Effect of Hydrogen Charging on Pop-in Behavior of a Zr-Based Metallic Glass
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
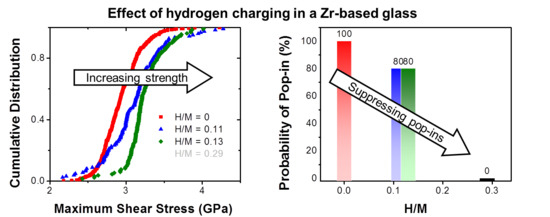
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klement, W.; Willens, R.H.; Duwez, P. Non-crystalline Structure in Solidified Gold-Silicon Alloys. Nature 1960, 187, 869–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Takeuchi, A. Recent Development and Applications of Bulk Glassy Alloys. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2010, 1, 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankmann, J.; Pundt, A.; Kirchheim, R. Hydrogen loading behaviour of multi-component amorphous alloys: Model and experiment. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 356–357, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zander, D.; Tal-Gutelmacher, E.; Jastrow, L.; Köster, U.; Eliezer, D. Hydrogenation of Pd-coated Zr-Cu-Ni-Al metallic glasses and quasicrystals. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 356–357, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.I.; Suh, J.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Shim, J.H.; Fleury, E.; Cho, Y.W.; Koh, S.U. Direct measurement of hydrogen diffusivity through Pd-coated Ni-based amorphous metallic membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 436, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaura, S.; Sakurai, M.; Hasegawa, M.; Wakoh, K.; Shimpo, Y.; Nishida, M.; Kimura, H.; Matsubara, E.; Inoue, A. Hydrogen permeation and structural features of melt-spun Ni-Nb-Zr amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 3703–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paglieri, S.N.; Pal, N.K.; Dolan, M.D.; Kim, S.M.; Chien, W.M.; Lamb, J.; Chandra, D.; Hubbard, K.M.; Moore, D.P. Hydrogen permeability, thermal stability and hydrogen embrittlement of Ni-Nb-Zr and Ni-Nb-Ta-Zr amorphous alloy membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 378, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, M.D.; Dave, N.C.; Ilyushechkin, A.Y.; Morpeth, L.D.; McLennan, K.G. Composition and operation of hydrogen-selective amorphous alloy membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 285, 30–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Su, Y.; Luo, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Guo, J.; Fu, H. Enhanced plasticity in Zr-based bulk metallic glasses by hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 14697–14701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Dong, F.; Luo, L.; Guo, J.; Han, B.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Fu, H. Bulk metallic glass formation: The positive effect of hydrogen. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2012, 358, 2606–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Choi, I.C.; Seok, M.Y.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, D.H.; Ramamurty, U.; Suh, J.Y.; Jang, J.i. Effect of hydrogen on the yielding behavior and shear transformation zone volume in metallic glass ribbons. Acta Mater. 2014, 78, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandana, W.; Yousfi, M.; Hajlaoui, K.; Gamaoun, F.; Yavari, A. Thermal stability and hydrogen-induced softening in Zr57Al10Cu15.4Ni12.6Nb5 metallic glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2017, 456, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, H.W.; Koster, U. Hydrogen embrittlement of metallic glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1983, 56, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Perng, T.P. Embrittlement of amorphous Fe40Ni38Mo4B18 alloy by electrolytic hydrogen. Metall. Mater. Trans. A-Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 1995, 26, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalakshmi, S.; Fleury, E. Hydrogen embrittlement in metallic amorphous alloys: An overview. J. ASTM Int. 2010, 7, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, F.; Lu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, L.; Su, Y.; Wang, B.; Huang, H.; Xiang, Q.; Yuan, X.; Zuo, X. Effect of hydrogen addition on the mechanical properties of a bulk metallic glass. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 3183–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, D.; Fischer, E.; Löffler, J.F. Hydrogen microalloying as a viable strategy for enhancing the glass-forming ability of Zr-based bulk metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 2015, 103, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, D.; Fischer, E.; Löffler, J.F. Effectiveness of hydrogen microalloying in bulk metallic glass design. Acta Mater. 2015, 99, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, S.; Tanaka, T.; Miyake, M. Effect of oxygen on hydrogen solubility in zirconium. J. Nucl. Mater. 1989, 167, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Choi, I.C.; Seok, M.Y.; Ramamurty, U.; Suh, J.Y.; Jang, J.i. Hydrogen-induced hardening and softening of Ni-Nb-Zr amorphous alloys: Dependence on the Zr content. Scr. Mater. 2014, 93, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ding, J.; Yan, F.; Asta, M.; Ritchie, R.O.; Li, L. Spatial correlation of elastic heterogeneity tunes the deformation behavior of metallic glasses. npj Comput. Mater. 2018, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packard, C.; Schuh, C. Initiation of shear bands near a stress concentration in metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 5348–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, A.L.