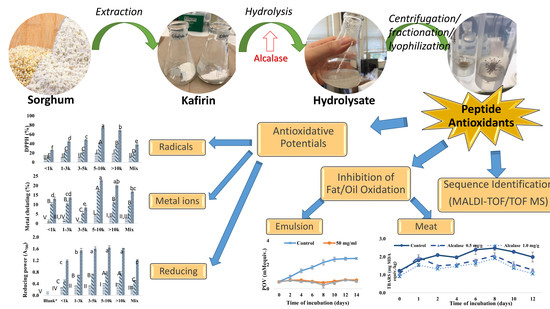
Antioxidant Activities of Sorghum Kafirin Alcalase Hydrolysates and Membrane/Gel Filtrated Fractions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Sorghum Protein Hydrolysates
2.3. Hydrolysate Fractionation and Peptide Identification
2.3.1. Ultrafiltration with Stirred Cell
2.3.2. Gel Filtration Chromatography
2.3.3. Identification of Kafirin Proteins and Peptide Sequences
2.4. Characterization of Protein Hydrolysate and Antioxidant Properties
2.4.1. Total Protein Recovery
2.4.2. Degree of Hydrolysis
2.4.3. Total Phenolic Content
2.4.4. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
2.4.5. ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity
2.4.6. Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity
2.4.7. Ferric Ion Reducing Power
2.4.8. Metal Chelating Capacity
2.4.9. Inhibition of Lipid Oxidation in Oil-in-Water Emulsion Systems
2.4.10. Inhibition of Lipid Oxidation in Meat Systems
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Reaction Time and Enzyme-to-Substrate Ratio on Hydrolysis Process and Antioxidant Activity
3.2. Ultrafiltration of Kafirin Alcalase Hydrolysates
3.3. Inhibition of Lipid Oxidation in Model Systems
3.3.1. Oil-in-Water Emulsion System
3.3.2. Ground Meat System
3.4. Purification and Identification of Antioxidative Peptides from Kafirin Hydrolysates
3.4.1. Gel Filtration
3.4.2. Identification of Representative Peptide Sequences from Gel Filtration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Awika, J.M. Major cereal grains production and use around the world. ACS Symp. Ser. 2011, 1089, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.H.; Weller, C.L.; Cuppett, S.L.; Carr, T.P.; Walter, J.; Martínez, I.; Schlegel, V.L. Grain sorghum lipids: Extraction, characterization, and health potential. ACS Symp. Ser. 2011, 1089, 149–170. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, M.S. Natural antioxidants: Sources, compounds, mechanisms of action, and potential applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masisi, K.; Beta, T.; Moghadasian, M.H. Antioxidant properties of diverse cereal grains: A review on in vitro and in vivo studies. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, R.J.; Kellerby, S.S.; Decker, E.A. Antioxidant activity of proteins and peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarmadi, B.H.; Ismail, A. Antioxidative peptides from food proteins: A review. Peptides 2010, 31, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Selomulya, C.; Wang, S.; Xiong, H.; Chen, X.D.; Li, W.; Peng, H.; Xie, J.; Sun, W.; Zhou, Q. Enhancing the oxidative stability of food emulsions with rice dreg protein hydrolysate. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.X.; Liu, X.L.; Zheng, X.Q.; Wang, X.J.; He, J.F. Preparation of antioxidative corn protein hydrolysates, purification and evaluation of three novel corn antioxidant peptides. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alashi, A.M.; Blanchard, C.L.; Mailer, R.J.; Agboola, S.O.; Mawson, A.J.; He, R.; Girgih, A.; Aluko, R.E. Antioxidant properties of Australian canola meal protein hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Bamdad, F.; Gänzle, M.; Chen, L. Fractionation and characterization of antioxidant peptides derived from barley glutelin by enzymatic hydrolysis. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, B.; Xiong, Y.L. Antioxidant activity of zein hydrolysates in a liposome system and the possible mode of action. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6059–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.Q.; Li, L.T.; Liu, X.L.; Wang, X.J.; Lin, J.; Li, D. Production of hydrolysate with antioxidative activity by enzymatic hydrolysis of extruded corn gluten. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 73, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Zhou, H.; Qian, H. Antioxidant and free radical-scavenging activities of wheat germ protein hydrolysates (WGPH) prepared with alcalase. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Kim, Y.T.; Byun, H.G.; Nam, K.S.; Joo, D.S.; Shahidi, F. Isolation and characterization of antioxidative peptides from gelatin hydrolysate of Alaska pollack skin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 1984–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, P.J.; Jung, W.K.; Nam, K.S.; Shahidi, F.; Kim, S.K. Purification and characterization of antioxidative peptides from protein hydrolysate of lecithin-free egg yolk. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2001, 78, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamnarathip, P.; Jangchud, K.; Nitisinprasert, S.; Vardhanabhuti, B. Identification of peptide molecular weight from rice bran protein hydrolysate with high antioxidant activity. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 69, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, H.; Joshi, R.; Gupta, M. Isolation and characterisation of enzymatic hydrolysed peptides with antioxidant activities from green tender sorghum. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 84, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Zhou, K. Chelating and radical scavenging activities of soy protein hydrolysates prepared from microbial proteases and their effect on meat lipid peroxidation. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 2084–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, T.; Mu, W.; Liu, J. Antioxidant and free radical-scavenging activities of chickpea protein hydrolysate (CPH). Food Chem. 2008, 106, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, X.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) albumin hydrolysates. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Jiang, T.S.; Pan, J.L. Antioxidant activities of rapeseed protein hydrolysates. Food Bioprocess Tech. 2011, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougatef, A.; Nedjar-Arroume, N.; Manni, L.; Ravallec, R.; Barkia, A.; Guillochon, D.; Nasri, M. Purification and identification of novel antioxidant peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) by-products proteins. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, É.A.; Marineli, R.D.S.; Lenquiste, S.A.; Steel, C.J.; de Menezes, C.B.; Queiroz, V.A.V.; Maróstica Júnior, M.R. Sorghum flour fractions: Correlations among polysaccharides, phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity and glycemic index. Food Chem. 2015, 180, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Du, J.; Jia, J.; Kuang, C. Production of ACE inhibitory peptides from sweet sorghum grain protein using alcalase: Hydrolysis kinetic, purification and molecular docking study. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortíz Cruz, R.A.; Cárdenas López, J.L.; González Aguilar, G.A.; Astiazarán García, H.; Gorinstein, S.; Canett Romero, R.; Robles Sánchez, M. Influence of sorghum kafirin on serum lipid profile and antioxidant activity in hyperlipidemic rats (in vitro and in vivo studies). Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 164725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, A.C.; Pangloli, P.; Dia, V.P. Kafirin from Sorghum bicolor inhibition of inflammation in THP-1 human macrophages is associated with reduction of intracellular reactive oxygen species. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 111, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, V.; Niketh, S.; Chandrashekar, A.; Rajini, P.S. Chymotryptic hydrolysates of α-kafirin, the storage protein of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) exhibited angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory activity. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tilley, M.; Bean, S.; Susan Sun, X.; Wang, D. Comparison of methods for extracting kafirin proteins from sorghum distillers dried grains with solubles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 8366–8372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, P.M.; Petersen, D.; Dambmann, C. Improved method for determining food protein degree of hydrolysis. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Ou, B.; Hampsch-Woodill, M.; Flanagan, J.A.; Deemer, E.K. Development and validation of oxygen radical absorbance capacity assay for lipophilic antioxidants using randomly methylated β-cyclodextrin as the solubility enhancer. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1815–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duh, P.D.; Tu, Y.Y.; Yen, G.C. Antioxidant activity of water extract of harng jyur (Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat). LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 32, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, E.A.; Welch, B. Role of ferritin as a lipid oxidation catalyst in muscle food. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 674–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, H.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Role of continuous phase protein on the oxidative stability of fish oil-in-water emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 4558–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, L.; Yang, Q.; Sun, J.; Bi, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, C.; Tang, L. Optimization of a microwave-coupled enzymatic digestion process to prepare peanut peptides. Molecules 2012, 17, 5661–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Chen, Z.; Shao, J.; Wang, C.; Zhan, C. Effect of fermentation on the peptide content, phenolics and antioxidant activity of defatted wheat germ. Food Biosci. 2017, 20, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, X.; Kopparapu, N.; Cong, W.; Deng, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, X. Purification and evaluation of a novel antioxidant peptide from corn protein hydrolysate. Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Zhuang, H. Evaluation of antioxidant activities of zein protein fractions. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, C2174–C2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, Y. Antioxidant properties of papain hydrolysates of wheat gluten in different oxidation systems. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 1658–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xiong, Y.L.; Chen, J. Antioxidant and emulsifying properties of potato protein hydrolysate in soybean oil-in-water emulsions. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Muramoto, K.; Yamauchi, F. Structural analysis of antioxidative peptides from soybean β-conglycinin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1995, 43, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaranayaka, A.G.P.; Li-Chan, E.C.Y. Food-derived peptidic antioxidants: A review of their production, assessment, and potential applications. J. Funct. Foods 2011, 3, 229–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Kouzuma, Y.; Yonekura, M. Structures and properties of antioxidative peptides derived from royal jelly protein. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| RP-HPLC Peak | 1.6 min | 3.6 min | 35.0 min | 36.0 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area% | 30.62% | 11.03% | 2.34% | 4.15% |
| Coverage% | 36.50% | 82.80% | 54.70% | 27.10% |
| Sequences * | KMVIV | QWQQ | QQWQ | KMVIV |
| LAVCLA | QQWQ | QWQQ | AVCLAL | |
| AVCLAL | GVVQSV | GVVQSV | LAVCLA | |
| QQWQ | QLQGVA | QQWQ | ||
| QWQQ | VQQLQ | QWQQ | ||
| RQQCC | VAQVAQ | |||
| MCGWQ | RQQCC | |||
| CATSAAI | MCGWVVQ | |||
| CATSAAI | ||||
| DMQSR |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.; Shen, Y.; Li, Y. Antioxidant Activities of Sorghum Kafirin Alcalase Hydrolysates and Membrane/Gel Filtrated Fractions. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8050131
Xu S, Shen Y, Li Y. Antioxidant Activities of Sorghum Kafirin Alcalase Hydrolysates and Membrane/Gel Filtrated Fractions. Antioxidants. 2019; 8(5):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8050131
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Shiwei, Yanting Shen, and Yonghui Li. 2019. "Antioxidant Activities of Sorghum Kafirin Alcalase Hydrolysates and Membrane/Gel Filtrated Fractions" Antioxidants 8, no. 5: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8050131
APA StyleXu, S., Shen, Y., & Li, Y. (2019). Antioxidant Activities of Sorghum Kafirin Alcalase Hydrolysates and Membrane/Gel Filtrated Fractions. Antioxidants, 8(5), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8050131