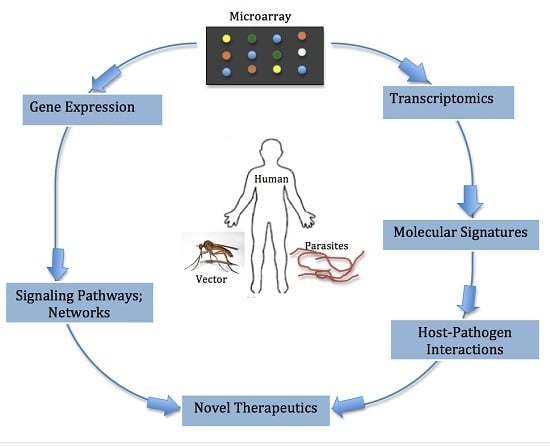
The Potentials and Pitfalls of Microarrays in Neglected Tropical Diseases: A Focus on Human Filarial Infections
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Life-Cycle of Filarial Parasites (W. bancrofti and O. volvulus)
2. Microarray Unravels Host Immune Responses during Filarial Infection
3. Prospects of Whole Blood Microarray in Filarial Infections
4. Appreciating the Interplay between the Filarial Parasite and Human Host: The Role of Microarray Technology
5. Capacity of Microarray to Reveal Induced Signaling Pathways and Networks during Filarial Infections
6. Potential of Other Microarray Platforms
6.1. microRNA Microarrays
6.2. Functional Protein Microarray
7. Trends of Microarray Technologies over a 10-Year Period
8. The Future of Microarray in Developing Countries
9. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFA | Circulating Filarial Antigen |
| MF | Microfilaria |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| miRNA | Micro-Ribonucleic acid |
| NGS | Next Generation Sequencing |
References
- Awadzi, K.; Attah, S.K.; Addy, E.T.; Opoku, N.O.; Quartey, B.T.; Lazdins-Helds, J.K.; Ahmed, K.; Boatin, B.A.; Boakye, D.A.; Edwards, G. Thirty-month follow-up of sub-optimal responders to multiple treatments with ivermectin, in two onchocerciasis-endemic foci in Ghana. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2004, 98, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osei-Atweneboana, M.Y.; Eng, J.K.; Boakye, D.A.; Gyapong, J.O.; Prichard, R.K. Prevalence and intensity of onchocerca volvulus infection and efficacy of ivermectin in endemic communities in Ghana: A two-phase epidemiological study. Lancet 2007, 369, 2021–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei-Atweneboana, M.Y.; Awadzi, K.; Attah, S.K.; Boakye, D.A.; Gyapong, J.O.; Prichard, R.K. Phenotypic evidence of emerging ivermectin resistance in onchocerca volvulus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, T.; Yang, P.C. Western blot: Technique, theory, and trouble shooting. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 4, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arya, M.; Shergill, I.S.; Williamson, M.; Gommersall, L.; Arya, N.; Patel, H.R. Basic principles of real-time quantitative PCR. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2005, 5, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoheisel, J.D. Microarray technology: Beyond transcript profiling and genotype analysis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogner, V.; Mutschler, W. Microarrays as biomarkers in trauma. Unfallchirurg 2014, 117, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kammenga, J.E.; Herman, M.A.; Ouborg, N.J.; Johnson, L.; Breitling, R. Microarray challenges in ecology. Trends. Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobert, G.N.; Moertel, L.P.; McManus, D.P. Microarrays: New tools to unravel parasite transcriptomes. Parasitology 2005, 131, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufva, M. Introduction to microarray technology. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 529, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.B.; Tang, Y.-W. Basic concepts of microarrays and potential applications in clinical microbiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 611–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.A. 3.3 filarial genomics. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2004, 71, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy, R.K. Clinical and pathological aspects of filarial lymphedema and its management. Korean J. Parasitol. 2008, 46, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.-W.; Wang, Z.; Rush, A.C.; Mitreva, M.; Weil, G.J. Transcription profiling reveals stage- and function-dependent expression patterns in the filarial nematode Brugia malayi. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, T.W.; Penninger, J.M.; Ohashi, P.S. Knockout mice: A paradigm shift in modern immunology. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 1, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adjobimey, T.; Hoerauf, A. Induction of immunoglobulin g4 in human filariasis: An indicator of immunoregulation. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2010, 104, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Else, K.; Wakelin, D. The effects of H-2 and non-H-2 genes on the expulsion of the nematode Trichuris muris from inbred and congenic mice. Parasitology 1988, 96 Pt 3, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellaby, T.; Robinson, K.; Wakelin, D. Induction of differential T-helper-cell responses in mice infected with variants of the parasitic nematode Trichuris muris. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bretscher, P.A.; Wei, G.; Menon, J.N.