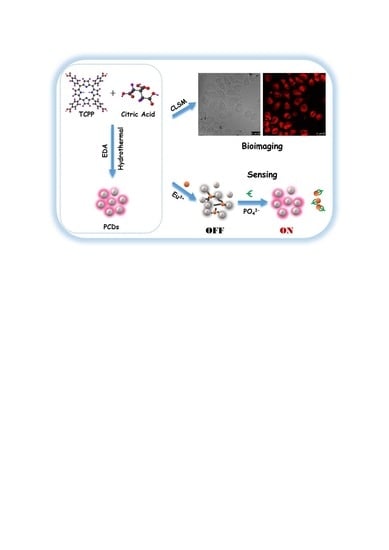
Porphin-Based Carbon Dots for “Turn Off–On” Phosphate Sensing and Cell Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Synthesis of PCDs
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assay and Cell Imaging
2.5. Formation of PCDs-Europium Aggregates (PCDs-Eu3+)
2.6. The Sensing of Phosphate (PO43−)
2.7. Sample and Sample Pretreatment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of PCDs
3.2. Optical Properties of PCDs
3.3. Cytotoxicity Assay and Cell Imaging
3.4. Fluorescence Quenching Behavior of PCDs to Eu3+
3.5. Mechanism of Fluorescent Response to Phosphate
3.6. Selectivity Study for Phosphate Detection
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.Y.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.L.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.Q.; Zhu, A.W.; Tian, Y. Functional surface engineering of C dots for fluorescent biosensing and in vivo bioimaging. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, S.; Ding, H.Z.; Xu, M.S.; Hu, X.L.; Li, Z.Z.; Wang, J.M.; Liu, L.; Jiang, L.; Wang, D.; Dong, C.; et al. Recent advances in synthesis, optical properties, and biomedical applications of carbon dots. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 2317–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.J.; Sheng, Z.H.; Han, H.Y.; Zou, M.Q.; Li, C.X. Facile synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots using watermelon peel as a carbon source. Mater. Lett. 2012, 66, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Cao, L.; Luo, P.G.; Lu, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Meziani, M.J.; Liu, Y.; Qi, G.; Sun, Y. Carbon dots for optical imaging in vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11308–11309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wen, Y.; Xu, M.Y.; Liu, X.; Jin, X.Y.; Kang, J.Q.; Xu, D.; Sang, H.Y.; Gao, P.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L. Magnetofluorescent nanohybrid comprising polyglycerol grafted carbon dots and iron oxides: Colloidal synthesis and applications in cellular imaging and magnetically enhanced drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 173, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Ai, X.Z.; Ong, H.M.; Zhao, Y.L. Dual-responsive carbon dots for tumor extracellular microenvironment triggered targeting and enhanced anticancer drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 18732–18740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Xia, J.M.; Hai, X.; Chen, M.L.; Wang, J.H. A hybrid of carbon dots with 4-chloro-7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole for selective detection of p-phenylenediamine. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarra, M.; Campos, B.B.; Radoti, K.; Mutavdzic, D.; Bandosz, T.; Jimenez-Jimenez, J.; Rodriguez-Castellon, E.; da Silva, J.C.G.E. Luminescent carbon nanoparticles: Effects of chemical functionalization, and evaluation of Ag+ sensing properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 8342–8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.X.; Liu, L.Q.; Liu, Z.D.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.J.; Huang, C.Z. Highly selective detection of phosphate in very complicated matrixes with an off–on fluorescent probe of europium-adjusted carbon dots. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2604–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hnayn, R.; Canabady-Rochelle, L.; Desmarets, C.; Balan, L.; Rinner, H.; Joubert, O.; Medjahdi, G.; Ouada, B.H.; Schneider, R. One-step synthesis of diamine-functionalized graphene quantum dots from graphene oxide and their chelating and antioxidant activities. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharyya, D.; Sarswat, P.K.; Free, M.L. Quantum dots and carbon dots based fluorescent sensors for TB biomarkers detection. Vacuum 2017, 146, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.L.; Zhou, Y.F.; Xue, C.R.; Yang, J.L.; Chang, Q. A solid reaction towards in-situ hybridization of carbon dots and conjugated polymer for enhanced light absorption and conversion. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 9426–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Das, K.; Das, P.K. Hydrophobically tailored carbon dots toward modulating microstructure of reverse micelle and amplification of lipase catalytic response. Langmuir 2016, 32, 3890–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhao, H.; Chen, X.; Fan, H. Recent advance in red-emissive carbon dots and their photoluminescent mechanisms. