Multi-Locus Sequence Analysis Indicates Potential Cryptic Speciation in the Chigger Mite Neoschoengastia gallinarum (Hatori, 1920) Parasitising Birds in Asia
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
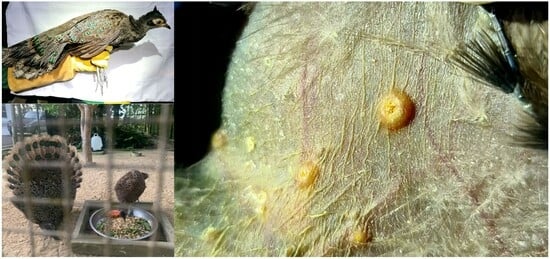
2.1. Study Sites and Chigger Collections
2.2. DNA Extraction from Chiggers
2.3. PCR Amplification and Sequencing of PCR Products
2.4. Sequence Alignment
2.5. Phylogenetic Reconstruction and Haplotype Network
2.6. Species Delimitation Analyses
2.7. Population Genetic and Demographic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification Confirmation and Sequence Characteristics
3.2. Phylogenetic Reconstruction
3.3. Pairwise Distance and Species Delimitation Analysis
3.4. Haplotype Resolution and Network Analysis
3.5. Genetic Differentiation and Gene Flow
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Stekolnikov, A.A.; Waap, H.; Gomes, J.; Antune, T. Chigger mites of the genus Ericotrombidium (Acariformes: Trombiculidae) attacking pets in Europe. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 221, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molín, J.; Asín, J.; Stekolnikov, A.A.; de Miguel, R.; Pérez, M.; Gimeno, M.; Pinczowski, P.; Luján, L. Pathology of trombiculosis caused by Neoschoengastia simonovichi in wild red-legged partridges (Alectoris rufa). J. Comp. Pathol. 2020, 181, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisiri, K.; Linsuwanon, P.; Makepeace, B.L. The chigger microbiome: Big questions in a tiny world. Trends Parasitol. 2023, 39, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.M. The penetration of the host tissue by the harvest mite, Trombicula autumnalis Shaw. Parasitology 1950, 40, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hase, T.; Roberts, L.W.; Hildebrandt, P.K.; Cavanaugh, D.C. Stylostome formation by Leptotrombidium mites (Acari: Trombiculidae). J. Parasitol. 1978, 64, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.M.; Wikel, S.K.; Wrenn, W.J. Host immune responsiveness to the chigger, Eutrombicula cinnabaris. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1988, 82, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Chaisiri, K.; Xia, D.; Armstrong, S.D.; Fang, Y.; Donnelly, M.J.; Kadowaki, T.; McGarry, J.W.; Darby, A.C.; Makepeace, B.L. Genomes of trombidid mites reveal novel predicted allergens and laterally transferred genes associated with secondary metabolism. GigaScience 2018, 7, giy127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, S.E.; Carmichael, K.P.; Rakich, P.M. Trombidiosis-induced dermatitis in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Vet. Pathol. 1997, 34, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.A.; Shama, V.; Knapp, J.F.; Shields, B.J. The summer penile syndrome: Seasonal acute hypersensitivity reaction caused by chigger bites on the penis. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 1998, 14, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, F.; Di Bella, A.; Vercelli, A.; Cornegliani, L. Feline trombiculosis: A retrospective study in 72 cats. Vet. Dermatol. 2013, 24, 535-e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.F. The larval trombiculid mites of South African vertebrates. Ann. Natal. Mus. 1949, 11, 405–486. [Google Scholar]
- Traub, R.; Morrow, M.L. A revision of the chiggers of the subgenus Gahrliepia (Acarina: Trombiculidae). Smithson. Misc. Collect. 1955, 128, 1–88. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, C.E. Chiggers of the genus Euschoengastia (Acarina: Trombiculidae) in North America. Proc. U. S. Natl. Mus. 1956, 106, 85–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanigoshi, L.K.; Loomis, R.B. Genus Hyponeocula (Acarina, Trombiculidae) of western North America. Melanderia 1974, 17, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn, W.J. Notes on the ecology of chiggers (Acarina: Trombiculidae) from Northern Michigan and the description of a new species of Euschoengastia. J. Kansas Entomol. Soc. 1974, 47, 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn, W.J.; Baccus, J.T.; Loomis, R.B. Two new species of North American mites in the genus Euschoengastia (Acarina: Trombiculidae). Southwest Nat. 1976, 21, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sileo, L.; Sievert, P.R.; Samuel, M.D. Causes of mortality of albatross chicks at Midway Atoll. J. Wildl. Dis. 1990, 26, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornelas-Almeida, M.A.; de Oliveira, F.R.B.; da Silva, A.E.; Moreira, E.L.T.; Maia, P.C.C.; Duarte, L.d.F.C.; Murphy, G.; Ayres, M.C.C. Nodular trombiculinosis caused by Apolonia tigipioensis, Torres and Braga (1938), in an ostrich (Struthio camelus) and a house sparrow (Passer domesticus). Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 15, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, I.; Pearson, I.; Dahal, P.; Thomas, N.V.; Roberts, T.; Newton, P.N. Scrub typhus ecology: A systematic review of Orientia in vectors and hosts. Parasite Vectors 2019, 12, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Womersley, H. The scrub-typhus and scrub-itch mites (Trombiculidae, Acarina) of the Asiatic-Pacific region. Rec. S. Aust. Mus. 1952, 10, 438–673. [Google Scholar]
- Nadchatram, M.; Upham, R.W., Jr. Two new larval trombiculid mites (Acarina, Trombiculidae) collected from ground holes and birds in Malaysia. J. Med. Entomol. 1966, 3, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassini-Silva, R.; Jacinavicius, F.D.C.; Welbourn, C.; Huang-Bastos, M.; Ochoa, R.; Barros-Battesti, D.M. Taxonomic notes on Neoschoengastia esorhina Brennan, 1971 (Trombidiformes: Trombiculidae), a chigger species from Brazil. Int. J. Acarol. 2021, 47, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekolnikov, A.A. A checklist of chigger mites (Acariformes: Trombiculidae) of Southeast Asia. Zootaxa 2021, 4913, 1–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeruham, I.; Rosen, S.; Hadani, A.; Braverman, Y. Arthropod parasites of Nubian ibexes (Capra ibex nubiana) and gazelles (Gazella gazella) in Israel. Vet. Parasitol. 1999, 83, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, K.; Krasnov, B.R.; Goff, L.; Matthee, S. Infracommunity dynamics of chiggers (Trombiculidae) parasitic on a rodent. Parasitology 2015, 142, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, S.E.; Price, M.A.; Graham, O.H. Biology and economic importance of the chigger Neoschongastia americana on Turkeys. J. Econ. Entomol. 1969, 62, 872–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaki, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Ishizu, K.; Uchikawa, K. Fatal cases of pheasants Phasianus colchicus var. tenebrosus, heavily infested with Neoschoengastia shiraii. Jpn. J. Sanit. Zool. 1991, 42, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.C.; Ho, C.C.; Kuo, M.C.; Robbins, R.G. Case Report: Trombidiasis in native chicken (Prostigmata: Trombiculidae). Taiwan Vet. J. 2004, 30, 301–306. [Google Scholar]
- Koosakulnirand, S.; Rajasegaran, P.; Alkathiry, H.A.; Chaisiri, K.; Round, P.D.; Eiamampai, K.; Khusaini, M.K.S.A.; Ramji, M.F.S.; Abubakar, S.; Ya’cob, Z.; et al. On the taxonomy of chigger mites (Acariformes: Trombiculidae) parasitizing birds in Thailand and Malaysia, with the description of a new species. Acarologia 2023, 64, 1109–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, Z.-X.; Tao, J.-M.; Qin, J.-P.; Lu, J.-P.; Lin, R.-Q.; Wang, L.-M.; Weng, Y.-B.; Tan, Z.-J. Characterization of Neoschoengastia gallinarum from subtropical China by rDNA and identification of two genotypes based on mitochondrial cox1. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 3339–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumlert, R.; Chaisiri, K.; Anantatat, T.; Stekolnikov, A.A.; Morand, S.; Prasartvit, A.; Makepeace, B.L.; Sungvornyothin, S.; Paris, D.H. Autofluorescence microscopy for paired-matched morphological and molecular identification of individual chigger mites (Acari: Trombiculidae), the vectors of scrub typhus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Choi, K.S. Genetic variation of chigger mites in the Republic of Korea. Entomol. Res. 2022, 52, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajkowska, P.; Mąkol, J. Parasitism, seasonality, and diversity of trombiculid mites (Trombidiformes: Parasitengona, Trombiculidae) infesting bats (Chiroptera) in Poland. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2022, 86, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, M.; Takada, N.; Noda, S.; Takahashi, M.; Matsutani, M.; Kageyama, D.; Ebihara, H. Genetic variation of Leptotrombidium (Acari: Trombiculidae) mites carrying Orientia tsutsugamushi, the bacterial pathogen causing scrub typhus. J. Parasitol. 2023, 109, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajkowska, P.; Postawa, T.; Mąkol, J. Let me know your name: A study of chigger mites (Acariformes: Trombiculidae) associated with the edible dormouse (Glis glis) in the Carpathian–Balkan distribution gradient. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2023, 91, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatori, J. “Tsutsugamushi” disease in Formosa (5th Communication). Taiwan Igakkai Zasshi (J. Formosa Med. Soc.) 1920, 209, 317–352. [Google Scholar]
