Tetracycline Removal by Hercynite-Biochar from the Co-Pyrolysis of Red Mud-Steel Slag-Sludge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sludge Conditioning with Red Mud and Steel Slag
2.3. Preparation of Biochar Co-Pyrolysis of Sludge and Solid Wastes
2.4. Removal of Tetracycline
2.5. Analysis Method
2.5.1. XRD Rietveld Refinement
2.5.2. FTIR Analysis
2.5.3. Microstructure of Biochar
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sludge Dewatering Performance
3.1.1. Sludge Dewatering Performance after Conditioning with Solid Wastes
3.1.2. The Improvement Mechanism for Sludge Dewatering Performance
3.2. Effect of Red Mud and Steel Slag Content on the Phase Composition of Sludge Biochar
3.3. Tetracycline Removal by Sludge Biochar
3.3.1. Tetracycline Removal with Different Sludge-Waste Content, Biochar Dosage, and pH
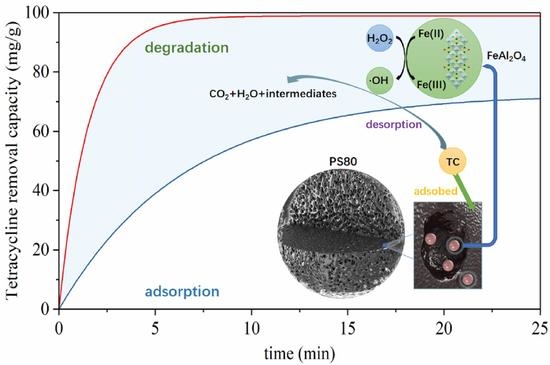
3.3.2. Tetracycline Removal Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biganzoli, L.; Grosso, M.; Giugliano, M.; Campolunghi, M. Chemical and sewage sludge co-incineration in a full-scale MSW incinerator: Toxic trace element mass balance. Waste Manag. Res. J. A Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2012, 30, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Sheng, Q.; Dai, X.; Dong, B. Upgrading of sewage sludge by low temperature pyrolysis: Biochar fuel properties and combustion behavior. Fuel 2021, 300, 121007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Shang, H.; Tao, S.; Wang, X.; Zhan, G.; Li, H.; Ai, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L. Visible Light Driven Organic Pollutants Degradation with Hydrothermally Carbonized Sewage Sludge and Oxalate Via Molecular Oxygen Activation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12656–12666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadi, P.; Xu, M.; Ning, C.; Sze Ki Lin, C.; McKay, G. A critical review on preparation, characterization and utilization of sludge-derived activated carbons for wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, Z. Effect of inherent minerals on sewage sludge pyrolysis: Product characteristics, kinetics and thermodynamics. Waste Manage. 2018, 80, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Zhu, N.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; He, S.; Yang, C.; Yao, H. A comprehensive insight into the combined effects of Fenton’s reagent and skeleton builders on sludge deep dewatering performance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 258–259, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Yang, J.; Hou, H.; Liang, S.; Xiao, K.; Qiu, J.; Hu, J.; Liu, B.; Yu, W.; Deng, H. Enhanced sludge dewatering via homogeneous and heterogeneous Fenton reactions initiated by Fe-rich biochar derived from sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 372, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomaa, S.; Shanableh, A.; Khalil, W.; Trebilco, B. Hydrothermal decomposition and oxidation of the organic component of municipal and industrial waste products. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2003, 7, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, D.; Chai, X.; Zhao, W. Hybrid cement-assisted dewatering, solidification and stabilization of sewage sludge with high organic content. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2016, 18, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, M.; Han, Y.; Shi, B.; Xiong, Q.; Hou, H. Mechanism of red mud combined with steel slag conditioning for sewage sludge dewatering. Desalination Water Treat. 2018, 135, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wan, S.; Xue, F.; Liang, A.; Yuan, J.; Hou, H. Optimization of sludge dewatering process by inorganic conditioners under mild thermal treatment. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 28661–28669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Han, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Y.; Huang, F.; Luo, T.; Zheng, Y.; Hou, H. Improvement of sewage sludge dewaterability and immobilization of the heavy metals by using pretreated steel slag. Desalination Water Treat. 2020, 182, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X. Preparation of Cotton Linters’ Aerogel-Based C/NiFe2O4 Photocatalyst for Efficient Degradation of Methylene Blue. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y.; Tian, S.; Kong, L.; Xiong, Y. Co-catalytic effect of sewage sludge-derived char as the support of Fenton-like catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 185–186, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Zhu, N.; Guo, H.; Huang, S.; Lou, Z.; Yuan, H. Adsorption and Fenton-like degradation of naphthalene dye intermediate on sewage sludge derived porous carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 246–247, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Yang, X.; Peng, Y.; Yu, J. Preparation, Characterization and Application of Epitaxial Grown BiOBr (110) Film on ZnFe2O4 Surface with Enhanced Photocatalytic Fenton Oxidation Properties. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Hou, J.; Yao, L.-H.; Jin, H.-M.; Qian, G.-R.; Xu, Z.P. Ferrite materials prepared from two industrial wastes: Electroplating sludge and spent pickle liquor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 75, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.-J.; Dai, X.-H. Sewage sludge-based functional nanomaterials: Development and applications. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Ruan, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Qian, G. Electroplating sludge derived zinc-ferrite catalyst for the efficient photo-Fenton degradation of dye. J. Environ. Manage. 2017, 193, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Ou, C.; Shen, J.; Yu, H.; Jiao, Z.; Han, W.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Reuse of Fenton sludge as an iron source for NiFe 2 O 4 synthesis and its application in the Fenton-based process. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Liang, S.; Chen, Y.; Yu, W.; Hou, H.; Qiu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, K.; Hu, J.; Liu, B.; et al. Enhanced sludge dewaterability with sludge-derived biochar activating hydrogen peroxide: Synergism of Fe and Al elements in biochar. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yao, Z.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Q.; Jiang, Z. A Fe3O4/FeAl2O4 composite coating via plasma electrolytic oxidation on Q235 carbon steel for Fenton-like degradation of phenol. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 14927–14936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Xu, G.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Z. Preparation of ferric-activated sludge-based adsorbent from biological sludge for tetracycline removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.; He, P.; Yu, G.; He, P. Effect of proteins, polysaccharides, and particle sizes on sludge dewaterability. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyens, E. Advanced sludge treatment affects extracellular polymeric substances to improve activated sludge dewatering. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 106, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, P.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Xiao, F.; Wang, D.; Chow, C.W.K. Understanding the impact of chemical conditioning with inorganic polymer flocculants on soluble extracellular polymeric substances in relation to the sludge dewaterability. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 132, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Pei, K.; Wang, H.; Yu, W.; Liang, S.; Hu, J.; Hou, H.; Liu, B.; Yang, J. Citric acid assisted Fenton-like process for enhanced dewaterability of waste activated sludge with in-situ generation of hydrogen peroxide. Water Res. 2018, 140, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Dai, T.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Kan, X.; Hou, H.; Han, Y. Enhanced sludge dewaterability by Fe-rich biochar activating hydrogen peroxide: Co-hydrothermal red mud and reed straw. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 296, 113239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Yu, J.; Fu, H.; Guo, M.; Xu, X. Improvement of activated sludge dewaterability by mild thermal treatment in CaCl2 solution. Water Res. 2012, 46, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajra, S.; Padhan, A.M.; Sahu, M.; Alagarsamy, P.; Lee, K.; Kim, H.J. Lead-free flexible Bismuth Titanate-PDMS composites: A multifunctional colossal dielectric material for hybrid piezo-triboelectric nanogenerator to sustainably power portable electronics. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Qin, J.; Wu, Y.; Feng, F. Tetracycline adsorption on magnetic sludge biochar: Size effect of the Fe3O4 nanoparticles. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2022, 9, 210805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William Kajjumba, G.; Emik, S.; Öngen, A.; Kurtulus Özcan, H.; Aydın, S. Modelling of Adsorption Kinetic Processes—Errors, Theory and Application. In Advanced Sorption Process Applications; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2018; p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- de’Gennaro, R.; Graziano, S.F.; Cappelletti, P.; Colella, A.; Dondi, M.; Langella, A.; Gennaro, M.d. Structural Concretes with Waste-Based Lightweight Aggregates: From Landfill to Engineered Materials. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7123–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Xie, Q.; Tang, L.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Fan, C.; Zhang, S. The reduction of nitrobenzene by extracellular electron transfer facilitated by Fe-bearing biochar derived from sewage sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolo, M.E.; Savini, M.C.; Vallés, J.M.; Baschini, M.T.; Avena, M.J. Tetracycline adsorption on montmorillonite: pH and ionic strength effects. Appl. Clay Sci. 2008, 40, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangaran, F.