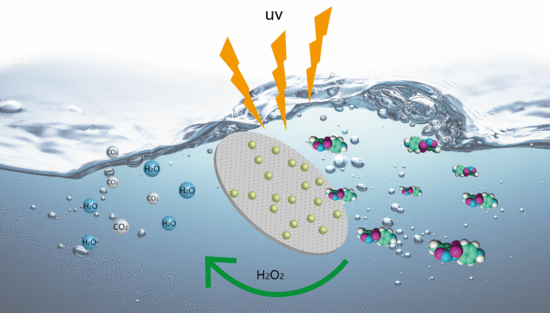
Enhanced Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole (SMX) in Toilet Wastewater by Photo-Fenton Reactive Membrane Filtration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
2.1. Functionalization of Ceramic Membrane
2.2. Batch Degradation Experiments under Different Conditions
2.3. Filtration Experiments
2.3.1. Operation of Continuous Filtration Experiments
2.3.2. Degradation of SMX Spiked in Toilet Wastewater via Photocatalytic Membrane Filtration
2.4. Analysis of Photocatalytic Degradation Mechanisms
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Catalyst Coating Density and Impacts of Membrane Permeability
3.2. Assessment of Pollutant Degradation in Batch Experiments
3.3. Pollutant Removal and Degradation in Continuous Filtration
3.3.1. Removal of SMX under Different Membrane Filtration Conditions
3.3.2. Assessment of SMX Removal in Toilet Wastewater
3.4. Analysis of Photocatalytic Degradation Mechanisms
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Acosta-Rangel, A.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; Polo, A.M.S.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Berber-Mendoza, M.S. Sulfonamides degradation assisted by UV, UV/H2O2 and UV/K2S2O8: Efficiency, mechanism and byproducts cytotoxicity. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 225, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Farid, M.U.; Lee, E.-J.; Yan, D.Y.-S.; Jeong, S.; Kyoungjin An, A. Fouling behavior of negatively charged PVDF membrane in membrane distillation for removal of antibiotics from wastewater. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 551, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarizia, L.; Russo, D.; Di Somma, I.; Marotta, R.; Andreozzi, R. Homogeneous photo-Fenton processes at near neutral pH: A review. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 209, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-F.; He, M.; Wu, T.-F.; Hao, A.-P.; Zhang, S.-B.; Chen, Y.-D.; Zhou, S.-B.; Zhen, L.-Y.; Wang, R.; Yuan, Z.-L.; et al. Sulfadiazine oxidation by permanganate: Kinetics, mechanistic investigation and toxicity evaluation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 349, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Dong, F.; Luo, F.; Li, C. Degradation of sulfonamides and formation of trihalomethanes by chlorination after pre-oxidation with Fe(VI). J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 73, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, J.; Amin, N.A.S.; Shahzad, K. A review on removal of pharmaceuticals from water by adsorption. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 12842–12860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.S.P.; Neghi, N.; Kumar, M.; Varghese, G.K. Photocatalytic-oxidation and photo-persulfate-oxidation of sulfadiazine in a laboratory-scale reactor: Analysis of catalyst support, oxidant dosage, removal-rate and degradation pathway. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 222, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Li, Y.; Meng, T.; Zhang, R.; Song, M.; Ren, J. Removal of sulfonamide antibiotics and human metabolite by biochar and biochar/H2O2 in synthetic urine. Water Res. 2018, 147, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-C.; Huang, C.-L.; Cheng, T.-C.; Lai, H.-T. Inhibitory effect of salinity on the photocatalytic degradation of three sulfonamide antibiotics. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 102, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronk, W.; Palmquist, H.; Biebow, M.; Boller, M. Nanofiltration for the separation of pharmaceuticals from nutrients in source-separated urine. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landry, K.A.; Boyer, T.H. Fixed Bed Modeling of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug Removal by Ion-Exchange in Synthetic Urine: Mass Removal or Toxicity Reduction? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10072–10080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pronk, W.; Zuleeg, S.; Lienert, J.; Escher, B.; Koller, M.; Berner, A.; Koch, G.; Boller, M. Pilot experiments with electrodialysis and ozonation for the production of a fertiliser from urine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 56, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemacheevakul, P.; Chuangchote, S.; Otani, S.; Matsuda, T.; Shimizu, Y. Phosphorus recovery: Minimization of amount of pharmaceuticals and improvement of purity in struvite recovered from hydrolysed urine. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 3011–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abellán, M.N.; Bayarri, B.; Giménez, J.; Costa, J. Photocatalytic degradation of sulfamethoxazole in aqueous suspension of TiO2. Appl. Catal. B 2007, 74, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Cai, J.; Huai, X.; Liu, B. A novel antibiotic wastewater degradation technique combining cavitating jets impingement with multiple synergetic methods. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 44, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Li, D.; Yang, X.; Cai, Q.; Peng, S.; Peng, X.; Yao, H.; Xie, B. Novel characteristics on micro-electrolysis mediated Fe(0)-oxidizing autotrophic denitrification with aeration: Efficiency, iron-compounds transformation, N2O and accumulation, and microbial characteristics. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 123409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, M.N.; Sharma, A.K.; Burn, S.; Saint, C.P. Feasibility study on the application of advanced oxidation technologies for decentralised wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 35 (Suppl. C), 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnik, B.S.; Davies, S.H.; Baumann, M.J.; Masten, S.J. Fabrication of Catalytic Membranes for the Treatment of Drinking Water Using Combined Ozonation and Ultrafiltration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7656–7661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlichter, B.; Mavrov, V.; Chmiel, H. Study of a hybrid process combining ozonation and microfiltration/ultrafiltration for drinking water production from surface water. Desalination 2004, 168, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-F.; Xu, Z.-L.; Yang, H.; Yu, L.-Y.; Liu, M. Effect of TiO2 nanoparticles on the surface morphology and performance of microporous PES membrane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 4725–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, B.; Qi, F. A novel ceramic membrane coated with MnO2–Co3O4 nanoparticles catalytic ozonation for benzophenone-3 degradation in aqueous solution: Fabrication, characterization and performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 287, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.-H.; Tseng, D.-H.; Hsu, W.-C. Effect and mechanism of ultrafiltration membrane fouling removal by ozonation. Desalination 2007, 202, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Davies, S.H.R.; Baumann, M.J.; Tarabara, V.V.; Masten, S.J. Effect of ozone dosage and hydrodynamic conditions on the permeate flux in a hybrid ozonation–ceramic ultrafiltration system treating natural waters. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 311, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yao, H.; Fu, W.; Hua, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, W. Reactive Photo-Fenton ceramic membranes: Synthesis, characterization and antifouling performance. Water Res. 2018, 144, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Yao, H.; Fu, W.; Xue, S.; Zhang, W. Enhanced degradation of antibiotics by photo-fenton reactive membrane filtration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 386, 121955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, L.; de Cortalezzi, M.M.F. Improved membrane flux recovery by Fenton-type reactions. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 500, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ruan, S.; Xu, X.; Zou, R.; Hu, J. One-dimensional nanomaterial-assembled macroscopic membranes for water treatment. Nano Today 2017, 17, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Song, Z.; Xu, B.; Li, Y.; Qi, F.; Croue, J.-P.; Yuan, D. A novel catalytic ceramic membrane fabricated with CuMn2O4 particles for emerging UV absorbers degradation from aqueous and membrane fouling elimination. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Zhang, W. Microwave-enhanced membrane filtration for water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 568, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Shen, Z.-P.; Shi, L.; Cheng, R.; Yuan, D.-H. Photocatalytic Membrane Reactors (PMRs) in Water Treatment: Configurations and Influencing Factors. Catalysts 2017, 7, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatmaz, H.C.; Dizge, N.; Kurt, M.S. Combination of photocatalytic and membrane distillation hybrid processes for reactive dyes treatment. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 2743–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alias, S.S.; Harun, Z.; Latif, I.S.A. Characterization and performance of porous photocatalytic ceramic membranes coated with TiO2 via different dip-coating routes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 53, 11534–11552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Xu, S.; Wu, Z. Development of an Electrochemical Ceramic Membrane Filtration System for Efficient Contaminant Removal from Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4117–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heddrich, M.P.; Gupta, S.; Santhanam, S. Electrochemical Ceramic Membrane Reactors in Future Energy and Chemical Process Engineering. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2019, 91, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Wang, X.; Zheng, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z. Antifouling performance and mechanisms in an electrochemical ceramic membrane reactor for wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 570–571, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganiyu, S.O.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Cretin, M.; Esposito, G.; Oturan, M.A. Coupling of membrane filtration and advanced oxidation processes for removal of pharmaceutical residues: A critical review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 891–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, T.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, P. Effects of organic acids and initial solution pH on photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A (BPA) in a photo-Fenton-like process using goethite (α-FeOOH). Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2016, 15, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Yan, S. Enhanced heterogeneous Fenton degradation of Methylene Blue by nanoscale zero valent iron (nZVI) assembled on magnetic Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 5, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-H.; Dong, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, D.-X.; Meng, D. A review on Fenton process for organic wastewater treatment based on optimization perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, T.L.P.; José, H.J.; Moreira, R. Fenton and Photo-Fenton oxidation of tannery wastewater. Acta Sci. Technol. 2003, 25, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Niu, J.; Chen, Y. Mechanism of photogenerated reactive oxygen species and correlation with the antibacterial properties of engineered metal-oxide nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5164–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Fan, Y.; Liu, K.; Kong, D.; Lu, J. Thermo activated persulfate oxidation of antibiotic sulfamethoxazole and structurally related compounds. Water Res. 2015, 87, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, G.-H.; Kim, J.-E.; Park, Y.-J. Development of stabilized tenofovir disoproxil tablet: Degradation profile, stabilization, and bioequivalence in beagle dogs. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-T.; Oh, W.-D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, E.-H.; Lim, T.-T. Controllable mullite bismuth ferrite micro/nanostructures with multifarious catalytic activities for switchable/hybrid catalytic degradation processes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 509, 502–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Moussavi, G. Investigation of chemical-less UVC/VUV process for advanced oxidation of sulfamethoxazole in aqueous solutions: Evaluation of operational variables and degradation mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 190, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameters | pH | TOC (mg·L−1) | SS (mg·L−1) | NH4+-N (mg·L−1) | TP (mg·L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw | 6.94 ± 0.01 | 1712 ± 18 | 983 ± 9 | 1218 ± 16 | 66 ± 3 |
| Pre-filtered | 6.94 ± 0.01 | 1524 ± 21 | N.A. | 1168 ± 13 | 62 ± 2 |
| Membrane Type | Reaction Type | First-Order Kinetic Rate Constant (min−1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| No membrane | UV only | 0.0126 | 0.9654 |
| H2O2 only | 0.0005 | 0.9346 | |
| UV + H2O2 | 0.0411 | 0.9436 | |
| Uncoated membrane | No UV or H2O2 | 0.0001 | 0.9855 |
| UV only | 0.0213 | 0.9781 | |
| H2O2 only | 0.0005 | 0.9345 | |
| UV + H2O2 | 0.0928 | 0.9776 | |
| Coated membrane | No UV or H2O2 | 0.0001 | 0.9674 |
| UV only | 0.1435 | 0.9532 | |
| H2O2 only | 0.0005 | 0.9762 | |
| UV + H2O2 | 1.0031 | 0.9683 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, S.; Yao, H.; Li, X.; Deng, S.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, W. Enhanced Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole (SMX) in Toilet Wastewater by Photo-Fenton Reactive Membrane Filtration. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010180
Sun S, Yao H, Li X, Deng S, Zhao S, Zhang W. Enhanced Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole (SMX) in Toilet Wastewater by Photo-Fenton Reactive Membrane Filtration. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(1):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010180
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Shaobin, Hong Yao, Xinyang Li, Shihai Deng, Shenlong Zhao, and Wen Zhang. 2020. "Enhanced Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole (SMX) in Toilet Wastewater by Photo-Fenton Reactive Membrane Filtration" Nanomaterials 10, no. 1: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010180
APA StyleSun, S., Yao, H., Li, X., Deng, S., Zhao, S., & Zhang, W. (2020). Enhanced Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole (SMX) in Toilet Wastewater by Photo-Fenton Reactive Membrane Filtration. Nanomaterials, 10(1), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10010180