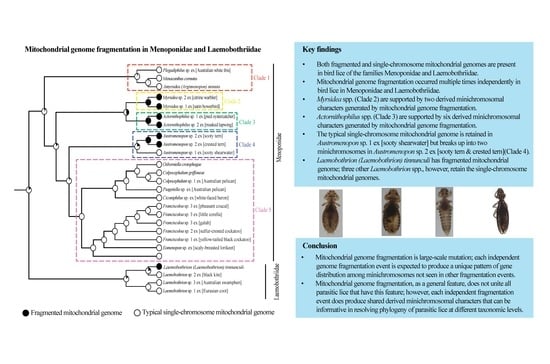
Mitochondrial Genome Fragmentation Occurred Multiple Times Independently in Bird Lice of the Families Menoponidae and Laemobothriidae
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Bird Lice
2.2. DNA Extraction, Mitochondrial Genome Sequencing, and Assembly
2.3. PCR Verification of Mitochondrial Minichromosomes
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bird Lice Have Both Fragmented and Typical Single-Chromosome Mitochondrial Genome Organization
3.2. The Typical Single-Chromosome Mitochondrial Genome Was Retained in Austromenopon sp. 1 ex [Sooty Shearwater] but Broke Up into Two Chromosomes in Austromenopon sp. 2 ex [Sooty Tern and Crested Tern]
3.3. Mitochondrial Karyotype Differs between Two Actornithophilus Species
3.4. The Mitochondrial Genome of Myrsidea sp. 1 ex [Satin Bowerbird] Comprises at Least Four Minichromosomes
3.5. Three Species of Laemobothrion Retained the Typical Single-Chromosome Mitochondrial Genome Organization
3.6. Phylogeny of Menoponidae Lice Inferred with Mitochondrial Genome Sequences
4. Discussion
4.1. Mitochondrial Genome Fragmentation Occurred Multiple Times Independently in the Species of Menoponidae and Laemobothriidae
4.2. Minichromosomal Characters Derived from Mitochondrial Genome Fragmentation Provide Valuable Information for Resolving Phylogenetic Relationships at Different Taxonomic Levels
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Price, R.D.; Clayton, D.; Hellenthal, R.A.; Johnson, K.P.; Palma, R. The Chewing Lice: World Checklist and Biological Overview; Illinois Natural History Survey Special Publication 24; INHS: Champaign, IL, USA, 2003; pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Durden, L.A.; Musser, G.G. The sucking lice (Insecta, Anoplura) of the world: A taxonomic checklist with records of mammalian hosts and geographical distributions. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 1994, 218, 1–90. [Google Scholar]
- De Moya, R.S.; Yoshizawa, K.; Walden, K.K.; Sweet, A.D.; Dietrich, C.H.; Kevin, P.J. Phylogenomics of parasitic and nonparasitic lice (Insecta: Psocodea): Combining sequence data and exploring compositional bias solutions in next generation data sets. Syst. Biol. 2021, 70, 719–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, R.; Kirkness, E.F.; Barker, S.C. The single mitochondrial chromosome typical of animals has evolved into 18 minichromosomes in the human body louse, Pediculus humanus. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 904–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, R.; Zhu, X.-Q.; Barker, S.C.; Herd, K. Evolution of extensively fragmented mitochondrial genomes in the lice of humans. Genome Biol. Evol. 2012, 4, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Barker, S.C.; Shao, R. Substantial variation in the extent of mitochondrial genome fragmentation among blood-sucking lice of mammals. Genome Biol. Evol. 2013, 5, 1298–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.G.; Song, S.; Guo, X.G.; Jin, D.C.; Yang, Q.; Barker, S.C.; Shao, R. Fragmented mitochondrial genomes are present in both major clades of the blood-sucking lice (suborder Anoplura): Evidence from two Hoplopleura rodent lice (family Hoplopleuridae). BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.G.; Song, S.; Jin, D.C.; Guo, X.G.; Shao, R. Fragmented mitochondrial genomes of the rat lice, Polyplax asiatica and Polyplax spinulosa: Intra-genus variation in fragmentation pattern and a possible link between the extent of fragmentation and the length of life cycle. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, S.; Barker, S.C.; Shao, R. Variation in mitochondrial minichromosome composition between blood-sucking lice of the genus Haematopinus that infest horses and pigs. