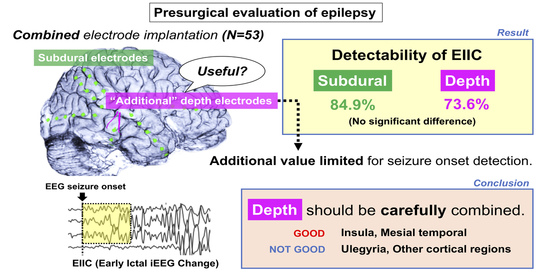
Single-Institutional Experience of Chronic Intracranial Electroencephalography Based on the Combined Usage of Subdural and Depth Electrodes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Presurgical Comprehensive Epilepsy Evaluations
2.3. Electrode Implantation
2.4. iEEG Monitoring
2.5. Resective Surgery
2.6. Surgical Outcome
2.7. Etiology
2.8. Factors Related to the Detectability of EIIC
2.9. Factors Related to the Seizure Freedom
2.10. Impact of Intracranial EEG on Surgical Strategy in the Patients with Focal MRI Lesion
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of Patients
3.2. Electrode Implantation
3.3. Resective Surgery
3.4. Surgical Outcome
3.5. Detectability of EIIC
3.6. Morphological Patterns of EIIC
3.7. Factors Associated with Detectability of EIIC and LVFA
3.7.1. Etiology
3.7.2. Suspected Temporal Lobe Epileptogenic Zone
3.7.3. Other Factors
3.8. Association between the Detectability of EIIC and Seizure Freedom
3.9. Factors Related to the Chance of Seizure Freedom
4. Discussion
4.1. Significance of Adding Depth Electrodes to Subdural Electrode Implantation in Detection of EIIC
4.2. Etiology Unsuitable for Additional Depth Electrodes
4.3. Association with Seizure Outcome
4.4. Exploration of Suspected TLE
4.5. Advantages and Limitations of Combined Electrode Implantation
4.6. Limitation of Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- González-Martínez, J.; Bulacio, J.; Thompson, S.; Gale, J.; Smithason, S.; Najm, I.; Bingaman, W. Technique, results, and complications related to robot-assisted Stereoelectroencephalography. Neurosurgery 2016, 78, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alomar, S.; Mullin, J.P.; Smithason, S.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J. Indications, technique, and safety profile of insular stereoelectroencephalography electrode implantation in medically intractable epilepsy. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 128, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Mullin, J.; Vadera, S.; Bulacio, J.; Hughes, G.; Jones, S.; Enatsu, R.; Najm, I. Stereotactic placement of depth electrodes in medically intractable epilepsy. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 120, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, F.; Rizzi, M.; Vignati, E.; Cossu, M.; Castana, L.; d’Orio, P.; Revay, M.; Costanza, M.D.; Tassi, L.; Mai, R.; et al. Stereoelectroencephalography: Retrospective analysis of 742 procedures in a single centre. Brain 2019, 142, 2688–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedegärd, E.; Bjellvi, J.; Edelvik, A.; Rydenhag, B.; Flink, R.; Malmgren, K. Complications to invasive epilepsy surgery workup with subdural and depth electrodes: A prospective population-based observational study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mullin, J.P.; Shriver, M.; Alomar, S.; Najm, I.; Bulacio, J.; Chauvel, P.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J. Is SEEG safe? A systematic review and meta-analysis of stereo-electroencephalography-related complications. Epilepsia 2016, 57, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perucca, P.; Dubeau, F.; Gotman, J. Intracranial electroencephalographic seizure-onset patterns: Effect of underlying pathology. Brain 2014, 137, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieser, H.G.; Blume, W.T.; Fish, D.; Goldensohn, E.; Hufnagel, A.; King, D.; Sperling, M.R.; Lüders, H.; Pedley, T.A.; Commission on Neurosurgery of the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE). Proposal for a new classification of outcome with respect to epileptic seizures following epilepsy surgery. Epilepsia 2001, 42, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blume, W.T.; Kaibara, M. The start-stop-start phenomenon of subdurally recorded seizures. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1993, 86, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchukhidze, G.; Unterberger, I.; Dobesberger, J.; Embacher, N.; Walser, G.; Haberlandt, E.; Gotwald, T.; Maier, H.; Ortler, M.; Felber, S. Electroclinical and imaging findings in ulegyria and epilepsy: A study on 25 patients. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, Y.; Ikegaya, N.; Iijima, K.; Kimura, Y.; Muraoka, N.; Kaneko, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Iwasaki, M. Is intracranial electroencephalography useful for planning resective surgery in intractable epilepsy with ulegyria? J. Neurosurg. 2019, 25, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.A.; Spencer, D.D.; Spencer, S.S. Intracranial EEG seizure-onset patterns in neocortical epilepsy. Epilepsia 2000, 41, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lagarde, S.; Buzori, S.; Trebuchon, A.; Carron, R.; Scavarda, D.; Milh, M.; McGonigal, A.; Bartolomei, F. The repertoire of seizure onset patterns in human focal epilepsies: Determinants and prognostic values. Epilepsia 2019, 60, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Sandy, S.; Wiebe, S. Ictal onset on intracranial EEG: Do we know it when we see it? State of the evidence. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorfer, C.; Czech, T.; Aull-Watschinger, S.; Baumgartner, C.; Jung, R.; Kasprian, G.; Novak, K.; Pirker, S.; Seidl, B.; Stefanits, H.; et al. Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy: Long-term seizure outcome of patients primarily treated with transsylvian selective amygdalohippocampectomy. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dupont, S.; Tanguy, M.L.; Clemenceau, S.; Adam, C.; Hazemann, P.; Baulac, M. Long-term prognosis and psychosocial outcomes after surgery for MTLE. Epilepsia 2006, 47, 2115–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiebe, S.; Blume, W.T.; Girvin, J.P.; Eliasziw, M.; Effectiveness and Efficiency of Surgery for Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Study Group. A randomized, controlled trial of surgery for temporal-lobe epilepsy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Tisi, J.; Bell, G.S.; Peacock, J.L.; McEvoy, A.W.; Harkness, W.F.; Sander, J.W.; Duncan, J.S. The long-term outcome of adult epilepsy surgery, patterns of seizure remission, and relapse: A cohort study. Lancet 2011, 378, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Téllez-Zenteno, J.F.; Dhar, R.; Wiebe, S. Long-term seizure outcomes following epilepsy surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain 2005, 128, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, D.; Stavem, K. Long-term seizure outcome of surgery versus no surgery for drug-resistant partial epilepsy: A review of controlled studies. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba, C.; Rheims, S.; Minotti, L.; Guénot, M.; Hoffmann, D.; Chabardès, S.; Isnard, J.; Kahane, P.; Ryvlin, P. Temporal plus epilepsy is a major determinant of temporal lobe surgery failures. Brain 2016, 139, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barba, C.; Minotti, L.; Job, A.S.; Kahane, P. The Insula in Temporal Plus Epilepsy. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2017, 34, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, C.; Barbati, G.; Minotti, L.; Hoffmann, D.; Kahane, P. Ictal clinical and scalp-EEG findings differentiating temporal lobe epilepsies from temporal ‘plus’ epilepsies. Brain 2007, 130, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diehl, B.; Lüders, H.O. Temporal lobe epilepsy: When are invasive recordings needed? Epilepsia 2000, 41 (Suppl. 3), S61–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enatsu, R.; Bulacio, J.; Najm, I.; Wyllie, E.; So, N.K.; Nair, D.R.; Foldvary-Schaefer, N.; Bingaman, W.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J. Combining stereo-electroencephalography and subdural electrodes in the diagnosis and treatment of medically intractable epilepsy. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 1441–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, K.; Otsubo, H. Stereoelectroencephalography: Indication and efficacy. Neurol. Med. Chir. (Tokyo) 2017, 57, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reinacher, P.C.; Altenmüller, D.M.; Krüger, M.T.; Schulze-Bonhage, A.; Urbach, H.; Trippel, M.; Coenen, V.A.; Delev, D. Simultaneous frame-assisted stereotactic placement of subdural grid electrodes and intracerebral depth electrodes. J. Neurol. Surg. Part A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2019, 80, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surbeck, W.; Bouthillier, A.; Weil, A.G.; Crevier, L.; Carmant, L.; Lortie, A.; Major, P.; Nguyen, D.K. The combination of subdural and depth electrodes for intracranial EEG investigation of suspected insular (perisylvian) epilepsy. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, S.S.; Spencer, D.D.; Williamson, P.D.; Mattson, R. Combined depth and subdural electrode investigation in uncontrolled epilepsy. Neurology 1990, 40, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, M.R.; O’Connor, M.J. Comparison of depth and subdural electrodes in recording temporal lobe seizures. Neurology 1989, 39, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, E.; Zentner, J.; van Roost, D.; Hufnagel, A.; Elger, C.E.; Schramm, J. Subdural and depth electrodes in the presurgical evaluation of epilepsy. Acta Neurochir. (Wien) 1994, 128, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagahama, Y.; Schmitt, A.J.; Nakagawa, D.; Vesole, A.S.; Kamm, J.; Kovach, C.K.; Hasan, D.; Granner, M.; Dlouhy, B.J.; Howard, M.A.; et al. Intracranial EEG for seizure focus localization: Evolving techniques, outcomes, complications, and utility of combining surface and depth electrodes. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 130, 1180–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bulacio, J.C.; Jehi, L.; Wong, C.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Kotagal, P.; Nair, D. Long-term seizure outcome after resective surgery in patients evaluated with intracranial electrodes. Epilepsia 2012, 53, 1722–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Age, mean (range), years | 17.6 (3–53) |
| Female sex, n (%) | 28 (52.8) |
| Follow-up duration after resective surgery, mean (range), months | 27.5 (12.2–49.5) |
| Seizure semiology, n (%) | |
| Impaired awareness or behavior arrest | 24 (45.3) |
| Tonic | 19 (35.8) |
| Hyperkinetic | 8 (15.1) |
| Versive | 7 (13.2) |
| Clonic | 4 (7.5) |
| Epileptic spasms | 4 (7.5) |
| Auras | 18 (34.0) |
| Focal to bilateral tonic-clonic | 5 (9.4) |
| Side of estimated epileptogenic zone, n (%) | |
| Right | 29 (54.7) |
| Left | 23 (43.4) |
| Undetermined | 1 (1.9) |
| Localization of estimated epileptogenic zone, n (%) | |
| Localized in 1–2 lobes | 50 (94.3) |
| Frontal | 14 (26.4) |
