Reliability Analysis of RC Slab-Column Joints under Punching Shear Load Using a Machine Learning-Based Surrogate Model
Abstract
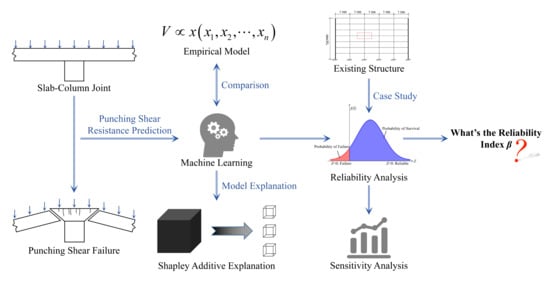
:1. Introduction
2. Punching Shear Resistance Database of RC Slab-Column Joints
3. Machine Learning Model for Punching Shear Resistance Prediction
3.1. Overview of Machine Learning Models
Extreme Gradient Boosting
3.2. Prediction Results of Machine Learning Models
3.3. Interpretation of the ML Prediction Model
3.3.1. Overview of Shapley Additive Explanation
3.3.2. Model Interpretation Using Shapley Additive Explanation
4. Reliability Analysis: RC Slab-Column Joint of an Office Building
4.1. Results of Structural Reliability Analysis
4.2. Sensitivity Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Kotsovos, M.D. Design for Punching of Flat Slabs. In Compressive Force-Path Method, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; Volume 5, pp. 83–107. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.Z.; Diao, M.Z.; Li, Y.; Guan, H.; Lu, X.Z. Post-punching failure mechanism and resistance of flat plate-column joints with in-plane constraints. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 138, 106360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, S.; Delatte, N.J. Collapse of 2000 Commonwealth Avenue: Punching Shear Case Study. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2004, 18, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schellhammer, J.; Delatte, N.J.; Bosela, P.A. Another Look at the Collapse of Skyline Plaza at Bailey’s Crossroads, Virginia. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2013, 27, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinnunen, S.; Nylander, H. Punching of Concrete Slabs without Shear Reinforcement; KTH Royal Institute of Technology: Stockholm, Sweden, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Broms, C.E. Elimination of flat plate punching failure mode. ACI Struct. J. 2000, 97, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Broms, C.E. Concrete Flat Slabs and Footings-Design Method for Punching and Detailing for Ductility. Ph.D. Thesis, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Jirsa, J.O.; Bayrak, O. Strength Evaluation of Interior Slab-Column Connections. ACI Struct. J. 2008, 105, 692–700. [Google Scholar]
- Stasio, D.; Buren, M.R.V. Transfer of Bending Moment between Flat Plate Floor and Column. ACI J. Proc. 1960, 57, 299–314. [Google Scholar]
- Moe, J. Shearing Strength of Reinforced Concrete Slabs and Footings under Concentrated Loads; Portland Cement Association: Portland, Oregon, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- MOHURD (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China). GB 50010—2010 Code for Design of Concrete Structures; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 232–236. [Google Scholar]
- ACI (American Concrete Institute). Building Code Requirements for Structure Concrete (ACI 318-19) and Commentary; American Concrete Institute: Farmington Hills, MI, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Muttoni, A. Punching shear strength of reinforced concrete slabs without transverse reinforcement. ACI Struct. J. 2008, 105, 440–450. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.F.; Huang, T.C.; Tong, Y.L.; Liang, S.X. A Modified Compression Field Theory Based Analytical Model of RC Slab-Column Joint without Punching Shear Reinforcement. Buildings 2022, 12, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetchotisak, P.; Ruengpim, P.; Chetchotsak, D.; Yindeesuk, S. Punching Shear Strengths of RC Slab-Column Connections: Prediction and Reliability. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 3066–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.D.; Truong, G.T.; Shin, M. Development of extreme gradient boosting model for prediction of punching shear resistance of r/c interior slabs. Eng. Struct. 2021, 235, 112067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalathu, S.; Shin, H.; Choi, E.; Jeon, J.S. Explainable machine learning models for punching shear strength estimation of flat slabs without transverse reinforcement. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 39, 102300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.G.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.Q.; Zuo, L.; Lu, M.J.; Zhou, Y.S. Compressive Strength Prediction of High-Strength Concrete Using Long Short-Term Memory and Machine Learning Algorithms. Buildings 2022, 12, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkhordari, M.S.; Armaghani, D.J.; Mohammed, A.S.; Ulrikh, D.V. Data-Driven Compressive Strength Prediction of Fly Ash Concrete Using Ensemble Learner Algorithms. Buildings 2022, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatnawi, A.; Alkassar, H.M.; Al-Abdaly, N.M.; Al-Hamdany, E.A.; Bernardo, L.F.A.; Imran, H. Shear Strength Prediction of Slender Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete Beams Using a Gradient Boosting Regression Tree Method. Buildings 2022, 12, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.M.; Li, H.Y.; Zhou, Y.S. Compressive Strength Prediction of Fly Ash Concrete Using Machine Learning Techniques. Buildings 2022, 12, 690. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.X.; Wu, L.F.; Liang, S.X. Explainable machine learning-based model for failure mode identification of RC flat slabs without transverse reinforcement. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 141, 106647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.X.; Sun, J.H.; Liang, S.X. Interpretable Machine Learning Models for Punching Shear Strength Estimation of FRP Reinforced Concrete Slabs. Crystals 2022, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, G.T.