Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al/Steel Friction Stir Lap Weld
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. General Features of Lap Joint
3.1.1. Macrostructure of Lap Joint
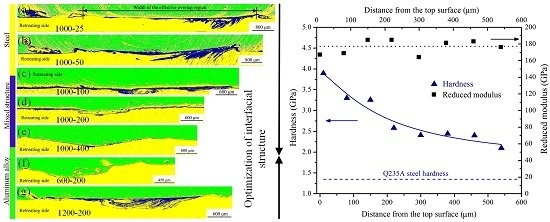
3.1.2. Microstructure of Lap Joint
3.2. Detailed Interfacial Macro- and Microstructure
3.3. Mechanical Properties of Lap Joint
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The basic constitutions of mixed stir zone changed from α-Fe fine grains, thin intermetallic compound (IMC) layer and Al/Fe composite structure to hook-like and chaotic mixed layered structure with decreasing the welding speed from 400 to 25 mm/min and increasing rotation speed from 600 to 1200 rpm.
- (2)
- The maximum shear load can reach 7500 N because of combined effects of stirring action, frictional heat and pressure. The nano-hardness of ultrafine structure in the steel surface layer close to the interface can reach about 3.9 GPa. The decrease of heat input and strain rate can improve joint strength, minimize the thickness of FeAl3 intermetallic layer at the interface and decrease steel grain size.
- (3)
- The sharp loss of the joint strength could not be completely attributed to the formation of a relatively thick and continuous IMC layer, but also the grain growth adjacent to steel grain size at the joint interface.
- (4)
- The morphology of layered structure, thickness of FeAl3 IMC layer and steel grain size at the interface can be controlled by selecting suitable welding parameters.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnes, T.A.; Pashby, I.R. Joining techniques for aluminum spaceframes used in automobiles: Part I—Solid and liquid phase welding. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2000, 99, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.H.; Liu, X.; Ni, J. Microstructural evolution during friction stir welding of dissimilar aluminum alloy to advanced high-strength steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 82, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdipour, A.; Heidarzadeh, A. Dissimilar butt friction stir welding of Al 5083-H321 and 316L stainless steel alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 87, 3105–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, R.S.; Kostka, A.; dos Santos, J.F.; Kaysser-Pyzalla, A. Friction stir dissimilar welding of aluminium alloy to high strength steels: Mechanical properties and their relation to microstructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 556, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilthey, U.; Stein, L. Multimaterial car body design: Challenge for welding and joining. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2006, 11, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajan, S.G.; Meshram, M.; Srinivas, P.P.; Dey, S.R. Friction Stir Welding of aluminum 6082 with mild steel and its joint analyses. Int. J. Adv. Mater. Manuf. Charact. 2013, 3, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, R.S.; Ma, Z.Y. Friction stir welding and processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2005, 50, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, R.; DebRoy, T.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Friction stir welding and processing. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2008, 53, 980–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibnia, M.; Shakeri, M.; Nourouzi, S.; Besharati Givi, M.K. Microstructural and mechanical properties of friction stir welded 5050 Al alloy and 304 stainless steel plates. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 76, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, T.; Tsubaki, M.; Fukumoto, M.; Shimoda, Y.; Ishii, T. High-speed weldability between 6063 and S45C by friction stir welding. Weld. Int. 2006, 20, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lan, S.H.; Ni, J. Analysis of process parameters effects on friction stir welding of dissimilar aluminum alloy to advanced high strength steel. Mater. Des. 2014, 59, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Amadeh, A.; Akbari Mousavi, S.A.A. Investigations on the effects of friction stir welding parameters on intermetallic and defect formation in joining aluminum alloy to mild steel. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Akbari Mousavi, S.A.A.; Amadeh, A. Effects of welding parameters and tool geometry on properties of 3003-H18 aluminum alloy to mild steel friction stir weld. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 1957–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.G.; Fujii, H.; Tsumur, T.; Komzaki, T.; Nakata, K. Three defect types in friction stir welding of aluminum die casting alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 415, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T. Process parameters study on FSW joint of dissimilar metals for aluminum-steel. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 2573–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippis, L.A.C.D.; Serio, L.M.; Facchini, F.; Mummolo, G.; Ludovico, A.D. Prediction of the Vickers Microhardness and Ultimate Tensile Strength of AA5754 H111 Friction Stir Welding Butt Joints Using Artificial Neural Network. Materials 2016, 9, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naghibi, H.D.; Shakeri, M.; Hosseinzadeh, M. Neural network and genetic algorithm based modeling and optimization of tensile properties in FSW of AA 5052 to AISI 304 dissimilar joints. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2016, 69, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimapong, K.; Watanabe, T. Effect of welding process parameters on mechanical property of FSW lap joint between aluminum alloy and steel. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, M.; Kokabi, A.; Reihani, S.; Najafi, H. Effect of tool travel and rotation speeds on weld zone defects and joint strength of aluminium steel lap joints made by friction stir welding. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2012, 17, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Choi, D.H.; Yeon, Y.M.; Jung, S.B. Dissimilar friction stir spot welding of low carbon steel and Al-Mg alloy by formation of IMCs. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2009, 14, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Komazaki, T.; Tsumura, T.; Nakata, K. Role of zinc coat in friction stir lap welding Al and zinc coated steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2008, 24, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Komazaki, T.; Kim, Y.G.; Tsumura, T.; Nakata, K. Interface microstructure study of friction stir lap joint of AC4C cast aluminum alloy and zinc-coated steel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 111, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, A.; Zhang, Z.; De, A.; Debroy, T. Strains and strain rates during friction stir welding. Scr. Mater. 2009, 61, 863–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandan, R.; Roy, G.G.; Lienert, T.J.; Debroy, T. Three-dimensional heat and material flow during friction stir welding of mild steel. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Kailas, S.V. The role of friction stir welding tool on material flow and weld formation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 485, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, M.; Kokabi, A.H.; Seyed Reihani, S.M.; Cheng, W.J.; Wang, C.J. Effect of annealing treatment on joint strength of aluminum/steel friction stir lap weld. Mater. Des. 2013, 44, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Haghshenas, M.; Gerlich, A.P. Role of welding parameters on interfacial bonding in dissimilar steel/aluminum friction stir welds. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2015, 18, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, T.; Kilbourne, J.; Gerlich, A.P.; North, T.H. Joint formation in dissimilar Al alloy/steel and Mg alloy/steel friction stir spot welds. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2009, 14, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghshenas, M.; Abdel-Gwad, A.; Omran, A.M.; Gökçe, B.; Sahraeinejad, S.; Gerlich, A.P. Friction stir weld assisted diffusion bonding of 5754 aluminum alloy to coated high strength steels. Mater. Des. 2014, 55, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

















| Base Metal | Chemical Compositions (wt %) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Al | Si | Mg | C | Mn | Cu | Cr | Ti | P | S | |
| 6082-T6 | 0.5 | Bal | 1.0 | 0.8 | - | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.25 | 0.1 | - | 0.8 |
| Q235A | Bal | - | 0.3 | - | 0.18 | 0.45 | - | - | - | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Samples | Rotational Speed (r/min) | Welding Speed (mm/min) | Shoulder Plunge Depth (mm) | Tilt Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 600 | 200 | 0.2 | 2.5 |
| 2 | 800 | 200 | 0.2 | 2.5 |
| 3 | 1000 | 200 | 0.2 | 2.5 |
| 4 | 1200 | 200 | 0.2 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 1000 | 25 | 0.2 | 2.5 |
| 6 | 1000 | 50 | 0.2 | 2.5 |
| 7 | 1000 | 100 | 0.2 | 2.5 |
| 8 | 1000 | 400 | 0.2 | 2.5 |
| Points | Fe | Al | Mg | Possible Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 45.49 | 49.90 | 2.74 | FeAl |
| 2 | 64.92 | 31.79 | 1.09 | Fe2Al |
| 3 | 47.35 | 47.62 | 2.88 | FeAl |
| 4 | 74.62 | 21.74 | 1.47 | Fe3Al |
| 5 | 68.11 | 28.47 | 0.98 | Fe3Al |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, L.; Huang, Y. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al/Steel Friction Stir Lap Weld. Metals 2017, 7, 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7120542
Wan L, Huang Y. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al/Steel Friction Stir Lap Weld. Metals. 2017; 7(12):542. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7120542
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Long, and Yongxian Huang. 2017. "Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al/Steel Friction Stir Lap Weld" Metals 7, no. 12: 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7120542
APA StyleWan, L., & Huang, Y. (2017). Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al/Steel Friction Stir Lap Weld. Metals, 7(12), 542. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7120542