| Temporal | 15 (28.3) |
| Fronto-temporal | 1 (1.9) |
| Fronto-parietal | 5 (9.4) |
| Parietal | 6 (11.3) |
| Temporo-occipital | 4 (7.5) |
| Insulo-opercular | 3 (5.7) |
| Occipital | 1 (1.9) |
| Temporo-parietal | 1 (1.9) |
| Lateralized in unilateral hemisphere | 3 (5.7) |
| FDG-PET abnormality, n (%) | 49 (92.5) |
| Consistent localization with MRI lesion | 39 (73.6) |
| Inconsistent localization with MRI lesion | 6 (11.3) |
| No concomitant MRI lesion | 4 (7.5) |
| Resective surgery, n (%) | |
| Temporal lobe surgery | |
| ATL with hippocampectomy | 4 (7.5) |
| ATL without hippocampectomy | 5 (9.4) |
| Focal cortical resection and/or lesionectomy | 5 (9.4) |
| Selective resection of uncus and amygdala | 1 (1.9) |
| Extra-temporal lobe surgery | |
| Focal cortical resection and/or lesionectomy | 34 (64.2) |
| Lobectomy | 4 (7.5) |
| Etiology of epilepsy, n (%) | |
| MCD | 34 (64.2) |
| Focal cortical dysplasia | 28 (52.8) |
| Type 1 | 6 (11.3) |
| Type 2 | 18 (34.0) |
| Microdysgenesis | 4 (7.5) |
| Polymicrogyria | 1 (1.9) |
| Tuberous sclerosis | 1 (1.9) |
| Other MCD | 4 (7.5) |
| Ulegyria | 6 (11.3) |
| Hippocampal sclerosis | 2 (3.8) |
| Middle fossa encephalocele | 1 (1.9) |
| Arteriovenous malformation | 1 (1.9) |
| Tumor | 1 (1.9) |
| Unknown | 8 (15.1) |
| 1. Focal MRI lesion | 29 (54.7) |
| Inconsistent electro-clinical findings | 2 (3.8) |
| Functional mapping | 14 (26.4) |
| 2. Non-focal MRI lesion | 16 (30.2) |
| Bilateral MRI lesions | 2 (3.8) |
| Inconsistent electro-clinical findings | 1 (1.9) |
| Multiple MRI lesions | 1 (1.9) |
| Diffuse MRI lesion | 10 (18.9) |
| Inconsistent electro-clinical findings | 1 (1.9) |
| Functional mapping | 1 (1.9) |
| Ambiguous MRI findings | 3 (5.7) |
| Inconsistent electro-clinical findings | 1 (1.9) |
| 3. No MRI lesions | 8 (15.1) |
| No. of Depth Electrode Implantation, Median (Range) | |
| Depth electrode leads per patient | 3 (1–10) |
| Depth electrode contacts per patient | 22 (6–60) |
| Method of depth electrode implantation, n (%) | |
| VarioGuide® | 48 (90.6) |
| Leksell stereotactic frame | 4 (7.5) |
| Manual insertion | 1 (1.9) |
| Target of depth electrode, number of leads (number of patients) | |
| Focal MRI lesion | 83 (29) |
| Bottom-of-sulcus FCD | 33 (10) |
| Non-focal MRI lesion | 39 (14) |
| Non-lesional cortex | 71 (30) |
| Symptomatogenic cortex | 14 (9) |
| Suspected area of ictal propagation | 47 (19) |
| Cortex with FDG-PET abnormality | 10 (3) |
| No. of subdural electrode implantation, median (range) | |
| Subdural electrode leads per patient | 7 (2–16) |
| Subdural electrode contacts per patient | 62 (10–136) |
| ILAE Class | Overall (n = 53) n (%) | TLE (n = 15) n (%) | Extra-TLE (n = 38) n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22 (41.5) | 3 (20.0) * | 19 (50.0) * |
| 1a | 20 (37.7) | 2 (13.3) | 18 (47.4) |
| 2 | 6 (11.3) | 3 (20.0) | 3 (7.9) |
| 3 | 8 (15.1) | 1 (6.7) | 7 (18.4) |
| 4 | 12 (22.6) | 6 (40.0) | 6 (15.8) |
| 5 | 4 (7.5) | 2 (13.3) | 2 (5.3) |
| 6 | 1 (1.9) | 0 | 1 (2.6) |
| EIIC Detectability, n (%) | LVFA Detectability, n (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Depth Electrodes | Subdural Electrodes | ||
| Overall | 39 (73.6) | 45 (84.9) | 41 (77.4) |
| Etiology | |||
| Malformation of cortical development (n = 34) | 26 (76.5) | 28 (82.4) | 26 (76.5) |
| Ulegyria (n = 6) | 1 (16.7) * | 6 (100) | 4 (66.7) |
| Other etiologies (n = 13) | 12 (92.3) | 11 (84.6) | 11 (84.6) |
| Location of suspected epileptogenic zone | |||
| TLE (n = 15) | 15 (100) | 12 (80.0) | 14 (93.3) |
