Dependence of Water-Permeable Chitosan Membranes on Chitosan Molecular Weight and Alkali Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Chitosan Membrane
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.4. Water Content
2.5. Mechanical Strength
2.6. Water Permeability
2.7. Measurement of the Mass Transfer Flux
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.2. Volumetric Water Content
3.3. Mechanical Strength
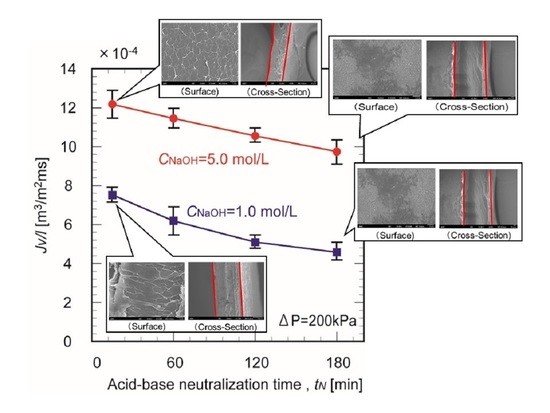
3.4. Water Permeability
3.5. Mass Permeation Performance of the Chitosan Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, S.; Ye, F.; Dobretsov, S.; Dutta, J. Chitosan nanocomposite coatings for food, paints, and water treatment applications. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dodane, Y.; Vilivalam, V.D. Pharmaceutical applications of chitosan. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 1998, 1, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.V.R. A review of chitin and chitosan application. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierszewska, M.; Czubenko, J.O.; Chrzanowska, E. pH-responsive chitosan/alginate polyelectrolyte complex membranes reinforced by tripolyphosphate. Euro. Poly. J. 2018, 101, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.R.; Hsu, L.H.; Xiao, E.S.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y. Using genipin as a “green” crosslinker to fabricate chitosan membranes for pervaporative dehydration of isopropanol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 244, 116843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Poym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X. Flocculation prperties of biodegradable amphoteric chitosan-based flocculants. Biochem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- Igberase, E.; Osifo, P. Equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic and desorption studies of cadmium and lead by polyaniline grafted cross-linked chitosan beads from aqueous. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 26, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.C.; Tseng, R.L.; Juang, R.S. A review and experimental verification of using chitosan and its derivatives as adsorbents for selected heavy metals. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, C.K.S.; Paul, W.; Sharma, C.P. Chitin and chitosan polymers: Chemistry, solubility and fiber formation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 641–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Teng, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q. Development of carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel beads in alcohol-aqueous binary solvent for nutrient delivery applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofuji, K.; Murata, Y.; Kawashima, S. Sustained insulin release with biodegradation chitosan gel beads prepared by copper ions. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 303, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, F.; Rizvi, M.M.; Kar, S.K. Oral delivery of curcumin bound to chitosan nanoparticles cured Plasmodium yoelii infected mice. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juang, R.S.; Shiau, R.C. Metal removal from aqueous solutions using chitosan-enhanced membrane filtration. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 165, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.D.; Chu, L.Y.; Song, H.; Yang, J.P.; Xie, R.; Yang, M. Preparation and enantiomer separation characteristics of chitosan/β-cyclodextrin composite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 297, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Azzanmi, L.A.; Grulke, E.A. Carbon dioxide separation from hydrogen and nitrogen by fixed facilitated transport in swollen chitosan membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 323, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, I.B.; Miranda, N.G.M.; Gomes, F.S.; Santos, M.C.S.; Freitas, D.G.C.; Tonon, R.V.; Cabral, L.M.C. Physicochemical and sensory properties of apple juice concentrated by reverse osmosis and osmotic evaporation. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2012, 16, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatialis, D.F.; Papenburg, B.J.; Girones, M.; Saiful, S.; Mettahalli, S.N.M.; Schmitmeier, S.; Wessling, M. Medical applications of membranes: Drug delivery, artificial organs and tissue engineering. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 308, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Yu, S.; Gao, C. Preparation, structure characteristics and separation properties of thin-film composited polyamideurethane seawater reverse osmosis membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 947–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimczak, K.; Stanislawek, E. Reclamation of water form dairy wastewater using polymeric nanofiltration membranes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2018, 128, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibal, E.; Milot, C.; Eterradossi, O.; Gauffier, C.; Domar, A. Study of molybdate ion sorption on chitosan gel beads by different spectrometric analyses. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1999, 24, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewska, B. Pore structure of gel chitosan membrane III. Pressure-driven mass transport measurements. Polym. Gles. Netw. 1996, 4, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aznar, E.; Oroval, M.; Pascual, L.; Murguia, J.R.; Manez, M.R.; Sancenon, F. Gated materials for on-command release of guest molecules. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 561–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osifo, P.O.; Neomagus, H.W.J.P.; Merwe, H.V.D.; Branken, D.J. Transport properties of chitosan membranes for zinc (II) removal from aqueous systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 179, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, R.; Yano, T.; Imai, M.; Namiki, N. Highly Size-Selective Water-Insoluble Cross-Linked Carboxymethyl Cellulose Membranes. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 2439–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, L.; Cao, X.; Liu, Y. Structure and microporous formation of cellulose/silk fibroin blend membranes Part II. Effect of post-treatment by alkali. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 210, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Copeland, L. Effect of alkali treatment on structure and function of pea starch granules. Food Chem. 2002, 135, 1635–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uragami, T.; Matsuda, T.; Okuno, H.; Miyata, T. Structure of chiemically modified chitosan membranes and their charactersitics of permeation and separation of aqueous ethanol solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 1994, 88, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siroky, J.; Blackburn, R.S.; Bechtold, T.; Taylor, J.; White, P. Alkali treatment of cellulose II fibers and effect on dye sorption. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuluaga, R.; Putaux, J.L.; Cruz, J.; Velez, J.; Mondragon, I.; Ganan, P. Cellulose microfibrils from banana rachis: Effect of alkaline treatments on structural and morphological features. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Type of Chitosan | Manufacture | Intrinsic Viscosity | Mean Molecular Weight, MW [Da] * | Guarantee Viscosity [cP] ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chitosan (Low Viscosity) | Sigma-Aldrich | 8.2 | 3.81 × 105 | 20–200 |
| Chitosan (Medium Viscosity) | Sigma-Aldrich | 10.5 | 4.45 × 105 | 200–800 |
| Chitosan (High Viscosity) | Sigma-Aldrich | 14.9 | 7.15 × 105 | 800–2000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakayama, R.-i.; Katsumata, K.; Niwa, Y.; Namiki, N. Dependence of Water-Permeable Chitosan Membranes on Chitosan Molecular Weight and Alkali Treatment. Membranes 2020, 10, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110351
Nakayama R-i, Katsumata K, Niwa Y, Namiki N. Dependence of Water-Permeable Chitosan Membranes on Chitosan Molecular Weight and Alkali Treatment. Membranes. 2020; 10(11):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110351
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakayama, Ryo-ichi, Koki Katsumata, Yuta Niwa, and Norikazu Namiki. 2020. "Dependence of Water-Permeable Chitosan Membranes on Chitosan Molecular Weight and Alkali Treatment" Membranes 10, no. 11: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110351
APA StyleNakayama, R. -i., Katsumata, K., Niwa, Y., & Namiki, N. (2020). Dependence of Water-Permeable Chitosan Membranes on Chitosan Molecular Weight and Alkali Treatment. Membranes, 10(11), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110351