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Nouri, S. Surface modification of Fe3O4@SiO2 microsphere by silane coupling agent. Nano Lett. 2013, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani-Choghamarani, A.; Mohammadi, M.; Shiri, L.; Taherinia, Z. Synthesis and characterization of spinel FeAl2O4 (hercynite) magnetic nanoparticles and their application in multicomponent reactions. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2019, 45, 5705–5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, D.; Zhang, R.; Ding, Y.; Ren, Z.; Fu, M.; Cao, X.; Zeng, G. Singlet oxygen-dominated activation of peroxymonosulfate by passion fruit shell derived biochar for catalytic degradation of tetracycline through a non-radical oxidation pathway. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Guo, T.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G. Efficient activation of persulfate by a magnetic recyclable rape straw biochar catalyst for the degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride in water. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.-P.; Zhang, L.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Shi, F.-N. Design of Z-scheme g-C3N4/BC/Bi25FeO40 photocatalyst with unique electron transfer channels for efficient degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride waste. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Ren, X.; Dong, W.; Chen, H.; Cai, T.; Zeng, W.; Li, W.; Tang, L. Soybean residue based biochar prepared by ball milling assisted alkali activation to activate peroxydisulfate for the degradation of tetracycline. J Colloid Interf. Sci. 2021, 599, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Ning, T.; Chen, P.; Yu, J.; Di, S.; Zhu, S. Magnetic porous biochar as a renewable and highly effective adsorbent for the removal of tetracycline hydrochloride in water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2021, 28, 61513–61525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Constituents | CaO | MgO | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | MnO | P2O5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS | 41.09 | 19.40 | 15.68 | 12.21 | 6.36 | 2.36 | 1.10 |
| RS | 2.69 | 1.48 | 55.74 | 5.86 | 23.62 | - | 5.13 |
| RM | 0.96 | 0.17 | 15.33 | 36.21 | 25.21 | 0.03 | 0.16 |
| Sample | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | Weber Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | K1 (min−1) | Qe(mg·g−1) | R2 | K2 (g·mg−1·min−1) | Qe(mg·g−1) | R2 | K3 (g·mg−1·min−1) | |
| PS80-H2O2 | 0.9963 | 0.6467 | 98.87 | 1.0000 | 4.4258 | 100.13 | - | - |
| PS80 | 0.9932 | 0.1538 | 72.63 | 0.9871 | 0.1740 | 91.15 | - | - |
| PS80-H2O2 /scavenger | 0.9995 | 0.1297 | 74.80 | 0.9982 | 0.0013 | 95.86 | - | - |
| PS0-H2O2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.8985 | 0.0262 |
| PS0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.9340 | 0.0229 |
| PS0 | PS33 | PS60 | PS80 | PS100 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 0.1579 | 0.1837 | 0.2049 | 0.2205 | 0.2362 |
| Fe2O3 | 0.2421 | 0.1815 | 0.1320 | 0.0953 | 0.0586 |
| K * | 0.5052 | 0.9708 | 0.5415 | 0.3265 | 0.1635 |
| A/F | 0.6520 | 1.0119 | 1.5520 | 2.3141 | 4.0307 |
| yields | 0.9876 | 0.9202 | 0.8844 | 0.8215 | 0.7730 |
| BET (m2/g) | 4.36 | 28.66 | 40.17 | 46.40 | 37.52 |
| Wave Number (cm−1) | Assignment | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PS80 | PS80-TC | PS80-H2O2-TC | |
| 3428 | 3428 | 3428 | -OH stretching |
| 2648 | |||
| 2463 | |||
| 2517 | |||
| 1625 | stretching vibration of -OH | ||
| 1600 | C=O bond in the TC [35] | ||
| 1428 | |||
| 1043 | 1043 | C-O-C stretching vibration [31] and Si-O bonds | |
| 988 | |||
| 794 | 794 | Al-O bending vibration | |
| 775 | 775 | Al-O bending vibration | |
| 598 | Fe-O bonds | ||
| 564 | 564 | Fe-O bending vibration [36,37] | |
| 469 | 469 | 469 | Si-O-Si bonds |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Han, W.; Han, Y.; Guo, M.; Peng, Z.; Fan, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wan, S. Tetracycline Removal by Hercynite-Biochar from the Co-Pyrolysis of Red Mud-Steel Slag-Sludge. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2595. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152595
Zhou X, Chen X, Han W, Han Y, Guo M, Peng Z, Fan Z, Shi Y, Wan S. Tetracycline Removal by Hercynite-Biochar from the Co-Pyrolysis of Red Mud-Steel Slag-Sludge. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(15):2595. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152595
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xian, Xia Chen, Wei Han, Yi Han, Mengxin Guo, Ziling Peng, Zeyu Fan, Yan Shi, and Sha Wan. 2022. "Tetracycline Removal by Hercynite-Biochar from the Co-Pyrolysis of Red Mud-Steel Slag-Sludge" Nanomaterials 12, no. 15: 2595. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152595
APA StyleZhou, X., Chen, X., Han, W., Han, Y., Guo, M., Peng, Z., Fan, Z., Shi, Y., & Wan, S. (2022). Tetracycline Removal by Hercynite-Biochar from the Co-Pyrolysis of Red Mud-Steel Slag-Sludge. Nanomaterials, 12(15), 2595. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12152595