NemoTrainer: Automated Conditioning for Stimulus-Directed Navigation and Decision Making in Free-Swimming Zebrafish
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design Philosophy
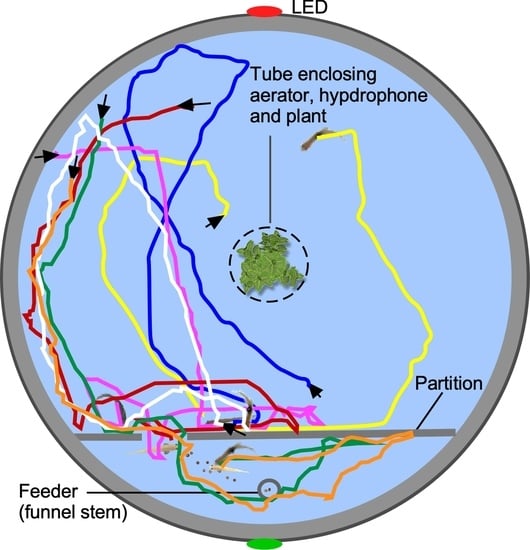
2.2. Training Apparatus
2.3. Hardware and Software Design Features
2.4. Computer Interface and Operation
2.5. Example Training Paradigm
2.6. Measures and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Classical Conditioning
3.2. Operant Conditioning
3.3. Learning Dynamics
4. Discussion
4.1. Notable Program Features
4.2. Audiovisual Learning in Zebrafish
4.3. Imaging and Tracking Options
4.4. Caveats and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
- Systems and Methods for Automated Control of Animal Training and Discrimination Learning; US Patent No.: 10,568,305 B2; Date of Patent: 25 February 2020. Assignee: Georgetown University.
- Systems and Methods for Automated Control of Animal Training and Discrimination Learning; US Patent No.: 11,369,093 B2; Date of Patent: 28 June 2022. Assignee: Georgetown University.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Pradel, G.; Schachner, M.; Schmidt, R. Inhibition of memory consolidation by antibodies against cell adhesion molecules after active avoidance conditioning in zebrafish. J. Neurobiol. 1999, 39, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradel, G.; Schmidt, R.; Schachner, M. Involvement of L 1. 1 in memory consolidation after active avoidance conditioning in zebrafish. J. Neurobiol. 2000, 43, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, F.E.; White, D.; Messer, W.S. A simple spatial alternation task for assessing memory function in zebrafish. Behav. Process. 2002, 58, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Kim, W.; Choi, B.-H.; Koh, H.-Y.; Lee, C.-J. Alcohol impairs learning of T-maze task but not active avoidance task in zebrafish. Korean J. Biol. Sci. 2003, 7, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pather, S.; Gerlai, R. Shuttle box learning in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 196, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colwill, R.M.; Raymond, M.P.; Ferreira, L.; Escudero, H. Visual discrimination learning in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Process. 2005, 70, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Tucci, V.; Kishi, S.; Zhdanova, I.V. Cognitive aging in zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arthur, D.; Levin, E. Spatial and non-spatial visual discrimination learning in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Anim. Cogn. 2001, 4, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.D.; Chrysanthis, E.; Yacisin, K.; Linney, E. Chlorpyrifos exposure of developing zebrafish: Effects on survival and long-term effects on response latency and spatial discrimination. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2003, 25, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.D.; Chen, E. Nicotinic involvement in memory function in zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2004, 26, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddins, D.; Petro, A.; Williams, P.; Cerutti, D.T.; Levin, E.D. Nicotine effects on learning in zebrafish: The role of dopaminergic systems. Psychopharmacology 2009, 202, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlai, R. Using zebrafish to unravel the genetics of complex brain disorders. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2012, 12, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, R.J.; Bergner, C.L.; Hart, P.C.; Cachat, J.M.; Canavello, P.R.; Elegante, M.F.; Elkhayat, S.I.; Bartels, B.K.; Tien, A.K.; Tien, D.H.; et al. Understanding behavioral and physiological phenotypes of stress and anxiety in zebrafish. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 205, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakravarty, S.; Reddy, B.R.; Sudhakar, S.R.; Saxena, S.; Das, T.; Meghah, V.; Brahmendra Swamy, C.V.; Kumar, A.; Idris, M.M. Chronic unpredictable stress (CUS)-induced anxiety and related mood disorders in a zebrafish model: Altered brain proteome profile implicates mitochondrial dysfunction. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lau, B.; Bretaud, S.; Huang, Y.; Lin, E.; Guo, S. Dissociation of food and opiate preference by a genetic mutation in zebrafish. Genes Brain Behav. 2006, 5, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darland, T.; Dowling, J.E. Behavioral screening for cocaine sensitivity in mutagenized zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11691–11696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manabe, K.; Dooling, R.J.; Takaku, S. An automated device for appetitive conditioning in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Zebrafish 2013, 10, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Escudero, A.; Vicente-Page, J.; Hinz, R.C.; Arganda, S.; de Polavieja, G.G. idTracker: Tracking individuals in a group by automatic identification of unmarked animals. