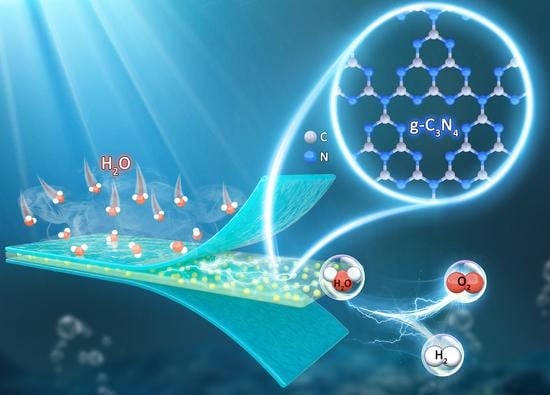
Novel Nafion/Graphitic Carbon Nitride Nanosheets Composite Membrane for Steam Electrolysis at 110 °C
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of g-C3N4 Nanosheets
2.3. Fabrication of the Nafion/g-C3N4 Membrane
2.4. Physical Characterization
2.5. Water Absorption and Degree of Swelling
2.6. Proton Conductivity Tests
2.7. Electrolysis Tests
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of g-C3N4
3.2. Properties of Nafion/X wt.% g-C3N4 Modified Membranes
3.3. Water Absorption, Swelling Degree, and Mechanical Properties
3.4. Proton Conductivity
3.5. Electrolysis Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hosseini, S.E.; Wahid, M.A. Hydrogen production from renewable and sustainable energy resources: Promising green energy carrier for clean development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 850–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, C.; Ge, M. Review of the Research Status of Cost−Effective Zinc–Iron Redox Flow Batteries. Batteries 2022, 8, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Shehzad, M.A.; Yang, X.; Li, G.; Wang, H.; Yu, W.; Liang, X.; Ge, X.; Wu, L.; Xu, T. High−performance bipolar membrane for electrochemical water electrolysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 656, 120660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriev, S.A.; Porembsky, V.I.; Fateev, V.N. Pure hydrogen production by PEM electrolysis for hydrogen energy. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2006, 31, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, M.; Fritz, D.L.; Mergel, J.; Stolten, D. A comprehensive review on PEM water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 4901–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Gong, X.; Guo, Z. The intensification technologies to water electrolysis for hydrogen production—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijani, A.S.; Rahim, A.H.A. Numerical Modeling the Effect of Operating Variables on Faraday Efficiency in PEM Electrolyzer. Procedia Technol. 2016, 26, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, K.G.D.; Eckert, C.; de Rossi, E.; Bariccatti, R.A.; Frigo, E.P.; Lindino, C.A.; Alves, H.J. Hydrogen production in the electrolysis of water in Brazil, a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttler, A.; Spliethoff, H. Current status of water electrolysis for energy storage, grid balancing and sector coupling via power−to−gas and power−to−liquids: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2440–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, H.R. Polymer electrolytes for low and high temperature PEM electrolyzers. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2022, 36, 101109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkous, C.A.; Anderson, H.R.; Kopitzke, R.W.; Nelson, G.L. Development of new proton exchange membrane electrolytes for water electrolysis at higher temperatures. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 1998, 23, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforov, A.V.; Tomás García, A.L.; Petrushina, I.M.; Christensen, E.; Bjerrum, N.J. Preparation and study of IrO2/SiC–Si supported anode catalyst for high temperature PEM steam electrolysers. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 5797–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforov, A.V.; Petrushina, I.M.; Christensen, E.; Alexeev, N.V.; Samokhin, A.V.; Bjerrum, N.J. WC as a non−platinum hydrogen evolution electrocatalyst for high temperature PEM water electrolysers. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 18591–18597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksey, N.; Erik, C.; Irina, P.; Jens Oluf, J.; Niels, J.B. Advanced Construction Materials for High Temperature Steam PEM Electrolysers. In Electrolysis; Vladimir, L., Janis, K., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M.K. PEM Water Electrolysis at Elevated Temperatures; Department of Energy Conversion and Storage, Technical University of Denmark: Kongens Lyngby, Denmark, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, X.; Zhang, F.; Wu, L.; Yang, Z.; Xu, T. Current Challenges and Perspectives of Polymer Electrolyte Membranes. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 3773–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; Wu, L.; He, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Ge, L.; Bakangura, E.; Xu, T. Ion exchange membranes: New developments and applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 522, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, D.; Hansen, M.K.; Pan, C.; Li, Q.; Christensen, E.; Jensen, J.O.; Bjerrum, N.J. Phosphoric acid doped membranes based on Nafion®, PBI and their blends—Membrane preparation, characterization and steam electrolysis testing. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 6985–6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Kuila, T.; Nguyen, T.X.H.; Kim, N.H.; Lau, K.-t.; Lee, J.H. Polymer membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell: Recent advances and challenges. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 813–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, V.; Di Blasi, A.; Baglio, V.; Ornelas, R.; Matteucci, F.; Ledesma−Garcia, J.; Arriaga, L.G.; Aricò, A.S. High temperature operation of a composite membrane−based solid polymer electrolyte water electrolyser. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 7350–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglio, V.; Ornelas, R.; Matteucci, F.; Martina, F.; Ciccarella, G.; Zama, I.; Arriaga, L.G.; Antonucci, V.; Aricò, A.S. Solid Polymer Electrolyte Water Electrolyser Based on Nafion−TiO2 Composite Membrane for High Temperature Operation. Fuel Cells 2009, 9, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Scott, K.; Basu, S. Performance of a high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolyser. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 8918–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz−Abad, S.; Fernández−Mancebo, S.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Lobato, J. Characterization of PBI/Graphene Oxide Composite Membranes for the SO2 Depolarized Electrolysis at High Temperature. Membranes 2022, 12, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Ying, Y.; Liu, G.; Chen, H.; Fan, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Guo, Z.; Zeng, G. High Proton−Conductive and Temperature−Tolerant PVC−P4VP Membranes towards Medium−Temperature Water Electrolysis. Membranes 2022, 12, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaroddin, M.F.A.; Sabli, N.; Nia, P.M.; Abdullah, T.A.T.; Abdullah, L.C.; Izhar, S.; Ripin, A.; Ahmad, A. Phosphoric acid doped composite proton exchange membrane for hydrogen production in medium−temperature copper chloride electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 22209–22222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Kamaroddin, M.F.; Sabli, N.; Tuan Abdullah, T.A.; Siajam, S.I.; Abdullah, L.C.; Abdul Jalil, A.; Ahmad, A. Membrane−Based Electrolysis for Hydrogen Production: A Review. Membranes 2021, 11, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.E.; Kim, J.; Han, J.; Kim, K.; Park, S.; Kim, S.; Park, H.S.; Cho, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-C.; Sung, Y.-E. High−performance proton−exchange membrane water electrolysis using a sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) membrane and ionomer. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Antonietti, M. Polymeric Graphitic Carbon Nitride as a Heterogeneous Organocatalyst: From Photochemistry to Multipurpose Catalysis to Sustainable Chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, J.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S.Z. Graphitic carbon nitride materials: Controllable synthesis and applications in fuel cells and photocatalysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6717–6731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Low, J.; Yu, J.; Jaroniec, M. Polymeric Photocatalysts Based on Graphitic Carbon Nitride. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2150–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xiao, P.; Li, H.; Carabineiro, S.A. Graphitic carbon nitride: Synthesis, properties, and applications in catalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 16449–16465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mori, T.; Niu, L.; Ye, J. Non−covalent doping of graphitic carbon nitride polymer with graphene: Controlled electronic structure and enhanced optoelectronic conversion. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 4517–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.S.; Jorge, A.B.; Suter, T.M.; Sella, A.; Corà, F.; McMillan, P.F. Carbon nitrides: Synthesis and characterization of a new class of functional materials. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 15613–15638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mansor, N.; Miller, T.S.; Dedigama, I.; Jorge, A.B.; Jia, J.; Brázdová, V.; Mattevi, C.; Gibbs, C.; Hodgson, D.; Shearing, P.R.; et al. Graphitic Carbon Nitride as a Catalyst Support in Fuel Cells and Electrolyzers. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 222, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, R.; Kong, L.; Zheng, L.; Wang, H.; Shi, H. Novel graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets/sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) acid−base hybrid membrane for vanadium redox flow battery. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 525, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Deng, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, R. Novel sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)/oxidized g−C3N4 composite membrane for vanadium redox flow battery applications. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 797, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, M.; He, G.; Li, Z.; Cao, K.; Li, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets/sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) nanocomposite membrane for direct methanol fuel cell application. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 507, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xu, K.; Chen, P.; Jia, K.; Liu, S.; Wu, C. Facile one step method realizing scalable production of g-C3N4nanosheets and study of their photocatalytic H2evolution activity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 18924–18928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Chu, Z.; Li, G.; Jiang, Z.; Hu, T.