Reelin Haploinsufficiency and Late-Adolescent Corticosterone Treatment Induce Long-Lasting and Female-Specific Molecular Changes in the Dorsal Hippocampus
Abstract
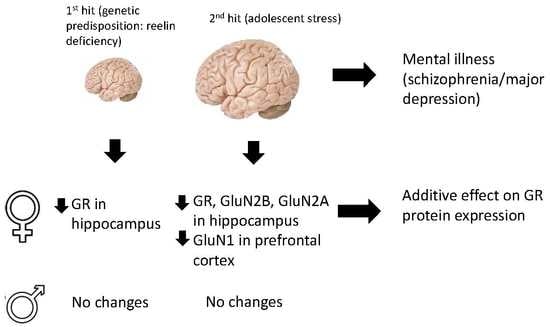
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Corticosterone Treatment
2.3. Detection of CORT
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Adrenal Weight
3.2. CORT Levels
3.3. GR Expression
3.4. NMDAr Protein Expression
3.4.1. NMDAr Subunit Protein Expression in the Dorsal Hippocampus (Figure 3A–D)
3.4.2. NMDAr Protein Expression in Ventral Hippocampus (Figure 3E–H)
3.4.3. NMDAr Protein Expression in PFC (Figure 3I–L)
3.5. PV and GAD67 Protein Expression
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Darcangelo, G.; Miao, G.G.; Chen, S.C.; Soares, H.D.; Morgan, J.I.; Curran, T. A protein related to extracellular matrix proteins deleted in the mouse mutant reeler. Nature 1995, 374, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesold, C.; Impagnatiello, F.; Pisu, M.G.; Uzunov, D.P.; Costa, E.; Guidotti, A.; Caruncho, H.J. Reelin is preferentially expressed in neurons synthesizing gamma-aminobutyric acid in cortex and hippocampus of adult rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3221–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DelRio, J.A.; Heimrich, B.; Borrell, V.; Forster, E.; Drakew, A.; Alcantara, S.; Nakajima, K.; Miyata, T.; Ogawa, M.; Mikoshiba, K.; et al. A role for Cajal-Retzius cells and reelin in the development of hippocampal connections. Nature 1997, 385, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldowitz, D.; Cushing, R.C.; Laywell, E.; Darcangelo, G.; Sheldon, M.; Sweet, H.O.; Davisson, M.; Steindler, D.; Curran, T. Cerebellar disorganization characteristic of reeler in scrambler mutant mice despite presence of reelin. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 8767–8777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brigman, J.L.; Padukiewicz, K.E.; Sutherland, M.L.; Rothblat, L.A. Executive functions in the heterozygous reeler mouse model of schizophrenia. Behav. Neurosci. 2006, 120, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podhorna, J.; Didriksen, M. The heterozygous reeler mouse: Behavioural phenotype. Behav. Brain Res. 2004, 153, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tueting, P.; Doueiri, M.S.; Guidotti, A.; Davis, J.M.; Costa, E. Reelin down-regulation in mice and psychosis endo-phenotypes. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2006, 30, 1065–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, J.; Hoffman, J.S.; Guidotti, A.; Costa, E. Olfactory discrimination learning deficit in heterozygous reeler mice. Brain Res. 2003, 971, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.H.; D’Arcangelo, G. New Insights into Reelin-Mediated Signaling Pathways. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaar, D.A.; Shao, Y.; Haines, J.L.; Stenger, J.E.; Jaworski, J.; Martin, E.R.; DeLong, G.R.; Moore, J.H.; McCauley, J.L.; Sutcliffe, J.S.; et al. Analysis of the RELN gene as a genetic risk factor for autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2005, 10, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, A.; Auta, J.; Davis, J.M.; Gerevini, V.D.; Dwivedi, Y.; Grayson, D.R.; Impagnatiello, F.; Pandey, G.; Pesold, C.; Sharma, R.; et al. Decrease in reelin and glutamic acid decarboxylase(67) (GAD(67)) expression in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder—A postmortem brain study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2000, 57, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trommsdorff, M.; Gotthardt, M.; Hiesberger, T.; Shelton, J.; Stockinger, W.; Nimpf, J.; Hammer, R.E.; Richardson, J.A.; Herz, J. Reeler/disabled-like disruption of neuronal migration in knockout mice lacking the VLDL receptor and ApoE receptor 2. Cell 1999, 97, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beffert, U.; Morfini, G.; Bock, H.H.; Reyna, H.; Brady, S.T.; Herz, J. Reelin-mediated signaling locally regulates protein kinase B/Akt and glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 49958–49964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, C.; Sinagra, M.; Verrier, D.; Manzoni, O.J.; Chavis, P. Reelin Secreted by GABAergic Neurons Regulates Glutamate Receptor Homeostasis. PLoS ONE 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iafrati, J.; Orejarena, M.J.; Lassalle, O.; Bouamrane, L.; Gonzalez-Campo, C.; Chavis, P. Reelin, an extracellular matrix protein linked to early onset psychiatric diseases, drives postnatal development of the prefrontal cortex via GluN2B-NMDARs and the mTOR pathway. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventruti, A.; Kazdoba, T.M.; Niu, S.; D’Arcangelo, G. Reelin deficiency causes specific defects in the molecular composition of the synapses in the adult brain. Neuroscience 2011, 189, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafini, G.; Hayley, S.; Pompili, M.; Dwivedi, Y.; Brahmachari, G.; Girardi, P.; Amore, M. Hippocampal neurogenesis, neurotrophic factors and depression: Possible therapeutic targets? CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 13, 1708–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinagra, M.; Verrier, D.; Frankova, D.; Korwek, K.M.; Blahos, J.; Weeber, E.J.; Manzoni, O.J.; Chavis, P. Reelin, very-low-density lipoprotein receptor, and apolipoprotein E receptor 2 control somatic NMDA receptor composition during hippocampal maturation in vitro. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6127–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrant, M.; Feldmeyer, D.; Takahashi, T.; Cullcandy, S.G. NMDA-receptor channel diversity in the developing cerebellum. Nature 1994, 368, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Clemente, A.; Nicoll, R.A.; Roche, K.W. Diversity in NMDA Receptor Composition: Many Regulators, Many Consequences. Neuroscientist 2013, 19, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, E.; Pesold, C.; Auta, J.; Caruncho, H.; Davis, J.M.; Davidkova, G.; Dwivedi, Y.; Grayson, D.R.; Rodriguez, M.; Uzunov, D.; et al. Reelin and GAD67 downregulation and psychosis vulnerability. Biol. Psychiatry 2000, 47, 68S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanoli, S.; Weber, L.; Meyer, U. Single and combined effects of prenatal immune activation and peripubertal stress on parvalbumin and reelin expression in the hippocampal formation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 40, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nullmeier, S.; Panther, P.; Dobrowolny, H.; Frotscher, M.; Zhao, S.; Schwegler, H.; Wolf, R. Region-specific alteration of GABAergic markers in the brain of heterozygous reeler mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buret, L.; van den Buuse, M. Corticosterone treatment during adolescence induces down-regulation of reelin and NMDA receptor subunit GLUN2C expression only in male mice: Implications for schizophrenia. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 17, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, R.A.; Wu, Y.W.; Gogos, A.; van den Buuse, M. Sex-dependent alterations in BDNF-TrkB signaling in the hippocampus of reelin heterozygous mice: A role for sex steroid hormones. J. Neurochem. 2013, 126, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biamonte, F.; Assenza, G.; Marino, R.; D’Amelio, M.; Panteri, R.; Caruso, D.; Scurati, S.; Yague, J.G.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Cesa, R.; et al. Interactions between neuroactive steroids and reelin haploinsufficiency in Purkinje cell survival. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 36, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCarthy, M.M.; Auger, A.P.; Perrot-Sinal, T.S. Getting excited about GABA and sex differences in the brain. Trends Neurosci. 2002, 25, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, M.H.J.; van Mens-Verhulst, J. Anxiety disorders: Sex differences in prevalence, degree, and background, but gender-neutral treatment. Gend. Med. 2007, 4, S178–S193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenburg, J.; Tracy, D.K. Sex and schizophrenia: A review of gender differences. Psychosis 2014, 6, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, T.M.; Sikich, L.; Lieberman, J.A.; LaMantia, A.S. Neural development, cell-cell signaling, and the “two-hit” hypothesis of schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2001, 27, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, Z.A.; Romeo, R.D. Changes in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal stress responsiveness before and after puberty in rats. Horm. Behav. 2013, 64, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilabert-Juan, J.; Bueno-Fernandez, C.; Castillo-Gomez, E.; Nacher, J. Reduced interneuronal dendritic arborization in CA1 but not in CA3 region of mice subjected to chronic mild stress. Brain Behav. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosal, S.; Hare, B.D.; Duman, R.S. Prefrontal cortex GABAergic deficits and circuit dysfunction in the pathophysiology and treatment of chronic stress and depression. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2017, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oitzl, M.S.; Champagne, D.L.; van der Veen, R.; de Kloet, E.R. Brain development under stress: Hypotheses of glucocorticoid actions revisited. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 34, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.M.; Wang, G.Y.; Ma, K.; Cui, S.; Wang, J.H. GABAergic neurons in nucleus accumbens are correlated to resilience and vulnerability to chronic stress for major depression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 35933–35945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, A.G.; Arp, M.; Velzing, E.; Lesuis, S.L.; Schmidt, M.V.; Holsboer, F.; Joels, M.; Krugers, H.J. Early life stress determines the effects of glucocorticoids and stress on hippocampal function: Electrophysiological and behavioral evidence respectively. Neuropharmacology 2018, 133, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, A.; Buret, L.; Hill, R.; van den Buuse, M. Gene-environment interaction of reelin and stress in cognitive behaviours in mice: Implications for schizophrenia. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 287, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lussier, A.L.; Romay-Tallon, R.; Kalynchuk, L.E.; Caruncho, H.J. Reelin as a putative vulnerability factor for depression: Examining the depressogenic effects of repeated corticosterone in heterozygous reeler mice. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, N.; Workman, J.L.; Lee, T.T.; Innala, L.; Viau, V. Sex differences in the HPA axis. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 1121–1155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klug, M.; Hill, R.A.; Choy, K.H.C.; Kyrios, M.; Hannan, A.J.; van den Buuse, M. Long-term behavioral and NMDA receptor effects of young-adult corticosterone treatment in BDNF heterozygous mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herz, J.; Chen, Y. Reelin, lipoprotein receptors and synaptic plasticity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatsoreos, I.N.; Bhagat, S.M.; Bowles, N.P.; Weil, Z.M.; Pfaff, D.W.; McEwen, B.S. Endocrine and Physiological Changes in Response to Chronic Corticosterone: A Potential Model of the Metabolic Syndrome in Mouse. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Notaras, M.J.; Vivian, B.; Wilson, C.; van den Buuse, M. Interaction of reelin and stress on immobility in the forced swim test but not dopamine-mediated locomotor hyperactivity or prepulse inhibition disruption: Relevance to psychotic and mood disorders. Schizophr. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, R.A.; Wu, Y.W.C.; Kwek, P.; van den Buuse, M. Modulatory Effects of Sex Steroid Hormones on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor-Tyrosine Kinase B Expression during Adolescent Development in C57Bl/6 Mice. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2012, 24, 774–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touma, C.; Palme, R.; Sachser, N. Analyzing corticosterone metabolites in fecal samples of mice: A noninvasive technique to monitor stress hormones. Horm. Behav. 2004, 45, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanos, P.K.; Cavigelli, S.A.; Michaelides, M.; Olvet, D.M.; Patel, U.; Diep, M.N.; Volkow, N.D. A Non-Invasive Method for Detecting the Metabolic Stress Response in Rodents: Characterization and Disruption of the Circadian Corticosterone Rhythm. Physiol. Res. 2009, 58, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ninnes, C.E.; Waas, J.R.; Ling, N.; Nakagawa, S.; Banks, J.C.; Bell, D.G.; Bright, A.; Carey, P.W.; Chandler, J.; Hudson, Q.J.; et al. Comparing plasma and faecal measures of steroid hormones in Adelie penguins Pygoscelis adeliae. J. Comp. Physiol. B Biochem. Syst. Environ. Physiol. 2010, 180, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raps, D.; Barthe, P.L.; Desaulle, P. Plasma and adrenal corticosterone levels during the different phases of the sexual cycle in normal female rats. Experientia 1971, 27, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gala, R.R.; Westphal, U. Corticosteroid-Binding Globulin in the Rat: Studies on the Sex Difference. Endocrinology 1965, 77, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, H.C.; Waddell, B.J. Circadian variation in basal plasma corticosterone and adrenocorticotropin in the rat: Sexual dimorphism and changes across the estrous cycle. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 3842–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Critchlow, V.; Barsela, M.; Mountcastle, W.; Liebelt, R.A.; Lipscomb, H.S. Sex difference in resting pituitary-adrenal function in rat. Am. J. Physiol. 1963, 205, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisari, A.; Carino, M.; Perone, M.; Gaillard, R.C.; Spinedi, E. Sex and strain variability in the rat hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis function. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 1995, 18, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, A.C.; Whitacre, C.C. Sex and strain differences in the circadian rhythm fluctuation of endocrine and immune function in the rat: Implications for rodent models of autoimmune disease. J. Neuroimmunol. 1991, 35, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seale, J.V.; Wood, S.A.; Atkinson, H.C.; Bate, E.; Lightman, S.L.; Ingram, C.D.; Jessop, D.S.; Harbuz, M.S. Gonadectomy reverses the sexually diergic patterns of circadian and stress-induced hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity in male and female rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2004, 16, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seale, J.V.; Wood, S.A.; Atkinson, H.C.; Harbuz, M.S.; Lightman, S.L. Gonadal steroid replacement reverses gonadectomy-induced changes in the corticosterone pulse profile and stress-induced hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity of male and female rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2004, 16, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, F.; Manalo, S.; Dallman, M.F. Androgen-sensitive changes in regulation of restraint-induced adrenocorticotropin secretion between early and late puberty in male rats. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, C.M.; Mahoney, E. Persistent effects of prenatal, neonatal, or adult treatment with flutamide on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal stress response of adult male rats. Horm. Behav. 1999, 35, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesniewska, B.; Nowak, M.; Malendowicz, L.K. Sex Differences in Adrenocortical Structure and Function. Horm. Metab. Res. 1990, 22, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiser, M.J.; Handa, R.J. Estrogen impairs glucocorticoid dependent negative feedback on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis via estrogen receptor alpha within the hypothalamus. Neuroscience 2009, 159, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weathington, J.M.; Arnold, A.R.; Cooke, B.M. Juvenile social subjugation induces a sex-specific pattern of anxiety and depression-like behaviors in adult rats. Horm. Behav. 2012, 61, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kloet, E.R.; Vreugdenhil, E.; Oitzl, M.S.; Joels, M. Brain corticosteroid receptor balance in health and disease. Endocr. Rev. 1998, 19, 269–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beato, M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell 1989, 56, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, A.D.; Cidlowski, J.A. Proteasome-mediated glucocorticoid receptor degradation restricts transcriptional signaling by glucocorticoids. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 42714–42721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, T.J.; Blendy, J.A.; Monaghan, A.P.; Krieglstein, K.; Schmid, W.; Aguzzi, A.; Fantuzzi, G.; Hummler, E.; Unsicker, K.; Schutz, G. Targeted disruption of the glucocorticoid receptor gene blocks adrenergic chromaffin cell development and severely retards lung maturation. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 1608–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.N.; Sloan, S.A.; Bennett, M.L.; Scholze, A.R.; O’Keeffe, S.; Phatnani, H.P.; Guarnieri, P.; Caneda, C.; Ruderisch, N.; et al. An RNA-Sequencing Transcriptome and Splicing Database of Glia, Neurons, and Vascular Cells of the Cerebral Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 11929–11947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sivukhina, E.; Schafer, H.H.; Jirikowski, G.F. Differences in colocalization of corticosteroid-binding globulin and glucocorticoid receptor immunoreactivity in the rat brain. Ann. Anat. 2013, 195, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korn, M.J.; Mandle, Q.J.; Parent, J.M. Conditional Disabled-1 Deletion in Mice Alters Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Reduces Seizure Threshold. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warde-Farley, D.; Donaldson, S.L.; Comes, O.; Zuberi, K.; Badrawi, R.; Chao, P.; Franz, M.; Grouios, C.; Kazi, F.; Lopes, C.T.; et al. The GeneMANIA prediction server: Biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W214–W220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuloaga, D.G.; Carbone, D.L.; Handa, R.J. Prenatal dexamethasone selectively decreases calretinin expression in the adult female lateral amygdala. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 521, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alcantara, S.; Ruiz, M.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Ezan, F.; de Lecea, L.; Curran, T.; Sotelo, C.; Soriano, E. Regional and cellular patterns of reelin mRNA expression in the forebrain of the developing and adult mouse. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 7779–7799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedenoja, J.; Loukola, A.; Tuulio-Henriksson, A.; Paunio, T.; Ekelund, J.; Silander, K.; Varilo, T.; Heikkila, K.; Suvisaari, J.; Partonen, T.; et al. Replication of linkage on chromosome 7q22 and association of the regional Reelin gene with working memory in schizophrenia families. Mol. Psychiatry 2008, 13, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shifman, S.; Johannesson, M.; Bronstein, M.; Chen, S.X.; Collier, D.A.; Craddock, N.J.; Kendler, K.S.; Li, T.; O’Donovan, M.; O’Neill, F.A.; et al. Genome-wide association identifies a common variant in the reelin gene that increases the risk of schizophrenia only in women. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, S.; Osanai, H.; Monma, T.; Harada, T.; Hirano, A.; Saito, M.; Kawato, S. Acute effect of corticosterone on N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-mediated Ca2+ elevation in mouse hippocampal slices. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 2005, 321, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Sheng, H.; Qi, J.S.; Ma, B.; Sun, J.H.; Li, S.F.; Ni, X. Glucocorticoid acts on a putative G protein-coupled receptor to rapidly regulate the activity of NMDA receptors in hippocampal neurons. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 302, E747–E758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van den Buuse, M.; Halley, P.; Hill, R.; Labots, M.; Martin, S. Altered N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor function in reelin heterozygous mice: Male-female differences and comparison with dopaminergic activity. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 37, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorski, J.A.; Zeiler, S.R.; Tamowski, S.; Jones, K.R. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is required for the maintenance of cortical dendrites. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 6856–6865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.J.; Kirkwood, A.; Pizzorusso, T.; Porciatti, V.; Morales, B.; Bear, M.F.; Maffei, L.; Tonegawa, S. BDNF regulates the maturation of inhibition and the critical period of plasticity in mouse visual cortex. Cell 1999, 98, 739–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.; Davis, J.; Grayson, D.R.; Guidotti, A.; Pappas, G.D.; Pesold, C. Dendritic spine hypoplasticity and downregulation of reelin and GABAergic tone in schizophrenia vulnerability. Neurobiol. Dis. 2001, 8, 723–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lussier, A.L.; Romay-Tallon, R.; Caruncho, H.J.; Kalynchuk, L.E. Altered GABAergic and glutamatergic activity within the rat hippocampus and amygdala in rats subjected to repeated corticosterone administration but not restraint stress. Neuroscience 2013, 231, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipovic, D.; Zlatkovic, J.; Gass, P.; Inta, D. The differential effects of acute vs. chronic stress and their combination on hippocampal parvalbumin and inducible heat shock protein 70 expression. Neuroscience 2013, 236, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Male | Female | |
|---|---|---|
| WT Contr | 1.13 ± 0.05 | 2.10 ± 0.11 # |
| HRM Contr | 1.13 ± 0.09 | 1.97 ± 0.09 # |
| WT CORT | 0.92 ± 0.02 * | 1.85 ± 0.09 *,# |
| HRM CORT | 0.96 ± 0.08 * | 1.82 ± 0.08 *,# |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schroeder, A.; Van den Buuse, M.; Hill, R.A. Reelin Haploinsufficiency and Late-Adolescent Corticosterone Treatment Induce Long-Lasting and Female-Specific Molecular Changes in the Dorsal Hippocampus. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8070118
Schroeder A, Van den Buuse M, Hill RA. Reelin Haploinsufficiency and Late-Adolescent Corticosterone Treatment Induce Long-Lasting and Female-Specific Molecular Changes in the Dorsal Hippocampus. Brain Sciences. 2018; 8(7):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8070118
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchroeder, Anna, Maarten Van den Buuse, and Rachel A. Hill. 2018. "Reelin Haploinsufficiency and Late-Adolescent Corticosterone Treatment Induce Long-Lasting and Female-Specific Molecular Changes in the Dorsal Hippocampus" Brain Sciences 8, no. 7: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8070118
APA StyleSchroeder, A., Van den Buuse, M., & Hill, R. A. (2018). Reelin Haploinsufficiency and Late-Adolescent Corticosterone Treatment Induce Long-Lasting and Female-Specific Molecular Changes in the Dorsal Hippocampus. Brain Sciences, 8(7), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci8070118