Efficacy of Two Neonicotinoid Insecticides against Invasive Wood Borer Aromia bungii Larvae in Dietary Toxicity Test
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects and Insecticides
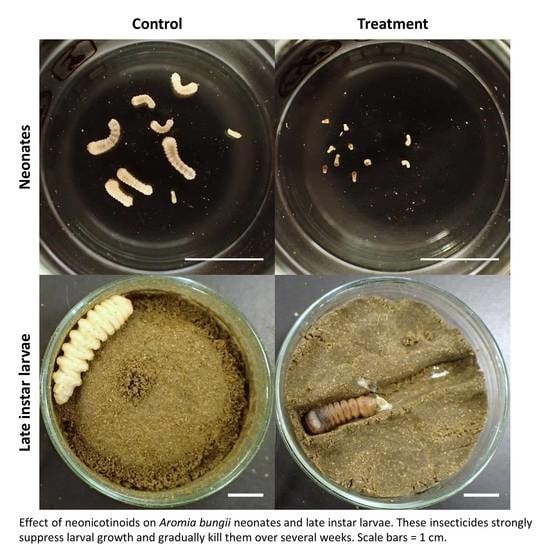
2.2. Dietary Toxicity Test against Neonates
2.3. Dietary Toxicity Test against Late Instar Larvae
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dietary Toxicity Test against Neonates
3.2. Dietary Toxicity Test against Late Instar Larvae
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Insecticide | Effect | Estimate | SE | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thiamethoxam | 0.01 ppm | −8.97 | 5.91 | −1.52 | 0.13 |
| 0.1 ppm | −6.04 | 5.91 | −1.02 | 0.31 | |
| 1 ppm | −22.2 | 5.91 | −3.76 | <0.001 | |
| 10 ppm | −50.6 | 5.91 | −8.56 | <0.001 | |
| Day 1 | 0.23 | 0.20 | 1.16 | 0.25 | |
| 0.01 ppm:day 2 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 0.88 | 0.38 | |
| 0.1 ppm:day | −0.66 | 0.28 | −2.35 | <0.05 | |
| 1 ppm:day | −1.74 | 0.28 | −6.18 | <0.001 | |
| 10 ppm:day | −0.82 | 0.28 | −2.92 | <0.005 | |
| Dinotefuran | 0.01 ppm | −12.3 | 5.60 | −2.20 | <0.05 |
| 0.1 ppm | 0.52 | 5.60 | 0.093 | 0.93 | |
| 1 ppm | −7.08 | 5.60 | −1.27 | 0.21 | |
| 10 ppm | −40.1 | 5.60 | −7.17 | <0.001 | |
| Day | 0.23 | 0.17 | 1.36 | 0.18 | |
| 0.01 ppm:day | 0.31 | 0.24 | 1.29 | 0.20 | |
| 0.1 ppm:day | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.85 | 0.39 | |
| 1 ppm:day | −1.93 | 0.24 | −8.00 | <0.001 | |
| 10 ppm:day | −0.84 | 0.24 | −3.48 | <0.001 |
Appendix B
| Insecticide | Effect | Estimate | SE | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thiamethoxam | 0.01 ppm | 0.017 | 0.53 | 0.033 | 0.97 |
| 0.1 ppm | 0.0070 | 0.53 | 0.013 | 0.99 | |
| 1 ppm | 0.0040 | 0.53 | 0.007 | 0.99 | |
| 10 ppm | 0.014 | 0.53 | 0.025 | 0.98 | |
| Day 1 | 0.38 | 0.025 | 15 | <0.001 | |
| 0.01 ppm:day 2 | −0.14 | 0.036 | −4.0 | <0.001 | |
| 0.1 ppm:day | −0.20 | 0.036 | −5.6 | <0.001 | |
| 1 ppm:day | −0.39 | 0.036 | −11 | <0.001 | |
| 10 ppm:day | −0.39 | 0.036 | −11 | <0.001 | |
| Dinotefuran | 0.01 ppm | 0.0080 | 0.82 | 0.010 | 0.99 |
| 0.1 ppm | 0.0089 | 0.82 | 0.011 | 0.99 | |
| 1 ppm | 0.0014 | 0.82 | 0.002 | 0.999 | |
| 10 ppm | −0.0020 | 0.82 | −0.002 | 0.998 | |
| Day | 0.38 | 0.039 | 9.9 | <0.001 | |
| 0.01 ppm:day | −0.11 | 0.055 | −1.9 | 0.055 | |
| 0.1 ppm:day | −0.0030 | 0.055 | −0.10 | 0.92 | |
| 1 ppm:day | −0.38 | 0.055 | −7.0 | <0.001 | |
| 10 ppm:day | −0.39 | 0.055 | −7.0 | <0.001 |
Appendix C
| Insecticide | Effect | Estimate | SE | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thiamethoxam | 0.01 ppm | −0.013 | 0.069 | −0.18 | 0.86 |
| 0.1 ppm | 6.1 × 10−16 | 0.069 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| 1 ppm | 4.8 × 10−16 | 0.069 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| 10 ppm | −0.069 | 0.069 | −1.00 | 0.33 | |
