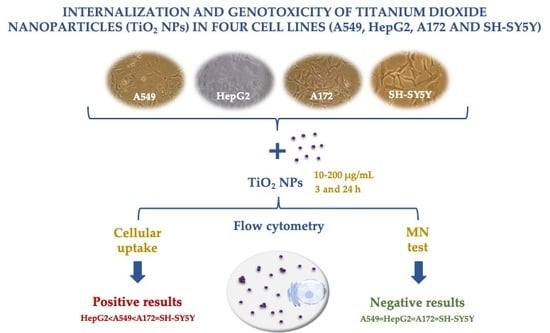
Genotoxicity of TiO2 Nanoparticles in Four Different Human Cell Lines (A549, HEPG2, A172 and SH-SY5Y)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Nanoparticle Suspension: Preparation and Characterization
2.4. Exposure to TiO2 NPs
2.5. Cellular Viability
2.6. Cellular Uptake Evaluation by Flow Cytometry
2.7. Micronuclei Evaluation by Flow Cytometry
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nanoparticle Characterization
3.2. Cellular Viability
3.3. Uptake Behavior
3.4. Genotoxicity Assessed with Micronucleus Test
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, H.; Magaye, R.; Castranova, V.; Zhao, J. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: A review of current toxicological data. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weir, A.; Westerhoff, P.; Fabricius, L.; Hristovski, K.; von Goetz, N. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles in food and personal care products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, P.-J.; Huang, S.-C.; Chen, Y.-P.; Chiueh, L.-C.; Shih, D.Y.-C. Analysis of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles in cosmetics. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 23, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.; Martucci, N.J.; Moreno-Olivas, F.; Tako, E.; Mahler, G.J. Titanium dioxide nanoparticle ingestion alters nutrient absorption in an in vitro model of the small intestine. NanoImpact 2017, 5, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnston, H.J.; Hutchison, G.R.; Christensen, F.M.; Peters, S.; Hankin, S.; Stone, V. Identification of the mechanisms that drive the toxicity of TiO2 particulates: The contribution of physicochemical characteristics. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2009, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsiedel, R.; Ma-Hock, L.; Hofmann, T.; Wiemann, M.; Strauss, V.; Treumann, S.; Wohlleben, W.; Groters, S.; Wiench, K.; van Ravenzwaay, B. Application of short-term inhalation studies to assess the inhalation toxicity of nanomaterials. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magdolenova, Z.; Collins, A.; Kumar, A.; Dhawan, A.; Stone, V.; Dusinska, M. Mechanisms of genotoxicity: A review of in vitro and in vivo studies with engineered nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 233–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, R.Y.; Simmons, S.O.; Killius, M.G.; Zucker, R.M.; Kligerman, A.D.; Blackman, C.F.; Fry, R.C.; Demarini, D.M. Cellular interactions and biological responses to titanium dioxide nanoparticles in HepG2 and BEAS-2B cells: Role of cell culture media. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2014, 55, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Chen, M.; Liu, Q. Cytotoxicity, DNA damage, and apoptosis induced by titanium dioxide nanoparticles in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 5519–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, L.; Tarantini, A.; Beal, D.; Biola-Clier, M.; Bobyk, L.; Sorieul, S.; Pernet-Gallay, K.; Marie-Desvergne, C.; Lynch, I.; Herlin-Boime, N. Long-term exposure of A549 cells to titanium dioxide nanoparticles induces DNA damage and sensitizes cells towards genotoxic agents. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yan, J.; Ding, W.; Chen, Y.; Pack, L.M.; Chen, T. Genotoxicity and gene expression analyses of liver and lung tissues of mice treated with titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Møller, P.; Jensen, D.M.; Wils, R.S.; Andersen, M.H.G.; Danielsen, P.H.; Roursgaard, M. Assessment of evidence for nanosized titanium dioxide-generated DNA strand breaks and oxidatively damaged DNA in cells and animal models. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 1237–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC. Carbon black, titanium dioxide, and talc. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2010; Volume 93, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Pujalte, I.; Dieme, D.; Haddad, S.; Serventi, A.M.; Bouchard, M. Toxicokinetics of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles after inhalation in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 265, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma-Hock, L.; Burkhardt, S.; Strauss, V.; Gamer, A.O.; Wiench, K.; van Ravenzwaay, B.; Landsiedel, R. Development of a short-term inhalation test in the rat using nano-titanium dioxide as a model substance. Inhalation Toxicol. 2009, 21, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, M.; Duan, Y.; Li, N.; Gong, X.; Hu, R.; Hong, M.; Hong, F. Signaling pathway of inflammatory responses in the mouse liver caused by TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2011, 96, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, M.; Wang, B. Health effects of exposure to nano-TiO2: A meta-analysis of experimental studies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, L.; Song, B. Toxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on brain. In Neurotoxicity of Nanomaterials and Nanomedicine; Elsevier: London, UK, 2017; pp. 99–125. [Google Scholar]