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herd, K.E.; Barker, S.C.; Shao, R. The mitochondrial genome of the chimpanzee louse, Pediculus schaeffi: Insights into the process of mitochondrial genome fragmentation in the blood-sucking lice of great apes. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, R.; Li, H.; Barker, S.C.; Song, S. The mitochondrial genome of the guanaco louse, Microthoracius praelongiceps: Insights into the ancestral mitochondrial karyotype of sucking lice (Anoplura, Insecta). Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.T.; Dong, Y.; Wang, W.; Nie, Y.; Liu, G.H.; Shao, R. Fragmented mitochondrial genomes evolved in opposite directions between closely related macaque louse Pedicinus obtusus and colobus louse Pedicinus badii. Genomics 2020, 112, 4924–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.G.; Dong, Y.; Guo, X.G.; Shao, R. Frequent tRNA gene translocation towards the boundaries with control regions contributes to the highly dynamic mitochondrial genome organization of the parasitic lice of mammals. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Zhao, M.; Shao, R. Fragmented mitochondrial genomes of seal lice (Family Echinophthiriidae) and gorilla louse (Family Pthiridae): Frequent minichromosomal splits and a host switch of lice between seals. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, R.; Barker, S.C.; Li, H.; Song, S.; Poudel, S.; Su, Y. Fragmented mitochondrial genomes in two suborders of parasitic lice of eutherian mammals (Anoplura and Rhynchophthirina, Insecta). Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, F.; Li, H.; Liu, G.H.; Wang, W.; James, P.; Colwell, D.D.; Tran, A.; Gong, S.; Cai, W.; Shao, R. Mitochondrial genome fragmentation unites the parasitic lice of eutherian mammals. Syst. Biol. 2019, 68, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spradling, T.A.; Place, A.C.; Campbell, A.L.; Demastes, J.W. Mitochondrial genome of geomydoecus aurei, a pocket-gopher louse. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.L.; Yoshizawa, K.; Mizukoshi, A.; Whiting, M.F.; Johnson, K.P. Mitochondrial genome deletions and minicircles are common in lice (Insecta: Phthiraptera). BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sweet, A.D.; Johnson, K.P.; Cameron, S.L. Mitochondrial genomes of Columbicola feather lice are highly fragmented, indicating repeated evolution of minicircle-type genomes in parasitic lice. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sweet, A.D.; Johnson, K.P.; Cameron, S.L. Independent evolution of highly variable, fragmented mitogenomes of parasitic lice. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, A.D.; Johnson, K.P.; Cao, Y.; de Moya, R.S.; Skinner, R.K.; Tan, M.; Virrueta Herrera, S.; Cameron, S.L. Structure, gene order, and nucleotide composition of mitochondrial genomes in parasitic lice from Amblycera. Gene 2021, 768, 145312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, R.; Campbell, N.J.; Barker, S.C. Numerous gene rearrangements in the mitochondrial genome of the wallaby louse, Heterodoxus macropus (Phthiraptera). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, S.; Gong, S.; Xu, Y.; Xu, S.; Liang, Y.; Tian, L.; Cai, W.; Li, H.; Song, F. The complete mitochondrial genome of the chicken body louse, Menacanthus cornutus, and evolutionary patterns of extensive gene rearrangements in the mitochondrial genomes of Amblycera (Psocodea: Phthiraptera). Genes 2022, 13, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzey, G.; Knight, F.; Pizzey, S. The Field Guide to the Birds of Australia, 9th ed.; HarperCollins: Sydney, Australia, 2012; pp. 1–608. [Google Scholar]