| 100 ppm | 0.028 | 0.069 | 0.40 | 0.69 | |
| Week 1 | 7.6 × 10−17 | 0.0081 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| 0.01 ppm:week 2 | −0.0019 | 0.011 | −0.17 | 0.87 | |
| 0.1 ppm:week | −8.5 × 10−17 | 0.011 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| 1 ppm:week | −6.5 × 10−17 | 0.011 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| 10 ppm:week | −0.053 | 0.011 | −4.64 | <0.001 | |
| 100 ppm:week | −0.089 | 0.011 | −7.81 | <0.001 | |
| Dinotefuran | 0.01 ppm | −0.035 | 0.097 | −0.36 | 0.72 |
| 0.1 ppm | 0.021 | 0.097 | 0.22 | 0.83 | |
| 1 ppm | −0.0063 | 0.097 | −0.066 | 0.95 | |
| 10 ppm | 0.13 | 0.097 | 1.35 | 0.19 | |
| 100 ppm | −0.014 | 0.097 | −0.14 | 0.89 | |
| Week | −5.8 × 10−17 | 0.011 | 0.00 | 1.00 | |
| 0.01 ppm:week | 0.0048 | 0.016 | 0.30 | 0.77 | |
| 0.1 ppm:week | −0.011 | 0.016 | −0.70 | 0.49 | |
| 1 ppm:week | −9.5 × 10−4 | 0.016 | −0.060 | 0.95 | |
| 10 ppm:week | −0.069 | 0.016 | −4.33 | <0.001 | |
| 100 ppm:week | −0.059 | 0.016 | −3.73 | <0.005 |
Appendix D
| Insecticide | Effect | Estimate | SE | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thiamethoxam | 0.01 ppm | 0.0093 | 0.029 | 0.33 | 0.75 |
| 0.1 ppm | 0.051 | 0.029 | 1.77 | 0.079 | |
| 1 ppm | −0.067 | 0.029 | −2.32 | 0.021 | |
| 10 ppm | −0.27 | 0.031 | −8.55 | <0.001 | |
| 100 ppm | −0.28 | 0.031 | −9.01 | <0.001 | |
| Week 1 | −0.010 | 0.0031 | −3.36 | <0.001 | |
| 0.01 ppm:week 2 | −0.0033 | 0.0044 | −0.75 | 0.45 | |
| 0.1 ppm:week | −0.0065 | 0.0043 | −1.52 | 0.13 | |
| 1 ppm:week | 0.0084 | 0.0043 | 1.95 | 0.053 | |
| 10 ppm:week | 0.0075 | 0.0069 | 1.09 | 0.28 | |
| 100 ppm:week | 0.023 | 0.0073 | 3.19 | <0.005 | |
| Dinotefuran | 0.01 ppm | −0.035 | 0.030 | −1.18 | 0.24 |
| 0.1 ppm | 0.032 | 0.029 | 1.10 | 0.27 | |
| 1 ppm | −0.054 | 0.029 | −1.85 | 0.065 | |
| 10 ppm | −0.21 | 0.030 | −6.85 | <0.001 | |
| 100 ppm | −0.27 | 0.032 | −8.57 | <0.001 | |
| Week | −0.010 | 0.0030 | −3.43 | <0.001 | |
| 0.01 ppm:week | 0.0088 | 0.0043 | 2.05 | <0.05 | |
| 0.1 ppm:week | −0.0030 | 0.0044 | −0.70 | 0.49 | |
| 1 ppm:week | 0.011 | 0.0043 | 2.52 | <0.05 | |
| 10 ppm:week | 0.0049 | 0.0052 | 0.94 | 0.35 | |
| 100 ppm:week | 0.019 | 0.0062 | 3.03 | <0.005 |
Appendix E
| Insecticide | Effect | Estimate | SE | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thiamethoxam | 0.01 ppm | −0.030 | 0.17 | −0.18 | 0.86 |
| 0.1 ppm | −0.083 | 0.17 | −0.49 | 0.62 | |
| 1 ppm | −0.092 | 0.17 | −0.55 | 0.58 | |
| 10 ppm | −1.08 | 0.17 | −6.22 | <0.001 | |
| 100 ppm | −1.47 | 0.17 | −8.56 | <0.001 | |
| Week 1 | −0.081 | 0.014 | −5.66 | <0.001 | |
| 0.01 ppm:week 2 | −0.0037 | 0.021 | −0.18 | 0.86 | |
| 0.1 ppm:week | 0.034 | 0.020 | 1.70 | 0.091 | |
| 1 ppm:week | 0.043 | 0.020 | 2.12 | <0.05 | |
| 10 ppm:week | −0.082 | 0.029 | −2.89 | <0.005 | |
| 100 ppm:week | 0.0034 | 0.027 | 0.13 | 0.90 | |
| Dinotefuran | 0.01 ppm | −0.084 | 0.18 | −0.46 | 0.65 |