- Song, B.; Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Wei, L.; Shao, L. A review on potential neurotoxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, F.; Li, W.; Lao, F.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Ge, C.; Zhou, G. Potential neurological lesion after nasal instillation of TiO2 nanoparticles in the anatase and rutile crystal phases. Toxicol. Lett. 2008, 183, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bai, R.; Liu, Y.; Meng, L.; Li, B.; Wang, L.; Xu, L.; Le Guyader, L.; Chen, C. The dose-dependent toxicological effects and potential perturbation on the neurotransmitter secretion in brain following intranasal instillation of copper nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology 2012, 6, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsyganova, N.; Khairullin, R.; Terentyuk, G.; Khlebtsov, B.; Bogatyrev, V.; Dykman, L.; Erykov, S.; Khlebtsov, N. Penetration of pegylated gold nanoparticles through rat placental barrier. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 157, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, W.-S.; Kang, B.-C.; Lee, J.K.; Jeong, J.; Che, J.-H.; Seok, S.H. Comparative absorption, distribution, and excretion of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles after repeated oral administration. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valdiglesias, V.; Costa, C.; Sharma, V.; Kilic, G.; Pasaro, E.; Teixeira, J.P.; Dhawan, A.; Laffon, B. Comparative study on effects of two different types of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on human neuronal cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 57, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ba, T.; Li, Y.; Pu, J.; Chen, T.; Song, Y.; Gu, Y.; Qian, Q.; Yang, J. Genotoxic evaluation of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 226, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Yan, J.; Li, Y. Genotoxicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles. J. Food Drug Anal. 2014, 22, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.K.; Kumar, A.; Gurbani, D.; Pandey, A.K.; Singh, S.; Dhawan, A. TiO2 nanoparticles induce oxidative DNA damage and apoptosis in human liver cells. Nanotoxicology 2013, 7, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdolenova, Z.; Bilaničová, D.; Pojana, G.; Fjellsbø, L.M.; Hudecova, A.; Hasplova, K.; Marcomini, A.; Dusinska, M. Impact of agglomeration and different dispersions of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the human related in vitro cytotoxicity and genotoxicity. J. Environ. Monit. 2012, 14, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Patel, P.; Bakshi, S.R. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: An in vitro study of DNA binding, chromosome aberration assay, and comet assay. Cytotechnology 2017, 69, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gea, M.; Bonetta, S.; Iannarelli, L.; Giovannozzi, A.M.; Maurino, V.; Bonetta, S.; Hodoroaba, V.-D.; Armato, C.; Rossi, A.M.; Schilirò, T. Shape-engineered titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2-NPs): Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity in bronchial epithelial cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 127, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, K.; Davoren, M.; Boertz, J.; Schins, R.P.; Hoffmann, E.; Dopp, E. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and DNA-adduct formation but not DNA-breakage in human lung cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2009, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petkovic, J.; Zegura, B.; Stevanovic, M.; Drnovsek, N.; Uskokovic, D.; Novak, S.; Filipic, M. DNA damage and alterations in expression of DNA damage responsive genes induced by TiO2 nanoparticles in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Nanotoxicology 2011, 5, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, R.; Rahman, Q.; Kashyap, M.; Singh, A.; Jain, G.; Jahan, S.; Lohani, M.; Lantow, M.; Pant, A. Nano-titanium dioxide induces genotoxicity and apoptosis in human lung cancer cell line, A549. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2013, 32, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansara, K.; Patel, P.; Shah, D.; Shukla, R.K.; Singh, S.; Kumar, A.; Dhawan, A. TiO2 nanoparticles induce DNA double strand breaks and cell cycle arrest in human alveolar cells. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2015, 56, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biola-Clier, M.; Beal, D.; Caillat, S.; Libert, S.; Armand, L.; Herlin-Boime, N.; Sauvaigo, S.; Douki, T.; Carriere, M. Comparison of the DNA damage response in BEAS-2B and A549 cells exposed to titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lankoff, A.; Sandberg, W.J.; Wegierek-Ciuk, A.; Lisowska, H.; Refsnes, M.; Sartowska, B.; Schwarze, P.E.; Meczynska-Wielgosz, S.; Wojewodzka, M.; Kruszewski, M. The effect of agglomeration state of silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on cellular response of HepG2, A549 and THP-1 cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 208, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jochums, A.; Friehs, E.; Sambale, F.; Lavrentieva, A.; Bahnemann, D.; Scheper, T. Revelation of different nanoparticle-uptake behavior in two standard cell lines NIH/3T3 and A549 by flow cytometry and time-lapse imaging. Toxics 2017, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tedja, R.; Marquis, C.; Lim, M.; Amal, R. Biological impacts of TiO2 on human lung cell lines A549 and H1299: Particle size distribution effects. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 3801–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoli, C.; Leter, G.; De Berardis, B.; Degan, P.; De Angelis, I.; Pacchierotti, F.; Crebelli, R.; Barone, F.; Zijno, A. Critical issues in genotoxicity assessment of TiO2 nanoparticles by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 1471–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jugan, M.L.; Barillet, S.; Simon-Deckers, A.; Herlin-Boime, N.; Sauvaigo, S.; Douki, T.; Carriere, M. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles exhibit genotoxicity and impair DNA repair activity in A549 cells. Nanotoxicology 2012, 6, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchin, K.T.; Richards, J.; Robinette, B.L.; Wallace, K.A.; Coates, N.H.; Castellon, B.T. Biochemical effects of six TiO2 and four CeO2 nanomaterials in HepG2 cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016, 16, 9505–9534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Toyooka, T.; Ibuki, Y. Simple and easy method to evaluate uptake potential of nanoparticles in mammalian cells using a flow cytometric light scatter analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3018–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucker, R.M.; Daniel, K.M. Detection of TiO2 nanoparticles in cells by flow cytometry. In Nanoparticles in Biology and Medicine; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 497–509. [Google Scholar]
- Valdiglesias, V.; Laffon, B.; Pásaro, E.; Méndez, J. Evaluation of okadaic acid-induced genotoxicity in human cells using the micronucleus test and γH2AX analysis. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2011, 74, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landsiedel, R.; Sauer, U.G.; Ma-Hock, L.; Schnekenburger, J.; Wiemann, M. Pulmonary toxicity of nanomaterials: A critical comparison of published in vitro assays and in vivo inhalation or instillation studies. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 2557–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudefoi, W.; Terrisse, H.; Richard-Plouet, M.; Gautron, E.; Popa, F.; Humbert, B.; Ropers, M.-H. Criteria to define a more relevant reference sample of titanium dioxide in the context of food: A multiscale approach. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2017, 34, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucker, R.M.; Massaro, E.J.; Sanders, K.M.; Degn, L.L.; Boyes, W.K. Detection of TiO2 nanoparticles in cells by flow cytometry. Cytometry A 2010, 77, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.A.; Aberg, C.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K.A. Role of cell cycle on the cellular uptake and dilution of nanoparticles in a cell population. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 7, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Xu, B.; Ji, X.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Han, X.; Tang, Q.; Wang, X.; Xia, Y. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles alter cellular morphology via disturbing the microtubule dynamics. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 8466–8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithrani, B.D.; Chan, W.C. Elucidating the mechanism of cellular uptake and removal of protein-coated gold nanoparticles of different sizes and shapes. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, B.C.; Wright, C.W.; Ibuki, Y.; Moreno-Villanueva, M.; Karlsson, H.L.; Hendriks, G.; Sims, C.M.; Singh, N.; Doak, S.H. Emerging metrology for high-throughput nanomaterial genotoxicology. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, E.D.; Anderson, D.; Dhawan, A.; Rayburn, A.L.; Plewa, M.J. Evaluation of EMS-induced DNA damage in the single cell gel electrophoresis (Comet) assay and with flow cytometric analysis of micronuclei. Teratog. Carcinog. Mutagen. 