Interconnected PolymerS TeChnology (IPSTiC): An Effective Approach for the Modulation of 5α-Reductase Activity in Hair Loss Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
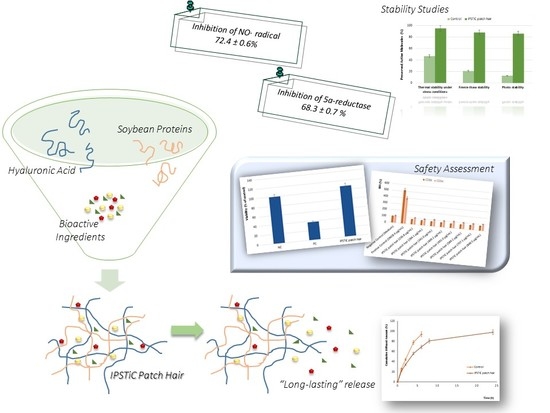
2.1. Scavenging Effect on NO· Radical: Anti-Inflammatory Properties
2.2. Determination of 5α-Reductase Inhibition Activity
2.3. In Vitro Diffusion Studies: Long-Lasting Efficacy
2.4. Stability Studies
2.4.1. Thermal Stability under Stress Conditions
2.4.2. Freeze–Thaw Stability
2.4.3. Photo-Stability
2.5. Safety Assessment
2.5.1. Skin Irritation
2.5.2. In Vitro Analysis of the Pro-Sensitising Potential
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Cell Cultures
3.3. Instrumentation
3.4. Scavenging Effect on NO· Radical
3.5. Determination of 5a-Reductase Inhibition Activity
3.6. In Vitro Diffusion Studies by Vertical Franz Cells
3.7. Stability Studies
3.7.1. Thermal Stability under Stress Conditions
3.7.2. Freeze–Thaw Stability
3.7.3. Photo-Stability
3.8. Safety Assessment
3.8.1. Skin Irritation
3.8.2. In Vitro Analysis of the Pro-Sensitising Potential
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, N.; Rungseevijitprapa, W.; Narkkhong, N.-A.; Suttajit, M.; Chaiyasut, C. 5α-reductase inhibition and hair growth promotion of some Thai plants traditionally used for hair treatment. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, A.; Anzalone, A.; Fortuna, M.C.; Caro, G.; Garelli, V.; Pranteda, G.; Carlesimo, M. Multi-therapies in androgenetic alopecia: Review and clinical experiences. Dermatol. Ther. 2016, 29, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.-Y.; Pi, L.-Q.; Hwang, S.T.; Lee, W.-S. Effect of IGF-I on hair growth is related to the anti-apoptotic effect of IGF-I and up-regulation of PDGF-A and PDGF-B. Ann. Dermatol. 2012, 24, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, J.A.; Sinclair, R.D. Male pattern baldness: Current treatments, future prospects. Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, J.A.; Sinclair, R.; Harrap, S.B. Androgenetic alopecia: Pathogenesis and potential for therapy. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2002, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiting, D.A. Diagnostic and predictive value of horizontal sections of scalp biopsy specimens in male pattern androgenetic alopecia. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1993, 28, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, A.; Midorikawa, T.; Yoshino, T.; Ohdera, M. Lipid peroxides induce early onset of catagen phase in murine hair cycles. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 22, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urysiak-Czubatka, I.; Kmieć, M.L.; Broniarczyk-Dyła, G. Assessment of the usefulness of dihydrotestosterone in the diagnostics of patients with androgenetic alopecia. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol. 2014, 31, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banka, N.; Bunagan, M.K.; Shapiro, J. Pattern hair loss in men: Diagnosis and medical treatment. Dermatol. Clin. 2013, 31, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.H.; Kwon, O.S.; Chung, J.H.; Cho, K.H.; Eun, H.C.; Kim, K.H. Effect of minoxidil on proliferation and apoptosis in dermal papilla cells of human hair follicle. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2004, 34, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libecco, J.F.; Bergfeld, W.F. Finasteride in the treatment of alopecia. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2004, 5, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, H.; Morikawa, S.; Fujiwara, C.; Terada, H.; Uehara, A.; Ohno, R. A case of acute myocardial infarction associated with topical use of minoxidil (RiUP®) for treatment of baldness. Jpn. Heart J. 2000, 41, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesoulis, Z.A.; Attarian, S.J.; Zeller, B.; Cole, F.S. Minoxidil-Associated Anorexia in an Infant with Refractory Hypertension. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2014, 34, e341–e344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mysore, V.; Shashikumar, B. Guidelines on the use of finasteride in androgenetic alopecia. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2016, 82, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiyana, W.; Punyoyai, C.; Somwongin, S.; Leelapornpisid, P.; Ingkaninan, K.; Waranuch, N.; Srivilai, J.; Thitipramote, N.; Wisuitiprot, W.; Schuster, R. Inhibition of 5α-Reductase, IL-6 Secretion, and Oxidation Process of Equisetum debile Roxb. ex Vaucher Extract as Functional Food and Nutraceuticals Ingredients. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentile, P.; Scioli, M.G.; Bielli, A.; Orlandi, A.; Cervelli, V. Concise Review: The Use of Adipose-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction Cells and Platelet Rich Plasma in Regenerative Plastic Surgery. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, A.K.; Udayan, U.K.; Roy, P.K.; Amar, A.K.J.; Chaudhary, R. Platelet-rich plasma with microneedling in androgenetic alopecia along with dermoscopic pre-and post-treatment evaluation. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orliac, S.; Serfaty, J.M.; Perozziello, A.; Zurlinden, O.; Louedec, L.; Dallaudière, B. Efficacy of subcutaneous injection of platelet-rich plasma in alopecia: A clinical and histological pilot study on a rat model with a six-month long-term follow-up experience. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2018, 17, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scioli, M.G.; Bielli, A.; Gentile, P.; Mazzaglia, D.; Cervelli, V.; Orlandi, A. The biomolecular basis of adipogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6517–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, C.H.; Park, G.-H.; Wu, X.; Tran, T.-N.; Park, K.-Y.; Park, B.-S.; Kim, D.Y.; Kwon, O.; Kim, K.-H. The Basic Mechanism of Hair Growth Stimulation by Adipose-derived Stem Cells and Their Secretory Factors. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 12, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avci, P.; Gupta, G.K.; Clark, J.; Wikonkal, N.; Hamblin, M.R. Low-level laser (light) therapy (LLLT) for treatment of hair loss. Lasers Surg. Med. 2014, 46, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwin, E.; Heyes, A.; Hirt, P.A.; Wikramanayake, T.C.; Jimenez, J.J. Low-level laser therapy for the treatment of androgenic alopecia: A review. Lasers Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afifi, L.; Maranda, E.L.; Zarei, M.; Delcanto, G.M.; Falto-Aizpurua, L.; Kluijfhout, W.P.; Jimenez, J.J. Low-level laser therapy as a treatment for androgenetic alopecia. Lasers Surg. Med. 2017, 49, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kintzios, S. Oregano: The Genera Origanum and Lippia (Medicinal and Aromatic Plants-Industrial Profiles); CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tada, M. Biological activities of antioxidants from herbs in Labiatae. FFIJOURNAL 2000, 184, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Shetty, K. Stimulation of rosmarinic acid in shoot cultures of oregano (Origanum vulgare) clonal line in response to proline, proline analogue, and proline precursors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 2888–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, K.; Higashi, N.; Koga, K. Antioxidant and antiinflammatory activities of oregano extract. J. Health Sci. 2006, 52, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujicic, M.; Nikolic, I.; Kontogianni, V.G.; Saksida, T.; Charisiadis, P.; Orescanin-Dusic, Z.; Blagojevic, D.; Stosic-Grujicic, S.; Tzakos, A.G.; Stojanovic, I. Methanolic extract of Origanum vulgare ameliorates type 1 diabetes through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic activity. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 113, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-L.; Guo, Y.-S.; Wang, C.-H.; Li, G.-Q.; Xu, J.-J.; Chung, H.Y.; Ye, W.-C.; Li, Y.-L.; Wang, G.-C. Phenolic compounds from Origanum vulgare and their antioxidant and antiviral activities. Food Chem. 2014, 152, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.-H.; Ding, H.-Y.; Lin, R.-J.; Liang, J.-Y.; Liang, C.-H. Inhibition of melanogenesis and oxidation by protocatechuic acid from Origanum vulgare (oregano). J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.-Y.; Chou, T.-H.; Liang, C.-H. Antioxidant and antimelanogenic properties of rosmarinic acid methyl ester from Origanum vulgare. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.-H.; Chan, L.-P.; Ding, H.-Y.; So, E.C.; Lin, R.-J.; Wang, H.-M.; Chen, Y.-G.; Chou, T.-H. Free radical scavenging activity of 4-(3,4-dihydroxybenzoyloxymethyl)phenyl-O-β-d-glucopyranoside from Origanum vulgare and its protection against oxidative damage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7690–7696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, R.; Nagpal, D.; Gullaiya, S.; MadanS, A.S. Phytochemical, Pharmacological and Beneficial Effects of Green Tea. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2014, 6, 420–426. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, S. Green tea and the skin. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 52, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Bachrach, U. The specific anti-cancer activity of green tea (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). Amino Acids 2002, 22, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benencia, F.; Courrèges, M.C.; Coulombie, F.C. In vivo and in vitro immunomodulatory activities of Trichilia glabra aqueous leaf extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 69, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katiyar, S.K.; Agarwal, R.; Ekker, S.; Wood, G.S.; Mukhtar, H. Protection against 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-caused inflammation in SENCAR mouse ear skin by polyphenolic fraction isolated from green tea. Carcinogenesis 1993, 14, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhtar, H.; Katiyar, S.K.; Agarwal, R. Green tea and skin—Anticarcinogenic effects. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1994, 102, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esfandiari, A.; Kelly, A.P. The effects of tea polyphenolic compounds on hair loss among rodents. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2005, 97, 1165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kwon, O.; Han, J.; Yoo, H.; Chung, J.; Cho, K.; Eun, H.; Kim, K. Human hair growth enhancement in vitro by green tea epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). Phytomedicine 2007, 14, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prager, N.; Bickett, K.; French, N.; Marcovici, G. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to determine the effectiveness of botanically derived inhibitors of 5-α-reductase in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2002, 8, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, S.; Hiipakka, R.A. Selective-Inhibition of Steroid 5 α-Reductase Isozymes by Tea Epicatechin-3-Gallate and Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 214, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, T.; Akhtar, N.; Khan, B.A.; Khan, H.M.S.; Saeed, T. Outcomes of 3% green tea emulsion on skin sebum production in male volunteers. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2010, 10, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Mascio, P.; Kaiser, S.; Sies, H. Lycopene as the most efficient biological carotenoid singlet oxygen quencher. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1989, 274, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krinsky, N.I.; Yeum, K.-J. Carotenoid–radical interactions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 305, 754–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, W.; Sies, H. Antioxidant activity of carotenoids. Mol. Asp. Med. 2003, 24, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.A.; Yokozawa, T. Protection against oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis of high-glucose-exposed proximal tubular epithelial cells by astaxanthin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 8793–8797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, N.; Okajima, K.; Arai, M.; Kurihara, H.; Nakagata, N. Administration of capsaicin and isoflavone promotes hair growth by increasing insulin-like growth factor-I production in mice and in humans with alopecia. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2007, 17, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paus, R.; Heinzelmann, T.; Schultz, K.-D.; Furkert, J.; Fechner, K.; Czarnetzki, B.M. Hair growth induction by substance P. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 1994, 71, 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, J.P.; Ocampo, Y.C.; Franco, L.A. In vivo and in vitro anti-inflammatory activity of Cryptostegia grandiflora Roxb. ex R. Br. leaves. Biol. Res. 2014, 47, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, O.I.; Aiello, D.; Casula, M.F.; Puoci, F.; Malivindi, R.; Scrivano, L.; Testa, F. Mesoporous nanocrystalline tio 2 loaded with ferulic acid for sunscreen and photo-protection: Safety and efficacy assessment. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 83767–83775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Ma, L.; Li, X.; Ding, W.; Chen, X. Hair growth promoting effect of white wax and policosanol from white wax on the mouse model of testosterone-induced hair loss. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, O.I.; Malivindi, R.; Amone, F.; Ruffo, M.; Malanchin, R.; Carlomagno, F.; Piangiolino, C.; Nobile, V.; Pezzi, V.; Scrivano, L. Safety and Efficacy of Dextran-Rosmarinic Acid Conjugates as Innovative Polymeric Antioxidants in Skin Whitening: What Is the Evidence? Cosmetics 2017, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, O.I.; Puoci, F.; Iemma, F.; Curcio, M.; Cirillo, G.; Spizzirri, U.G.; Picci, N. Flavonoids preservation and release by methacrylic acid-grafted (N-vinyl-pyrrolidone). Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2013, 18, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parisi, O.I.; Scrivano, L.; Amone, F.; Malivindi, R.; Ruffo, M.; Vattimo, A.F.; Pezzi, V.; Puoci, F. Interconnected PolymerS TeChnology (IPSTiC): An Effective Approach for the Modulation of 5α-Reductase Activity in Hair Loss Conditions. J. Funct. Biomater. 2018, 9, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb9030044
Parisi OI, Scrivano L, Amone F, Malivindi R, Ruffo M, Vattimo AF, Pezzi V, Puoci F. Interconnected PolymerS TeChnology (IPSTiC): An Effective Approach for the Modulation of 5α-Reductase Activity in Hair Loss Conditions. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2018; 9(3):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb9030044
Chicago/Turabian StyleParisi, Ortensia Ilaria, Luca Scrivano, Fabio Amone, Rocco Malivindi, Mariarosa Ruffo, Anna Francesca Vattimo, Vincenzo Pezzi, and Francesco Puoci. 2018. "Interconnected PolymerS TeChnology (IPSTiC): An Effective Approach for the Modulation of 5α-Reductase Activity in Hair Loss Conditions" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 9, no. 3: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb9030044
APA StyleParisi, O. I., Scrivano, L., Amone, F., Malivindi, R., Ruffo, M., Vattimo, A. F., Pezzi, V., & Puoci, F. (2018). Interconnected PolymerS TeChnology (IPSTiC): An Effective Approach for the Modulation of 5α-Reductase Activity in Hair Loss Conditions. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 9(3), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb9030044