- Chaisiri, K.; Kittiyakan, A.; Kumlert, R.; Lajaunie, C.; Makaew, P.; Morand, S.; Paladsing, Y.; Tanita, M.; Thinphovong, C. A social-ecological and One Health observatory: Ten years of collaborative studies in Saen Thong (Nan, Thailand). One Health Cases 2023, ohcs20230008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folmer, O.; Hoeh, W.R.; Black, M.B.; Vrijenhoek, R.C. Conserved primers for PCR amplification of mitochondrial DNA from different invertebrate phyla. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, J.M.; Ashram, S.E.; Alouffi, A.; Zhang, Y.; Weng, Y.B.; Lin, R.Q. Population genetic structure of Neoschoengastia gallinarum in South China based on mitochondrial DNA markers. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 2793–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. In Nucleic Acids Symposium Series; Information Retrieval Ltd.: London, UK, 1999; pp. 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The CLUSTAL_X Windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swoford, D.L. PAUP: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony Version 4; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, M.A. Simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. JModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. The CIPRES science gateway: A community resource for phylogenetic analyses. In Proceedings of the TeraGrid 2011 Conference: Extreme Digital Discovery, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–21 July 2011; Volume 41, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandelt, H.J.; Forster, P.; Röhl, A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clement, M.; Snell, Q.; Walke, P.; Posada, D.; Crandall, K. TCS: Estimating gene genealogies. In Proceedings of the 16th International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium, Ft. Lauderdale, FL, USA, 15–19 April 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Leigh, J.W.; Bryant, D. POPART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puillandre, N.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G. ASAP: Assemble species by automatic partitioning. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puillandre, N.; Lambert, A.; Brouillet, S.; Achaz, G.J.M.E. ABGD, Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery for primary species delimitation. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 1864–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapli, P.; Lutteropp, S.; Zhang, J.; Kobert, K.; Pavlidis, P.; Stamatakis, A.; Flouri, T. Multi-rate Poisson tree processes for single-locus species delimitation under maximum likelihood and Markov chain Monte Carlo. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 1630–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, T.; Barraclough, T.G. Delimiting species using single-locus data and the Generalized Mixed Yule Coalescent approach: A revised method and evaluation on simulated data sets. Syst. Biol. 2013, 62, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulpeau, A.; Penel, B.; Maggia, M.E.; Marchán, D.F.; Steinke, D.; Hedde, M.; Decaëns, T. OTU delimitation with earthworm DNA barcodes: A comparison of methods. Diversity 2022, 14, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.; Vaughan, T.G.; Barido-Sottani, J.; Duchêne, S.; Fourment, M.; Gavryushkina, A.; Heled, J.; Jones, G.; Kühnert, D.; De Maio, N.; et al. BEAST 2.5: An advanced software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES science gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the 2010 Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Paradis, E.; Schliep, K. ape 5.0: An environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in R. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinno, A. Package ‘Paran’ (R package Version 1.5.2). Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/paran/paran.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2024).