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C. Water−soluble ribbon−like graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4): Green synthesis, self−assembly and unique optical properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 8212–8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Hwang, S.; Yu, J.-S. Novel ordered nanoporous graphitic C3N4 as a support for Pt–Ru anode catalyst in direct methanol fuel cell. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 1656–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, J. Photo−induced reduction of biomass−derived 5−hydroxymethylfurfural using graphitic carbon nitride supported metal catalysts. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 101968–101973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonda, S.; Kumar, S.; Kandula, S.; Shanker, V. Fe−doped and −mediated graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets for enhanced photocatalytic performance under natural sunlight. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 6772–6780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Geng, K.; Yin, H.; Yang, C.; Hao, J.; Luan, Z.; Huang, Z.; Qin, X.; Song, W.; Li, N.; et al. Polybenzimidazole/cerium dioxide/graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets for high performance and durable high temperature proton exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 639, 119760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, C.-C.; Li, X.-J.; Shen, Q.; Qu, S.-G.; Shao, Z.-G.; Yi, B.-L. Investigation on sulfuric acid sulfonation of in−situ sol–gel derived Nafion/SiO2 composite membrane. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 3606–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yi, B.; Xing, D.; Liu, F.; Shao, Z.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, H. Degradation mechanism of polystyrene sulfonic acid membrane and application of its composite membranes in fuel cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003, 5, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yi, B.; Xing, D.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H. Nafion/PTFE composite membranes for fuel cell applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 212, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Désilets, F.; Felice, V.; Mecheri, B.; Licoccia, S.; Tavares, A.C. On the proton conductivity of Nafion–Faujasite composite membranes for low temperature direct methanol fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 9176–9187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Palma, L.; Bavasso, I.; Sarasini, F.; Tirillò, J.; Puglia, D.; Dominici, F.; Torre, L. Synthesis, characterization and performance evaluation of Fe3O4/PES nano composite membranes for microbial fuel cell. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 99, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velayutham, P.; Sahu, A.K. Graphitic Carbon Nitride Nanosheets—Nafion as a Methanol Barrier Hybrid Membrane for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 21735–21744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.K.; Aili, D.; Christensen, E.; Pan, C.; Eriksen, S.; Jensen, J.O.; von Barner, J.H.; Li, Q.; Bjerrum, N.J. PEM steam electrolysis at 130 °C using a phosphoric acid doped short side chain PFSA membrane. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 10992–11000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Membranes | Water Absorption (%) | Degree of Swelling (%) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nafion/0% g-C3N4 | 17.61 | 15.50 | 12.03 | 135.15 |
| Nafion/0.2% g-C3N4 | 21.88 | 16.88 | 13.02 | 57.20 |
| Nafion/0.4% g-C3N4 | 26.87 | 18.25 | 13.44 | 52.06 |
| Nafion/0.8% g-C3N4 | 30.65 | 23.63 | 14.63 | 63.20 |
| Membranes | Peak Current Density (A cm−2) | Anode Catalyst Quantity (mg cm−2) | Operating Temperature (°C) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nafion/0.4% g-C3N4 | 2.26 @2 V | 1.5 | 110 | This study |
| Nafion 212 | 1.38 @2 V | 1.5 | 110 | This study |
| Nafion/PA | 0.3 @1.75 V | 4 | 130 | [18] |
| PBI/PA | 0.5 @1.75 V | 4 | 130 | [18] |
| Nafion−SiO2 | 1.18 @1.9 V | 5 | 110 | [20] |
| Nafion−TiO2 | 0.7 @1.8 V | 5 | 120 | [21] |
| Aquivion/PA | 0.775 @1.8 V | 1 | 130 | [50] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.; Lv, B.; Sun, S.; Hao, J.; Shao, Z. Novel Nafion/Graphitic Carbon Nitride Nanosheets Composite Membrane for Steam Electrolysis at 110 °C. Membranes 2023, 13, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030308
Chen T, Lv B, Sun S, Hao J, Shao Z. Novel Nafion/Graphitic Carbon Nitride Nanosheets Composite Membrane for Steam Electrolysis at 110 °C. Membranes. 2023; 13(3):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030308
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Taipu, Bo Lv, Shucheng Sun, Jinkai Hao, and Zhigang Shao. 2023. "Novel Nafion/Graphitic Carbon Nitride Nanosheets Composite Membrane for Steam Electrolysis at 110 °C" Membranes 13, no. 3: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030308
APA StyleChen, T., Lv, B., Sun, S., Hao, J., & Shao, Z. (2023). Novel Nafion/Graphitic Carbon Nitride Nanosheets Composite Membrane for Steam Electrolysis at 110 °C. Membranes, 13(3), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13030308