 0.50 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.27 ± 0.09 | 0.04 ± 0.03 | 0.11 ± 0.14 | 0.25 ± 0.18 | 0.58 ± 0.21 | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| Tap | 3.90 ± 1.04 | 0.13± 0.06 | 0.23 ± 0.08 | 0.14 ± 0.21 | 0.24 ± 0.36 | 0.19 ± 0.24 | 0.41 ± 0.31 | 0.01 ± 0.02 |
| Well | 4.43 ± 0.53 | 0.14 ± 0.06 | 0.34 ± 0.05 | 0.13 ± 0.12 | 0.42 ± 0.20 | 0.26 ± 0.12 | 0.17 ± 0.17 | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| WW | 4.55 ± 0.69 | 0.14 ± 0.06 | 0.31 ± 0.05 | 0.20 ± 0.22 | 0.40 ± 0.21 | 0.23 ± 0.19 | 0.16 ± 0.19 | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| Order | Family | Genus | Species | Distribution/Origin | Relevance | Rainfed | Tap | Well | WW | Total Abundance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Araneae | Agelenidae | Agelenopsis | aperta | Dry regions | Carnivore/Pest regulator | 12 | 24 | 29 | 442 | 507 |
| Coleoptera | Chrysomelidae | Ootheca | mutabilis | Afrotropic | Herbivore | 10 | 17 | 4 | 66 | 97 |
| Podagrica | sjostedti | n.a. | Herbivore | 15 | 8 | 90 | 50 | 163 | ||
| Scarabaeidae | Sarcophaga | carnaria | Worldwide | Decomposer | 0 | 32 | 1 | 7 | 40 | |
| Diptera | Calliphoridae | Calliphora | sp. | n.a. | Decomposer | 1 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 7 |
| Chironomidae | Chironomus | plumosus | Northern hemisphere | Decomposer | 0 | 5 | 56 | 33 | 94 | |
| Chloropidae | Hippelates | pusio | Nearctic, Neotropic | Decomposer/Vector | 191 | 1120 | 817 | 2883 | 5011 | |
| Muscidae | Musca | domestica | Worldwide | Decomposer | 11 | 15 | 0 | 22 | 48 | |
| Stratiomyidae | Hermetia | illucens | Worldwide | Decomposer | 1 | 50 | 0 | 1 | 52 | |
| Hemiptera | Cicadellidae | Empoasca | facialis | Neotropic | Herbivore | 36 | 41 | 60 | 105 | 242 |
| Delphacidae | Javesella | pellucida | Worldwide | Herbivore/Vector | 29 | 0 | 10 | 14 | 53 | |
| Miridae | Lygus | sp. | n.a. | Herbivore | 0 | 6 | 9 | 3 | 18 | |
| Pentatomidae | Aspavia | armigera | Neotropic | Herbivore | 0 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 8 | |
| Hymenoptera | Apidae | Apis | mellifera | Worldwide | Herbivore | 10 | 6 | 9 | 6 | 31 |
| Formicidae | Camponotus | sp. | n.a. | Omnivore | 22 | 237 | 0 | 60 | 319 | |
| Monomorium | pharaonis | Neotropic, Palaearctic | Omnivore | 320 | 72 | 0 | 205 | 597 | ||
| Solenopsis | xyloni | USA | Omnivore | 501 | 256 | 60 | 146 | 963 | ||
| Tetramorium | caespitum | Europe | Omnivore | 169 | 0 | 121 | 392 | 682 | ||
| Megachilidae | Megachile | latimanus | Worldwide | Pollinator | 0 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 8 | |
| Scelionidae | Eumicrosoma | beneficum | Worldwide | Carnivore/Pest regulator | 2 | 4 | 0 | 5 | 11 | |
| Lepidoptera | Crambidae | Hellula | undalis | Worldwide | Herbivore | 15 | 17 | 16 | 8 | 56 |
| Hesperiidae | Zophopetes | dysmephila | Afrotropic | Herbivore | 8 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 13 | |
| Orthoptera | Gryllidae | Gryllus | sp. | n.a. | Herbivore | 5 | 4 | 27 | 44 | 80 |
| Tetrigidae | Tetrix | subulata | Worldwide | Herbivore | 0 | 4 | 3 | 13 | 20 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amprako, L.; Stenchly, K.; Wiehle, M.; Nyarko, G.; Buerkert, A. Arthropod Communities in Urban Agricultural Production Systems under Different Irrigation Sources in the Northern Region of Ghana. Insects 2020, 11, 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11080488
Amprako L, Stenchly K, Wiehle M, Nyarko G, Buerkert A. Arthropod Communities in Urban Agricultural Production Systems under Different Irrigation Sources in the Northern Region of Ghana. Insects. 2020; 11(8):488. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11080488
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmprako, Louis, Kathrin Stenchly, Martin Wiehle, George Nyarko, and Andreas Buerkert. 2020. "Arthropod Communities in Urban Agricultural Production Systems under Different Irrigation Sources in the Northern Region of Ghana" Insects 11, no. 8: 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11080488
APA StyleAmprako, L., Stenchly, K., Wiehle, M., Nyarko, G., & Buerkert, A. (2020). Arthropod Communities in Urban Agricultural Production Systems under Different Irrigation Sources in the Northern Region of Ghana. Insects, 11(8), 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11080488