Study in Wire Feedability-Related Properties of Al-5Mg Solid Wire Electrodes Bearing Zr for High-Speed Train
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructures of As-Cast Al-5Mg-xZr Wire Alloys
3.2. Mechanical Properties of 1.2 mm Al-5Mg-xZr Wire Electrodes
3.3. Roughness of 1.2 mm Al-5Mg-xZr Wire Electrodes
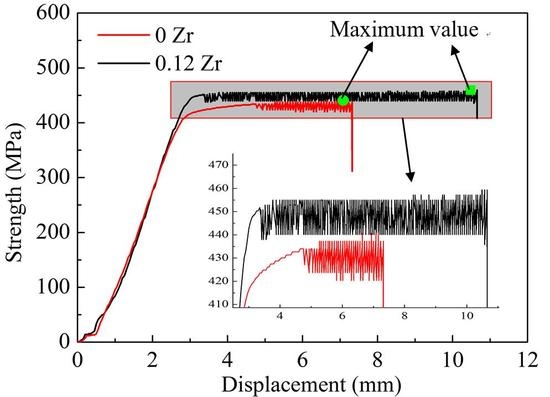
3.4. Mechanical Properties of Welded Joints Welded Using 1.2 mm Al-5Mg-xZr Wires
3.5. Novel Apparatus for Adjusting Wire Feedability-Related Properties during Drawing Process
3.5.1. Cast and Helix of Wire Electrode on a Spool
3.5.2. Principle of the Novel Adjustable Apparatus
3.5.3. Structure and Application of the Novel Adjustable Apparatus
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The addition of 0.12 wt % Zr could refine α-Al dendrites of the as-cast Al-5Mg wire alloy due to the increased amount of heterogeneous substrates for nucleation of α-Al grains, while an excess addition of Zr could result in the coarsening of the α-Al dendrites.
- (2)
- The tensile strength, microhardness, and surface roughness of 1.2 mm Al-5Mg wire electrodes, as well as the tensile strength and elongation of the resulting welded joints, were improved by adding an appropriate amount of Zr, which indicated that Zr addition could improve not only the mechanical properties of welded joints, but also the wire feedability of the Al-5Mg wire electrode bearing Zr.
- (3)
- The cast and helix of wire electrode are two key indices for wire feedability of the Al-5Mg wire electrode, which are affected by the two characteristic angles α and β between the exit die and the pulling capstan. The novel apparatus, which consisted of five parts and four screws, could achieve the rough and fine adjustments of the angle α and β, producing a perfect alignment of exit die with capstan to ensure consistency in wire characteristics.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Filippis, L.A.C.; Serio, L.M.; Facchini, F.; Mummolo, G.; Ludovico, A.A. Prediction of the vickers microhardness and ultimate tensile strength of AA5754 H111 friction stir welding butt joints using artificial neural network. Materials 2016, 9, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddag, B.; Atlati, S.; Nouari, M.; Moufki, A. Dry machining aeronautical aluminum alloy AA2024-T351: Analysis of cutting forces, chip segmentation and built-up edge formation. Metals 2016, 6, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Chen, H.; Che, X.L.; Xu, L.D. Corrosion–fatigue crack propagation of aluminum alloys for high-speed trains. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2017, 31, 1744009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee Paik, J.; Thayamballi, A.K.; Sung Kim, G. The strength characteristics of aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels. Thin-Walled Struct. 1999, 35, 205–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, V.; Ravisankar, V.; Madhusudhan Reddy, G. Effect of pulsed current welding on mechanical properties of high strength aluminum alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2008, 36, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalemba-Rec, I.; Hamilton, C.; Kopyściański, M.; Miara, D.; Krasnowski, K. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir welded 5083 and 7075 aluminum alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xue, S.B.; Ma, C.L.; Wang, J.X.; Lin, Z.Q. Effects of porosity, heat input and post-weld heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of TIG welded joints of AA6082-T6. Metals 2017, 7, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enz, J.; Riekehr, S.; Ventzke, V.; Huber, N.; Kashaev, N. Fibre laser welding of high-alloyed Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 237, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.X.; Huang, X.X.; Li, Y.F.; Wang, X.J. Shallow of aluminum and aluminum alloy MIG welding wire feed stability influence factors. Weld. Appl. 2015, 7, 41–43. [Google Scholar]
- Padilla, T.M.; Quinn, T.P.; Munoz, D.R.; Rorrer, R.A.L. A mathematical model of wire feeding mechanisms in GMAW. Weld. J. 2003, 82, 100–109. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R.H. Control of pitch and relaxation diameter in welding wire production. Met. Prod. 2013, 39, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, B.E. Lubricated Aluminum Weld Wire and Process for Spooling It. U.S. Patent 4,913,927, 3 April 1990. Available online: http://www.freepatentsonline.com/4913927.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2017).
- Aluminum GMAW-Gas Metal Arc Welding for Aluminum Guide. Available online: http://www.lincolnelectric.com/assets/global/Products/Consumable_AluminumMIGGMAWWires-SuperGlaze-SuperGlaze5356TM/c8100.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2017).
- AlcoTec Aluminum Technical Guide. Available online: http://www.esabna.com/shared/documents/litdownloads/alc-10029b_alcotec_technical_guide.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2017).
