Desalination Technology in South Korea: A Comprehensive Review of Technology Trends and Future Outlook
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Fresh Water Resources and the Desalination Industry in South Korea
2.1. Fresh Water Resources and Desalination Facilities in South Korea
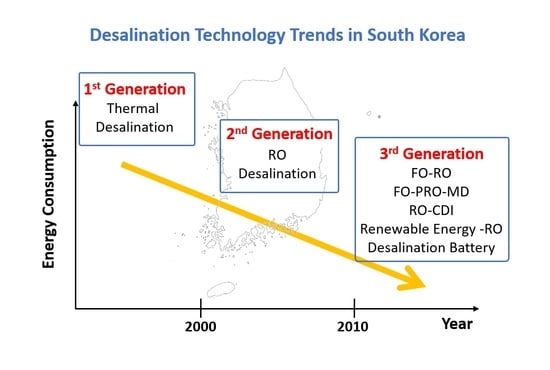
2.2. Overview of Desalination Technology Trends and the Desalination Industry in South Korea
3. Status of Desalination Research in South Korea
3.1. Roadmap of Desalination Research in South Korea
3.2. Reverse Osmosis
3.3. Forward Osmosis
3.4. Pressure-Retarded Osmosis
3.5. Membrane Distillation
3.6. Capacitive Deionization
3.7. Renewable-Energy-Powered Desalination
3.8. Desalination Battery
4. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Sustainability: Four billion people facing severe water scarcity. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boretti, A.; Rosa, L. Reassessing the projections of the World Water Development Report. Npj Clean Water 2019, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziolkowska, J.R.; Reyes, R. Impact of socio-economic growth on desalination in the US. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 167, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.-H.; Kim, I.S. Comparative analysis of seawater desalination technology in Korea and overseas. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2016, 38, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nam, S.; Chun, K.-W.; Lee, J.U.; Kang, W.S.; Jang, S.-J. Hydrograph separation and flow characteristic analysis for observed rainfall events during flood season in a forested headwater stream. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2021, 54, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-K.; Yum, S.S.; Oh, S.-N.; Nam, J.-C.; Chang, K.-H. A feasibility study of winter orographic cloud seeding experiments in the korean peninsula. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 41, 997–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, Y.; Shin, J.-Y.; Ahn, H.; Heo, J.-H. The Spatial and temporal structure of extreme rainfall trends in South Korea. Water 2017, 9, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daesan, First Large Capacity Desalination Plant in South Korea. Available online: https://inima.com/en/comunicacion/detalle/daesan-primera-planta-desaladora-de-gran-capacidad-en-corea-del-sur (accessed on 11 December 2021).
- Desalination Faccility in South Korea. Available online: http://www.roplant.or.kr/contents.asp?Depth1=7&Depth2=5 (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Current Status of Seawater Desalination Facility. Available online: http://www.me.go.kr/home/web/policy_data/read.do?pagerOffset=0&maxPageItems=10&maxIndexPages=10&searchKey=title&searchValue=%ED%95%B4%EC%88%98&menuId=10264&orgCd&seq=6565 (accessed on 30 November 2021).
- Choi, J.-S.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.-M.; Choi, S. Small-scale desalination plants in Korea: Technical challenges. Desalination 2009, 247, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curto, D.; Franzitta, V.; Guercio, A. A Review of the Water Desalination Technologies. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaisi, A.; Mossad, R.; Sharifian-Barforoush, A. A review of the water desalination systems integrated with renewable energy. Energy Procedia 2017, 110, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, L.F.; Lawler, D.F.; Freeman, B.D.; Marrot, B.; Moulin, P. Reverse osmosis desalination: Water sources, technology, and today’s challenges. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2317–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najid, N.; Fellaou, S.; Kouzbour, S.; Gourich, B.; Ruiz-García, A. Energy and environmental issues of seawater reverse osmosis desalination considering boron rejection: A comprehensive review and a case study of exergy analysis. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 156, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, K.; Yang, D.R.; Hong, S. A comprehensive review of energy consumption of seawater reverse osmosis desalination plants. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabatake, H.; Taniguchi, M.; Kurihara, M. Advanced technologies for stabilization and high performance of seawater RO membrane desalination plants. Membranes 2021, 11, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abengoa Water Desalination. Available online: https://www.abengoa.com/export/sites/abengoa_corp/resources/pdf/noticias_y_publicaciones/Presentacion-Desalacion-Agua_en.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2021).