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 9, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.J.; Zhai, Y.L.; Li, Z.H.; Zhu, P.Y.; Mao, S.; Zhu, C.Z.; Du, D.; Belfiore, L.A.; Tang, J.G.; Lin, Y.H. Red carbon dots optical property regulations and applications. Mater. Today 2019, 30, 52–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.L.; Zhang, Z.L.; Huang, B.H.; Peng, J.; Zhang, M.; Pang, D.W. Facile preparation of low cytotoxicity fluorescent carbon nanocrystals by electrooxidation of graphite. Chem. Commun. 2008, 41, 5116–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.L.; Pang, D.W. Photoluminescence-tunable carbon nanodots: Surface-state energy-gap tuning. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, A.D.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, L.; Dong, C.Q.; Huang, Q.; Wu, A.G.; Lin, H.W. Truly fluorescent excitation-dependent carbon dots and their applications in multicolor cellular imaging and multidimensional sensing. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7782–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Li, M.J.; Li, Q.S.; Liang, S.J.; Tan, Y.Y.; Sheng, L.; Shi, W.; Zhang, S.X.A. Carbon dots with continuously tunable full-color emission and their application in ratiometric pH sensing. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 3104–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.N.; Zhou, D.; Li, D.; Ji, W.Y.; Jing, P.T.; Han, D.; Liu, L.; Zeng, H.B.; Shen, D.Z. Toward efficient orange emissive carbon nanodots through conjugated sp2-domain controlling and surface charges engineering. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3516–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Zhang, X.T.; Li, D.; Zhou, D.; Jing, P.T.; Shen, D.Z.; Qu, S.N.; Zboril, R.; Rogach, A.L. Full-color inorganic carbon dot phosphors for white-light-emitting diodes. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017, 5, 1700416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wei, J.S.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Gao, Q.Y.; Xiong, H.M. Solvent-controlled synthesis of highly luminescent carbon dots with a wide color gamut and narrowed emission peak widths. Small 2018, 14, 1800612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.Y.; Li, Y.C.; Li, X.H.; Zhou, S.X.; Fan, L.Z.; Yang, S.H. Electrochemical synthesis of small-sized red fluorescent graphene quantum dots as a bioimaging platform. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 2544–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Yu, S.B.; Wei, J.S.; Xiong, H.M. Full-color light-emitting carbon dots with a surface-state-controlled luminescence mechanism. ACS Nano 2015, 10, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.L.; Trinchi, A.; Atkin, P.; Cole, I. Tunable photoluminescence across the entire visible spectrum from carbon dots excited by white light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2970–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, G.; Xie, A.M.; Li, J.J.; Su, T.; Pan, X.H.; Dong, W. Large emission red-shift of carbon dots by fluorine doping and their applications for red cell imaging and sensitive intracellular Ag+ detection. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 26558–26565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Su, Q.; Yang, X.M. Exploration of the synthesis of three types of multicolor carbon dot originating from isomers. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 11312–11315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Zhu, S.J.; Li, Z.L.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Sun, L.; Tang, W.; Liu, R.; Sun, Y.; Yu, M. Nitrogen-doped carbon dots with excitation-independent long-wavelength emission produced by room-temperature reaction. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11912–11914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wei, J.S.; Zhong, N.; Gao, Q.Y.; Xiong, H.M. Highly efficient red-emitting carbon dots with gram-scale yield for bioimaging. Langmuir 2017, 33, 12635–12642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Yuan, J.; Wei, J.S.; Gao, Q.Y.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Xiong, H.M. Facile synthesis of red-emitting carbon dots from pulp-free lemon juice for bioimaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 5272–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.; Li, D.; Zhang, K.; Yang, M.X.; Sun, H.C.; Yang, B. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped conjugated carbonized polymer dots with 31% efficient red emission for in vivo imaging. Small 2018, 14, 1703919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.F.; Yuan, F.L.; Li, X.H.; Li, Y.C.; Zhong, H.Z.; Fan, L.Z.; Yang, S.H. 53% Efficient red emissive carbon quantum dots for high color rendering and stable warm white-light-emitting diodes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, W.; Ye, M.; Cai, T.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, S. Tuning of the hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity of nitrogen doped carbon dots: A facile approach towards high efficient lubricant nanoadditives. