Effect of Ball Milling Parameters on the Refinement of Tungsten Powder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
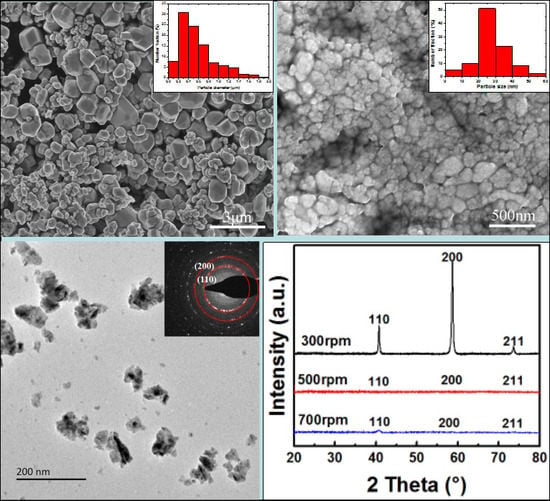
3.1. Initial Tungsten Powder
3.2. The Effect of Milling Speed
3.3. The Effect of Additive Amounts of Process Control Agent (PCA)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, J.W.; Barabash, V.R.; Makhankov, A.; Plochl, L.; Slattery, K.T. Assessment of tungsten for use in the ITER plasma facing components. J. Nucl. Mater. 1998, 258–263, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norajitra, P.; Boccaccini, L.V.; Diegele, E.; Filatov, V.; Gervash, A.; Giniyatulin, R.; Gordeev, S.; Heinzel, V.; Janeschitz, G.; Konys, J.; et al. Development of a helium-cooled divertor concept: Design-related requirements on materials and fabrication technology. J. Nucl. Mater. 2004, 329–333, 1594–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petti, D.A.; McCarthy, K.A.; Gulden, W.; Piet, S.J.; Seki, Y.; Kolbasov, B. An overview of safety and environmental considerations in the selection of materials for fusion facilities. J. Nucl. Mater. 1996, 233–237, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smid, I.; Akiba, M.; Diegele, E.; Vieider, G.; Plochl, L. Development of tungsten armor and bonding to copper for plasma-interactive components. J. Nucl. Mater. 1998, 253–263, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philipps, V. Tungsten as material for plasma-facing components in fusion devices. J. Nucl. Mater. 2011, 415, S2–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linke, J. Plasma facing materials and components for future fusion devices—Development, characterization and performance under fusion specific loading conditions. Phys. Scr. 2006, 123, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singheiser, L.; Hirai, T.; Linke, J.; Pintsuk, G.; Rödig, M. Plasma-facing materials for thermo-nuclear fusion devices. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2009, 62, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathaudhu, S.N.; de Rosset, A.J.; Hartwig, K.T.; Kecskes, L.J. Microstructures and recrystallization behavior of severely hot-deformed tungsten. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 503, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilnathan, N.; Annamalaia, A.R.; Venkatachalam, G. Microstructure and mechanical properties of spark plasma sintered tungsten heavy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 710, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.M.; Miao, S.; Zhang, T.; Liu, R.; Wang, X.P.; Fang, Q.F.; Hao, T.; Zhuang, Z.; Liu, C.S.; Lian, Y.Y.; et al. Recrystallization behavior and thermal shock resistance of the W-1.0 wt % TaC alloy. J. Nucl. Mater. 2018, 501, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.B.; Zhu, D.H.; Li, C.J.; Chen, J.L. Cracking and grain refining behaviors of tungsten based plasma facing materials under fusion relevant transient heat flux. Fusion Eng. Des. 2017, 125, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.N.; Xu, L.J.; Zhou, Y.C.; Pan, K.M.; Li, J.W.; Liu, W.; Wei, S.Z. Preparation, microstructure, and properties of tungsten alloys reinforced by ZrO2 particles. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2017, 64, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.G.; Feng, P.; Dong, L.L.; Liu, B.; Ren, S.X.; Fu, Y.Q. Experimental and theoretical analysis of microstructural evolution and deformation behaviors of CuW composites during equal channel angular pressing. Mater. Des. 2018, 142, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, M.W.; Usher, J.M. Recycling welding rod residuals based on development of a top-down nanomanufacturing system employing indexing equal channel angular pressing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 94, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edalati, K.; Hashiguchi, Y.; Pereira, P.H.R.; Horita, Z.; Langdon, T.G. Effect of temperature rise on microstructural evolution during high-pressure torsion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 714, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazarnik, B.; Huang, Y.; Lewandowska, M.; Langdon, T.G. Enhanced grain refinement and microhardness by hybrid processing using hydrostatic extrusion and high-pressure torsion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 712, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattah-alhosseini, A.; Reza Ansari, A.; Mazaheri, Y.; Karimi, M.; Haghshenas, M. An Investigation of mechanical properties in accumulative roll bonded nano-grained pure titanium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 688, 218–224. [Google Scholar]