- Michonneau, F.; Bolker, B.; Holder, M.; Lewis, P.; O’Meara, B. Package ‘rncl’: An Interface to the Nexus Class Library (R Package Version 0.8.3). Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/rncl/rncl.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2024).
- Ezard, T.; Fujisawa, T.; Barraclough, T.G. splits: SPecies’ LImits by Threshold Statistics (R Package Version 1.0-14/r31). Available online: https://r-forge.r-project.org/projects/splits/ (accessed on 16 March 2024).
- Rozas, J.; Ferrer-Mata, A.; Sánchez-DelBarrio, J.C.; Guirao-Rico, S.; Librado, P.; Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. DnaSP 6: DNA Sequence Polymorphism Analysis of Large Data Sets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 3299–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Laval, G.; Schneider, S. Arlequin (version 3.5): An integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol. Bioinform. Online 2007, 23, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Slatkin, M. Inbreeding coefficients and coalescence times. Genet Res. 1991, 58, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Smouse, P.E.; Quattro, J.M. Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distances among DNA haplotypes: Application to human mitochondrial DNA restriction data. Genetics 1992, 131, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domrow, R.; Nadchatram, M. XLIII Neoschongastia in Malaya (Acarina, Trombiculidae). In: Macdonald, WW, editor. Malaysian Parasites XXXV-XLIX. Studies from the Institute for Medical Research. Kuala Lumpur Gov. Fed. Malaya 1960, 29, 185–193. [Google Scholar]
- Bickford, D.; Lohman, D.J.; Sodhi, N.S.; Ng, P.K.; Meier, R.; Winker, K.; Das, I. Cryptic species as a window on diversity and conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struck, T.H.; Feder, J.L.; Bendiksby, M.; Birkeland, S.; Cerca, J.; Gusarov, V.I.; Dimitrov, D. Finding evolutionary processes hidden in cryptic species. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoracka, A.; Magalhaes, S.; Rector, B.G.; Kuczyński, L. Cryptic speciation in the Acari: A function of species lifestyles or our ability to separate species? Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2015, 67, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, H.S.; Lim, P.E.; Tan, J.; Song, S.L.; Suana, I.W.; Eamsobhana, P. Multigene phylogeography of Bactrocera caudata (Insecta: Tephritidae): Distinct genetic lineages in Northern and Southern hemispheres. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.W.; Jacobson, D.J.; Kroken, S.; Kasuga, T.; Geiser, D.M.; Hibbett, D.S.; Fisher, M.C. Phylogenetic species recognition and species concepts in fungi. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2000, 31, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, N.A.; Nordborg, M. Genealogical trees, coalescent theory and the analysis of genetic polymorphisms. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2000, 3, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khafaji, A.M.; Clegg, S.R.; Pinder, A.C.; Luu, L.; Hansford, K.M.; Seelig, F.; Dinnis, R.E.; Margos, G.; Medlock, J.M.; Feil, E.J.; et al. Multi-locus sequence typing of Ixodes ricinus and its symbiont Candidatus Midichloria mitochondrii across Europe reveals evidence of local co-cladogenesis in Scotland. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghamdi, S.Q.; Low, V.L.; Alkathiry, H.A.; Alagaili, A.N.; McGarry, J.W.; Makepeace, B.L. Automatic barcode gap discovery reveals diverse clades of Rhipicephalus spp. and Haemaphysalis spp. ticks from small mammals in Asir, Saudi Arabia. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitencourth, K.; Amorim, M.; Oliveira, S.V.D.; Gazêta, G.S. Amblyomma aureolatum genetic diversity and population dynamics are not related to spotted fever epidemiological scenarios in Brazil. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páez-Triana, L.; Muñoz, M.; Herrera, G.; Moreno-Pérez, D.A.; Tafur-Gómez, G.A.; Montenegro, D.; Patarroyo, M.A.; Paniz-Mondolfi, A. Genetic diversity and population structure of Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato across different regions of Colombia. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.; Koskella, B.; Schaack, S. Mutation pressure and the evolution of organelle genomic architecture. Science 2006, 311, 1727–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharbrough, J.; Bankers, L.; Cook, E.; Fields, P.D.; Jalinsky, J.; McElroy, K.E.; Neiman, M.; Logsdon, J.M.; Boore, J.L. Single-molecule sequencing of an animal mitochondrial genome reveals chloroplast-like architecture and repeat-mediated recombination. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2023, 40, msad007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoracka, A.; Kuczyński, L.; de Mendonça, R.S.; Dabert, M.; Szydło, W.; Knihinicki, D.; Truol, G.; Navia, D. Cryptic species within the wheat curl mite Aceria tosichella (Keifer) (Acari: Eriophyoidea), revealed by mitochondrial, nuclear, and morphometric data. Invert. Syst. 2012, 26, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, J.; Currie, D.C. Identification of Nearctic black flies using DNA barcodes (Diptera: Simuliidae). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramual, P.; Adler, P.H. DNA barcoding of tropical black flies (Diptera: Simuliidae) of Thailand. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 14, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hew, Y.X.; Ya’cob, Z.; Adler, P.H.; Chen, C.D.; Lau, K.W.; Sofian-Azirun, M.; Muhammad-Rasul, A.H.; Putt, Q.Y.; Izwan-Anas, N.; Hadi, U.K.; et al. DNA barcoding of black flies (Diptera: Simuliidae) in Indonesia. Parasites Vectors 2023, 16, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramual, P.; Simwisat, K.; Martin, J. Identification and reassessment of the specific status of some tropical freshwater midges (Diptera: Chironomidae) using DNA barcode data. Zootaxa 2016, 4072, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopman, W.J.M.; Li, Y.; Coart, E.; Van de Weg, W.E.; Vosman, B.; Roldán-Ruiz, I.; Smulders, M.J.M. Linked vs. unlinked markers: Multilocus microsatellite haplotype-sharing as a tool to estimate gene flow and introgression. Mol. Ecol. 2007, 16, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. Intraspecific gene genealogies: Trees grafting into networks. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2001, 16, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Mai, J.-W.; Yu, B.-J.; Hu, H.-X.; Yuan, L.; Jashenko, R.; Ji, R. Study on the genetic differentiation of geographic populations of Calliptamus italicus (Orthoptera: Acrididae) in Sino-Kazakh border areas based on mitochondrial COI and COII genes. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 1912–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacinavicius, F.C.; Bassini-Silva, R.; Muñoz-Leal, S.; Welbourn, C.; Ochoa, R.; Labruna, M.B.; Barros-Battesti, D.M. Molecular detection of Rickettsia genus in chigger mites (Trombidiformes: Trombiculidae) collected on small mammals in southeastern Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2019, 28, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.W.; Ha, N.Y.; Ryu, B.; Bang, J.H.; Song, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, G.; Oh, M.D.; Cho, N.H.; Lee, J.K. Urbanization of scrub typhus disease in South Korea. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramual, P.; Kongim, B.; Nanork, P. Phylogeography of Simulium siamense Takaoka and Suzuki complex (Diptera: Simuliidae) in Thailand. Entomol. Sci. 2011, 14, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.H.; Luan, F.G.; Zhang, D.M.; Chen, M.J.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.Z. Genetic differentiation of Isaria farinosa populations in Anhui Province of East China. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 22, 3039–3046. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Wildlife and National Parks (PERHILITAN). Laws of Malaysia, Act 716, Wildlife Conservation Act 2010. Available online: https://storage.unitedwebnetwork.com/files/478/2bcd898fbf196a7cc36b99572fbc3a70.pdf (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- BirdLife International. Lophura rufa. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020: E.T22727445A184588512. 2020. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22727445/184588512 (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- BirdLife International. Polyplectron inopinatum. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2023: E.T22679365A218821910. 2016. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22679365/218821910 (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- BirdLife International. Polyplectron malacense. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2022: E.T22679385A137837773. 2022. Available online: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22679385/137837773 (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- Savini, T.; Namkhan, M.; Sukumal, N. Conservation status of Southeast Asian natural habitat estimated using Galliformes spatio-temporal range decline. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 29, e01723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corder, J.; Davison, G. Captive breeding challenges posed by Malaysian and Bornean Peacock-pheasants (Polyplectron malacense and P. schleiermacheri). Zoo Biol. 2021, 40, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniuszko, H.; Zaleśny, G.; Mąkol, J. Host-associated differences in morphometric traits of parasitic larvae Hirsutiella zachvatkini (Actinotrichida: Trombiculidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2015, 67, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungvornyothin, S.; Kumlert, R.; Paris, D.H.; Prasartvit, A.; Sonthayanon, P.; Apiwathnasorn, C.; Morand, S.; Stekolnikov, A.A.; Sumruayphol, S. Geometric morphometrics of the scutum for differentiation of trombiculid mites within the genus Walchia (Acariformes: Prostigmata: Trombiculidae), a probable vector of scrub typhus. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2019, 10, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariou, M.; Duret, L.; Charlat, S. The global impact of Wolbachia on mitochondrial diversity and evolution. J. Evol. Biol. 2017, 30, 2204–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Country | Population Code | Locality | Coordinates | Habitat Type | Host Species | Chigger ID | GenBank Accession No. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COX1 | ITS2 | 18S | |||||||
| Peninsular Malaysia | SWCC | Sungkai Wildlife Conservation Centre, Perak | E101.36623, N4.06430 | Sanctuary | Lophura rufa | SWX3 | OR632279 | OR636401 | OR632359 |
| Polyplectron inopinatum | SWX10 | OR632280 | OR636402 | OR632360 | |||||
| P. inopinatum | SWX12 | OR632281 | OR636403 | OR632361 | |||||
| P. inopinatum | SWX13 | OR632282 | OR636404 | OR632362 | |||||
| P. inopinatum | SWX14 | OR632283 | OR636405 | OR632363 | |||||
| P. inopinatum | SWX15 | OR632284 | OR636406 | OR632364 | |||||
| P. inopinatum | SWX19 | OR632285 | OR636407 | OR632365 | |||||
| P. inopinatum | SWX21 | OR632286 | OR636408 | OR632366 | |||||
| P. inopinatum | SWX22 | OR632287 | OR636409 | OR632367 | |||||