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 266, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.C.; Lan, M.H.; Zhou, B.J.; Liu, W.M.; Guo, L.; Wang, H.; Jia, Q.Y.; Niu, G.L.; Huang, X.; Zhou, H.Y.; et al. A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhan, J.; Geng, B.J.; Wu, K.; Xu, G.; Wang, L.; Guo, R.Y.; Lei, B.; Zheng, F.F.; Pan, D.Y.; Wu, M.H. A solvent-engineered molecule fusion strategy for rational synthesis of carbon quantum dots with multicolor bandgap fluorescence. Carbon 2018, 130, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.L.; Song, H.H.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.Q.; Pang, X.B.; Zhou, Y.M.; Gao, B.; Peng, X.J. Carbon dots with red emission for sensing of Pt2+, Au3+ and Pd2+ and their bio-applications in vitro and in vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 10, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Chen, J.; Jiang, K.; Tang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Wu, A.; Lin, H. Ce6-modified carbon dots for multimodal-imaging-guided and single-NIR-laser-triggered photothermal/photodynamic synergistic cancer therapy by reduced irradiation power. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5791–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, C.; Sun, X.; Pan, W.; Wang, J. Carbon-dot-based ratiometric fluorescent pH sensor for the detections of very weak acids assisted by auxiliary reagents that contribute to the release of protons. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 244, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Amat, D.; Peng, Z.; Vanni, S.; Raskin, S.; Angulo, G.D.; Othman, A.M.; Grahamb, R.M.; Leblanc, R.M. Transferrin conjugated nontoxic carbon dots for doxorubicin delivery to target pediatric brain tumor cells. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 16662–16669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, K.; Suo, W.; Shao, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Fang, M.; Zhu, Y. Nitrogen doped MoS2 and nitrogen doped carbon dots composite catalyst for electroreduction CO2 to CO with high Faradaic efficiency. Nano Energy 2019, 63, 103834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Milic, T.; Xu, C.; Batteas, J.D.; Drain, C.M. Preparation and characterization of porphyrin nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14290–14291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Jiang, D.; Kamkaew, A.; Valdovinos, H.F.; Im, H.J.; Feng, L.; England, C.G.; Goel, S.; Barnhart, T.E.; Liu, Z.; et al. Renal-clearable PEGylated porphyrin nanoparticles for image-guided photodynamic cancer therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Dang, W.; Chang, J.; Wu, C. Ultrathin Cu-TCPP MOF nanosheets: A new theragnostic nanoplatform with magnetic resonance/near-infrared thermal imaging for synergistic phototherapy of cancers. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4086–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Lv, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, J.; Xu, C. One-step synthesis of uniform nanoparticles of porphyrin functionalized ceria with promising peroxidase mimetics for H2O2 and glucose colorimetric detection. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 240, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Huang, Q.; Tanveer, Z.I.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, J.; Pan, H.; Luan, L.; Liu, X.; Han, Z.; Wu, Y. “Turn off–on” fluorescent sensor based on quantum dots and self-assembled porphyrin for rapid detection of ochratoxin A. Sens. Actuators B 2020, 302, 127212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Feng, H.; Ren, X.; Ji, J.; Bai, F.; Fan, H. Microemulsion-assisted self-assembly and synthesis of size-controlled porphyrin nanocrystals with enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 2614–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.M.; Chakraborty, A.; Alatis, J.; Cai, M.; Danilov, E.; Morris, A.J. Light harvesting and energy transfer in a porphyrin-based metal organic framework. Faraday Discuss. 2019, 216, 174–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengasi, G.; Baba, K.; Frache, G.; Desport, J.; Gratia, P.; Heinze, K.; Boscher, N.D. Conductive fused porphyrin tapes on sensitive substrates by a chemical vapor deposition approach. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2103–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mauzerall, D. Spectra of molecular complexes of porphyrins in aqueous solution. Biochemistry 1965, 4, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.J.; Du, X.F.; Zhang, M.; Yang, J.F.; Zhang, J.N.; Luo, T.; Liu, H.; Xu, H.; Cui, G.L. A large p-conjugated tetrakis (4-carboxyphenyl) porphyrin anode enables high specific capacity and superior cycling stability in lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 11370–11373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patriquin, L.; Merrick, D.T.; Hill, D.; Holcomb, R.G.; Lemieux, M.E.; Bennett, G.; Karia, B.; Rebel, V.I.; Bauer, T. Early detection of lung cancer with meso tetra (4-carboxyphenyl) porphyrin-labeled sputum. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lavi, A.; Weitman, H.; Holmes, R.T.; Smith, K.M.; Ehrenberg, B. The depth of porphyrin in a membrane and the membrane’s physical properties affect the photosensitizing efficiency. Biophys. J. 2002, 82, 2101–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Zhang, S.W. Creating high yield water soluble luminescent graphene quantum dots via exfoliating and disintegrating carbon nanotubes and graphite flakes. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10177–10179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wei, J.S.; Zhang, P.; Niu, X.Q.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Ding, H.; Xiong, H.M. Red-emissive carbon dots for fingerprints detection by spray method: Coffee ring effect and unquenched fluorescence in drying process. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18429–18433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, K.; Lin, H.W. Near-infrared emissive carbon dots for two-photon fluorescence bioimaging. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 17350–17356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.L.; Xu, C.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.S.; Ren, J.S.; Qu, X.G. Non-enzymatic-browning-reaction: A versatile route for production of nitrogen-doped carbon dots with tunable multicolor luminescent display. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ganiga, M.; Cyriac, J. Understanding the photoluminescence mechanism of nitrogen-doped carbon dots by selective interaction with copper ions. ChemPhysChem 2016, 17, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Cole, I.S.; Zhao, D.Y.; Li, Q. The dual roles of functional groups in the photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 7449–7458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eda, G.; Lin, Y.Y.; Mattevi, C.; Yamaguchi, H.; Chen, H.A.; Chen, I.S.; Chen, C.W.; Chhowalla, M. Blue photoluminescence from chemically derived graphene oxide. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarswat, M.L.; Free, P.K. Light emitting diodes based on carbon dots derived from food, beverage, and combustion wastes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 27642–27652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samy, R.; Faustino, P.J.; Adams, W.; Yu, L.; Khan, M.A.; Yang, Y.S. Development and validation of an ion chromatography method for the determination of phosphate-binding of lanthanum carbonate. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, M.; Liu, Y.; Feng, X.Z.; Yin, X.B.; He, X.W.; Zhang, Y.K. Nitrogen-doped carbon dots: A facile and general preparation method, photoluminescence investigation, and imaging applications. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 2276–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.P.; Lu, Y.C.; Huang, H.; Wang, A.J.; Chen, J.R.; Feng, J.J. Facile synthesis of N, S-codoped fluorescent carbon nanodots for fluorescent resonance energy transfer recognition of methotrexate with high sensitivity and selectivity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.B.; Ji, R.B.; Cao, X.K.; Lin, J.Y.; Jiang, H.X.; Li, X.M.; Teng, K.S.; Luk, C.M.; Zeng, S.J.; Hao, J.H.; et al. Deep ultraviolet photoluminescence of water-soluble self-passivated graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5102–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, H.S.; Lee, S.W. Lanthanide-oxalate coordination polymers formed by reductive coupling of carbon dioxide to oxalate: [Ln2(3,5-pdc)2(C2O4)(H2O)4]·2H2O (Ln = Eu, Sm, Ho, Dy; pdc = Pyridinedicarbox. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2006, 27, 1839–1843. [Google Scholar]
