Effect of Remelting Temperature and Soaking Time on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Thixoformed Part of Nano-Sized SiCp/7075 Composite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- Nano-sized SiCp/7075 composite cylinder parts with good surface quality and dense microstructure were obtained via thixoforming technology. The deformation mechanism of the top side wall depends mainly on the liquid flow (LF), the flow of liquid incorporating solid grains (FLS), and sliding between solid grains (SSS). The plastic deformation (PDS) mechanism dominates the deformation of the middle side wall, the bottom side wall, and the bottom itself.
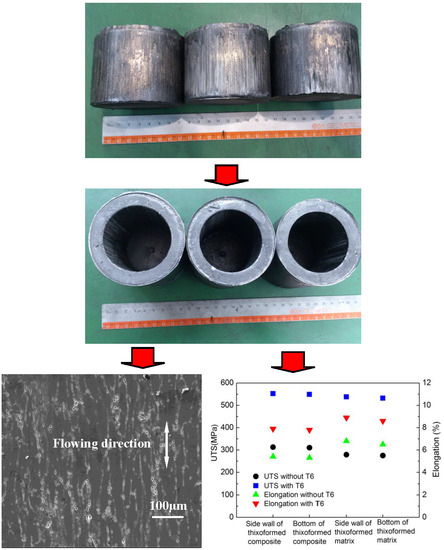
- The optimal process parameters obtained according to the UTS and elongation results are soaking time between 10 min and 15 min and remelting temperatures between 590 °C and 600 °C. The highest UTS and elongation of the thixoformed composite part without T6 were 313 MPa and 5.4% respectively.
- A mixed fracture morphology was found in the SEM image of tensile fracture due to the simultaneous existence of some small-sized dimples and quasi-cleavage steps. The fracture of the composite part thixoformed at 580 °C is characterized by transgranular fracture. A mixed fracture of transgranular fracture and intergranular fracture was found in the composite part thixoformed at 590 °C. The intergranular fracture was dominant in the composite parts thixoformed at 600 °C and 610 °C due to increasing liquid film thickness and liquid segregation.
- The mechanical properties were improved significantly after the thixoformed composite parts were treated by T6. The highest UTS of 552 MPa and the highest elongation of 7.9% were obtained in the thixoformed composite parts treated by T6. Uniform precipitation of η phase (MgZn2) after T6 led to improvement of the mechanical properties of the thixoformed composite part. The UTS of the thixoformed parts with and without T6 was improved compared with the thixoformed 7075 alloy parts with and without T6 due to the addition of nano-sized SiC particles. The UTS of the thixoformed parts with T6 was higher than that of the rheoformed composite part.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spencer, D.B. Rheology of liquid-solid mixtures of lead-tin. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Massachusetts, MA, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Spencer, D.B.; Mehrabian, R.; Flemings, M.C. Rheological behavior of Sn-15 pct Pb in the crystallization range. Metall. Trans. B 1972, 3, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemings, M.C. Behavior of metal alloys in the semisolid state. Metall. Trans. A 1991, 22, 957–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghayeghi, R.; Zoqui, E.J.; Halvaee, A.; Emamy, M. An investigation on semi-solid Al-7Si-0.3Mg alloy produced by mechanical stirring. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2005, 169, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.N.; Luo, J.R.; Wu, S.S.; Xiao, Z.H.; Mao, Y.W.; Song, X.J.; Wu, G.Z. Study on the semi-solid rheocasting of magnesium alloy by mechanical stirring. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2002, 129, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Chen, A.T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, W.C.; Wu, G.H.; Ding, W.J. Preparation of an Mg-Gd-Zn alloy semisolid slurry by low frequency electro-magnetic stirring. Mater. Des. 2015, 84, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Z.F.; Shi, L.K. Annulus electromagnetic stirring for preparing semisolid A357 aluminum alloy slurry. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2009, 19, 1104–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.P.; Kyonka, C.P.; Courtois, J.A. Fine Grained metal composition. U.S. Patent 4415374, 30 March 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Saklakoglu, N.; Saklakoglu, I.E.; Tanoglu, M.; Oztas, O.; Cubukcuoglu, O. Mechanical properties and microstructural evaluation of AA5013 aluminum alloy treated in the semi-solid state by SIMA process. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 148, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolouri, A.; Shahmiri, M.; Kang, C.G. Coarsening of equiaxed microstructure in the semisolid state of aluminum 7075 alloy through SIMA processing. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 3544–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkwood, D.H.; Sellars, C.M.; Elias Boyed, L.G. Thixotropic Materials. European Patent 0305375 B1, 28 October 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Bolouri, A.; Kang, C.G. Correlation between solid fraction and tensile properties of semisolid RAP processed aluminum alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 516, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yuan, B.G.; Lin, J.; Xia, XS.; Zhao, Z.D.; Shu, D.Y. Comparisons of microstructure, thixoformability and mechanical properties of high performance wrought magnesium alloys reheated from the as-cast and extruded states. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 584, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, Z.D.; Chen, G.; Wang, B. Effect of accumulative plastic deformation on generation of spheroidal structure, thixoformability and mechanical properties of large-size AM60 magnesium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 632, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, G.; Ji, X.H.; Han, F.; Zhao, Z.D.; Wan, J.; Xiao, X.Q. Compound forming of 7075 aluminum alloy based on functional integration of plastic deformation and thixoformation. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 246, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaio, N.C.; Cecília, T.W.P.; Eugênio, J.Z. Influence of the processing route on the microstructure of aluminum alloy A356 for thixoforming. Mater. Charact. 2013, 85, 26–37. [Google Scholar]