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H. Establishment of stable, cell-mediated immunity that makes “susceptible” mice resistant to leishmania major. Science 1992, 257, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirokawa, K.; Utsuyama, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Kitagawa, M.; Makinodan, T.; Fulop, T. Slower immune system aging in women versus men in the Japanese population. Immun. Ageing 2013, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Meydani, S.N. Age-associated changes in immune and inflammatory responses: Impact of vitamin E intervention. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 84, 900–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macgregor, P.F.; Squire, J.A. Application of microarrays to the analysis of gene expression in cancer. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blader, I.J.; Manger, I.D.; Boothroyd, J.C. Microarray analysis reveals previously unknown changes in toxoplasma gondii-infected human cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 24223–24231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steel, C.; Varma, S.; Nutman, T.B. Regulation of global gene expression in human Loa loa infection is a function of chronicity. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, A.D.; Gillan, V.; Maitland, K.; Emes, R.D.; Roberts, B.; McCormack, G.; Weir, W.; Protasio, A.V.; Holroyd, N.; Berriman, M.; et al. A novel member of the let-7 microRNA family is associated with developmental transitions in filarial nematode parasites. BMC Genom. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Liao, Q.; He, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J.; Wu, J.; Cheng, L.; et al. Comparison of six different pretreatment methods for blood RNA extraction. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2015, 13, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoolnik, G.K. Microarray analysis of bacterial pathogenicity. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2002, 46, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Slobedman, B.; Cheung, A.K. Microarrays for the study of viral gene expression during human cytomegalovirus latent infection. Methods Mol. Med. 2008, 141, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Walter, E.; Stenger, D.; Thach, D. Effects of globin mRNA reduction methods on gene expression profiles from whole blood. J. Mol. Diagn. 2006, 8, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Dix, D.J.; Thompson, K.E.; Murrell, R.N.; Schmid, J.E.; Gallagher, J.E.; Rockett, J.C. Effects of storage, RNA extraction, genechip type, and donor sex on gene expression profiling of human whole blood. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debey, S.; Schoenbeck, U.; Hellmich, M.; Gathof, B.S.; Pillai, R.; Zander, T.; Schultze, J.L. Comparison of different isolation techniques prior gene expression profiling of blood derived cells: Impact on physiological responses, on overall expression and the role of different cell types. Pharmacogenom. J. 2004, 4, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainen, L.; Oelmueller, U.; Jurgensen, S.; Wyrich, R.; Ballas, C.; Schram, J.; Herdman, C.; Bankaitis-Davis, D.; Nicholls, N.; Trollinger, D.; et al. Stabilization of mRNA expression in whole blood samples. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feezor, R.J.; Baker, H.V.; Mindrinos, M.; Hayden, D.; Tannahill, C.L.; Brownstein, B.H.; Fay, A.; MacMillan, S.; Laramie, J.; Xiao, W.; et al. Whole blood and leukocyte RNA isolation for gene expression analyses. Physiol. Genom. 2004, 19, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maerkedahl, R.B.; Frokiaer, H.; Lauritzen, L.; Metzdorff, S.B. Evaluation of a low-cost procedure for sampling, long-term storage, and extraction of RNA from blood for qPCR analyses. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2015, 53, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricano, M.M.; Ditewig, A.C.; Jung, P.M.; Liguori, M.J.; Blomme, E.A.; Yang, Y. Global transcriptomic profiling using small volumes of whole blood: A cost-effective method for translational genomic biomarker identification in small animals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 2502–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vartanian, K.; Slottke, R.; Johnstone, T.; Casale, A.; Planck, S.R.; Choi, D.; Smith, J.R.; Rosenbaum, J.T.; Harrington, C.A. Gene expression profiling of whole blood: Comparison of target preparation methods for accurate and reproducible microarray analysis. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, H.; Hasegawa, M.; Wakimoto, K.; Miyamoto-Sato, E. Next-generation technologies for multiomics approaches including interactome sequencing. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero, F.; Botta, M.; Calogero, R.A. Microarray data analysis and mining approaches. Brief. Funct. Genom. Proteom. 2007, 6, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, G.A. Transcriptomics in Health and Disease; Springer: Sao Paulo, Brazil, 2014; pp. 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Xiao, G.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, M.Q.; Corey, D.R.; Xie, Y. Design and bioinformatics analysis of genome-wide clip experiments. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2015, 43, 5263–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.E.; Maizels, R.M. Diversity and dialogue in immunity to helminths. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wammes, L.J.; Hamid, F.; Wiria, A.E.; Wibowo, H.; Sartono, E.; Maizels, R.M.; Smits, H.H.; Supali, T.; Yazdanbakhsh, M. Regulatory T cells in human lymphatic filariasis: Stronger functional activity in microfilaremics. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuya, K.N.; Gebhardt, R.; Schuetz, E.G.; Schuetz, J.D. Isolation of rat PGP3 cDNA: Evidence for gender and zonal regulation of expression in the liver. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1994, 1219, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, I.N.; Hanaoka, T.; Sugimura, H.; Nagura, K.; Ihara, M.; Li, X.J.; Arai, T.; Hamada, G.S.; Kowalski, L.P.; Tsugane, S. Cytochrome p450 2e1 polymorphism in gastric cancer in Brazil: Case-control studies of Japanese brazilians and non-Japanese Brazilians. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2000, 9, 675–680. [Google Scholar]
- Shimada, S.; Shiomori, K.; Tashima, S.; Tsuruta, J.; Ogawa, M. Frequent p53 mutation in brain (fetal)-type glycogen phosphorylase positive foci adjacent to human “de novo” colorectal carcinomas. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 84, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, G.; Lu, Y.; Zlotnikov, G.; Thor, A.D.; Smith, H.S. Loss of heterozygosity in normal tissue adjacent to breast carcinomas. Science 1996, 274, 2057–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, H.C.; Sinha, A.A. Gene expression profile analysis by DNA microarrays: Promise and pitfalls. JAMA 2001, 286, 2280–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershon, D. Microarray technology: An array of opportunities. Nature 2002, 416, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.C. MicroRNAs: Potential biomarkers for cancer diagnosis, prognosis and targets for therapy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2010, 42, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilakka-Kanthikeel, S.; Saiyed, Z.M.; Napuri, J.; Nair, M.P. MicroRNA: Implications in HIV, a brief overview. J. Neurovirol. 2011, 17, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codocedo, J.F.; Ríos, J.A.; Godoy, J.A.; Inestrosa, N.C. Are microRNAs the molecular link between metabolic syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease? Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 53, 2320–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamanian, M.; Fraser, L.M.; Agbedanu, P.N.; Harischandra, H.; Moorhead, A.R.; Day, T.A.; Bartholomay, L.C.; Kimber, M.J. Release of small RNA-containing exosome-like vesicles from the human filarial parasite Brugia malayi. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tritten, L.; O’Neill, M.; Nutting, C.; Wanji, S.; Njouendoui, A.; Fombad, F.; Kengne-Ouaffo, J.; Mackenzie, C.; Geary, T. Loa loa and Onchocerca ochengi miRNAs detected in host circulation. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2014, 198, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, C.B.; Gu, W.; Kumar, S.; Jin, J.; Davis, P.J.; Bauche, D.; McReynolds, L.A. Diversity and expression of micrornas in the filarial parasite, Brugia malayi. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tritten, L.; Burkman, E.; Moorhead, A.; Satti, M.; Geary, J.; Mackenzie, C.; Geary, T. Detection of circulating parasite-derived microRNAs in filarial infections. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintana, J.F.; Makepeace, B.L.; Babayan, S.A.; Ivens, A.; Pfarr, K.M.; Blaxter, M.; Debrah, A.; Wanji, S.; Ngangyung, H.F.; Bah, G.S.; et al. Extracellular onchocerca-derived small RNAs in host nodules and blood. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, P.; Hou, N.; Piao, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Yang, F.; Wang, J.; Jin, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, Q. Profiles of small non-coding RNAs in Schistosoma japonicum during development. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzano-Román, R.; Siles-Lucas, M. MicroRNAs in parasitic diseases: Potential for diagnosis and targeting. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2012, 186, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, M.; Nara, T.; Mita, T.; Mikoshiba, K. Morpholino antisense oligo inhibits trans-splicing of pre-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor mRNA of Trypanosoma cruzi and suppresses parasite growth and infectivity. Parasitol. Int. 2015, 65, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, S.; Eberle, M.E.; Wölfle, S.J.; Heeg, K.; Bekeredjian-Ding, I. Bifunctional oligodeoxynucleotide/antagomir constructs: Evaluation of a new tool for microRNA silencing. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013, 23, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stears, R.L.; Martinsky, T.; Schena, M. Trends in microarray analysis. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacBeath, G.; Schreiber, S.L. Printing proteins as microarrays for high-throughput function determination. Science 2000, 289, 1760–1763. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Bilgin, M.; Bangham, R.; Hall, D.; Casamayor, A.; Bertone, P.; Lan, N.; Jansen, R.; Bidlingmaier, S.; Houfek, T.; et al. Global analysis of protein activities using proteome chips. Science 2001, 293, 2101–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.S.; Korobkova, E.; Chen, H.; Zhu, J.; Jian, X.; Tao, S.C.; He, C.; Zhu, H. A proteome chip approach reveals new DNA damage recognition activities in Escherichia coli. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, S.C.; Popescu, G.V.; Bachan, S.; Zhang, Z.; Seay, M.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M.; Dinesh-Kumar, S.P. Differential binding of calmodulin-related proteins to their targets revealed through high-density arabidopsis protein microarrays. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4730–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, D.A.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, X.; Royce, T.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. Regulation of gene expression by a metabolic enzyme. Science 2004, 306, 482–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, S.W.; Jona, G.; Chen, C.T.; Johnston, M.; Snyder, M. Linking DNA-binding proteins to their recognition sequences by using protein microarrays. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9940–9945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Xie, Z.; Onishi, A.; Yu, X.; Jiang, L.; Lin, J.; Rho, H.S.; Woodard, C.; Wang, H.; Jeong, J.S.; et al. Profiling the human protein-DNA interactome reveals erk2 as a transcriptional repressor of interferon signaling. Cell 2009, 139, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Gopinath, K.; Murali, A.; Yi, G.; Hayward, S.D.; Zhu, H.; Kao, C. RNA-binding proteins that inhibit RNA virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3129–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Zhu, H.; Haggarty, S.J.; Spring, D.R.; Hwang, H.; Jin, F.; Snyder, M.; Schreiber, S.L. Finding new components of the target of rapamycin (tor) signaling network through chemical genetics and proteome chips. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16594–16599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, L.A.; Tao, S.C.; Qian, J.; Smith, M.G.; Snyder, M.; Zhu, H. Global analysis of the glycoproteome in Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals new roles for protein glycosylation in eukaryotes. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2009, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ptacek, J.; Devgan, G.; Michaud, G.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, X.; Fasolo, J.; Guo, H.; Jona, G.; Breitkreutz, A.; Sopko, R.; et al. Global analysis of protein phosphorylation in yeast. Nature 2005, 438, 679–684. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.Y.; Lu, J.Y.; Zhang, J.; Walter, W.; Dang, W.; Wan, J.; Tao, S.C.; Qian, J.; Zhao, Y.; Boeke, J.D.; et al. Protein acetylation microarray reveals that NuA4 controls key metabolic target regulating gluconeogenesis. Cell 2009, 136, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Klemic, J.F.; Chang, S.; Bertone, P.; Casamayor, A.; Klemic, K.G.; Smith, D.; Gerstein, M.; Reed, M.A.; Snyder, M. Analysis of yeast protein kinases using protein chips. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schnack, C.; Hengerer, B.; Gillardon, F. Identification of novel substrates for CDK5 and new targets for Cdk5 inhibitors using high-density protein microarrays. Proteomics 2008, 8, 1980–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.Y.; Lin, Y.Y.; Qian, J.; Tao, S.C.; Zhu, J.; Pickart, C.; Zhu, H. Functional dissection of a HECT ubiquitin E3 ligase. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2008, 7, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Xie, Z.; Qian, J.; Blackshaw, S.; Zhu, H. Functional protein microarray technology. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2011, 3, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwarteng, A.; Ahuno, S.T. The Potentials and Pitfalls of Microarrays in Neglected Tropical Diseases: A Focus on Human Filarial Infections. Microarrays 2016, 5, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays5030020
Kwarteng A, Ahuno ST. The Potentials and Pitfalls of Microarrays in Neglected Tropical Diseases: A Focus on Human Filarial Infections. Microarrays. 2016; 5(3):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays5030020
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwarteng, Alexander, and Samuel Terkper Ahuno. 2016. "The Potentials and Pitfalls of Microarrays in Neglected Tropical Diseases: A Focus on Human Filarial Infections" Microarrays 5, no. 3: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays5030020
APA StyleKwarteng, A., & Ahuno, S. T. (2016). The Potentials and Pitfalls of Microarrays in Neglected Tropical Diseases: A Focus on Human Filarial Infections. Microarrays, 5(3), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/microarrays5030020