- Lackowiz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.B.; Zhu, S.J.; Xiang, S.Y.; Zhao, X.H.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Y.; Yang, B. Investigation into the fluorescence quenching behaviors and applications of carbon dots. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 4676–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Liu, S.B.; Yang, Y.L.; Wang, P.Z.; Zhang, A.J.; Peng, Y. A terbium(III)-complex-based on–off fluorescent chemosensor for phosphate anions in aqueous solution and its application in molecular logic gates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4415–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.S.; Kim, D.H. Naked-eye detection of phosphate ions in water at physiological pH: A remarkably selective and easy-to-assemble colorimetric phosphate-sensing probe. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 41, 3809–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryther, J.H.; Dunstan, W.M. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and eutrophication in the coastal marine environment. Science 1971, 171, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, S.N.; Li, C.M.; Gao, B.H.; Kargbo, O.; Wan, N.; Chen, X.; Zhou, C. Probing phosphate ion via the europium(III)-modulated fluorescence of gold nanoclusters. Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 1957–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dai, Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.S.; Zhuang, Q.X.; Shi, J.L.; Gu, J.L. Metal–organic frameworks with inherent recognition sites for selective phosphate sensing through their coordination-induced fluorescence enhancement effect. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 7445–7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.C.; Mandal, S. Europium-based metal–organic framework as a dual luminescence sensor for the selective detection of the phosphate anion and Fe3+ ion in aqueous media. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 11855–11858. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, S.Q.; He, J.H.; Zhan, L. Dy(III)-induced aggregation emission quenching effect of single-layered graphene quantum dots for selective detection of phosphate in the artificial wetlands. Talanta 2019, 196, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, N.; Huang, J.; Wang, L.Y.; Feng, J.Y.; Huang, P.C.; Wu, F.Y. Ratiometric fluorescence detection of phosphate in human serum with a metal-organic frameworks-based nanocomposite and its immobilized agarose hydrogels. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 459, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.M.; Zhang, L.; Liang, R.P.; Qiu, J.D. Graphene-quantum dots combined with europium ions as photoluminescent probes for phosphate sensing. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 3822–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.L.; Sue, J.W.; Chen, W.C.; Chang, J.; Zen, J.M. Activated nickel platform for electrochemical sensing of phosphate. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, G.; Iyer, P.K. A remarkable superquenching and superdequenching sensor for the selective and noninvasive detection of inorganic phosphates in saliva. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 3753–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Method | Linear Range/μmol L−1 | LOD/μmol·L−1 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amino derivative of UiO-66 | 5–150 | 1.25 | 73 |
| Europium-based metal-organic framework | 3–30 | 6.62 | 74 |
| Single-layered graphene quantum dots | 0.2–30 | 0.1 | 75 |
| Metal- organic frameworks-based nanocomposite | 80–400 | 2 | 76 |
| Graphene quantum dots combined with europium ions | 0.5–190 | 0.1 | 77 |
| Europium-adjusted carbon dots | 0.4–15 | 5.1 × 10−2 | 10 |
| PCDs | 0.02–0.2 | 3.59 × 10−3 | This work |
| Practical Samples | Original (mmol·L−1) | Spiked (mmol·L−1) | Found (mmol·L−1) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Artificial lake | (0.51 ± 0.02) × 10−3 | 0.25 × 10−3 | (0.75 ± 0.02) × 10−3 | 96.47 ± 5.82 |
| 0.40 × 10−3 | (0.90 ± 0.01) × 10−3 | 98.86 ± 2.75 | ||
| 0.60 × 10−3 | (1.09 ± 0.04) × 10−3 | 96.36 ± 6.20 | ||
| Saliva | 4.02 ± 0.66 | 2.00 | 6.01 ± 0.05 | 100.12 ± 2.75 |
| 4.00 | 7.95 ± 0.07 | 98.60 ± 1.66 | ||
| 6.00 | 10.16 ± 0.25 | 102.46 ± 3.90 | ||
| Urine | 26.40 ± 2.86 | 12.50 | 39.17 ± 0.58 | 101.94 ± 4.78 |
| 30.00 | 56.65 ± 1.61 | 100.85 ± 3.08 | ||
| 40.00 | 65.35 ± 0.66 | 97.37 ± 1.61 | ||
| Blood serum | 0.98 ± 0.30 | 0.50 | 1.49 ± 0.10 | 102.85 ± 2.26 |
| 1.50 | 2.50 ± 0.05 | 101.72 ± 3.22 | ||
| 2.00 | 2.94 ± 0.04 | 98.18 ± 2.03 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z. Porphin-Based Carbon Dots for “Turn Off–On” Phosphate Sensing and Cell Imaging. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020326
Wu J, Wang W, Wang Z. Porphin-Based Carbon Dots for “Turn Off–On” Phosphate Sensing and Cell Imaging. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(2):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020326
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Jing, Wenjing Wang, and Zonghua Wang. 2020. "Porphin-Based Carbon Dots for “Turn Off–On” Phosphate Sensing and Cell Imaging" Nanomaterials 10, no. 2: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020326
APA StyleWu, J., Wang, W., & Wang, Z. (2020). Porphin-Based Carbon Dots for “Turn Off–On” Phosphate Sensing and Cell Imaging. Nanomaterials, 10(2), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10020326