- Menkhorst, P.; Rogers, D.; Clarke, R.; Davies, J.; Marsack, P.; Franklin, K. The Australian Bird Guide, Revised ed.; CSIRO Publishing: Clayton, VIC, Australia, 2019; pp. 1–566. [Google Scholar]
- Drown, D.M.; Clayton, D.H. Critical evaluation of five methods for quantifying chewing lice (insecta: Phthiraptera). J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crampton-Platt, A.; Yu, D.W.; Zhou, X.; Vogler, A.P. Mitochondrial metagenomics: Letting the genes out of the bottle. GigaScience 2016, 5, s13742-016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, M.; Zaretskaya, I.; Raytselis, Y.; Merezhuk, Y.; McGinnis, S.; Madden, T.L. NCBI BLAST: A better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36 (Suppl. S2), W5–W9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laslett, D.; Canback, B. ARWEN: A program to detect tRNA genes in metazoan mitochondrial nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 172–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowe, T.M.; Eddy, S.R. tRNAscan-SE: A program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abascal, F.; Zardoya, R.; Telford, M.J. TranslatorX: Multiple alignment of nucleotide sequences guided by amino acid translations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W7–W13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talavera, G.; Castresana, J. Improvement of phylogenies after removing divergent and ambiguously aligned blocks from protein sequence alignments. Syst. Biol. 2007, 56, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maddison, W.P.; Maddison, D.R. Mesquite: A Modular System for Evolutionary Analysis. Version 3.81. Available online: https://www.mesquiteproject.org (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Boore, J.L. Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavrov, D.V. Mitochondrial genomes in invertebrate animals. In Molecular Life Sciences; Bell, E., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Covacin, C.; Shao, R.; Cameron, S.L.; Barker, S.C. Extraordinary number of gene rearrangements in the mitochondrial genomes of lice (Phthiraptera: Insecta). Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Louse Species | Host | SRA Biosample Accession Number | Number of Illumina Sequence Reads Obtained | GenBank Accession Number | References | Collection Location | Number of Specimens Used in DNA Extraction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actornithophilus sp. 1 | Pied oystercatcher (Haematopus longirostris) | SAMN29722645 | 19,486,216 | ON417463-67 | Present study | Manly, QLD * | 21 |
| Actornithophilus sp. 2 | Masked lapwing (Vanellus miles) | SAMN29722639 | 20,263,604 | ON380416-21 | Present study | North Aramara, QLD | 30 |
| Amyrsidea (Argimenopon) minuta (Emerson, 1961) | Green peafowl (Pavo muticus) | MH001227 | Song et al., 2019 [16] | Changsha, China | |||
| Austromenopon sp. 1 | Sooty shearwater (Ardenna grisea) | SAMN29722648 | 17,438,954 | ON380415 | Present study | Minyama, QLD | 19 |
| Austromenopon sp. 2 | Sooty tern (Onychoprion fuscatus) | SAMN29722646 | 20,656,938 | ON380413-14 | Present study | Kings Beach, QLD | 20 |
| Austromenopon sp. 2 | Crested tern (Thalasseus bergii) | SAMN29722643 | 15,659,674 | ON380422-23 | Present study | Caloundra, QLD | 39 |
| Ciconiphilus sp. | White-faced heron (Egretta novaehollandiae) | SAMN29722644 | 23,418,092 | OM912467 | Present study | Rothwell, QLD | 31 |
| Colpocephalum sp. 1 | Australian pelican (Pelecanus conspicillatus) | SAMN29722638 | 12,309,898 | ON204017 | Present study | Amity Pt, QLD | 31 |
| Colpocephalum griffoneae (Ansari, 1955) | Himalayan vulture (Gyps himalayensis) | MH001228 | Song et al., 2019 [16] | Changsha, China | |||
