Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticles as Smart Carriers for Self-Healing Coatings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Modification of CeO2 Nanoparticles
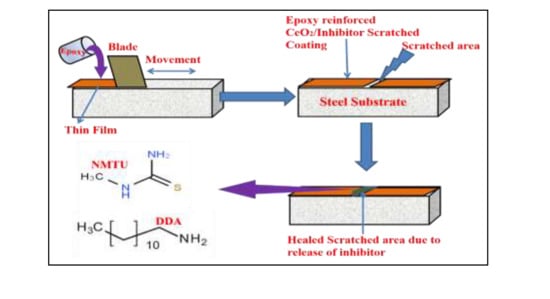
2.3. Preparation of Epoxy-Based Nanocomposite Smart Coatings
2.4. Coating Application
2.5. Characterization of Modified Nanoparticles
2.6. Characterization of Smart Coatings
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological and Structural Analysis
3.2. FTIR Analysis of Unmodified, Modified CeO2 and Nanocomposite Coatings
3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis of Unmodified and Modified CeO2 Nanoparticles
3.4. pH-Responsive Behavior of Inhibitors
3.5. Zeta Potential Measurements
3.6. Self-Healing of Inhibitor from Nanoparticles
3.7. Corrosion Inhibition Behavior
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability
References
- Revie, R.W.; Uhlig, H.H. Corrosion and Corrosion Control: An Introduction to Corrosion Science and Engineering, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 9780471732792. [Google Scholar]
- Montemor, M.F.; Vicente, C.; Técnico, I.S. Functional Self-Healing Coatings: A New Trend in Corrosion Protection by Organic Coatings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Philip, A.; Schweitzer, P.E. Paint and Coatings: Applications and Corrosion Resistance, 1st ed.; CRC Press (Taylor and Francis Group): Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; ISBN 9781574447026. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, M.; Habib, S.; Khan, A.; Shakoor, R.A.; Kahraman, R. Cellulose microfibers (CMFs) as a smart carrier for autonomous self-healing in epoxy coatings. New J. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.; Khan, A.; Nawaz, M.; Sliem, M.H.; Shakoor, R.A.; Kahraman, R.; Abdullah, A.M.; Zekri, A. Self-healing performance of multifunctional polymeric smart coatings. Polymers (Basel) 2019, 11, 1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, L.; Whalen, J.; Schutte, G.; Weder, C. Stimuli-responsive epoxy coatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotting, F.; Aoki, I.V. Smart protection provided by epoxy clear coating doped with polystyrene microcapsules containing silanol and Ce (III) ions as corrosion inhibitors. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behpour, M.; Ghoreishi, S.M.; Khayatkashani, M.; Soltani, N. The effect of two oleo-gum resin exudate from Ferula assa-foetida and Dorema ammoniacum on mild steel corrosion in acidic media. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 2489–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehri, I.; Erbil, M. Organic sulphur-containing compounds as corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in acidic media: Correlation between inhibition efficiency and chemical structure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 236, 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Zahidah, K.A.; Kakooei, S.; Ismail, M.C.; Bothi Raja, P. Halloysite nanotubes as nanocontainer for smart coating application: A review. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 111, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.M.; Shchukin, D.G.; Mohwald, H.; Price, R.R. Halloysite clay nanotubes for controlled release of protective agents. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poornima Vijayan, P.; Al-Maadeed, M.A.S.A. TiO2 nanotubes and mesoporous silica as containers in self-healing epoxy coatings. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.A.; Pham, T.L.; Dinh TM, T.; Thai, H.; Shi, X. Application of Nano-SiO2 and Nano-Fe2O3 for Protection of Steel Rebar in Chloride Contaminated Concrete: Epoxy Nanocomposite Coatings and Nano-Modified Mortars. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soestbergen, M.; Baukh, V.; Erich, S.J.F.; Huinink, H.P.; Adan, O.C.G. Release of cerium dibutylphosphate corrosion inhibitors from highly filled epoxy coating systems. Prog. Org. Coat. 2014, 77, 1562–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy, N.; Thi, T.; Hang, X.; Nicolay, A.; Paint, Y. Progress in Organic Coatings Corrosion protection of carbon steel by solvent free epoxy coating containing hydrotalcites intercalated with different organic corrosion inhibitors. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 101, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastri, V.S.; Perumareddi, J.R. Molecular Orbital Theoretical Studies of Some Organic Corrosion Inhibitors. Corrosion 1997, 53, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamaka, S.V.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Yasakau, K.A.; Montemor, M.F.; Ferreira, M.G.S. High effective organic corrosion inhibitors for 2024 aluminium alloy. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 7231–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khramov, A.N.; Voevodin, N.N.; Balbyshev, V.N.; Mantz, R.A. Sol—Gel-derived corrosion-protective coatings with controllable release of incorporated organic corrosion inhibitors. Thin Solid Films 2005, 483, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyad, E.M.; Almaadeed, M.A.; Jones, A.; Abdullah, A.M. Evaluation techniques for the corrosion resistance of self-healing coatings. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2014, 9, 4989–5011. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Gu, C.; Wen, Z.; Hou, B. Improvement of active corrosion protection of carbon steel by water-based epoxy coating with smart CeO2 nanocontainers. Prog. Org. Coat. 2018, 115, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zand, R.Z.; Flexer, V.; De Keersmaecker, M.; Verbeken, K.; Adriaens, A. Effects of activated ceria and zirconia nanoparticles on the protective behaviour of silane coatings in chloride solutions. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 997–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Pirhady Tavandashti, N.; Ghorbani, M.; Shojaei, A.; Gonzalez-Garcia, Y.; Terryn, H.; Mol, J.M.C. pH responsive Ce(III) loaded polyaniline nanofibers for self-healing corrosion protection of AA2024-T3. Prog. Org. Coat. 2016, 99, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekeridis, E.; Kartsonakis, I.; Pappas, G. Release studies of corrosion inhibitors from Cerium Titanium Oxide Release studies of corrosion inhibitors from cerium titanium oxide nanocontainers. J. Nanopart. Res. 2011, 13, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelliah, M.; Rayappan, J.B.B.; Krishnan, U. Synthesis and Characterization of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles by Hydroxide Mediated Approach. J. Appl. Sci. 2012, 12, 1734–1737. [Google Scholar]
- Renu, G.; Divya Rani, V.V.; Nair, S.V.; Subramanian, K.R.V.; Lakshmanan, V.K. Development of cerium oxide nanoparticles and its cytotoxicity in prostate cancer cells. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2012, 6, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mido, Y.; Kitagawa, I.; Hashimoto, M.; Matsuura, H. Vibrational spectra and normal coordinate analysis of N-methylthiourea and three deuterated analogues. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 1999, 55, 2623–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubaid, F.; Radwan, A.B.; Naeem, N.; Shakoor, R.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Montemor, M.F.; Kahraman, R.; Abdullah, A.M.; Soliman, A. Multifunctional self-healing polymeric nanocomposite coatings for corrosion inhibition of steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 372, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacob, M.; Cazacu, M.; Racles, C.; Ignat, M.; Cozan, V.; Sacarescu, L.; Timpu, D.; Kajňaková, M.; Botko, M.; Feher, A.; et al. Iron-chromium oxide nanoparticles self-assembling into smectic mesophases. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 6293–6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Menezes, B.R.C.; Ferreira, F.V.; Silva, B.C.; Simonetti, E.A.N.; Bastos, T.M.; Cividanes, L.S.; Thim, G.P. Effects of octadecylamine functionalization of carbon nanotubes on dispersion, polarity, and mechanical properties of CNT/HDPE nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 14311–14327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Mahdi, H.S.; Parveen, A.; Azam, A. Optical properties of cerium oxide (CeO2) nanoparticles synthesized by hydroxide mediated method. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1953, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, N.C.; Shi, E.W.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Li, W.J. Effect of pH of medium on hydrothermal synthesis of nanocrystalline cerium(IV) oxide powders. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 85, 2462–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorana, A.; Spinella, S.; Gross, R.A. Bio-Based Alternative to the Diglycidyl Ether of Bisphenol A with Controlled Materials Properties. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carja, I.-D.; Serbezeanu, D.; Vlad-Bubulac, T.; Hamciuc, C.; Coroaba, A.; Lisa, G.; López, C.G.; Soriano, M.F.; Pérez, V.F.; Romero Sánchez, M.D. A straightforward, eco-friendly and cost-effective approach towards flame retardant epoxy resins. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16230–16241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.G.; Cabanelas, J.C.; Baselga, J. Applications of FTIR on Epoxy Resins - Identification, Monitoring the Curing Process, Phase Separation and Water Uptake. Infrared Spectrosc. Mater. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2012, 2, 261–284. [Google Scholar]
- Mariappan, M.; Madhurambal, G.; Ravindran, B.; Mojumdar, S.C. Thermal, FTIR and microhardness studies of bisthiourea-urea single crystal. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 104, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoku, D.I.; Cui, M.; Xiao, H.; Shang, B.; Li, Y. Understanding the anticorrosive protective mechanisms of modified epoxy coatings with improved barrier, active and self-healing functionalities: EIS and spectroscopic techniques. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Cheng, Y.F. An intelligent coating doped with inhibitor-encapsulated nanocontainers for corrosion protection of pipeline steel. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.; Yusuf, N.; Habib, S.; Shakoor, R.A.; Ubaid, F.; Ahmad, Z.; Kahraman, R.; Mansour, S.; Gao, W.; Nawaz, M.; et al. Development and Properties of Polymeric Nanocomposite Coatings. Polymers (Basel) 2019, 11, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, Y.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, D.; Ding, J. Mechanism of Acceleration of Iron Corrosion by a Polylactide Coating. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 202–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahle, J.T.; Livi, K.; Arai, Y. Effects of pH and phosphate on CeO2 nanoparticle dissolution. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Tu, Z.; Yu, J.; Xiong, C.; Pan, M. Impregnation of amine-tailored titanate nanotubes in polymer electrolyte membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2012, 423–424, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Chen, T.; Wang, M.; Yang, N.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Acid and Alkaline Dual Stimuli-Responsive Mechanized Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Smart Nanocontainers for Intelligent Anticorrosion Coatings. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 11397–11408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahgat Radwan, A.; Ali, K.; Shakoor, R.A.; Mohammed, H.; Alsalama, T.; Kahraman, R.; Yusuf, M.M.; Abdullah, A.M.; Fatima Montemor, M.; Helal, M. Properties enhancement of Ni-P electrodeposited coatings by the incorporation of nanoscale Y2O3 particles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 457, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jlassi, K.; Radwan, A.B.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Mrlik, M.; Abdullah, A.M.; Chehimi, M.M.; Krupa, I. Anti-corrosive and oil sensitive coatings based on epoxy/polyaniline/magnetite-clay composites through diazonium interfacial chemistry. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verma, C.; Quraishi, M.A.; Singh, A. 2-Amino-5-nitro-4,6-diarylcyclohex-1-ene-1,3,3-tricarbonitriles as new and effective corrosion inhibitors for mild steel in 1 M HCl: Experimental and theoretical studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 212, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.L.