- Fattah-alhosseini, A.; Keshavarz, M.K.; Mazaheri, Y.; Reza Ansari, A.; Karimi, M. Strengthening mechanisms of nano-grained commercial pure titanium processed by accumulative roll bonding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 693, 164–169. [Google Scholar]
- Bahl, S.; Suwas, S.; Ungàr, T.; Chatterjee, K. Elucidating microstructural evolution and strengthening mechanisms in nanocrystalline surface induced by surface mechanical attrition treatment of stainless steel. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 138–151. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, M.T.; Huang, J.C.; Tsai, W.Y.; Chou, T.H.; Chen, C.F.; Li, T.H.; Jang, J.S.C. Effects of ultrasonic surface mechanical attrition treatment on microstructures and mechanical properties of high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2018, 93, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameyama, K.; Oda, E.; Fujiwara, H. Superplasticity and high temperature deformation behaviour in nano grain tungsten compacts. Materialwiss. Werkstofftech. 2008, 39, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, E.; Fujiwara, H.; Ameyama, K. Nano grain formation in tungsten by severe plastic deformation-mechanical milling process. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, E.; Ameyama, K.; Yamaguchi, S. Fabrication of nano grain tungsten compact by mechanical milling process and its high temperature properties. Mater. Sci. Forum 2006, 503–504, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhou, Z.; Tan, J.; Ding, Q.; Zhong, M. Effects of ball milling parameters on microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of W–3% Y composites. J. Nucl. Mater. 2015, 465, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, L.; Lin, J.; Zan, X.; Zhu, X.; Luo, G.; Wu, Y. Influence of ball milling processing on the microstructure and characteristic of W-Nb alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 694, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debata, M.; Acharya, T.S.; Sengupta, P.; Acharya, P.P.; Baipai, S.; Jayasankkar, K. Effect of high energy ball milling on structure and properties of 95W-3.5Ni-1.5Fe heavy alloys. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2017, 69, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayour, H.; Abdellahi, M.; Bahmanpour, M. Optimization of the high energy ball-milling: Modeling and parametric study. Power Technol. 2016, 291, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C. Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2001, 46, 11–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.X.; Wu, Z.M.; Fu, E.G.; Du, J.L.; Wang, P.P.; Zhao, Y.B.; Qiu, Y.H.; Hu, Z.Y. Refinement process and mechanisms of tungsten powder by high energy ball milling. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2017, 67, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurlov, A.S.; Gusev, A.I. Model for milling of powders. Tech. Phys. 2011, 56, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Sample Number | Milling Speed (rpm) | PCA (%) | Total Milling Time (h) | D50 (nm) at 30 h Milling | D50 (nm) at 60 h Milling |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 300 | 8 | 60 | 1050 | 90 |
| 2 | 500 | 8 | 60 | 50 | 44 |
| 3 | 700 | 8 | 60 | 24 | 27 |
| 4 | 700 | 6 | 60 | 220 | 27 |
| 5 | 700 | 12 | 60 | 28 | 16 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Liang, Y.; Fu, E.; Du, J.; Wang, P.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, Y. Effect of Ball Milling Parameters on the Refinement of Tungsten Powder. Metals 2018, 8, 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8040281
Wu Z, Liang Y, Fu E, Du J, Wang P, Fan Y, Zhao Y. Effect of Ball Milling Parameters on the Refinement of Tungsten Powder. Metals. 2018; 8(4):281. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8040281
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zaoming, Yanxia Liang, Engang Fu, Jinlong Du, Peipei Wang, Yong Fan, and Yunbiao Zhao. 2018. "Effect of Ball Milling Parameters on the Refinement of Tungsten Powder" Metals 8, no. 4: 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8040281
APA StyleWu, Z., Liang, Y., Fu, E., Du, J., Wang, P., Fan, Y., & Zhao, Y. (2018). Effect of Ball Milling Parameters on the Refinement of Tungsten Powder. Metals, 8(4), 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8040281