| Colpocephalum sp. 2 | Straw-necked ibis (Threskiornis spinicollis) | SAMN29722649 | 15,812,316 | ON204018 | Present study | Beerburrum, QLD | 29 |
| Eomenopon sp. | Scaly-breasted lorikeet (Trichoglossus chlorolepidotus) | SAMN29722636 | 12,065,720 | ON184000 | Present study | Caloundra, QLD | 20 |
| Franciscoloa sp. 1 | Yellow-tailed black cockatoo (Calyptorhynchus funereus) | SAMN29722642 | 15,891,768 | ON016537 | Present study | Curramone, QLD | 30 |
| Franciscoloa sp. 2 | Sulfur-crested cockatoo (Cacatua galerita) | SAMN29722641 | 13,324,866 | ON016538 | Present study | Buderim, QLD | 40 |
| Franciscoloa sp. 3 | Little corella (Cacatua sanguinea) | SAMN29722635 | 9,794,058 | ON303707 | Present study | Moffat Beach, QLD | 50 |
| Franciscoloa sp. 3 | Galah (Eolophus roseicapilla) | SAMN29722640 | 14,514,292 | ON303708 | Present study | Glass House mountains, QLD | 30 |
| Franciscoloa sp. 3 | Pheasant coucal (Centropus phasianinus) | SAMN29722650 | 14,626,494 | ON303709 | Present study | Laceys Creek, QLD | 30 |
| Laemobothrion sp. 1 | Eurasian coot (Fulica atra) | SAMN29722652 | 12,096,816 | OM935763 | Present study | Warana, QLD | 1 |
| Laemobothrion sp. 2 | Black kite (Milvus migrans) | SAMN29722651 | 15,152,282 | OM935762 | Present study | Caloundra, QLD | 1 |
| Laemobothrion sp. 3 | Australian swamphen (Porphyrio porphyrio bellus) | SAMN29722653 | 23,631,838 | OM912466 | Present study | Caloundra, QLD | 1 |
| Laemobothrion (Laemobothrion) tinnunculi (Linnaeus, 1758) | Australian hobby (Falco longipennis) | MW199169 | Sweet et al., 2021 [21] | Australia | |||
| Menacanthus cornutus (Schömmer, 1913) | Red junglefowl (Gallus gallus) | NC062859 | Gong et al., 2022 [23] | Chongqing, China | |||
| Myrsidea sp. 1 | Satin bowerbird (Ptilonorhynchus violaceus) | SAMN29722647 | 25,679,092 | ON417459-60, ON417462, OP271738 | Present study | Maleny, QLD | 20 |
| Myrsidea sp. 2 | Citrine warbler (Myiothlypis luteoviridis) | MW199172-74 | Sweet et al., 2021 [21] | Peru | |||
| Osborniella crotophagae (Stafford, 1943) | Smooth-billed ani (Crotophaga ani) | MW199175 | Sweet et al., 2021 [21] | Panama | |||
| Piagetiella sp. | Australian Pelican (Pelecanus conspicillatus) | SAMN29722637 | 19,903,264 | ON417468 | Present study | Amity Pt, QLD | 14 |
| Plegadiphilus sp. | Australian white ibis (Threskiornis moluccus) | SAMN29722634 | 9,680,062 | ON183999 | Present study | Fraser Coast, QLD | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Y.; Jelocnik, M.; Gillett, A.; Valenza, L.; Conroy, G.; Potvin, D.; Shao, R. Mitochondrial Genome Fragmentation Occurred Multiple Times Independently in Bird Lice of the Families Menoponidae and Laemobothriidae. Animals 2023, 13, 2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13122046
Dong Y, Jelocnik M, Gillett A, Valenza L, Conroy G, Potvin D, Shao R. Mitochondrial Genome Fragmentation Occurred Multiple Times Independently in Bird Lice of the Families Menoponidae and Laemobothriidae. Animals. 2023; 13(12):2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13122046
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Yalun, Martina Jelocnik, Amber Gillett, Ludovica Valenza, Gabriel Conroy, Dominique Potvin, and Renfu Shao. 2023. "Mitochondrial Genome Fragmentation Occurred Multiple Times Independently in Bird Lice of the Families Menoponidae and Laemobothriidae" Animals 13, no. 12: 2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13122046
APA StyleDong, Y., Jelocnik, M., Gillett, A., Valenza, L., Conroy, G., Potvin, D., & Shao, R. (2023). Mitochondrial Genome Fragmentation Occurred Multiple Times Independently in Bird Lice of the Families Menoponidae and Laemobothriidae. Animals, 13(12), 2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13122046