| 0.1 ppm | 0.054 | 0.18 | 0.30 | 0.77 | |
| 1 ppm | −0.21 | 0.18 | −1.18 | 0.24 | |
| 10 ppm | −0.72 | 0.18 | −3.95 | <0.001 | |
| 100 ppm | −1.15 | 0.19 | −6.18 | <0.001 | |
| Week | −0.081 | 0.016 | −5.02 | <0.001 | |
| 0.01 ppm:week | 0.024 | 0.023 | 1.02 | 0.31 | |
| 0.1 ppm:week | 0.0048 | 0.023 | 0.21 | 0.84 | |
| 1 ppm:week | 0.060 | 0.023 | 2.59 | <0.05 | |
| 10 ppm:week | −0.076 | 0.025 | −3.09 | <0.005 | |
| 100 ppm:week | −0.030 | 0.028 | −1.04 | 0.30 |
References
- Holmes, S.B.; MacQuarrie, C.J.K. Chemical control in forest pest management. Can. Entomol. 2016, 148, S270–S295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haack, R.A.; Hérard, F.; Sun, J.; Turgeon, J.J. Managing invasive populations of Asian longhorned beetle and citrus longhorned beetle: A worldwide perspective. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 521–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herms, D.A.; McCullough, D.G. Emerald ash borer invasion of North America: History, biology, ecology, impacts, and management. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q. Chemical control of cerambycid pests. In Cerambycidae of the World: Biology and Pest Management; Wang, Q., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 329–350. [Google Scholar]
- Iwata, R. Aromia bungii (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae): Taxonomy, distribution, biology and eradication. For. Pests 2018, 67, 7–34. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Doccola, J.J.; Wild, P.M. Tree injection as an alternative method of insecticide application. In Insecticides—Basic and Other Applications; Soloneski, S., Larramendy, M., Eds.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 61–78. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, C.; Laurent, F. Trunk injection of plant protection products to protect trees from pests and diseases. Crop Prot. 2019, 124, 104831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferracini, C.; Alma, A. How to preserve horse chestnut trees from Cameraria ohridella in the urban environment. Crop Prot. 2008, 27, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolando, C.A.; Gous, S.F.; Berndt, L.A.; Bulman, L.S.; Carlson, C.A. Stem injection of a systemic insecticide to control Uraba lugens on urban Lophostemon confertus trees. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumaru, S.; Ueyama, H.; Shinya, S. Control effects of trunk injection of thiamethoxam against Corythucha ciliate (Say) (Heteroptera: Tingidae) on Platanus spp. Tree For. Health 2013, 17, 113–117. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Tsuruta, H.; Ino, M. Introduction of new pesticide~Pest control of afforestation trees/trunk injection formulation “Wood–Star”. Ryngyo Yakuzai 2015, 214, 13–18. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Poland, T.M.; Haack, R.A.; Petrice, T.R.; Miller, D.L.; Bauer, L.S.; Gao, R. Field evaluations of systemic insecticides for control of Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in China. J. Econ. Entomol. 2006, 99, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, N.; Helson, B.; Thompson, D.; Otis, G.; McFarlane, J.; Buscarini, T.; Meating, J. Azadirachtin: An effective systemic insecticide for control of Agrilus planipennis. J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, D.G.; Poland, T.M.; Anulewicz, A.C.; Lewis, P.; Cappaert, D. Evaluation of Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) control provided by emamectin benzoate and two neonicotinoid insecticides, one and two seasons after treatment. J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 1599–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sunamura, E.; Tamura, S.; Shoda-Kagaya, E. Efficacy of insecticide trunk injection against larvae of invasive red–necked longhorn beetle Aromia bungii in cherry blossom trees. Jpn. J. Environ. Entomol. Zool. 2020, 31, 13–19. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Sarto i Monteys, V.; Ribes, A.C.; Savin, I. The invasive longhorn beetle Xylotrechus chinensis, pest of mulberries, in Europe: Study on its local spread and efficacy of abamectin control. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, T.M.; Haack, R.A.; Petrice, T.R.; Miller, D.L.; Bauer, L.S. Laboratory evaluation of the toxicity of systemic insecticides for control of Anoplophora glabripennis and Plectrodera scalator (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2006, 99, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, T.M.; Ciaramitaro, T.M.; McCullough, D.G. Laboratory evaluation of the toxicity of systemic insecticides to emerald ash borer larvae. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EPPO. Data sheets on quarantine pests: Aromia bungii. EPPO Bull. 2015, 45, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoda-Kagaya, E. What happened after Aromia bungii’s invasion into Japan: Seven years trajectory from 2011. For. Pests 2018, 67, 4–6. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Funaki, Y. The emergency approach to pesticide registration for the red–necked longhorn beetle, Aromia bungii. Plant Prot. 2019, 73, 7–13. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Urano, T. Improvement of the method for pupation and adult eclosion of Aromia bungii (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) reared with artificial diets. Kanto J. For. Res. 2021, 72, 129–132. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Sunamura, E. Dynamics and distribution of trunk–injected insecticides in cherry trees for controlling Aromia bungii. Unpublished.
- The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: http://www.r-project.org/index.html (accessed on 10 June 2019).
