Effect of Catalyst Crystallinity on V-Based Selective Catalytic Reduction with Ammonia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 Catalysts
2.2. Catalyst Characterization
2.3. Catalytic Measurement
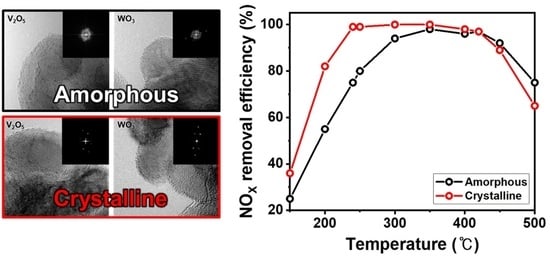
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boningari, T.; Smirniotis, P.G. Impact of nitrogen oxides on the environment and human health: Mn-based materials for the NOX abatement. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2016, 13, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Thompson, S.; Peng, J. Modelling and prediction of NOx emission in a coal-fired power generation plant. Control. Eng. Pract. 2004, 12, 707–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-J.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, M.; Ye, B.; Jeong, B.; Lee, D.; Kim, H.-D.; Lee, H. Enhanced NOx removal efficiency for SCR catalyst of well-dispersed Mn-Ce nanoparticles on hexagonal boron nitride. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 36107–36116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forzatti, P.; Nova, I.; Tronconi, E. Enhanced NH3 Selective Catalytic Reduction for NOx Abatement. Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 8516–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Lee, M.; Jeong, B.; Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Baik, J.; Kim, H. Partially reduced graphene oxide as a support of Mn-Ce/TiO2 cat-alyst for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Catal. Today 2019, 328, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, G.; Krishnan, R.M.; Beelen, R.; Preters, A.; Ostro, B.; Brunekreef, B. Long-term air pollution exposure and cardio- res-piratory mortality: A review. Environ. Health 2013, 12, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Radojevic, M. Reduction of nitrogen oxides in flue gases. Environ. Pollut. 1998, 102, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.; Ye, B.; Kim, E.-S.; Kim, H.-D. Characteristics of selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalyst adding graphene-tungsten nanocomposite. Catal. Commun. 2017, 93, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Hegde, M.; Madras, G. Catalysis for NOx abatement. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G.; Lietti, L.; Ramis, G.; Berti, F. Chemical and mechanistic aspects of the selective catalytic reduction of NO(X) by ammonia over oxide catalysts: A review. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 1998, 18, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Kong, T.; Yu, S.; Li, L.; Yang, F.; Dong, L. Influence of different supports on the physicochemical properties and de-nitration performance of the supported Mn-based catalysts for NH3-SCR at low temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 402, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Shan, W.; Lian, Z.; Xie, L.; Yang, W.; He, H. Novel MnWOx catalyst with remarkable performance for low tempera-ture NH3-SCR of NOx. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 2699–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Huang, R.; Jin, D.; Ye, D. Low temperature SCR of NO with NH3 over carbon nanotubes supported vanadium oxides. Catal. Today 2007, 126, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Q. Formation and reaction of ammonium sulfate salts on V2O5/AC catalysts during selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide by ammonia at low temperatures. J. Catal. 2003, 214, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzio, L.; Bogseth, S.; Himes, R.; Chien, Y.; Dunn–Rankin, D. Ammonium bisulfate formation and reduced load SCR opera-tion. Fuel 2017, 206, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yang, Q.; Hu, L.; Wang, D.; Peng, Y.; Shao, Z.; Lu, C.; Li, J. Insights over titanium modified FeMgOx catalysts for se-lective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: Influence of precursors and crystalline structures. Catalysts 2019, 9, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Zhong, Q.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, S. Enhanced NOx removal performance of amorphous Ce-Ti catalyst by hydrogen pre-treatment. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2016, 423, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, S.; Chang, H.; Peng, Y.; Li, J. Dispersion of tungsten oxide on SCR performance of V2O5AWO3/TiO2: Acidity, surface species and catalytic activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, Y.; Hata, S.; Mino, M.; Kiyonaga, E.; Morita, K.; Hikino, K.; Yoshida, K.; Kubota, H.; Toyao, T.; Shimizu, K.; et al. Bulk vanadium oxide versus conventional V2O5/TiO2: NH3-SCR catalysts working at a low tem-perature below 150 °C. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 9327–9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, Y.; Hata, S.; Kiyonaga, E.; Morita, K.; Yoshida, K.; Haruta, M.; Murayama, T. Synthesis of bulk vanadium oxide with a large surface area using organic acids and its low-temperature NH3-SCR activity. Catal. Today 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Deng, H.; Xin, S.; Shan, W.; Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; He, H. Significant promotion effect of the rutile phase on V2O5/TiO2 catalysts for NH3-SCR. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, Z.; Li, Y.; Shan, W.; He, H. Recent Progress on Improving Low-Temperature Activity of Vanadia-Based Catalysts for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with Ammonia. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xia, Y.; Fang, R.; Huang, H.; Gan, Y.; Liang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X. The effects of tungsten and hydro-thermal aging in promoting NH3-SCR activity on V2O5/WO3-TiO2 catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 459, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, W.; Xu, H.; Chen, T.; Ke, Y.; Qu, Z.; Yan, N. Alkali-induced deactivation mechanism of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 cata-lyst during selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 in aluminum hydrate calcining flue gas. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 270, 118872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.C.; Jung, Y.M.; Bin Kim, S. Size effects in the Raman spectra of TiO2 nanoparticles. Vib. Spectrosc. 2005, 37, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfaoui, J.; Boudali, L.K.; Ghorbel, A.; Delahay, G. Effect of vanadium on the behaviour of unsulfated and sulfated Ti-pillared clay catalysts in the SCR of NO by NH3. Catal. Today 2009, 142, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.-K.; Wachs, I.E. A Perspective on the Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) of NO with NH3 by Supported V2O5–WO3/TiO2 Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 6537–6551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Cha, W.S. Effect of vanadium oxide loading on SCR activity and SO2 resistance over TiO2-supported V2O5 com-mercial De-NOX catalysts. Appl. Chem. Eng. 2012, 23, 485–489. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, B.M.; Khan, A.; Yamada, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Loridant, S.; Volta, J.-C. Surface Characterization of CeO2/SiO2 and V2O5/CeO2/SiO2 Catalysts by Raman, XPS, and Other Techniques. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 10964–10972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, W.; Wang, L.; Song, M.; Yang, L.; Shen, K.; Xu, H.; Zhou, C. Characterization and activity of V2O5-CeO2/TiO2-ZrO2 catalysts for NH3-selective catalytic reduction of NOx. Chin. J. Catal. 2015, 36, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Choi, H.; Mhin, S.; Hong, Y.R.; Kim, K.M.; Kwon, J.; Ali, G.; Chung, K.Y.; Je, M.; Umh, H.M.; et al. Advantageous crystalline-amorphous phase boundary for enhanced electrochemical water oxi-dation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falqui, A.; Loche, D.; Casu, A. In Situ TEM Crystallization of Amorphous Iron Particles. Crystals 2020, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Shi, L.; Fang, C.; Li, H.; Gao, R.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J. In situ supported MnOx-CeOx on carbon nano-tubes for the low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; He, H. Structure-activity relationship of iron titanate catalysts in the selective catalytic reduction of NOX with NH3. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 16929–16936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Song, H.; Luo, Z.; Cen, K. Effects of PbCl2 on selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over vanadia-based catalysts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 274, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, X.; Ni, K.; Shen, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Jing, G. Molybdenum-decorated V2O5–WO3/TiO2: Surface engineering toward boosting the acid cycle and redox cycle of NH3-SCR. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 1746–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Zhong, Q. Promotional effect of F-doped V2O5–WO3/TiO2 catalyst for NH3-SCR of NO at low-temperature. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2012, 435-436, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, X.J. Efficient NH3-SCR removal of NOX with highly ordered mesoporous WO3(χ)-CeO2 at low temperatures. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 203, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greenhalgh, B.; Fee, M.; Dobri, A.; Moir, J.; Burich, R.; Charland, J.-P.; Stanciulescu, M. DeNOx activity–TPD correlations of NH3-SCR catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2010, 333, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Ge, J.; Huang, Z. Simultaneous removal of SO2 and NOx from flue gas using a CuO/Al2O3 catalyst sorbentII. Promotion of SCR activity by SO2 at high temperatures. J. Catal. 2004, 224, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wang, D.; Kumar, A.; Li, J.; Kamasamudram, K.; Currier, N.; Yezerets, A. Identification of two types of Cu sites in Cu/SSZ-13 and their unique responses to hydrothermal aging and sulfur poisoning. Catal. Today 2016, 267, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yu, W.; Si, Z.; Weng, D. Chemical deactivation of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 SCR catalyst by combined effect of potassium and chloride. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2013, 7, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Sample | BET Surface Area; SBET (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| One-sided | 69.6 | 0.252 | 14.48 |
| Isotropic | 70.2 | 0.257 | 14.67 |
| Sample | TiO2 | WO3 | V2O5 | SO3 | SiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One-sided | 86.92 | 10.19 | 2.02 | 0.70 | 0.17 |
| Isotropic | 87.05 | 10.04 | 2.03 | 0.66 | 0.22 |
| Sample | Oα/(Oα + Oβ) | V4+/(V4+ + V5+) | NH3 Desorption (cm3/g) | H2 Consumption (cm3/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amorphous | 0.30 | 0.23 | 13.74 | 40.17 |
| Crystalline | 0.33 | 0.38 | 16.97 | 46.06 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, M.S.; Kim, S.-I.; Lee, M.-j.; Ye, B.; Kim, T.; Kim, H.-D.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, D.H. Effect of Catalyst Crystallinity on V-Based Selective Catalytic Reduction with Ammonia. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061452
Lee MS, Kim S-I, Lee M-j, Ye B, Kim T, Kim H-D, Lee JW, Lee DH. Effect of Catalyst Crystallinity on V-Based Selective Catalytic Reduction with Ammonia. Nanomaterials. 2021; 11(6):1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061452
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Min Seong, Sun-I Kim, Myeung-jin Lee, Bora Ye, Taehyo Kim, Hong-Dae Kim, Jung Woo Lee, and Duck Hyun Lee. 2021. "Effect of Catalyst Crystallinity on V-Based Selective Catalytic Reduction with Ammonia" Nanomaterials 11, no. 6: 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061452
APA StyleLee, M. S., Kim, S. -I., Lee, M. -j., Ye, B., Kim, T., Kim, H. -D., Lee, J. W., & Lee, D. H. (2021). Effect of Catalyst Crystallinity on V-Based Selective Catalytic Reduction with Ammonia. Nanomaterials, 11(6), 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11061452