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, F.H.; Li, J.F.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, J.M.; Cao, C.N. A study of the corrosion of aluminum alloy 2024-T3 under thin electrolyte layers. Corros. Sci. 2004, 46, 1649–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welle, A.; Liao, J.D.; Kaiser, K.; Grunze, M.; Mäder, U.; Blank, N. Interactions of N,N′-dimethylaminoethanol with steel surfaces in alkaline and chlorine containing solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1997, 119, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekry, A.M.; Mohamed, R.R. Acetyl thiourea chitosan as an eco-friendly inhibitor for mild steel in sulphuric acid medium. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 1933–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, H.-Y.; Wang, F.-H. Corrosion inhibition by sorbitol/diethylenetriamine condensation product for carbon steel in 3.5% NaCl saturated Ca(OH)2 solution. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2011, 27, 647–654. [Google Scholar]













| Samples | Element Present | wt.% | at.% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unloaded CeO2 | Ce, O | Ce = 75.96, O = 16.22 | Ce = 24.68, O = 46.15 |
| CeO2/DDA (C43H53NO14) | Ce, O, C, N | Ce = 62.84, O = 14.72, C = 21.60, N = 0.48 | Ce = 13.95, O = 28.63, C = 55.97, N = 1.06 |
| CeO2/NMTU (NH2CSNHCH3) | Ce, O, C, N | Ce = 62.67, O = 14.79, C = 22.22, N = 0.23 | Ce = 13.84, O = 28.60, C = 57.23, N = 0.34 |
| Coatings | Time (h) | Rpo (MΩ·cm2) | CPE1 (F·cm−2·Sn−1) | Rct (MΩ·cm2) | CPE2 (F·cm−2·Sn−1) | W (MΩ·cm2·S−1/2) | IE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| blank epoxy | 24 | 0.226 | 1.608 × 10−7 | 1.250 | 1.522 × 10−10 | - | - |
| 48 | 0.106 | 7.701 × 10−6 | 1.172 | 4.259 × 10−9 | |||
| 72 | 0.104 | 7.34 × 10−6 | 0.714 | 2.605 × 10−9 | |||
| 96 | 0.084 | 2.908 × 10−6 | 0.549 | 1.488 × 10−9 | |||
| 120 | 0.029 | 1.08 × 10−6 | 0.249 | 1.206 × 10−9 | |||
| Epoxy/CeO2 | 24 | 0.075 | 1.459 × 10−6 | 1.947 | 9.518 × 10−10 | - | 84.9 |
| 48 | 0.043 | 6.613 × 10−6 | 0.266 | 1.048 × 10−9 | - | ||
| 72 | 0.055 | 3.710 × 10−6 | 0.235 | 1.280 × 10−9 | |||
| 96 | 0.022 | 3.532 × 10−6 | 0.166 | 1.408 × 10−9 | |||
| 120 | 0.028 | 6.562 × 10−6 | 0.155 | 1.994 × 10−9 | |||
| Epoxy/CeO2/DDA | 24 | 0.705 | 4.794 × 10−8 | 1.708 | 1.014 × 10−9 | - | 82.8 |
| 48 | 0.313 | 8.047 × 10−7 | 1.408 | 2.175 × 10−9 | - | - | |
| 72 | 0.966 | 1.628 × 10−9 | 2.238 | 5.937 × 10−10 | 2.83 | - | |
| 96 | 10.54 | 6.077 × 10−10 | 9.123 | 2.289 × 10−10 | 11.0 | - | |
| 120 | 42.77 | 8.101 × 10−11 | 167.3 | 1.081 × 10−10 | 47.5 | 99.8 | |
| Epoxy/CeO2/NMTU | 24 | 0.205 | 2.907 × 10−7 | 1.125 | 1.885 × 10−9 | - | 73.9 |
| 48 | 0.013 | 3.969 × 10−7 | 0.132 | 2.461 × 10−9 | - | - | |
| 72 | 0.839 | 1.625 × 10−8 | 0.695 | 6.962 × 10−10 | 1.70 | - | |
| 96 | 1.076 | 3.627 × 10−9 | 1.831 | 4.471 × 10−10 | 10.5 | - | |
| 120 | 1.614 | 1.233 × 10−9 | 6.892 | 1.145 × 10−10 | 13.5 | 95.7 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Habib, S.; Fayyad, E.; Nawaz, M.; Khan, A.; Shakoor, R.A.; Kahraman, R.; Abdullah, A. Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticles as Smart Carriers for Self-Healing Coatings. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040791
Habib S, Fayyad E, Nawaz M, Khan A, Shakoor RA, Kahraman R, Abdullah A. Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticles as Smart Carriers for Self-Healing Coatings. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(4):791. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040791
Chicago/Turabian StyleHabib, Sehrish, Eman Fayyad, Muddasir Nawaz, Adnan Khan, Rana A. Shakoor, Ramazan Kahraman, and Aboubakr Abdullah. 2020. "Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticles as Smart Carriers for Self-Healing Coatings" Nanomaterials 10, no. 4: 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040791
APA StyleHabib, S., Fayyad, E., Nawaz, M., Khan, A., Shakoor, R. A., Kahraman, R., & Abdullah, A. (2020). Cerium Dioxide Nanoparticles as Smart Carriers for Self-Healing Coatings. Nanomaterials, 10(4), 791. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10040791