2003, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bucchianico, S.; Cappellini, F.; Le Bihanic, F.; Zhang, Y.; Dreij, K.; Karlsson, H.L. Genotoxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles assessed by mini-gel comet assay and micronucleus scoring with flow cytometry. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Long, T.C.; Saleh, N.; Tilton, R.D.; Lowry, G.V.; Veronesi, B. Titanium dioxide (P25) produces reactive oxygen species in immortalized brain microglia (BV2): Implications for nanoparticle neurotoxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 4346–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, T.C.; Tajuba, J.; Sama, P.; Saleh, N.; Swartz, C.; Parker, J.; Hester, S.; Lowry, G.V.; Veronesi, B. Nanosize titanium dioxide stimulates reactive oxygen species in brain microglia and damages neurons in vitro. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1631–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simon-Deckers, A.; Gouget, B.; Mayne-L’hermite, M.; Herlin-Boime, N.; Reynaud, C.; Carriere, M. In vitro investigation of oxide nanoparticle and carbon nanotube toxicity and intracellular accumulation in A549 human pneumocytes. Toxicology 2008, 253, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhasmana, A.; Sajid Jamal, Q.M.; Mir, S.S.; Bhatt, M.L.; Rahman, Q.; Gupta, R.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Lohani, M. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles as guardian against environmental carcinogen benzo[alpha]pyrene. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongkam, W.; Gerloff, K.; van Berlo, D.; Albrecht, C.; Schins, R.P. Oxidant generation, DNA damage and cytotoxicity by a panel of engineered nanomaterials in three different human epithelial cell lines. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlinder, L.; Ekstrand-Hammarström, B.; Geladi, P.; Österlund, L. Large uptake of titania and iron oxide nanoparticles in the nucleus of lung epithelial cells as measured by Raman imaging and multivariate classification. Biophys. J. 2013, 105, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, P.; Van Kirk, E.A.; Zhan, Y.; Murdoch, W.J.; Radosz, M.; Shen, Y. Targeted charge-reversal nanoparticles for nuclear drug delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4999–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessa, M.J.; Costa, C.; Reinosa, J.; Pereira, C.; Fraga, S.; Fernandez, J.; Banares, M.A.; Teixeira, J.P. Moving into advanced nanomaterials. Toxicity of rutile TiO2 nanoparticles immobilized in nanokaolin nanocomposites on HepG2 cell line. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 316, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Yamani, N.; Collins, A.R.; Runden-Pran, E.; Fjellsbo, L.M.; Shaposhnikov, S.; Zienolddiny, S.; Dusinska, M. In vitro genotoxicity testing of four reference metal nanomaterials, titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, cerium oxide and silver: Towards reliable hazard assessment. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Nanoparticles | Morphology 1 | Crystalline Phase 1 | Size (nm) 1 (TEM) | Hydrodynamic Diameter (nm) (DLS) | Zeta Potential (mV) (DLS) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Degussa, Aeroxide TiO2 P25 NPs | Spherical | 80% anatase 20% rutile | 25 | Deionized Water | A549 medium | HepG2 and A172 medium | SH-SY5Y medium | Deionized Water | A549 medium | HepG2 and A172 medium | SH-SY5Y medium |
| 205.1 | 251.5 | 244 | 228.3 [24] | −25.3 | −11.1 | −11.1 | −10.7 [24] | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brandão, F.; Fernández-Bertólez, N.; Rosário, F.; Bessa, M.J.; Fraga, S.; Pásaro, E.; Teixeira, J.P.; Laffon, B.; Valdiglesias, V.; Costa, C. Genotoxicity of TiO2 Nanoparticles in Four Different Human Cell Lines (A549, HEPG2, A172 and SH-SY5Y). Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030412
Brandão F, Fernández-Bertólez N, Rosário F, Bessa MJ, Fraga S, Pásaro E, Teixeira JP, Laffon B, Valdiglesias V, Costa C. Genotoxicity of TiO2 Nanoparticles in Four Different Human Cell Lines (A549, HEPG2, A172 and SH-SY5Y). Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(3):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030412
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrandão, Fátima, Natalia Fernández-Bertólez, Fernanda Rosário, Maria João Bessa, Sónia Fraga, Eduardo Pásaro, João Paulo Teixeira, Blanca Laffon, Vanessa Valdiglesias, and Carla Costa. 2020. "Genotoxicity of TiO2 Nanoparticles in Four Different Human Cell Lines (A549, HEPG2, A172 and SH-SY5Y)" Nanomaterials 10, no. 3: 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030412
APA StyleBrandão, F., Fernández-Bertólez, N., Rosário, F., Bessa, M. J., Fraga, S., Pásaro, E., Teixeira, J. P., Laffon, B., Valdiglesias, V., & Costa, C. (2020). Genotoxicity of TiO2 Nanoparticles in Four Different Human Cell Lines (A549, HEPG2, A172 and SH-SY5Y). Nanomaterials, 10(3), 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030412