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, C.S. Assessment of punching shear strength of FRP-RC slab-column connections using machine learning algorithms. Eng. Struct. 2022, 255, 113898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Feng, D.C. A machine learning-based time-dependent shear strength model for corroded reinforced concrete beams. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 36, 102118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.C.; Ren, X.D.; Li, J. Stochastic damage hysteretic model for concrete based on micromechanical approach. Int. J. Non-Liner Mech. 2016, 83, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojaczyk, A.A.; Teixeira, A.P.; Neves, L.C.; Cardoso, J.B.; Soares, C.G. Review and application of Artificial Neural Networks models in reliability analysis of steel structures. Struct. Saf. 2015, 52, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.Q.; Du, X.P. Probabilistic uncertainty analysis by mean-value first order Saddlepoint Approximation. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2008, 93, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.C.; Xie, S.C.; Li, Y.; Jin, L. Time-dependent reliability-based redundancy assessment of deteriorated RC structures against progressive collapse considering corrosion effect. Struct. Saf. 2021, 89, 102061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Feng, D.C. Stochastic dynamic response analysis and reliability assessment of non-linear structures under fully non-stationary ground motions. Struct. Saf. 2019, 79, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassim, K.; Bouafia, Y.; Khalil, B. Reliability and punching shear resistance of slabs in non linear domain. Gradevinar 2016, 67, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar]
- Olmati, P.; Sagaseta, J.; Cormie, D.; Jones, A.E.K. Simplified reliability analysis of punching in reinforced concrete flat slab buildings under accidental actions. Eng. Struct. 2017, 130, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricker, M.; Feiri, T.; Nille-Hauf, K.; Adam, V.; Hegger, J. Enhanced reliability assessment of punching shear resistance models for flat slabs without shear reinforcement. Eng. Struct. 2021, 226, 111319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.P.; Huang, R.; Wang, X.J.; Qi, W.C. Structural reliability analysis and reliability-based design optimization: Recent advances. Sci. China-Phys. Mech. Astron. 2013, 56, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, M.; Ghavidel, A.; Arab, H.G.; Mousavi, S.R. Low-cost finite element method-based reliability analysis using adjusted control variate technique. Struct. Saf. 2018, 75, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, S.S.; Enayatollahi, F.; Xu, X.Y.; Liang, X.H. Machine learning-based methods in structural reliability analysis: A review. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2022, 219, 108223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakjira, T.G.; Ebead, U.; Alam, M.S. Machine learning-based shear capacity prediction and reliability analysis of shear-critical RC beams strengthened with inorganic composites. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e01008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deifalla, A. A comparative study and a simplified formula for punching shear design of concrete slabs with or without membrane tensile forces. Structures 2021, 33, 1936–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.H.; Deng, Y. Dependent Evidence Combination Based on Shearman Coefficient and Pearson Coefficient. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 11634–11640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.C.; Wang, W.J.; Mangalathu, S.; Taciroglu, E. Interpretable XGBoost-SHAP Machine-Learning Model for Shear Strength Prediction of Squat RC Walls. J. Struct. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, H.; Burgueno, R. Emerging artificial intelligence methods in structural engineering. Eng. Struct. 2018, 171, 170–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Q.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.C.; Wang, W.J.; Mangalathu, S.; Hu, G.; Wu, T. Implementing ensemble learning methods to predict the shear strength of RC deep beams with/without web reinforcements. Eng. Struct. 2021, 235, 111979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.X.; Shen, Y.X.; Ren, X.D. Comparative study of influential factors for punching shear resistance/failure of RC slab-column joints using machine-learning models. Structures 2022, 45, 1333–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, J.; Ahmed, K.S.; Khan, N.I.; Islam, K.; Mangalathu, S. Data-driven shear strength prediction of steel fiber reinforced concrete beams using machine learning approach. Eng. Struct. 2021, 233, 111743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalathu, S.; Karthikeyan, K.; Feng, D.C.; Jeon, J.S. Machine-learning interpretability techniques for seismic performance assessment of infrastructure systems. Eng. Struct. 2022, 250, 112883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Erion, G.; Chen, H.; DeGrave, A.; Prutkin, J.M.; Nair, B.; Katz, R.; Himmelfarb, J.; Bansal, N.; Lee, S.I. From local explanations to global understanding with explainable AI for trees. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2020, 2, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yitzhaki, D. Punching strength of reinforced concrete slabs. ACI J. Proc. 1966, 63, 527–542. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, N.M.; Fallsen, H.B.; Hinojosa, R.C. Influence of Column Rectangularity on the Behavior of Flat Plate Structures. ACI Spec. Publ. 1971, 30, 127–146. [Google Scholar]