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwald, D.J.; Eisen, J.S. Headwaters of the zebrafish—Emergence of a new model vertebrate. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulding, M. Circuits controlling vertebrate locomotion: Moving in a new direction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisen, J.S. Zebrafish make a big splash. Cell 1996, 87, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedrich, R.W.; Jacobson, G.A.; Zhu, P. Circuit neuroscience in zebrafish. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, R371–R381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Echevarria, D.J.; Jouandot, D.J.; Toms, C.N. Assessing attention in the zebrafish: Are we there yet? Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 1416–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhija, D.T.; Jagtap, A.G. Studies on sensitivity of zebrafish as a model organism for Parkinson’s disease: Comparison with rat model. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2014, 5, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seredick, S.D.; Van Ryswyk, L.; Hutchinson, S.A.; Eisen, J.S. Zebrafish Mnx proteins specify one motoneuron subtype and suppress acquisition of interneuron characteristics. Neural Dev. 2012, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, Q.; Garver, J.A.; Hukriede, N.A.; Burton, E.A. Generation of a transgenic zebrafish model of Tauopathy using a novel promoter element derived from the zebrafish eno2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 6501–6516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, Y.; Noble, S.; Ekker, M. Modeling neurodegeneration in zebrafish. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2011, 11, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Engeszer, R.E.; Ryan, M.J.; Parichy, D.M. Learned social preference in zebrafish. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, R.F. Mind the fish: Zebrafish as a model in cognitive social neuroscience. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abril-de-Abreu, R.; Cruz, J.; Oliveira, R.F. Social eavesdropping in zebrafish: Tuning of attention to social interactions. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.M.; Nguyen, M.; Wong, K.; Poudel, M.K.; Kalueff, A.V. Developing zebrafish models of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 50, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, J.S.; Singh, B.J. Systems and Methods for Automated Control of Animal Training and Discrimination Learning. U.S. Patent US 10568305, 25 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cervi, A.L.; Poling, K.R.; Higgs, D.M. Behavioral measure of frequency detection and discrimination in the zebrafish, Danio rerio. Zebrafish 2012, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilotta, J.; Saszik, S. The zebrafish as a model visual system. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2001, 19, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleisch, V.C.; Neuhauss, S.C.F. Visual behavior in zebrafish. Zebrafish 2006, 3, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeddies, D.G.; Fay, R.R. Development of the acoustically evoked behavioral response in zebrafish to pure tones. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 1363–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Song, Q.; Yu, D.; Yang, G.; Xia, L.; Su, K.; Shi, H.; Wang, J.; Yin, S. Ontogenetic development of the auditory sensory organ in zebrafish (Danio rerio): Changes in hearing sensitivity and related morphology. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Q.; DeSmidt, A.A.; Tekin, M.; Liu, X.; Lu, Z. Hearing assessment in zebrafish during the first week postfertilization. Zebrafish 2016, 13, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, R.F.; Silva, J.F.; Simões, J.M. Fighting zebrafish: Characterization of aggressive behavior and winner-loser effects. Zebrafish 2011, 8, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocki, L.E.; Ladich, F. The representation of conspecific sounds in the auditory brainstem of teleost fishes. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 2229–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ladich, F.; Bass, A.H. Underwater Sound Generation and Acoustic Reception in Fishes with Some Notes on Frogs. In Sensory Processing in Aquatic Environments; Collin, S.P., Marshall, N.J., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 173–193. ISBN 978-0-387-22628-6. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.; Elegante, M.; Bartels, B.; Elkhayat, S.; Tien, D.; Roy, S.; Goodspeed, J.; Suciu, C.; Tan, J.; Grimes, C.; et al. Analyzing habituation responses to novelty in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 208, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, A.; Wu, N.; Cachat, J.; Hart, P.; Gaikwad, S.; Wong, K.; Utterback, E.; Gilder, T.; Kyzar, E.; Newman, A.; et al. Pharmacological modulation of anxiety-like phenotypes in adult zebrafish behavioral models. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 35, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, C.H. Zebrafish behavioural assays of translational relevance for the study of psychiatric disease. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 22, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.O.; Millington, M.E.; Combe, F.J.; Brennan, C.H. Development and implementation of a three-choice serial reaction time task for zebrafish (Danio rerio). Behav. Brain Res. 2012, 227, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, P.; Khobragade, S.B.; Shingatgeri, V.M.; Rajaram, S.M. Assessment of locomotion behavior in adult Zebrafish after acute exposure to different pharmacological reference compounds. Drug Dev. Ther. 2014, 5, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, M.; Neely, C.B. Effects of sequence length and structure on implicit serial learning. Psychol. Res. 1997, 60, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropepe, V.; Sive, H.L. Can zebrafish be used as a model to study the neurodevelopmental causes of autism? Genes Brain Behav. 2003, 2, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-X.; Li, C.-Y.; Hu, C.-C.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Li, Q.; Xu, X. CRISPR/Cas9-induced shank3b mutant zebrafish display autism-like behaviors. Mol. Autism 2018, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burt de Perera, T. Fish can encode order in their spatial map. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2004, 271, 2131–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bretschneider, F.; van Veen, H.; Teunis, P.F.M.; Peters, R.C.; van den Berg, A.V. Zebrafish can hear sound pressure and particle motion in a synthesized sound field. Anim. Biol. 2013, 63, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruska, K.P.; Ung, U.S.; Fernald, R.D. The African cichlid fish Astatotilapia burtoni uses acoustic communication for reproduction: Sound production, hearing, and behavioral significance. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, A.N.; Sisneros, J.A. The sound world of zebrafish: A critical review of hearing assessment. Zebrafish 2022, 19, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, R.E.; Scholz, L.A.; Constantin, L.; Favre-Bulle, I.; Vanwalleghem, G.C.; Scott, E.K. Broad frequency sensitivity and complex neural coding in the larval zebrafish auditory system. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 1977–1987.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombarte, A.; Yan, H.Y.; Popper, A.N.; Chang, J.S.; Platt, C. Damage and regeneration of hair cell ciliary bundles in a fish ear following treatment with gentamicin. Hear. Res. 1993, 64, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathis, A.; Mamidanna, P.; Cury, K.M.; Abe, T.; Murthy, V.N.; Mathis, M.W.; Bethge, M. DeepLabCut: Markerless pose estimation of user-defined body parts with deep learning. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Ferrero, F.; Bergomi, M.G.; Hinz, R.C.; Heras, F.J.H.; de Polavieja, G.G. idtracker.ai: Tracking all individuals in small or large collectives of unmarked animals. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Restrepo, J.E.; Forero, D.A.; Vargas, R.A. A Review of Freely Available, Open-Source Software for the Automated Analysis of the Behavior of Adult Zebrafish. Zebrafish 2019, 16, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nema, S.; Hasan, W.; Bhargava, A.; Bhargava, Y. A novel method for automated tracking and quantification of adult zebrafish behaviour during anxiety. J. Neurosci. Methods 2016, 271, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likitlersuang, J.; Stephens, G.; Palanski, K.; Ryu, W.S. C. elegans tracking and behavioral measurement. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, e4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, B.J.; Zu, L.; Summers, J.; Asdjodi, S.; Glasgow, E.; Kanwal, J.S. NemoTrainer: Automated Conditioning for Stimulus-Directed Navigation and Decision Making in Free-Swimming Zebrafish. Animals 2023, 13, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13010116
Singh BJ, Zu L, Summers J, Asdjodi S, Glasgow E, Kanwal JS. NemoTrainer: Automated Conditioning for Stimulus-Directed Navigation and Decision Making in Free-Swimming Zebrafish. Animals. 2023; 13(1):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13010116
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Bishen J., Luciano Zu, Jacqueline Summers, Saman Asdjodi, Eric Glasgow, and Jagmeet S. Kanwal. 2023. "NemoTrainer: Automated Conditioning for Stimulus-Directed Navigation and Decision Making in Free-Swimming Zebrafish" Animals 13, no. 1: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13010116
APA StyleSingh, B. J., Zu, L., Summers, J., Asdjodi, S., Glasgow, E., & Kanwal, J. S. (2023). NemoTrainer: Automated Conditioning for Stimulus-Directed Navigation and Decision Making in Free-Swimming Zebrafish. Animals, 13(1), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13010116