- Chiang, S.-N. Cerambycid Larvae of China; Chongqing Publishing House: Chongqing, China, 1989; pp. 103–104. [Google Scholar]
- Boina, D.R.; Onagbola, E.O.; Salyani, M.; Stelinski, L.L. Antifeedant and sublethal effects of imidacloprid on Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri. Pest Manag. Sci. 2009, 65, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, M.; Bale, J.S.; Newbury, H.J.; Lind, R.J.; Pritchard, J. A sublethal dose of thiamethoxam causes a reduction in xylem feeding by the bird cherry–oat aphid (Rhopalosiphum padi), which is associated with dehydration and reduced performance. J. Insect Physiol. 2009, 55, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, J.; Du, Z.-B.; Wu, Y.-Q.; Gong, Z.-J.; Jiang, Y.-L.; Duan, Y.; Li, T.; Lei, C.-L. Sub-lethal effects of four neonicotinoid seed treatments on the demography and feeding behaviour of the wheat aphid Sitobion avenae. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palumbo, J.C.; Prabhaker, N.; Reed, D.A.; Perring, T.M.; Castle, S.J.; Huang, T.-I. Susceptibility of Bagrada hilaris (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) to insecticides in laboratory and greenhouse bioassays. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, H.M.; Wilkins, S.; Harkin, S.; Milner, S.; Walters, K.F.A. Neonicotinoids and bumblebees (Bombus terrestris): Effects on nectar consumption in individual workers. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinkwater, T.W. Bioassays to compare the systemic activity of three neonicotinoids for control of Heteronychus arator Fabricius (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) in maize. Crop Prot. 2003, 22, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Insecticide | Active Ingredient Concentration | Mean ± SD Weight of Individual Larva (mg) | Growth Rate (21 Days/0 Day) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 Day | 21 Days | |||
| Control (water) | 0 ppm | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 8.36 ± 2.50 | 28 |
| Thiamethoxam | 0.01 ppm | 0.32 ± 0.02 | 5.35 ± 2.04 | 17 |
| 0.1 ppm | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 4.13 ± 1.96 | 14 | |
| 1 ppm | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | 0.87 | |
| 10 ppm | 0.31 ± 0.01 | 0.23 ± 0.04 | 0.74 | |
| Dinotefuran | 0.01 ppm | 0.31 ± 0.01 | 6.12 ± 2.96 | 20 |
| 0.1 ppm | 0.31 ± 0.01 | 8.25 ± 4.28 | 27 | |
| 1 ppm | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 0.34 ± 0.05 | 1.1 | |
| 10 ppm | 0.30 ± 0.02 | 0.23 ± 0.02 | 0.77 | |
| Insecticide | Active Ingredient Concentration | Rate of Individuals Excreted (%) | Biweekly Rate of Individuals Excreted (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥Once | ≥Twice | 2W | 4W | 6W | 8W | 10W | 12W | ||
| Control (water) | 0 ppm | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Thiamethoxam | 0.01 ppm | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.1 ppm | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1 ppm | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | |
| 10 ppm | 93 | 67 | 33 | 29 | 69 | 78 | 75 | 50 | |
| 100 ppm | 87 | 47 | 20 | 29 | 42 | 56 | 60 | 0 | |
| Dinotefuran | 0.01 ppm | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0.1 ppm | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | |
| 1 ppm | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 10 ppm | 87 | 53 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 60 | 82 | 38 | |
| 100 ppm | 80 | 47 | 13 | 43 | 27 | 44 | 63 | 67 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sunamura, E.; Tamura, S.; Taki, H.; Sato, H.; Shoda-Kagaya, E.; Urano, T. Efficacy of Two Neonicotinoid Insecticides against Invasive Wood Borer Aromia bungii Larvae in Dietary Toxicity Test. Insects 2021, 12, 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12070592
Sunamura E, Tamura S, Taki H, Sato H, Shoda-Kagaya E, Urano T. Efficacy of Two Neonicotinoid Insecticides against Invasive Wood Borer Aromia bungii Larvae in Dietary Toxicity Test. Insects. 2021; 12(7):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12070592
Chicago/Turabian StyleSunamura, Eiriki, Shigeaki Tamura, Hisatomo Taki, Hiroki Sato, Etsuko Shoda-Kagaya, and Tadahisa Urano. 2021. "Efficacy of Two Neonicotinoid Insecticides against Invasive Wood Borer Aromia bungii Larvae in Dietary Toxicity Test" Insects 12, no. 7: 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12070592
APA StyleSunamura, E., Tamura, S., Taki, H., Sato, H., Shoda-Kagaya, E., & Urano, T. (2021). Efficacy of Two Neonicotinoid Insecticides against Invasive Wood Borer Aromia bungii Larvae in Dietary Toxicity Test. Insects, 12(7), 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12070592