- Goh, P.S.; Kang, H.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Hilal, N. The hybridization of thermally-driven desalination processes: The state-of-the-art and opportunities. Desalination 2021, 506, 115002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GS E&C to Finalize Acquisition Deal of Spain’s Water Treatment Company. Available online: https://pulsenews.co.kr/view.php?year=2012&no=312360 (accessed on 6 January 2022).
- GS Inima Environment Wins Desalination Project Worth $2.1 Billion in Oman. Available online: https://smartwatermagazine.com/news/smart-water-magazine/gs-inima-environment-wins-desalination-project-worth-21-billion-oman (accessed on 6 January 2022).
- National Science and Technology Information Service of Korea (NTIS). Available online: https://www.ntis.go.kr/ (accessed on 11 November 2021).
- Water Desalination Equipment Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Technology (Reverse Osmosis (RO), Multi-Stage Flash (MSF) Distillation), by Source, by Application, by Region, and Segment Forecasts, 2020–2028. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/water-desalination-equipment-market (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Zapata-Sierra, A.; Cascajares, M.; Alcayde, A.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Worldwide research trends on desalination. Desalination 2021, 519, 115305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Ma, Q.; Lu, H.; Fang, H.; Yang, P.; Fan, J. The research and application progress of the isobaric erd technique for swro desalination plant. Desalin. Water Treat. 2020, 202, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.C.; Kim, S.H.; Shon, H.K.; Tijing, L.D. Introduction: Membrane Desalination Today, Past, and Future; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. xxv–xlvi. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Oh, B.S.; Hwang, M.-H.; Hong, S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, I.S. An ambitious step to the future desalination technology: SEAHERO R&D program (2007–2012). Appl. Water Sci. 2011, 1, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- First Domestic Export of High-Pressure Pump for Seawater Desalination Plant. Available online: http://www.ikld.kr/news/articleView.html?idxno=10687 (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Cath, T.Y.; Childress, A.E.; Elimelech, M. Forward osmosis: Principles, applications, and recent developments. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zou, L.; Tang, C.Y.; Mulcahy, D. Recent developments in forward osmosis: Opportunities and challenges. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 396, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, D.L.; Werber, J.R.; Jaramillo, H.; Lin, S.; Elimelech, M. Forward osmosis: Where are we now? Desalination 2015, 356, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, N.Y.; Tiraferri, A.; Phillip, W.A.; Schiffman, J.D.; Elimelech, M. High performance thin-film composite forward osmosis membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3812–3818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Shi, W.; Yu, S. Research on forward osmosis membrane technology still needs improvement in water recovery and wastewater treatment. Water 2020, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S. Performance comparison of spiral-wound and plate-and-frame forward osmosis membrane module. Membranes 2020, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Blandin, G.; Phuntsho, S.; Verliefde, A.; Le-Clech, P.; Shon, H. Practical considerations for operability of an 8″ spiral wound forward osmosis module: Hydrodynamics, fouling behaviour and cleaning strategy. Desalination 2017, 404, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekli, L.; Phuntsho, S.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.Y.; Choi, J.-S.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, S.; Sohn, J.; et al. A comprehensive review of hybrid forward osmosis systems: Performance, applications and future prospects. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 430–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, L.A.; Phillip, W.A.; Tiraferri, A.; Yip, N.Y.; Elimelech, M. Forward with osmosis: Emerging applications for greater sustainability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9824–9830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, N.T.; Black, N.D.; Cath, T.Y. A comparative life cycle assessment of hybrid osmotic dilution desalination and established seawater desalination and wastewater reclamation processes. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Development of World’s First Forward Osmosis-Reverse Osmosis Hybrid Seawater Desalination Technology. Available online: http://www.energydaily.co.kr/news/articleView.html?idxno=103627 (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Jeon, J. Evaluation of Energy Consumption and Carbon Emission from a Forward Osmosis and reverse Osmosis Hybrid System for Seawater Desalination; Pukyong National University: Busan, Korea, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Klaysom, C.; Cath, T.Y.; Depuydt, T.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. Forward and pressure retarded osmosis: Potential solutions for global challenges in energy and water supply. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6959–6989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, N.Y.; Tiraferri, A.; Phillip, W.A.; Schiffman, J.D.; Hoover, L.A.; Kim, Y.C.; Elimelech, M. Thin-film composite pressure retarded osmosis membranes for sustainable power generation from salinity gradients. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4360–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achilli, A.; Childress, A.E. Pressure retarded osmosis: From the vision of Sidney Loeb to the first prototype installation—Review. Desalination 2010, 261, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Chung, T.-S. Progress in pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) membranes for osmotic power generation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 51, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarp, S.; Li, Z.; Saththasivam, J. Pressure retarded osmosis (PRO): Past experiences, current developments, and future prospects. Desalination 2016, 389, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, T.-S.; Park, Y.-G.; Lee, W.-I.; Kim, S.-H. Toward scale-up of seawater reverse osmosis (SWRO)—Pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) hybrid system: A case study of a 240 m3/day pilot plant. Desalination 2020, 491, 114429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, Y.C.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, S.-K.; Choi, H.-C. Experiment and modeling for performance of a spiral-wound pressure-retarded osmosis membrane module. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 10101–10110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Choi, J.; Park, Y.-G.; Shon, H.; Ahn, C.H.; Kim, S.-H. Hybrid desalination processes for beneficial use of reverse osmosis brine: Current status and future prospects. Desalination 2019, 454, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yeo, I.; Lee, W.; Park, T.; Park, Y. The study of a novel SWRO-PRO hybrid desalination technology. J. Korean Soc. Water Wastewater 2018, 32, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Elimelech, M. The Global rise of zero liquid discharge for wastewater management: Drivers, technologies, and future directions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6846–6855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drioli, E.; Ali, A.; Macedonio, F. Membrane distillation: Recent developments and perspectives. Desalination 2015, 356, 56–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, D.L.; Arias Chavez, L.H.; Ben-Sasson, M.; Romero-Vargas Castrillón, S.; Yip, N.Y.; Elimelech, M. Desalination and reuse of high-salinity shale gas produced water: Drivers, technologies, and future directions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9569–9583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taeshin, P.; Inho, Y.; Choi, J. Introduction of next-generation hybrid seawater desalination technology using membrane distillation (MD) and pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) technology. Water Future 2018, 51, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, Y.; Choi, J.; Park, Y.; Choi, Y.; Lee, S. Influence of operation conditions on the performance of pilot-scale vacuum membrane distillation (VMD). Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 97, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorji, P.; Choi, J.; Kim, D.I.; Phuntsho, S.; Hong, S.; Shon, H.K. Membrane capacitive deionisation as an alternative to the 2nd pass for seawater reverse osmosis desalination plant for bromide removal. Desalination 2018, 433, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Kim, T.; Shin, H.; Lee, J.; Ha, J.-I.; Yoon, J. Direct energy recovery system for membrane capacitive deionization. Desalination 2016, 398, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; He, C.; Fletcher, J.; Waite, T.D. Energy recovery in pilot scale membrane CDI treatment of brackish waters. Water Res. 2020, 168, 115146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omosebi, A.; Li, Z.; Holubowitch, N.; Gao, X.; Landon, J.; Cramer, A.; Liu, K. Energy recovery in capacitive deionization systems with inverted operation characteristics. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2020, 6, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Hong, S.P.; Lee, C.; Yoon, J.; Kim, C. Short review of multichannel membrane capacitive deionization: Principle, current status, and future prospect. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, M.; Deshmukh, A.; Epsztein, R.; Patel, S.K.; Owoseni, O.M.; Walker, W.S.; Elimelech, M. Comparison of energy consumption in desalination by capacitive deionization and reverse osmosis. Desalination 2019, 455, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybar, S.; Boda, R.; Bartels, C. Split partial second pass design for SWRO plants. Desalin. Water Treat. 2010, 13, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segal, H.; Birnhack, L.; Nir, O.; Lahav, O. Intensification and energy minimization of seawater reverse osmosis desalination through high-pH operation: Temperature dependency and second pass implications. Chem. Eng. Process. 2018, 131, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGovern, R.K.; Lienhard, V.J.H. On the potential of forward osmosis to energetically outperform reverse osmosis desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 469, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glueckstern, P.; Priel, M. Optimization of boron removal in old and new SWRO systems. Desalination 2003, 156, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, S.; Sivan, O.; Yechieli, Y.; Kasher, R.; Nir, O. An advantage for desalination of coastal saline groundwater over seawater in view of boron removal requirements. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 2241–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Hwang, M.-H.; Lim, S.k.; Chu, K.H.; Kim, N.; Park, K.; Kim, J. Development of the low energy seawater desalination technology optimized for the Middle East. J. Korean Soc. Civ. Eng. 2019, 62, 26–37. [Google Scholar]
- Voutchkov, N. Desalination Engineering: Planning and Design; McGraw Hill Professional: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sarant, L. The Middle East: An end to oil dependency. Nature 2016, 537, S6–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masdar’s Renewable Energy Desalination Pilot Programme Finds Solar Energy-Powered Desalination to be Commercially-Viable. Available online: https://news.masdar.ae/en/news/2019/02/19/10/00/masdars-renewable-energy-desalination-pilot-programme-finds-solar-energy-powered-desalination (accessed on 12 November 2021).
- Ghaffour, N.; Mujtaba, I.M. Desalination using renewable energy. Desalination 2018, 435, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, E.; McLellan, B.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Tezuka, T. The role of renewable energy resources in sustainability of water desalination as a potential freshwater source: An updated review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundschuh, J.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Ghaffour, N.; Tomaszewska, B. State-of-the-art of renewable energy sources used in water desalination: Present and future prospects. Desalination 2021, 508, 115035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hady, B.; Kashyout, A.; Hassan, A.; Hassan, G.; El-Banna Fath, H.; El-Wahab Kassem, A.; Elshimy, H.; Ranjanvepa; Shaheed, M.H. Hybrid renewable energy/hybrid desalination potentials for remote areas: Selected cases studied in Egypt. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 13201–13219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.H.; Jung, S.H.; Yang, D.K.; Kim, M.K.; Oh, S.J. A case study of automated energy independence island for Juk-do. In Proceedings of the Korean Institue of Power Elecronics, Hoengseong, Korea, 3 July 2018; pp. 171–173. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Ligaray, M.; Kim, Y.; Chon, K.; Son, M.; Cho, K.H. Investigating the influence of catholyte salinity on seawater battery desalination. Desalination 2021, 506, 115018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.E.; Khalil, A.; Hilal, N. Emerging desalination technologies: Current status, challenges and future trends. Desalination 2021, 517, 115183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, W.; Zhu, M.; Li, C. Recent advances in desalination battery: An initial review. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 57671–57685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dai, J.; Jiang, Z.; Chu, B.; Chen, F. Recent progress and prospect of flow-electrode electrochemical desalination system. Desalination 2021, 504, 114964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea East-West Power Company (KEWP) and Korean Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO) Invest 5 Billion Won in UNIST Seawater Battery Development. Available online: https://news.mt.co.kr/mtview.php?no=2017013109260876853 (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Son, M.; Park, S.; Kim, N.; Angeles, A.T.; Kim, Y.; Cho, K.H. Simultaneous energy storage and seawater desalination using rechargeable seawater battery: Feasibility and future directions. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2101289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.M.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, Y.; Go, W.; Han, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y. Rechargeable seawater batteries—From concept to applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1804936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.; Qadir, M.; van Vliet, M.T.H.; Smakhtin, V.; Kang, S.-M. The state of desalination and brine production: A global outlook. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1343–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Plant Location | Capacity (m3/day) | Feed Water Type | 1st Year of Production | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seosan | 16,000 | brackish water | 1988 | industrial water |
| Seosan | 25,000 | brackish water | 1990 | industrial water |
| Seosan | 84,000 | brackish water | 1991 | industrial water |
| Dangjin | 4500 | brackish water | 1997 | industrial water |
| Dangjin | 182,000 | brackish water | 2009 | industrial water |
| Daesan | 119,000 | brackish water | 2012 | industrial water |
| Gwangyang | 30,000 | seawater | 2014 | industrial water |
| Samcheok | 2400 | seawater | 2017 | power plant |
| Uljin | 10,000 | seawater | 2020 | power plant |
| Daesan | 100,000 | seawater | 2024 (plan) | industrial water |
| Capacity (m3/day) | Number of Facilities | Percentage (%) | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10–49 | 60 | 55.0 | municipal water |
| 50–99 | 29 | 26.6 | municipal water |
| 100–499 | 17 | 15.6 | municipal water |
| 500–1000 | 3 | 2.8 | municipal water |
| Rank | Keywords | Number |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | membrane, membranes, membrane technology | 569 |
| 2 | seawater, seawater desalination, sea water | 522 |
| 3 | reverse osmosis, seawater reverse osmosis, RO membrane, reverse osmosis desalination | 377 |
| 4 | water filtration, filtration | 377 |
| 5 | water treatment, water purification, purification | 275 |
| 6 | fouling, membrane fouling, fouling control | 226 |
| 7 | osmosis | 182 |
| 8 | wastewater treatment, wastewater, wastewater reclamation, waste water management | 162 |
| 9 | electrode, electrochemical electrode | 159 |
| 10 | energy efficiency, energy consumption, specific energy consumption | 152 |
| 11 | capacitive deionization, membrane capacitive deionization | 150 |
| 12 | distillation | 148 |
| 13 | water, water supply | 143 |
| 14 | sodium chloride | 119 |
| 15 | forward osmosis | 115 |
| 16 | membrane distillation, direct contact membrane distillation | 115 |
| 17 | energy utilization | 105 |
| 18 | concentration | 94 |
| 19 | polarization, concentration polarization | 93 |
| 20 | biofouling, biofilm | 89 |
| Research Program | Period | Technology | Pilot Scale (m3/day) | Major Achievements and Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEAHERO program | 2007–2012 | SWRO | 45,000 |
|
| Development of multi-purpose FO desalination plant | 2009–2014 | FO | 20 |
|
| Global MVP program | 2013–2018 | PRO MD | 240 (PRO) 400 (MD) |
|
| FOHC program | 2014–2019 | FO | 1000 |
|
| KORAE | 2016–2020 | RO CDI | 120 50 |
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Lee, S. Desalination Technology in South Korea: A Comprehensive Review of Technology Trends and Future Outlook. Membranes 2022, 12, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020204
Park J, Lee S. Desalination Technology in South Korea: A Comprehensive Review of Technology Trends and Future Outlook. Membranes. 2022; 12(2):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020204
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jongkwan, and Sungyun Lee. 2022. "Desalination Technology in South Korea: A Comprehensive Review of Technology Trends and Future Outlook" Membranes 12, no. 2: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020204
APA StylePark, J., & Lee, S. (2022). Desalination Technology in South Korea: A Comprehensive Review of Technology Trends and Future Outlook. Membranes, 12(2), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12020204