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Ma, E. Shear bands in metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2013, 74, 71–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; He, M.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, L.; Su, Y.; Wang, B.; Huang, H.; Xiang, Q.; Yuan, X.; Zuo, X.; et al. New insights into melt hydrogenation effects on glass-forming ability in a Zr-based bulk metallic glass. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 481, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gostin, P.F.; Eigel, D.; Grell, D.; Uhlemann, M.; Kerscher, E.; Eckert, J.; Gebert, A. Stress-corrosion interactions in Zr-based bulk metallic glasses. Metals 2015, 5, 1262–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tönnies, D.; Samwer, K.; Derlet, P.M.; Volkert, C.A.; Maaß, R. Rate-dependent shear-band initiation in a metallic glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 171907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.; Uhlemann, M.; Gebert, A.; Eckert, J. Hydrogenation and its effect on the crystallisation behaviour of Zr55Cu30Al10Ni5 metallic glass. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 298, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalakshmi, S.; Fleury, E.; Leey, D.Y.; Chang, H.J.; Kim, D.H. Hydrogenation of Ti50Zr25Co25 amorphous ribbons and its effect on their structural and mechanical properties. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2008, 88, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L. Contact Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Bei, H.; Lu, Z.; George, E. Theoretical strength and the onset of plasticity in bulk metallic glasses investigated by nanoindentation with a spherical indenter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 125504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufnagel, T.C.; Schuh, C.A.; Falk, M.L. Deformation of metallic glasses: Recent developments in theory, simulations, and experiments. Acta Mater. 2016, 109, 375–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, W.L.; Demetriou, M.D.; Harmon, J.S.; Lind, M.L.; Samwer, K. Rheology and Ultrasonic Properties of Metallic Glass-Forming Liquids: A Potential Energy Landscape Perspective. MRS Bull. 2011, 32, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samwer, K.; Johnson, W. Structure of glassy early-transition-metal-late-transition-metal hydrides. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 28, 2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spaepen, F. A microscopic mechanism for steady state inhomogeneous flow in metallic glasses. Acta Metall. 1977, 25, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Patinet, S.; Falk, M.L.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, E. Soft spots and their structural signature in a metallic glass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14052–14056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harris, J.; Curtin, W.; Tenhover, M. Universal features of hydrogen absorption in amorphous transition-metal alloys. Phys. Rev. B 1987, 36, 5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, A.C.-P.; Liu, Y.; Udovic, T.J.; Liaw, P.K.; Yu, G.-P.; Huang, J.-H. Inelastic neutron scattering study of the hydrogenated (Zr55Cu30Ni5Al10)99Y1 bulk metallic glass. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 174206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suh, D.; Asoka-Kumar, P.; Dauskardt, R.H. The effects of hydrogen on viscoelastic relaxation in Zr-Ti-Ni-Cu-Be bulk metallic glasses: Implications for hydrogen embrittlement. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; He, M.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, L.; Su, Y.; Wang, B.; Huang, H.; Xiang, Q.; Yuan, X.; Zuo, X.; et al. Effects of hydrogen on the nanomechanical properties of a bulk metallic glass during nanoindentation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 25436–25445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Yang, Y.-Q.; Zhao, X.-A.; Wang, Z.-J.; Xie, D.-G.; Tönnies, D.; Roddatis, V.; Volkert, C.; Shan, Z.-W.; Univerisity of Göttingen, Göttingen, Germany. Unpublished work. 2019.
- Gibson, J.M.; Treacy, M.M.J.; Voyles, P.M.; Jin, H.C.; Abelson, J.R. Structural disorder induced in hydrogenated amorphous silicon by light soaking. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 3093–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyles, P.M.; Gibson, J.M.; Treacy, M.M.J. Fluctuation microscopy: A probe of atomic correlations in disordered materials. J. Electron Microsc. 2000, 49, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, L.; Tönnies, D.; Hirsbrunner, M.; Sievert, T.; Shan, Z.; Volkert, C.A. Effect of Hydrogen Charging on Pop-in Behavior of a Zr-Based Metallic Glass. Metals 2020, 10, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10010022
Tian L, Tönnies D, Hirsbrunner M, Sievert T, Shan Z, Volkert CA. Effect of Hydrogen Charging on Pop-in Behavior of a Zr-Based Metallic Glass. Metals. 2020; 10(1):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10010022
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Lin, Dominik Tönnies, Moritz Hirsbrunner, Tim Sievert, Zhiwei Shan, and Cynthia A. Volkert. 2020. "Effect of Hydrogen Charging on Pop-in Behavior of a Zr-Based Metallic Glass" Metals 10, no. 1: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10010022
APA StyleTian, L., Tönnies, D., Hirsbrunner, M., Sievert, T., Shan, Z., & Volkert, C. A. (2020). Effect of Hydrogen Charging on Pop-in Behavior of a Zr-Based Metallic Glass. Metals, 10(1), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10010022