| P. inopinatum | SWX23 | OR632288 | OR636410 | OR632368 | |||||
| P. inopinatum | SWX37 | OR632289 | OR636411 | OR632369 | |||||
| P. inopinatum | SWX40 | OR632290 | OR636412 | OR632370 | |||||
| L. rufa | SWX43 | OR632291 | OR636413 | OR632371 | |||||
| BJV | Bestari Jaya Village, Selangor | E101.41022, N3.37801 | Village | Gallus gallus domesticus | KPGX5 | OR632292 | OR636414 | OR632372 | |
| G. gallus domesticus | KPGX6 | OR632293 | OR636415 | OR632373 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | KPGX9 | OR632294 | OR636416 | OR632374 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | KPGX10 | OR632295 | OR636417 | OR632375 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | KPGX11 | OR632296 | OR636418 | OR632376 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | KPGX18 | OR632297 | OR636419 | OR632377 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | KPGX19 | OR632298 | OR636420 | OR632378 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | KPGX20 | OR632299 | OR636421 | OR632379 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | KPGX21 | OR632300 | OR636422 | OR632380 | |||||
| JWCC | Jemaluang Wildlife Conservation Centre, Johor | E103.85297, N2.29136 | Sanctuary | L. rufa | JWX3 | OR632301 | OR636423 | OR632381 | |
| Polyplectron malacense | JWX17 | OR632302 | OR636424 | OR632382 | |||||
| P. malacense | JWX18 | OR632303 | OR636425 | OR632383 | |||||
| P. malacense | JWX20 | OR632304 | OR636426 | OR632384 | |||||
| KTP | Kota Tinggi Plantation, Johor | E103.86604, N2.03023 | Forest | G. gallus | KTX7 | OR632305 | OR636427 | OR632385 | |
| G. gallus | KTX8 | OR632306 | OR636428 | OR632386 | |||||
| G. gallus | UMPX2 | OR632307 | OR636429 | OR632387 | |||||
| G. gallus | CHX2 | OR632308 | OR636430 | OR632388 | |||||
| Thailand | BNAN | Ban Huay Muang and Ban Santisuk, Saen Thong subdistrict, Tha Wang Pha, Nan | E100.71897, N19.13999; E100.69891, N19.12957 | Village | G. gallus domesticus | BNANX2 | OR632309 | OR636431 | OR632389 |
| G. gallus domesticus | BNANX8 | OR632310 | OR636432 | OR632390 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | BNANX9 | OR632311 | OR636433 | OR632391 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | BNANX10 | OR632312 | OR636434 | OR632392 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | BNANX11 | OR632313 | OR636435 | OR632393 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | BNANX12 | OR632314 | OR636436 | OR632394 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | BNANX13 | OR632315 | OR636437 | OR632395 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | BNANX14 | OR632316 | OR636438 | OR632396 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | BNANX15 | OR632317 | OR636439 | OR632397 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | BNANX16 | OR632318 | OR636440 | OR632398 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | BNANX17 | OR632319 | OR636441 | OR632399 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | BNANX19 | OR632320 | OR636442 | OR632400 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | BNANX20 | OR632321 | OR636443 | OR632401 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | BNANX21 | OR632322 | OR636444 | OR632402 | |||||
| G. gallus domesticus | BNANX22 | OR632323 | OR636445 | OR632403 | |||||
| Morphometry Measurements (µm) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AW | PW | SB | ASB | PSB | AP | AM | AL | PL | S | H | IP | |
| Peninsular Malaysia | ||||||||||||
| n = 11 | ||||||||||||
| Mean | 52 | 67 | 42 | 21 | 25 | 28 | 30 | 43 | 39 | 26 | 43 | 686 |
| Min | 48 | 64 | 39 | 17 | 24 | 27 | 25 | 38 | 36 | 23 | 39 | 625 |
| Max | 60 | 74 | 44 | 25 | 30 | 31 | 34 | 48 | 46 | 31 | 49 | 704 |
| Thailand | ||||||||||||
| n = 7 | ||||||||||||
