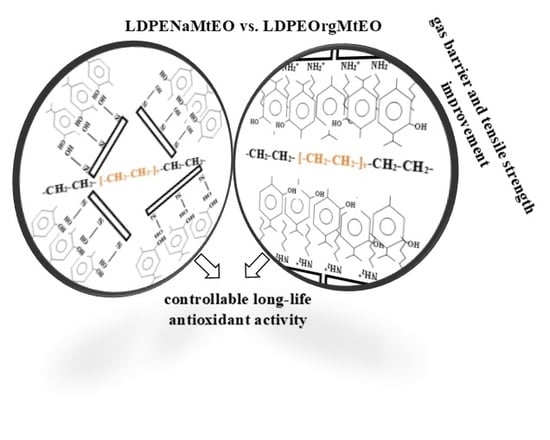
Na-Montmorillonite Vs. Organically Modified Montmorillonite as Essential Oil Nanocarriers for Melt-Extruded Low-Density Poly-Ethylene Nanocomposite Active Packaging Films with a Controllable and Long-Life Antioxidant Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Essential Oil Used
2.1.2. Nanoclay Used
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of NaMtEO and OrgMtEO Nanohybrids
2.2.2. Preparation of LDPENaMtEO and LDPEOrgMtEO Films
2.2.3. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.2.4. Tensile Properties
2.2.5. Water Vapor Transmission Rate (WVTR)
2.2.6. Oxygen Transmission Rate (OTR) Measurements
2.2.7. Antioxidant Activity Evaluation of Films
2.2.8. Lipid Oxidation
Sample Preparation
TBARS Method
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. XRD
3.2. Tensile Properties
3.3. Barrier Properties
3.4. Antioxidant Activity of Films
- (1)
- By increasing EO content, the antioxidant activity of all tested films further increased.
- (2)
- NaMtTO-, NaMtOO-, OrgMtTO-, and OrgMtOO-based films exhibited much higher antioxidant activity than NaMtBO- and OrgMtBO-based films.
- (3)
- Almost equal antioxidant activity values were recorded for both LDPENaMtEO and LDPEOrgMtEO films.
3.5. Lipid Oxidation
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bajpai, V.K.; Kamle, M.; Shukla, S.; Mahato, D.K.; Chandra, P.; Hwang, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Huh, Y.S.; Han, Y.-K. Prospects of using nanotechnology for food preservation, safety, and security. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 1201–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanches-Silva, A.; Costa, D.; Albuquerque, T.G.; Buonocore, G.G.; Ramos, F.; Castilho, M.C.; Machado, A.V.; Costa, H.S. Trends in the use of natural antioxidants in active food packaging: A review. Food Addit. Contam. Part. A 2014, 31, 374–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyldgaard, M.; Mygind, T.; Meyer, R.L. Essential Oils in Food Preservation: Mode of Action, Synergies, and Interactions with Food Matrix Components Essential oils in food preservation: Mode of action, synergies, and interactions with food matrix components. Front. Microbiol. Antimicrob. Resist. Chemother. 2012, 3, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-González, L.; Vargas, M.; González-Martínez, C.; Chiralt, A.; Cháfer, M. Use of Essential Oils in Bioactive Edible Coatings: A Review. Food Eng. Rev. 2011, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.J.; Chao, C.J.; Chang, H.Y.; Wu, P.C. The effects of evaporating essential oils on indoor air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Requena, V.H.; Rivas, B.L.; Pérez, M.A.; Garrido-Miranda, K.A.; Pereira, E.D. Polymer/clay nanocomposite films as active packaging material: Modeling of antimicrobial release. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 71, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakas, A.E.; Leontiou, A.A. Montmorillonite Composite Materials and Food Packaging. In Composites Materials for Food Packaging; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–71. ISBN 978-1-119-16024-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinninmonth, M.A.; Liauw, C.M.; Verran, J.; Taylor, R.; Edwards-Jones, V.; Shaw, D.; Webb, M. Investigation into the suitability of layered silicates as adsorption media for essential oils using FTIR and GC-MS. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 83–84, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakas, A.; Tsagkalias, I.; Achilias, D.S.; Ladavos, A. A novel method for the preparation of inorganic and organo-modified montmorillonite essential oil hybrids. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 146, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemesh, R.; Krepker, M.; Goldman, D.; Danin-Poleg, Y. Antibacterial and antifungal LDPE films for active packaging Antibacterial and antifungal LDPE films for active packaging. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2014, 26, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shemesh, R.; Krepker, M.; Natan, M.; Banin, E.; Kashi, Y.; Nitzan, N.; Vaxman, A.; Segal, E. RSC Advances Novel LDPE / halloysite nanotube films with sustained carvacrol release for broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity †. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 87108–87117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, H.J. Effect of halloysite nanoclay on the physical, mechanical, and antioxidant properties of chitosan films incorporated with clove essential oil. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Pereira, L.; Angulo, I.; Lagarón, J.M.; Paseiro-Losada, P.; Cruz, J.M. Development of new active packaging films containing bioactive nanocomposites. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 26, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busolo, M.A.; Lagaron, J.M. Antioxidant polyethylene films based on a resveratrol containing Clay of Interest in Food Packaging Applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2015, 6, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornuk, F.; Hancer, M.; Sagdic, O.; Yetim, H. LWT—Food Science and Technology LLDPE based food packaging incorporated with nanoclays grafted with bioactive compounds to extend shelf life of some meat products. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, M.; Rezaei, M.; Farzi, G. A novel active bionanocomposite film incorporating rosemary essential oil and nanoclay into chitosan. J. Food Eng. 2012, 111, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Requena, V.H.; Rivas, B.L.; Perez, M.A.; Figueroa, C.R.; Figueroa, N.E.; Sanfuentes, E.A. Thermoplastic starch/clay nanocomposites loaded with essential oil constituents as packaging for strawberries In vivo antimicrobial synergy over Botrytis cinerea. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2017, 129, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Requena, V.H.; Rivas, B.L.; Pérez, M.A.; Garrido-Miranda, K.A.; Pereira, E.D. Release of essential oil constituent from thermoplastic starch/layered silicate bionanocomposite film as a potential active packaging material. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 109, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakas, A.; Stathopoulou, P.; Tsiamis, G.; Salmas, C. The effect of different preparation methods on the development of chitosan/thyme oil/montmorillonite nanocomposite active packaging films. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakas, A.; Giannakas, A.; Ladavos, A. Preparation and Characterization of Polystyrene/Organolaponite Nanocomposites. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2012, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakas, A.; Grigoriadi, K.; Leontiou, A.; Barkoula, N.-M.; Ladavos, A. Preparation, characterization, mechanical and barrier properties investigation of chitosan–clay nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 108, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakas, A.; Vlacha, M.; Salmas, C.; Leontiou, A.; Katapodis, P.; Stamatis, H.; Barkoula, N.-M.; Ladavos, A. Preparation, characterization, mechanical, barrier and antimicrobial properties of chitosan/PVOH/clay nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 140, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panea, B.; Ripoll, G.; González, J.; Fernández-Cuello, Á.; Albertí, P. Effect of nanocomposite packaging containing different proportions of ZnO and Ag on chicken breast meat quality. J. Food Eng. 2014, 123, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquelot, E.; Espuche, E.; Gérard, J.