- Forn, A.; Vaneetveld, G.; Pierret, J.C.; Menarguess, S.; Baile, M.T.; Camillom, M.; Rassili, A. Thixoextrusion of A357 aluminium alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, s1005–s1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parshizfard, E.; Shabestari, S.G. An investigation on the microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of A380 aluminum alloy during SIMA process. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 9654–9658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapranos, P.; Kirkwood, D.H.; Atkinson, H.V.; Rheinlander, J.T.; Bentzen, J.J.; Toft, P.T.; Debel, C.P.; Laslaz, G.; Maenner, L.; Blais, S.; et al. Thixoforming of an automotive part in A390 hypereutectic Al–Si alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 135, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chayong, S.; Atkinson, H.V.; Kapranos, P. Thixoforming 7075 aluminium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 390, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abolhasani, D.; Ezatpour, H.R.; Sajjadi, S.A.; Abolhasani, Q. Microstructure and mechanical properties evolution of 6061 aluminum alloy formed by forward thixoextrusion process. Mater. Des. 2013, 49, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birol, Y. Thixoforming of EN AW-2014 alloy at high solid fraction. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 211, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birol, Y. Comparison of thixoformability of AA6082 reheated from the as-cast and extruded states. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 461, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.P.; Jiang, W.Y.; Chen, T.; Feng, Y.C.; Zhou, H.Y.; Zhao, S.C.; Liang, Z.Q.; Zhu, Y. Spheroidal microstructure formation and thixoforming of AM60B magnesium alloy prepared by SIMA process. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, s435–s444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.F.; Wang, Y.; Qu, J.J.; Du, Z.M.; Luo, S.J. Preparation and thixoforging of semisolid billet of AZ80 magnesium alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, M.Z.; Palmiere, E.J.; Howe, A.A.; Atkinson, H.V.; Kapranos, P. Thixoforming of a high performance HP9/4/30 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2005, 395, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierret, J.C.; Rassili, A.; Vaneetveld, G.; Lecote-Beckers, J. Stability of steel thixoforming process. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2010, 20, s937–s942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.L.; Chen, T.J.; Qi, Y.S.; Zhang, S.Q.; Yao, P. Effects of solution treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of thixoformed Mg2Sip/AM60B composite. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 636, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.N.; Geng, L.; Zhang, H.W.; Huang, L.J. Effects of stirring parameters on microstructure and tensile properties of (ABOw + SiCp)/6061Al composites fabricated by semi-solid stirring technique. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, s274–s279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhawari, K.S.; Omar, M.Z.; Ghazali, M.J.; Salleh, M.S.; Mohammed, M.N. Wear properties of A356/Al2O3 metal matrix composites produced by semisolid processing. Procedia Eng. 2013, 68, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.W.; Geng, L.; Guan, L.N.; Huang, L.J. Effects of SiC particle pretreatment and stirring parameters on the microstructure and mechanical properties of SiCp/Al-6.8Mg composites fabricated by semi-solid stirring technique. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 528, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koli, D.K.; Agnihotri, G.; Purohit, R. A review on properties, behaviour and processing methods for Al-nano Al2O3 composites. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 567–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazahery, A.; Shabani, M.O. Characterization of cast A356 alloy reinforced with nano SiC composites. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandemir, S. Microstructure and mechonicol properties of A357/SiC nonocomposites fobricated by ultrosonic covitotion-based dispersion of ball-milled nanoparticles. J. Compon. Mater. 2017, 51, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipour, M.; Pahlevani, Z.; Shabani, M.O.; Mazahery, A. Optimization of the EMS process parameters in compocasting of high-wear-resistant Al-nano-TiC composites. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofigh, A.A.; Rahimipour, M.R.; Shabani, M.O.; Davami, P. Application of the combined neuro-computing, fuzzy logic and swarm intelligence for optimization of compocast nanocomposites. J. Compon. Mater. 2015, 49, 1653–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipour, M.; Pahlevani, Z.; Shabani, M.O.; Mazahery, A. Squeeze casting of electromagnetically stirred aluminum matrix nanocomposites in semi-solid condition using hybrid algorithm optimized parameters. Kovove Mater. 2017, 55, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofigh, A.A.; Shabani, M.O. Efficient optimum solution for high strength Al alloys matrix composites. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 7483–7490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, M.O.; Rahimipour, M.R.; Tofigh, A.A.; Davami, P. Refined microstructure of compo cast nanocomposites: the performance of combined neuro-computing, fuzzy logic and particle swarm techniques, Neural Computing and Applications. Neural. Comput. Appl. 2015, 26, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, M.O.; Heydari, F.; Tofigh, A.A.; Rahimipour, M.R.; Razavi, M.; Mazahery, A.; Davami, P. Wear properties of rheo-squeeze cast aluminum matrix reinforced with nano particulates. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surfaces 2016, 52, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.F.; Wang, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the semisolid slurries and rheoformed component of nano-sized SiC/7075 aluminum matrix composite prepared by ultrasonic-assisted semisolid stirring. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 639, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.F.; Wang, Y. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the rheoformed cylindrical part of 7075 aluminum matrix composite reinforced with nano-sized SiC particles. Mater. Des. 2015, 79, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandemir, S.; Atkinson, H.V.; Weston, D.P.; Hainsworth, S.V. Thixoforming of A356/SiC and A356/TiB2 nanocomposites fabricated by a combination of green compact nanoparticle incorporation and ultrasonic treatment of the melted compact. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45A, 5782–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. ASTM Standard E8M, Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials [Metric]; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.P.; Tsao, C.Y.A. Semi-solid deformation of non-dendrtic structure-I. Phemonological behavior. Acta Mater. 1997, 45, 1955–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.F.; Luo, S.J. Reheating microstructure of refined AZ91D magnesium alloy in semi-solid state. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2004, 14, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Kubotak, K.; Mabuchi, M.; Higashi, K. Review processing and mechanical properties of fine-grained Mg alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 1999, 34, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.L.; Wong, W.L.E.; Gupta, M. Enhancing strength and ductility of magnesium by integrating it with aluminum nanoparticles. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 6338–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbalaei, M.; Mirzaee, O.; Baharvandi, H.R. Fabrication and study on mechanical properties and fracture behavior of nanometric Al2O3 particle-reinforced A356 composites focusing on the parameters of vortex method. Mater. Des. 2013, 46, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidelli, M.; Sebastiani, M.; Johanns, K.E.; Pharr, G.M. Effects of indenter angle on micro-scale fracture toughness measurement by pillar splitting. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 5731–5738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Elements | Al | Zn | Mg | Cu | Si | C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position A | wt% | 88.91 | 5.51 | 3.08 | 0.88 | 0.58 | 1.04 |
| at% | 90.86 | 2.32 | 3.49 | 0.38 | 0.57 | 2.38 | |
| Position B | wt% | 86.13 | 4.77 | 2.56 | 1.12 | 2.81 | 2.62 |
| at% | 86.13 | 1.97 | 2.84 | 0.47 | 2.70 | 5.88 | |
| Position C | wt% | 89.52 | 5.07 | 2.77 | 0.98 | 0.25 | 1.40 |
| at% | 91.07 | 2.07 | 3.04 | 0.41 | 0.24 | 3.18 | |
| Element | Series | Net | (wt%) | (norm. wt%) | (norm. at%) | Error in wt% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | K-series | 3216 | 2.49 | 2.49 | 5.69 | 0.332 |
| Aluminum | K-series | 269,060 | 87.22 | 87.22 | 88.84 | 7.942 |
| Copper | K-series | 5101 | 2.74 | 2.74 | 1.18 | 0.352 |
| Chromium | K-series | 1031 | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.25 | 0.14 |
| Manganese | K-series | 4941 | 2.08 | 2.08 | 1.04 | 0.29 |
| Iron | K-series | 8962 | 3.90 | 3.90 | 1.92 | 0.45 |
| Silicon | K-series | 3469 | 1.10 | 1.10 | 1.08 | 0.13 |
| Sum | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Element | Series | Net | (wt%) | (norm. wt%) | (norm. at%) | Error in wt% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | K-series | 69,567 | 12.21 | 12.21 | 23.96 | 1.18 |
| Aluminum | K-series | 1,174,789 | 86.43 | 86.43 | 75.52 | 7.86 |
| Chromium | K-series | 596 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.08 |
| Manganese | K-series | 749 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.09 |
| Copper | K-series | 10,023 | 1.22 | 1.22 | 0.45 | 0.19 |
| Sum | 100 | 100 | 100 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, J.; Xiao, G.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Nie, X. Effect of Remelting Temperature and Soaking Time on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Thixoformed Part of Nano-Sized SiCp/7075 Composite. Metals 2018, 8, 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8090709
Jiang J, Xiao G, Liu Y, Wang Y, Nie X. Effect of Remelting Temperature and Soaking Time on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Thixoformed Part of Nano-Sized SiCp/7075 Composite. Metals. 2018; 8(9):709. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8090709
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Jufu, Guanfei Xiao, Yingze Liu, Ying Wang, and Xi Nie. 2018. "Effect of Remelting Temperature and Soaking Time on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Thixoformed Part of Nano-Sized SiCp/7075 Composite" Metals 8, no. 9: 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8090709
APA StyleJiang, J., Xiao, G., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., & Nie, X. (2018). Effect of Remelting Temperature and Soaking Time on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of the Thixoformed Part of Nano-Sized SiCp/7075 Composite. Metals, 8(9), 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/met8090709