| Mean | 52 | 69 | 43 | 21 | 25 | 30 | 28 | 44 | 42 | 24 | 43 | 713 |
| Min | 49 | 63 | 41 | 19 | 24 | 28 | 25 | 41 | 38 | 18 | 39 | 701 |
| Max | 53 | 74 | 45 | 23 | 27 | 31 | 32 | 48 | 46 | 34 | 46 | 726 |
| Mann–Whitney U-test | ||||||||||||
| U | 36.000 | 28.500 | 30.500 | 37.000 | 36.000 | 17.000 | 27.000 | 32.000 | 22.000 | 19.000 | 33.500 | 1.500 |
| Z | −0.236 | −0.924 | −0.748 | −0.139 | −0.235 | −1.993 | −1.049 | −0.596 | −1.507 | −1.805 | −0.457 | −3.361 |
| P | 0.860 | 0.375 | 0.479 | 0.930 | 0.860 | 0.056 | 0.328 | 0.596 | 0.151 | 0.085 | 0.659 | <0.001 * |
| Hap | N. gallinarum Individuals from Each Study Region (n) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peninsular Malaysia | Thailand | ||||
| SWCC (13) | BJV (9) | JWCC (4) | KTP (4) | BNAN (15) | |
| 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 5 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 4 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Total hap | 5 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Source of Variation | d.f. | Sum of Square | Variance Components | Variation (%) | Fixation Index (Φ) | Significance Test (p) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among groups | 1 | 442.689 | 22.02220 | 96.41 | 0.96407 | 0.197 |
| Among populations within groups | 3 | 4.528 | 0.11737 | 0.51 | 0.14299 | 0.031 * |
| Within population | 40 | 28.138 | 0.70346 | 3.08 | 0.96920 | 0.00 * |
| Populations | Distance (km) | Migrant per Generation (Nm) | Population Subdivision (FST) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWCC | BJV | 108 | 1.51 | 0.14189 |
| SWCC | JWCC | 499 | 0.72 | 0.25882 |
| SWCC | KTP | 525 | 2.78 | 0.08247 |
| SWCC | BNAN | 2081 | 0.01 | 0.96553 |
| BJV | JWCC | 421 | 0.46 | 0.35294 |
| BJV | KTP | 437 | −6.38 | −0.04082 |
| BJV | BNAN | 2166 | 0.01 | 0.97279 |
| JWCC | KTP | 33 | 2.00 | 0.11111 |
| JWCC | BNAN | 2552 | 0.00 | 0.98168 |
| KTP | BNAN | 2598 | 0.01 | 0.97093 |
| Whole population | 0.02 | 0.93312 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajasegaran, P.; Koosakulnirand, S.; Tan, K.-K.; Khoo, J.J.; Suliman, Y.; Mansor, M.S.; Ahmad Khusaini, M.K.S.; AbuBakar, S.; Chaisiri, K.; Morand, S.; et al. Multi-Locus Sequence Analysis Indicates Potential Cryptic Speciation in the Chigger Mite Neoschoengastia gallinarum (Hatori, 1920) Parasitising Birds in Asia. Animals 2024, 14, 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060980
Rajasegaran P, Koosakulnirand S, Tan K-K, Khoo JJ, Suliman Y, Mansor MS, Ahmad Khusaini MKS, AbuBakar S, Chaisiri K, Morand S, et al. Multi-Locus Sequence Analysis Indicates Potential Cryptic Speciation in the Chigger Mite Neoschoengastia gallinarum (Hatori, 1920) Parasitising Birds in Asia. Animals. 2024; 14(6):980. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060980
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajasegaran, Praveena, Sirikamon Koosakulnirand, Kim-Kee Tan, Jing Jing Khoo, Youseuf Suliman, Mohammad Saiful Mansor, Mohd K. S. Ahmad Khusaini, Sazaly AbuBakar, Kittipong Chaisiri, Serge Morand, and et al. 2024. "Multi-Locus Sequence Analysis Indicates Potential Cryptic Speciation in the Chigger Mite Neoschoengastia gallinarum (Hatori, 1920) Parasitising Birds in Asia" Animals 14, no. 6: 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060980
APA StyleRajasegaran, P., Koosakulnirand, S., Tan, K.-K., Khoo, J. J., Suliman, Y., Mansor, M. S., Ahmad Khusaini, M. K. S., AbuBakar, S., Chaisiri, K., Morand, S., Ya’cob, Z., & Makepeace, B. L. (2024). Multi-Locus Sequence Analysis Indicates Potential Cryptic Speciation in the Chigger Mite Neoschoengastia gallinarum (Hatori, 1920) Parasitising Birds in Asia. Animals, 14(6), 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14060980