-F.; Duchet, J.; Mazabraud, P. Morphology and gas barrier properties of polyethylene-based nanocomposites. J. Polym. Sci. Part. B Polym. Phys. 2006, 44, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunvisut, S.; Phummanee, S.; Somwangthanaroj, A. Effect of clay on mechanical and gas barrier properties of blown film LDPE/clay nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 2210–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Lv, X.-Y.; Han, Z.-J.; Ci, J.-H.; Fang, C.-Q.; Ren, P.-G. Preparation and Performance of High-Barrier Low Density Polyethylene/Organic Montmorillonite Nanocomposite. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2012, 51, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinkhanli, H.; Sharif, A.; Aalaie, J.; Khalkhali, T.; Akhlaghi, S. Oxygen permeability and the mechanical and thermal properties of (low-density polyethylene)/poly (ethylene-co-vinyl acetate)/organoclay blown film nanocomposites. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2013, 19, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.A.; Rivas, B.L.; Garrido-Miranda, K.A.; Campos-Requena, V.H.; Martinez, M.; Castano, J.; Maldonado, A. Low Density Polyethylene (Ldpe) Nanocomposites With Passive and Active Barrier Properties. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2014, 59, 2442–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkali, F.; Averbeck, S.; Averbeck, D.; Idaomar, M. Biological effects of essential oils - A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 446–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Yadav, D.N.; Ahmad, T.; Narsaiah, K. Recent Trends in the Use of Natural Antioxidants for Meat and Meat Products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 796–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Persico, P.; Ambrogi, V.; Carfagna, C.; Cerruti, P.; Ferrocino, I.; Mauriello, G. Nanocomposite Polymer Films Containing Carvacrol for Antimicrobial Active Packaging. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Hernández, G.B.; Amodio, M.L.; Colelli, G. Carvacrol-loaded chitosan nanoparticles maintain quality of fresh-cut carrots. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 41, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunc, S.; Duman, O.; Polat, T.G.; Tunc, S.; Duman, O.; Polat, T.G. Effects of montmorillonite on properties of methyl cellulose/carvacrol based active antimicrobial nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 150, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Requena, V.H.; Figueroa, C.R.; Sanfuentes, E.A. LWT—Food Science and Technology The synergistic antimicrobial effect of carvacrol and thymol in clay/polymer nanocomposite films over strawberry gray mold. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azlin-Hasim, S.; Cruz-Romero, M.C.; Morris, M.A.; Cummins, E.; Kerry, J.P. Effects of a combination of antimicrobial silver low density polyethylene nanocomposite films and modified atmosphere packaging on the shelf life of chicken breast fillets. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2015, 4, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouliara, E.; Badeka, A.; Savvaidis, I.; Kontominas, M.G. Combined effect of irradiation and modified atmosphere packaging on shelf-life extension of chicken breast meat: Microbiological, chemical and sensory changes. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2008, 226, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latou, E.; Mexis, S.F.; Badeka, A.V.; Kontakos, S.; Kontominas, M.G. Combined effect of chitosan and modified atmosphere packaging for shelf life extension of chicken breast fillets. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample Code Name | d001/(Å) | Young’s Modulus E (St.Dev.) (MPa) | σ(uts) (St.Dev.)(MPa) | %εb (St.Dev.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDPE | 175.3 (10.1) | 11.7 (0.5) | 58.5 (4.5) | |
| LDPENaMt | n.p. | 165.1 (8.9) | 11.0 (0.5) | 35.5 (3.5) |
| LDPENaMtTO20 | n.p. | 160.5 (12.5) | 10.6 (0.8) | 32.4 (2.3) |
| LDPENaMtTO40 | n.p. | 158.4 (10.5) | 10.5 (0.7) | 31.6 (2.5) |
| LDPENaMtTO80 | n.p. | 141.5 (10.2) | 9.5 (0.6) | 25.5 (3.2) |
