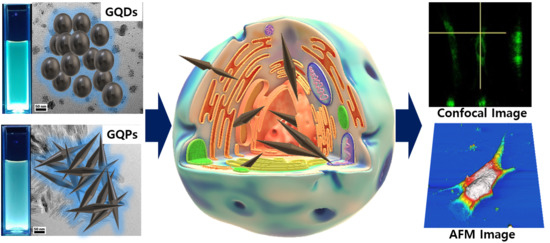
Cytotoxicity and Bioimaging Study for NHDF and HeLa Cell Lines by Using Graphene Quantum Pins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of GQPs
2.2. Cytotoxicity
2.3. Reactive Oxygen Species(ROS) Generation
2.4. AFM and SEM Imaging of Cells
2.5. Cellular Response
2.6. Bio-Imaging and Cellular Distribution
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Growth Mechanism and Characterization of GQPs
3.2. Cytotoxicity and ROS Measurement
3.3. Cellular Response
3.4. Bio-Imaging and Cellular Distribution
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geim, A.K. Graphene: Status and Prospects. Science 2009, 324, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Murali, S.; Cai, W.; Li, X.; Suk, J.W.; Potts, J.R.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene and Graphene Oxide: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3906–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Song, T.; Cui, W.; Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Lee, S.-T.; Sun, B. Solution-processed highly conductive PEDOT: PSS/AgNW/GO transparent film for efficient organic-Si hybrid solar cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 3272–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, M.; Lee, J.M.; Park, W.I.; Yi, D.K.; Paik, U.; Lee, C.-L. Surface morphology changes of graphene on flexible PET substrate upon thermal annealing. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 10069–10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, M.; Mohapatra, P.; Subbiah, R.; Lee, C.-L.; Anass, B.; Kim, J.A.; Yeom, G.Y.; Yi, D.K. InP/ZnS–graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites as fascinating materials for potential optoelectronic applications. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 9793–9805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Cui, L.; Losic, D. Graphene and graphene oxide as new nanocarriers for drug delivery applications. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 9243–9257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Z. Polyethylenimine-functionalized graphene oxide as an efficient gene delivery vector. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7736–7741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-Y.; Pang, D.-P.; Hwang, S.-M.; Tuan, H.-Y.; Hu, Y.-C. A graphene-based platform for induced pluripotent stem cells culture and differentiation. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarcan, R.; Todor-Boer, O.; Petrovai, I.; Leordean, C.; Astilean, S.; Botiz, I. Reduced graphene oxide today. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 1198–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partoens, B.; Peeters, F. From graphene to graphite: Electronic structure around the K point. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 075404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, J.; Aksay, I.A.; Lin, Y. Graphene Based Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors: A Review. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Wei, X.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the Elastic Properties and Intrinsic Strength of Monolayer Graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruge, J.M.; Halpert, J.E.; Wood, V.; Bulović, V.; Bawendi, M.G. Colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting diodes with metal-oxide charge transport layers. Nat. Photonics 2008, 2, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Z.M. Quantum Dot Solar Cells; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Na Yang, H.; Park, J.S.; Jeon, S.Y.; Park, W.; Na, K.; Park, K.-H. The effect of quantum dot size and poly(ethylenimine) coating on the efficiency of gene delivery into human mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 8439–8449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.J.; Zahid, M.; Le, P.; Ma, L.; Entenberg, D.; Harney, A.S.; Condeelis, J.; Smith, A.M. Brightness-equalized quantum dots. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, L.; Gao, Y.; Yan, F. Semiconductor Quantum Dots for Biomedicial Applications. Sensors 2011, 11, 11736–11751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valizadeh, A.; Mikaeili, H.; Samiei, M.; Farkhani, S.M.; Zarghami, N.; Kouhi, M.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Davaran, S. Quantum dots: Synthesis, bioapplications, and toxicity. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomes, S.A.; Vieira, C.S.; Almeida, D.B.; Santos-Mallet, J.R.; Menna-Barreto, R.F.S.; Cesar, C.L.; Feder, D. CdTe and CdSe Quantum Dots Cytotoxicity: A Comparative Study on Microorganisms. Sensors 2011, 11, 11664–11678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Jiang, G. Cytotoxicity of quantum dots and graphene oxide to erythroid cells and macrophages. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, F.; Chen, D.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, S.; Zheng, J.; Huang, N.; Gu, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Eco-friendly synthesis of size-controllable amine-functionalized graphene quantum dots with antimycoplasma properties. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, Z.; Huang, D.; Liu, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhong, H. Synergistic effect of chemo-photothermal therapy using PEGylated graphene oxide. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8555–8561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Dai, W.; Ju, H.; Lu, H.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Zhou, S.