- Long, A.E. A Two-Phase Approach to the Prediction of the Punching Strength of Slabs. ACI J. Proc. 1975, 72, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Regan, P.E. Symmetric punching of reinforced concrete slabs. Mag. Concr. Res. 1986, 38, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Yi, W.J.; Liu, L.W. Investigation on seismic performance of interior slab-column connections subjected to reversed cyclic loading. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Dynam. 2019, 39, 109–121. [Google Scholar]
- MOHURD (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China). GB 50011—2010 Code for Seismic Design of Buildings; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- MOHURD (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China). GB 50068—2018 Unified Standard for Reliability Design of Building Structures; China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wakjira, T.G.; Ibrahim, M.; Ebead, U.; Alam, M.S. Explainable machine learning model and reliability analysis for flexural capacity prediction of RC beams strengthened in flexure with FRCM. Eng. Struct. 2022, 255, 113903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooman, M.L. Probabilistic Reliability: An Engineering Approach; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hadianfard, M.A.; Malekpour, S.; Momeni, M. Reliability analysis of H-section steel columns under blast loading. Struct. Saf. 2018, 75, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.Y.; Quek, S.T.; Li, A.Q.; Li, J.H.; Duan, M.J. Hybrid approach to seismic reliability assessment of engineering structures. Eng. Struct. 2017, 153, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, A.; Hoffmann, S.; Wendner, R.; Bergmeister, K. Structural assessment and reliability analysis for existing engineering structures, applications for real structures. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2009, 5, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesund, H.; Kaushik, Y.P. Analysis of Punching Shear Failures in Slabs; International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering: Zurich, Switzerland, 1970; pp. 41–60. [Google Scholar]
- Ramdane, K.E. Punching shear of high performance concrete slabs. In Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Utilization of High Strength/High Performance Concrete, Paris, France, 29 May 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, R.Y.; Chin, C.S. Flat Slabs at Slab-Column Connection: Nonlinear Finite Element Modelling and Punching Shear Capacity Design Criterion. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2007, 10, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Parameter | Minimum | Maximum | Standard Deviation | Average | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s | 1.00 | 3.00 | 0.58 | 1.40 | Input |
| A (cm2) | 20.43 | 6375.87 | 596.68 | 489.31 | Input |
| d (mm) | 29.97 | 668.50 | 58.52 | 113.74 | Input |
| f’c (Mpa) | 9.40 | 130.10 | 18.56 | 35.39 | Input |
| fy (Mpa) | 234.70 | 749.00 | 115.83 | 456.60 | Input |
| ρ (%) | 0.25 | 7.31 | 0.70 | 1.26 | Input |
| λ | 0.61 | 32.51 | 4.83 | 6.59 | Input |
| V (kN) | 24.00 | 4915.00 | 406.56 | 403.25 | Output |
| ML Model | Optimal Hyper-Parameter |
|---|---|
| ANN | Learning rate = 0.1, neurons number of hidden layer = 17, maximum iteration = 2000 |
| DT | Maximum depth = 8 |
| RF | Number of weak learner = 100, maximum depth = 14 |
| XGBoost | Number of weak learners = 100, learning rate = 0.5, maximum depth = 3, γ = 0.9, λ’ = 1.4 |
| Empirical Model | Punching Shear Resistance Calculation Equation |
|---|---|
| GB 50010-2010 [11] | ; |
| ACI 318-19 [12] | ; |
| Tian et al. [8] | ; ; |
| Wu et al. [14] | ; ; ; |
| Chetchotisak et al. [15] | ; ; |
| s | A/cm2 | d/mm | f’c/Mpa | fy/Mpa | ρ/% | λ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2809 | 209 | 39.31 | 421 | 0.81 | 16.67 |
| Parameter | Average | Standard Deviation | COV | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| d: slab’s effective depth (mm) | 209 | 6.27 | 0.03 | Gaussian |
| f’c: compressive strength of concrete (Mpa) | 39.31 | 4.32 | 0.11 | Gaussian |
| fy: yield strength of reinforcement (Mpa) | 421 | 33.68 | 0.08 | Gaussian |
| SG: dead load (kN) | 393.75 | 27.56 | 0.07 | Gaussian |
| SQ: live load (kN) | 112.5 | 32.4 | 0.288 | Gumbel |
| Pf | β | αR | αS | r* | s* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00546 | 3.443 | −0.655 | 0.755 | 837.625 | 837.625 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, L.; Shen, Y.; Liang, S. Reliability Analysis of RC Slab-Column Joints under Punching Shear Load Using a Machine Learning-Based Surrogate Model. Buildings 2022, 12, 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12101750
Shen L, Shen Y, Liang S. Reliability Analysis of RC Slab-Column Joints under Punching Shear Load Using a Machine Learning-Based Surrogate Model. Buildings. 2022; 12(10):1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12101750
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Lulu, Yuanxie Shen, and Shixue Liang. 2022. "Reliability Analysis of RC Slab-Column Joints under Punching Shear Load Using a Machine Learning-Based Surrogate Model" Buildings 12, no. 10: 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12101750
APA StyleShen, L., Shen, Y., & Liang, S. (2022). Reliability Analysis of RC Slab-Column Joints under Punching Shear Load Using a Machine Learning-Based Surrogate Model. Buildings, 12(10), 1750. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12101750