| Extra-TLE (n = 38) | 24 (63.2) | 33 (86.8) | 27 (71.1) |
| MRI lesion localized in a single lobe (n = 31) | 23 (74.2) | 28 (90.3) | 28 (90.3) |
| FDG-PET findings consistent with MRI (n = 39) | 28 (71.8) | 33 (84.6) | 32 (82.1) |
| Case No. | Age-Range, Years | Etiology | Estimated Epileptogenic Zone | MRI Lesion | FDG-PET Lesion | Target of Subdural Electrode | Target of Depth Electrodes (No. of Leads Showing EIIC/No. of Leads) | Method of Depth Electrode Implantation | Seizure Outcome (ILAE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20–25 | FCD | L IO | L IO | None | L FP | L insula (5/5) Orbitofrontal (1/1) | LSF | 4 |
| 2 | 0–5 | FCD | L IO | L IO | L IO | L FTP | L insula (1/4) | LSF | 1a |
| 3 | 6–10 | FCD | R IO | R insula | R insula | R FT | R insula (2/4) | LSF | 1a |
| 4 | 20–25 | Other MCD | R T | R T/L F | R T | R FT | R hippo (0/1) R amygdala (1/1) MRI lesion (R T) (0/1) | VarioGuide | 4 |
| 5 | 40–45 | Unknown | R T | R T | R T | Bil FTP | Bil hippo (1/2) Bil amygdala (0/2) | VarioGuide | 2 |
| 6 | 50–55 | AVM | R T | R T | R T | R FTP | MRI lesion (R T) (1/3) R cingulate (0/2) R insula (0/1) | VarioGuide | 4 |
| 7 | 0–5 | FCD | R FP | R FP | R FP | R FP | MRI lesion (R FP) (1/4) | VarioGuide | 3 |
| 8 | 10–15 | FCD | L FP | L hemi | L FTP | L FP | MRI lesion (L FP) (1/2) L insula (0/5) | VarioGuide | 1a |
| Subdural Electrodes, n (%) | Depth Electrodes, n (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LVFA (n = 41) | 35 (77.8) | 33 (84.6) | 0.58 |
| Rhythmic delta activity (n = 7) | 7 (15.6) | 1 (2.6) | 0.062 |
| Spike-and-wave complex (n = 4) | 3 (6.7) | 4 (10.3) | 0.70 |
| Rhythmic theta activity with preceding polyspikes (n = 1) | 0 | 1 (2.6) | 0.46 |
| Variable | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 0.61 | 0.127 to 2.93 | 0.54 |
| Complete removal of MRI lesion | 6.32 | 1.62 to 24.7 | 0.0079 |
| Complete resection of EIIC | 0.61 | 0.114 to 3.26 | 0.56 |
| Suspected temporal lobe epileptogenic zone | 0.15 | 0.0297 to 0.775 | 0.023 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takayama, Y.; Ikegaya, N.; Iijima, K.; Kimura, Y.; Yokosako, S.; Muraoka, N.; Kosugi, K.; Kaneko, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Iwasaki, M. Single-Institutional Experience of Chronic Intracranial Electroencephalography Based on the Combined Usage of Subdural and Depth Electrodes. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030307
Takayama Y, Ikegaya N, Iijima K, Kimura Y, Yokosako S, Muraoka N, Kosugi K, Kaneko Y, Yamamoto T, Iwasaki M. Single-Institutional Experience of Chronic Intracranial Electroencephalography Based on the Combined Usage of Subdural and Depth Electrodes. Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(3):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030307
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakayama, Yutaro, Naoki Ikegaya, Keiya Iijima, Yuiko Kimura, Suguru Yokosako, Norihiro Muraoka, Kenzo Kosugi, Yuu Kaneko, Tetsuya Yamamoto, and Masaki Iwasaki. 2021. "Single-Institutional Experience of Chronic Intracranial Electroencephalography Based on the Combined Usage of Subdural and Depth Electrodes" Brain Sciences 11, no. 3: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030307
APA StyleTakayama, Y., Ikegaya, N., Iijima, K., Kimura, Y., Yokosako, S., Muraoka, N., Kosugi, K., Kaneko, Y., Yamamoto, T., & Iwasaki, M. (2021). Single-Institutional Experience of Chronic Intracranial Electroencephalography Based on the Combined Usage of Subdural and Depth Electrodes. Brain Sciences, 11(3), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11030307