-F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Multifunctional Poly(l-lactide)–Polyethylene Glycol-Grafted Graphene Quantum Dots for Intracellular MicroRNA Imaging and Combined Specific-Gene-Targeting Agents Delivery for Improved Therapeutics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 11015–11023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zong, S.; Chen, P.; Zhu, D.; Wu, L.; Cui, Y. A graphene quantum dot-based FRET system for nuclear-targeted and real-time monitoring of drug delivery. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 15477–15486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.-B.; Zhu, Z.-T.; Wang, H.-X.; Huang, X.; Qi, X.; Zhang, H.-L.; Zhu, Y.; Deng, X.; Peng, Y.; Hang-Xing, W.; et al. A general solid-state synthesis of chemically-doped fluorescent graphene quantum dots for bioimaging and optoelectronic applications. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 10162–10169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Fan, L.; Yang, S. Electrochemical synthesis of small-sized red fluorescent graphene quantum dots as a bioimaging platform. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2544–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, C.; Tang, S.; Li, Y.; Yuan, W.; Li, B.; Tian, L.; Liu, F.; Hu, R.; et al. Strongly green-photoluminescent graphene quantum dots for bioimaging applications. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6858–6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, M. Hydrothermal Route for Cutting Graphene Sheets into Blue-Luminescent Graphene Quantum Dots. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, D.B.; Pillai, V.K. Electrochemical Preparation of Luminescent Graphene Quantum Dots from Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 12522–12528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, K.; Park, W.I.; Kim, B.-H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, T.-H.; Bong, S.; Kim, C.-H.; Chae, G.; Jun, M.; et al. Uniform Graphene Quantum Dots Patterned from Self-Assembled Silica Nanodots. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 6078–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, C.; Luo, P.; Tao, L.; Wei, Y.; Shi, G. Large scale preparation of graphene quantum dots from graphite with tunable fluorescence properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 9907–9913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-L.; Ji, J.; Fei, R.; Wang, C.-Z.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, J.-R.; Jiang, L.-P.; Zhu, J.-J. A Facile Microwave Avenue to Electrochemiluminescent Two-Color Graphene Quantum Dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2971–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, N.; Moore, D.; Xu, Z.; Sreeprasad, T.; Nagaraja, A.; Rodriguez, A.A.; Berry, V. Nanotomy-based production of transferable and dispersible graphene nanostructures of controlled shape and size. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, L.; Jin, X.; Li, M.; Luo, X.; Liao, G.; Wei, T.; Li, Q. Top-down Strategy toward Versatile Graphene Quantum Dots for Organic/Inorganic Hybrid Solar Cells. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Shi, Z.; Yang, R.; Liu, D.; Yang, W.; Cheng, M.; Wang, D.; Shi, D.; Zhang, G. Graphene Edge Lithography. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4642–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samal, M.; Barange, N.; Ko, D.; Yun, K. Graphene Quantum Rings Doped PEDOT: PSS Based Composite Layer for Efficient Performance of Optoelectronic Devices. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 19619–19627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lin, J.; Peng, Z.; Wang, G.; Pembroke, E.; Zhou, H.; Xiang, C.; Raji, A.-R.O.; Samuel, E.L.; et al. Hexagonal Graphene Onion Rings. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10755–10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthanarayanan, A.; Wang, Y.; Routh, P.; Sk, M.A.; Than, A.; Lin, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Sun, H.; Chen, P. Nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped graphene quantum dots: Synthesis from adenosine triphosphate, optical properties, and cellular imaging. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 8159–8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Shao, J.-W.; Chen, C.; Li, H.; Wang, R.; Chi, Y.; Lin, X.; Chen, G. Blue luminescent graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide prepared by tuning the carbonization degree of citric acid. Carbon 2012, 50, 4738–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Ji, R.; Li, X.; Bai, G.; Liu, C.P.; Hao, J.; Lin, J.; Jiang, H.; Teng, K.S.; Yang, Z.; et al. Deep Ultraviolet to Near-Infrared Emission and Photoresponse in Layered N-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6312–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, R.; Ramasundaram, S.; Du, P.; Hyojin, K.; Sung, D.; Park, K.; Lee, N.-E.; Yun, K.; Choi, K.J. Evaluation of cytotoxicity, biophysics and biomechanics of cells treated with functionalized hybrid nanomaterials. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20130694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alessandrini, A.; Facci, P. AFM: A versatile tool in biophysics. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, R65–R92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cruz, R.D.; Fonseca, V.C.; Darling, E.M. Cellular mechanical properties reflect the differentiation potential of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1523–E1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacQueen, L.; Sun, Y.; Simmons, C.A. Mesenchymal stem cell mechanobiology and emerging experimental platforms. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20130179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, Y.; Deghorain, M.; Wang, L.; Xu, B.B.; Pollheimer, P.D.; Gruber, H.J.; Errington, J.; Hallet, B.; Haulot, X.; Verbelen, C.; et al. Single-Molecule Force Spectroscopy and Imaging of the Vancomycin/d-Ala-d-Ala Interaction. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Hu, M.; Guo, Q.; Ding, Z.; Sun, X.; Yang, J. High-yield synthesis of graphene quantum dots with strong green photoluminescence. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 50141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-F.; Zhu, L.; Chen, J.-F.; Dai, L. Can graphene quantum dots cause DNA damage in cells? Nanoscale 2015, 7, 9894–9901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, S.S.; Subbiah, R.; Jeon, S.B.; Park, K.; Yun, K.-S.; Ahn, S.J. Investigation of cellular responses upon interaction with silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeon, S.; Subbiah, R.; Bonaedy, T.; Van, S.; Park, K.; Yun, K. Surface functionalized magnetic nanoparticles shift cell behavior with on/off magnetic fields. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titirici, M.-M.; White, R.J.; Falco, C.; Sevilla, M. Black perspectives for a green future: Hydrothermal carbons for environment protection and energy storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6796–6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Jang, M.-H.; Ha, H.D.; Kim, J.-H.; Cho, Y.-H.; Seo, T.S. Facile Synthetic Method for Pristine Graphene Quantum Dots and Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots: Origin of Blue and Green Luminescence. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3657–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, B.; Rao, Z.; Zhang, B.; Gong, J.R. Strong Two-Photon-Induced Fluorescence from Photostable, Biocompatible Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots for Cellular and Deep-Tissue Imaging. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2436–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Zheng, B.; Wang, D.; Du, J.; Xiao, D. A FRET chemsensor based on graphene quantum dots for detecting and intracellular imaging of Hg2+. Talanta 2015, 143, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Gao, W.; Gupta, B.K.; Liu, Z.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Ge, L.; Song, L.; Alemany, L.B.; Zhan, X.; Gao, G.; et al. Graphene Quantum Dots Derived from Carbon Fibers. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Lu, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. Large scale preparation of graphene quantum dots from graphite oxide in pure water via one-step electrochemical tailoring. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 29704–29707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.K.; Luk, C.M.; Tang, L.; Teng, K.S.; Lau, S.P. Photoresponse of polyaniline-functionalized graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 5338–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Graupner, R.; Abraham, J.; Vencelová, A.; Seyller, T.; Hennrich, F.; Kappes, M.M.; Hirsch, A.; Ley, L. Doping of single-walled carbon nanotube bundles by Brønsted acids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003, 5, 5472–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montplaisir, D.; Daneault, C.; Chabot, B. Surface composition of grafted thermomechanical pulp through XPS measurement. BioResources 2008, 3, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Hercules, D.M. Electron Spectroscopy: Applications for Chemical Analysis. J. Chem. Educ. 2004, 81, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhu, X.; Shi, Z.L.; Neoh, A.K.G.; Kang, E.T. Polymer Microspheres with Permanent Antibacterial Surface from Surface-Initiated Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 7098–7104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Wang, G.; Gao, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y. Uniform and Conformal Carbon Nanofilms Produced Based on Molecular Layer Deposition. Materials 2013, 6, 5602–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Tian, F. Mg/N double doping strategy to fabricate extremely high luminescent carbon dots for bioimaging. RSC Adv. 2013, 4, 3201–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.L.; Gao, M.X.; Wang, T.T.; Wan, X.Y.; Zheng, L.L.; Huang, C.Z. A general quantitative pH sensor developed with dicyandiamide N-doped high quantum yield graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 3868–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourissou, D.; Guerret, O.; Gabbaï, F.P.; Bertrand, G. Stable Carbenes. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 39–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Li, B.; Cui, X.; Wei, Q.; Tajima, K.; Li, L.-S. Independent Tuning of the Band Gap and Redox Potential of Graphene Quantum Dots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wan, X.; Chen, Y. A hybrid material of graphene and poly (3,4-ethyldioxythiophene) with high conductivity, flexibility, and transparency. Nano Res. 2009, 2, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, B.; Liu, Q.; Yang, L.; Wu, X.; Liu, Z.; Hua, Y.; Yin, S.; Chen, Y. Buffer Layer of PEDOT: PSS/Graphene Composite for Polymer Solar Cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 1934–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, X.; Cui, X.; Li, L.-S. Synthesis of Large, Stable Colloidal Graphene Quantum Dots with Tunable Size. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 5944–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Meziani, M.J.; Sahu, S.; Sun, Y.-P. Photoluminescence Properties of Graphene versus Other Carbon Nanomaterials. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Brozena, A.H.; Mayes, M.L.; Banerjee, P.; Chiou, W.-A.; Rubloff, G.W.; Schatz, G.C.; Wang, Y. Confined propagation of covalent chemical reactions on single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, L.; Tang, X.; Zhong, Y.-X.; Liu, Y.-W.; Song, X.-H.; Deng, S.; Xie, S.-Y.; Yan, J.; Zheng, L.-S. Ultra-bright alkylated graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 12635–12643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eda, G.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Mattevi, C.; Yamaguchi, H.; Chen, H.-A.; Chen, I.-S.; Chen, C.-W.; Chhowalla, M. Blue Photoluminescence from Chemically Derived Graphene Oxide. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Tang, S.; Qiao, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Yu, W.; et al. Surface Chemistry Routes to Modulate the Photoluminescence of Graphene Quantum Dots: From Fluorescence Mechanism to Up-Conversion Bioimaging Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4732–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Pu, K.; Dong, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, W.; Zhu, Y. Role of surface charge and oxidative stress in cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of graphene oxide towards human lung fibroblast cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, W.; Li, J.; Tao, L.; Wei, Y. A comparative study of cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of multi-walled carbon nanotubes, graphene oxide, and nanodiamond. Toxicol. Res. 2012, 1, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Yang, S.-T.; Liu, J.; Dong, E.; Wang, Y.; Cao, A.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.-F. In vitro toxicity evaluation of graphene oxide on A549 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 200, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, A.; Sequedo, L.; Tolosa, L.; Quintas, G.; Burello, E.; Castell, J.; Gombau, L. Dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) assay: A quantitative method for oxidative stress assessment of nanoparticle-treated cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2013, 27, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogneva, I.V.; Buravkov, S.V.; Shubenkov, A.N.; Buravkova, L. Mechanical characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells under impact of silica-based nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yourek, G.; Hussain, M.A.; Mao, J.J. Cytoskeletal Changes of Mesenchymal Stem Cells During Differentiation. ASAIO J. 2007, 53, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, C.; Hu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, C.; Huang, Q. Intracellular Imaging with a Graphene-Based Fluorescent Probe. Small 2010, 6, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Xing, D.; Wu, B.; Wu, S.; Ou, Z.; Chen, W.R. New Insights of Transmembranal Mechanism and Subcellular Localization of Noncovalently Modified Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1677–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantarotto, D.; Briand, J.-P.; Prato, M.; Bianco, A. Translocation of bioactive peptides across cell membranes by carbon nanotubes. Chem. Commun. 2004, 7, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, A.E.; Gass, M.; Muller, K.; Skepper, J.N.; Midgley, P.A.; Welland, M. Direct imaging of single-walled carbon nanotubes in cells. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wu, C.; Zhou, X.; Han, T.; Xin, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, S. Enhancing Cell Nucleus Accumulation and DNA Cleavage Activity of Anti-Cancer Drug via Graphene Quantum Dots. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Han, T.; Zhou, X.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J. Insight into the Cellular Internalization and Cytotoxicity of Graphene Quantum Dots. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurunnabi, M.; Khatun, Z.; Huh, K.M.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Cho, K.J.; Lee, Y.-K. In Vivo Biodistribution and Toxicology of Carboxylated Graphene Quantum Dots. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6858–6867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankireddy, S.R.; Vo, V.G.; An, S.S.; Kim, J. Solvent-Free Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots: An Ecofriendly Approach for the Bioimaging and Screening of Anticancer Activity via Caspase-Induced Apoptosis. ACS Appl. Biol. Mater. 2020, 3, 4873–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, S.-B.; Samal, M.; Govindaraju, S.; Ragini Das, R.; Yun, K. Cytotoxicity and Bioimaging Study for NHDF and HeLa Cell Lines by Using Graphene Quantum Pins. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122550
Jeon S-B, Samal M, Govindaraju S, Ragini Das R, Yun K. Cytotoxicity and Bioimaging Study for NHDF and HeLa Cell Lines by Using Graphene Quantum Pins. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(12):2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122550
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Seong-Beom, Monica Samal, Saravanan Govindaraju, Rupasree Ragini Das, and Kyusik Yun. 2020. "Cytotoxicity and Bioimaging Study for NHDF and HeLa Cell Lines by Using Graphene Quantum Pins" Nanomaterials 10, no. 12: 2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122550
APA StyleJeon, S. -B., Samal, M., Govindaraju, S., Ragini Das, R., & Yun, K. (2020). Cytotoxicity and Bioimaging Study for NHDF and HeLa Cell Lines by Using Graphene Quantum Pins. Nanomaterials, 10(12), 2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10122550