| LDPENaMtOO20 | n.p. | 157.5 (16.2) | 10.9 (0.8) | 34.4 (4.2) |
| LDPENaMtOO40 | n.p. | 153.4 (14.8) | 10.4 (0.9) | 33.6 (4.1) |
| LDPENaMtOO80 | n.p. | 131.2 (10.8) | 10.2 (0.7) | 27.5 (2.8) |
| LDPENaMtBO20 | n.p. | 160.2 (17.8) | 10.0 (0.8) | 32.4 (3.5) |
| LDPENaMtBO40 | n.p. | 152.3 (15.9) | 10.7 (0.8) | 32.6 (3.4) |
| LDPENaMtBO80 | n.p. | 132.3 (13.5) | 8.9 (0.7) | 26.5 (2.7) |
| LDPEOrgMt | 32.0 | 195.0 (10.4) | 12.4 (0.6) | 38.3 (3.8) |
| LDPEOrgMtTO20 | 36.1 | 170.3 (12.2) | 11.6 (0.6) | 51.7 (5.6) |
| LDPEOrgMtTO40 | 36.2 | 185.8 (13.4) | 12.3 (0.7) | 41.3 (4.8) |
| LDPEOrgMtTO80 | 36.8 | 218.3 (9.5) | 13.6 (0.7) | 35.6 (3.9) |
| LDPEOrgMtOO20 | 36.5 | 171.5 (14.5) | 11.3 (0.7) | 39.6 (4.1) |
| LDPEOrgMtOO40 | 36.5 | 187.4 (14.2) | 12.3 (0.7) | 38.5 (3.8) |
| LDPEOrgMtOO80 | 36.8 | 224.2 (11.5) | 14.5 (0.5) | 34.5 (3.5) |
| LDPEOrgMtBO20 | 33.1 | 168.6 (15.6) | 11.2 (0.8) | 40.8 (4.3) |
| LDPEOrgMtBO40 | 33.5 | 182.2 (14.3) | 11.7 (0.7) | 37.5 (3.8) |
| LDPEOrgMtBO80 | 33.5 | 191.2 (13.8) | 12.6 (0.6) | 36.5 (4.2) |
| Sample Code Name | WVTR (St.Dev.) (g/h.m2) | OP (St.Dev.) (ccO2.mm/m2.day) | % Antioxidant Activity (St.Dev.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDPE | 3.19 (0.40) | 186.5 (3.7) | - |
| LDPENaMt | 3.82 (0.39) | 194.2 (2.6) | 8.2 (2.3) |
| LDPENaMtTO20 | 3.63 (0.38) | 188.4 (4.2) | 51.4 (3.8) |
| LDPENaMtTO40 | 3.72 (0.41) | 184.7 (6.4) | 60.1 (4.1) |
| LDPENaMtTO80 | 4.88 (0.36) | 192.5 (7.5) | 79.8 (3.9) |
| LDPENaMtOO20 | 3.56 (0.38) | 184.2 (2.8) | 53.8 (3.7) |
| LDPENaMtOO40 | 3.71 (0.40) | 186.8 (4.4) | 61.4 (3.9) |
| LDPENaMtOO80 | 4.92 (0.20) | 199.6 (6.8) | 76.7 (4.2) |
| LDPENaMtBO20 | 3.62 (0.42) | 191.2 (2.7) | 37.9 (3.8) |
| LDPENaMtBO40 | 3.72 (0.41) | 187.8 (4.3) | 47.8 (3.8) |
| LDPENaMtBO80 | 4.95 (0.41) | 196.6 (6.8) | 55.5 (4.2) |
| LDPEOrgMt | 2.65 (0.22) | 183 (4.2) | 12.0 (2.5) |
| LDPEOrgMtTO20 | 2.55 (0.20) | 165 (6.4) | 53.1 (4.7) |
| LDPEOrgMtTO40 | 2.50 (0.21) | 155 (5.5) | 58.5 (4.8) |
| LDPEOrgMtTO80 | 2.41 (0.23) | 131 (6.4) | 73.6 (4.9) |
| LDPEOrgMtOO20 | 2.52 (0.19) | 168 (6.6) | 56.0 (5.4) |
| LDPEOrgMtOO40 | 2.51 (0.20) | 159 (5.2) | 58.6 (5.3) |
| LDPEOrgMtOO80 | 2.21 (0.21) | 136 (6.1) | 73.2 (5.1) |
| LDPEOrgMtBO20 | 2.68 (0.21) | 175 (6.6) | 42.1 (5.0) |
| LDPEOrgMtBO40 | 2.48 (0.23) | 164 (5.3) | 46.1 (5.1) |
| LDPEOrgMtBO80 | 2.32 (0.21) | 147 (6.7) | 51.7 (5.3) |
| Sig | IA | |
|---|---|---|
| E | 0.002 | 96 |
| σuts | 0.005 | 90 |
| %εb | 0.003 | 94 |
| WVTR | 0.003 | 94 |
| OP | 0.004 | 92 |
| %Ct,DPPH/C0,DPPH | 0.001 | 98 |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giannakas, A. Na-Montmorillonite Vs. Organically Modified Montmorillonite as Essential Oil Nanocarriers for Melt-Extruded Low-Density Poly-Ethylene Nanocomposite Active Packaging Films with a Controllable and Long-Life Antioxidant Activity. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061027
Giannakas A. Na-Montmorillonite Vs. Organically Modified Montmorillonite as Essential Oil Nanocarriers for Melt-Extruded Low-Density Poly-Ethylene Nanocomposite Active Packaging Films with a Controllable and Long-Life Antioxidant Activity. Nanomaterials. 2020; 10(6):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061027
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiannakas, Aris. 2020. "Na-Montmorillonite Vs. Organically Modified Montmorillonite as Essential Oil Nanocarriers for Melt-Extruded Low-Density Poly-Ethylene Nanocomposite Active Packaging Films with a Controllable and Long-Life Antioxidant Activity" Nanomaterials 10, no. 6: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061027
APA StyleGiannakas, A. (2020). Na-Montmorillonite Vs. Organically Modified Montmorillonite as Essential Oil Nanocarriers for Melt-Extruded Low-Density Poly-Ethylene Nanocomposite Active Packaging Films with a Controllable and Long-Life Antioxidant Activity. Nanomaterials, 10(6), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10061027