- Belov, N.A.; Alabin, A.N.; Matveeva, I.A.; Eskin, D.G. Effect of Zr additions and annealing temperature on electrical conductivity and hardness of hot rolled Al sheets. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. 2015, 25, 2817–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, R.Z.; Guan, X.H.; Guan, R.G.; Tie, D.; Lian, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J. Effect of Zr and Sc on mechanical properties and electrical conductivities of Al wires. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. 2014, 24, 3164–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.F.; Guan, R.G.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Misra, R.D.K. Ultrafine-grained Al-0.2Sc-0.1Zr alloy: The mechanistic contribution of nano-sized precipitates on grain refinement during the novel process of accumulative continuous extrusion. Acta Mater. 2015, 100, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, Z.H.; Wang, G.S.; Zhang, C.; Cui, J.Z. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the welding joint filled with microalloying 5183 aluminum welding wires. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2014, 21, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Dong, S.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Xu, B.S.; Fang, J.X.; He, P. Microstructure characteristics of thick aluminum alloy plate joints welded by fiber laser. Mater. Des. 2015, 84, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taendl, J.; Orthacker, A.; Amenitsch, H.; Kothleitner, G.; Poletti, C. Influence of the degree of scandium supersaturation on the precipitation kinetics of rapidly solidified Al-Mg-Sc-Zr alloys. Acta Mater. 2016, 117, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, A.F.; Birley, S.S.; Prangnell, P.B. Development of new high strength Al-Sc filler wires for fusion welding 7000 series aluminium aerospace alloys. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2003, 8, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN 14532–3:2004(E), Welding Consumables-Test Methods and Quality Requirements-Part 3: Conformity Assessment of Wire Electrodes, Wires and Rods for Welding of Aluminum Alloys. Available online: http://www.anystandards.com/plus/download.php?open=0&aid=4926&cid=3 (accessed on 11 September 2017).
- Ma, C.G.; Qi, S.Y.; Li, S.; Xu, H.Y.; He, X.L. Melting purification process and refining effect of 5083 Al-Mg alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. 2014, 24, 1346–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, R.; Dashwood, R.J.; Harrison, A.W.; Flower, H.M. Development of a high strain rate superplastic Al-Mg-Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2000, 16, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocenasek, V.; Slamova, M. Resistance to recrystallization due to Sc and Zr addition to Al-Mg alloys. Mater. Charact. 2001, 47, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schempp, P.; Cross, C.E.; Pittner, A.; Oder, G.; Neumann, R.S.; Rooch, H.; Dörfel, I.; Österle, W.; Rethmeier, M. Solidification of GTA aluminum weld metal: Part I—Grain morphology dependent upon alloy composition and grain refiner content. Weld. J. 2014, 93, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.X.; Li, X.Y.; He, D.Y.; Huang, H. Effect of minor Er and Zr on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-Mg-Mn alloy (5083) welded joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 561, 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Knipling, K.E.; Dunand, D.C.; Seidman, D.N. Precipitation evolution in Al-Zr and Al-Zr-Ti alloys during aging at 450–600 °C. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hamid, A.A.; Zaid, A.I.O. Poisoning of grain refinement of some aluminium alloys. In Proceedings of the Current Advances in Mechanical Design and Production, Seventh Cairo University International MDP Conference, Cairo, Egypt, 15–17 February 2000; pp. 331–338. [Google Scholar]
- Gas Metal Arc Welding. Available online: https://www.lincolnelectric.com/assets/global/products/consumable_miggmawwires-superarc-superarcl-56/c4200.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2017).

















| No. | Material | Mg | Mn | Cr | Ti | Zr | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | Al-5Mg | 4.93 | 0.124 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.0003 | balance |
| 2# | Al-5Mg-0.06Zr | 5.03 | 0.122 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.058 | balance |
| 3# | Al-5Mg-0.12Zr | 5.05 | 0.123 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.123 | balance |
| 4# | Al-5Mg-0.24Zr | 4.98 | 0.121 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.236 | balance |
| 5# | Al-5Mg-0.5Zr | 5.07 | 0.122 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.52 | balance |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Xue, S.; Ma, C.; Wang, J.; Lin, Z. Study in Wire Feedability-Related Properties of Al-5Mg Solid Wire Electrodes Bearing Zr for High-Speed Train. Metals 2017, 7, 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7120520
Wang B, Xue S, Ma C, Wang J, Lin Z. Study in Wire Feedability-Related Properties of Al-5Mg Solid Wire Electrodes Bearing Zr for High-Speed Train. Metals. 2017; 7(12):520. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7120520
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Bo, Songbai Xue, Chaoli Ma, Jianxin Wang, and Zhongqiang Lin. 2017. "Study in Wire Feedability-Related Properties of Al-5Mg Solid Wire Electrodes Bearing Zr for High-Speed Train" Metals 7, no. 12: 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7120520
APA StyleWang, B., Xue, S., Ma, C., Wang, J., & Lin, Z. (2017). Study in Wire Feedability-Related Properties of Al-5Mg Solid Wire Electrodes Bearing Zr for High-Speed Train. Metals, 7(12), 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7120520