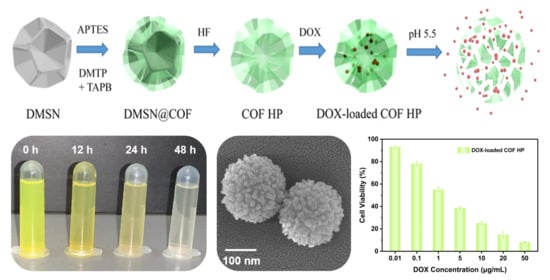
Templated Assembly of pH-Labile Covalent Organic Framework Hierarchical Particles for Intracellular Drug Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of the DMSN
2.3. Synthesis of the DMSN@COF and COF HP
2.4. Synthesis of the Bulk COF
2.5. Degradation Property of the Nanocarriers
2.6. DOX Loading and Release
2.7. MTT Assay
2.8. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diercks, C.S.; Yaghi, O.M. The Atom, the Molecule, and the Covalent Organic Framework. Science 2017, 355, eaal1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploetz, E.; Engelke, H.; Lächelt, U.; Wuttke, S. The Chemistry of Reticular Framework Nanoparticles: MOF, ZIF, and COF Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusran, Y.; Li, H.; Guan, X.; Fang, Q.; Qiu, S. Covalent Organic Frameworks for Catalysis. Energychem 2020, 2, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, N.; Ma, L. Recent Advances in Covalent Organic Frameworks for Catalysis. Chem. Asian J. 2020, 15, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, S. Covalent Organic Frameworks for Separation Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 708–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, G.; Van Puyvelde, P.; Van der Bruggen, B. Covalent Organic Frameworks for Membrane Separation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2665–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jing, X.C.; Li, Q.Q.; Li, S.W.; Gao, X.; Feng, X.; Wang, B. Bulk COFs and COF Nanosheets for Electrochemical Energy Storage and Conversion. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3565–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhong, Y.; Tang, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, M.; Xia, H. Covalent Organic Frameworks: From Materials Design to Electrochemical Energy Storage Applications. Nano Sel. 2021, 3, 320–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, D.; Lai, C.; Zeng, G.; Qin, L.; Wang, H.; Yi, H.; Li, B.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; et al. Recent Advances in Covalent Organic Frameworks (COFs) as a Smart Sensing Material. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 5266–5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, C.X.; Yan, X.P. A Versatile Covalent Organic Framework-Based Platform for Sensing Biomolecules. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 11469–11471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Son, S.; An, J.; Kim, I.; Choi, M.; Kong, N.; Tao, W.; Kim, J.S. Nanoscale Porous Organic Polymers for Drug Delivery and Advanced Cancer Theranostics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 12883–12896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scicluna, M.C.; Vella-Zarb, L. Evolution of Nanocarrier Drug-Delivery Systems and Recent Advancements in Covalent Organic Framework-Drug Systems. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 3097–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Wang, J.; Gu, S.; Kaspar, R.B.; Zhuang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Guo, H.; Qiu, S.; Yan, Y. 3D Porous Crystalline Polyimide Covalent Organic Frameworks for Drug Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 8352–8355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Phua, S.Z.; Lim, W.Q.; Jana, A.; Luo, Z.; Tham, H.P.; Zhao, L.; Gao, Q.; Zhao, Y. Nanoscale Covalent Organic Frameworks as Smart Carriers for Drug Delivery. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 4128–4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Liao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xi, K.; Huang, W.; Jia, X. Water-Dispersible PEG-Curcumin/Amine-Functionalized Covalent Organic Framework Nanocomposites as Smart Carriers for In Vivo Drug Delivery. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Chu, L.; Zhou, W.; Dou, J.; Teng, X.; Tan, W.; Zhou, B. A Diselenium-Bridged Covalent Organic Framework with pH/GSH/photo-triple-responsiveness for Highly Controlled Drug Release toward Joint Chemo/Photothermal/Chemodynamic Cancer Therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhu, G.; Chi, L.; Lu, G. Imparting Catalytic Activity to a Covalent Organic Framework Material by Nanoparticle Encapsulation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 7481–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhang, L.; He, B.; Lin, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, M. 8-Hydroxyquinoline Functionalized Covalent Organic Framework as a pH Sensitive Carrier for Drug Delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 117, 111243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hu, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Pang, M.; Lin, J. One-Pot Synthesis of DOX@Covalent Organic Framework with Enhanced Chemotherapeutic Efficacy. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 4315–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, L.; Hao, K.; Chen, J.; Tian, H.; Chen, X. Cyanine-Assisted Exfoliation of Covalent Organic Frameworks in Nanocomposites for Highly Efficient Chemo-Photothermal Tumor Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 39503–39512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, T.; Yang, Y.; Qian, M.; Jiang, H.; Du, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Huang, R. Versatile Hollow COF Nanospheres via Manipulating Transferrin Corona for Precise Glioma-Targeted Drug Delivery. Biomaterials 2020, 260, 120305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yin, Y. Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Hollow Micro-/Nanostructures. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10983–11060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, G.; Ren, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, L. Multishelled Metal Oxide Hollow Spheres: Easy Synthesis and Formation Mechanism. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 8864–8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, C.X.; Yan, X.P. Controllable Preparation of Core-Shell Magnetic Covalent-Organic Framework Nanospheres for Efficient Adsorption and Removal of Bisphenols in Aqueous Solution. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 2511–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Zhu, Q.; He, H. Ingenious Construction of an Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on a Au@COF/GO-NH2 Composite with Excellent Detection Performance. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 4576–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lv, H.; Li, Z.; Meng, X.; Lin, Z.; Wang, R.; Li, X. The Electrostatic Attraction and Catalytic Effect Enabled by Ionic-Covalent Organic Nanosheets on MXene for Separator Modification of Lithium-Sulfur Batteries. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2007803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Wang, D.; Wan, L. Template Synthesis of Imine-Based Covalent Organic Framework Core-Shell Structure and Hollow Sphere: A Case of COFTTA-DHTA. Sci. China Chem. 2017, 60, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Gu, J.; Meng, H.; Knebel, A.; Caro, J. High-Flux Membranes Based on the Covalent Organic Framework COF-LZU1 for Selective Dye Separation by Nanofiltration. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4083–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, F.; Deng, C.; Yan, Y.; Shen, H.-H.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y. Hierarchical Covalent Organic Frameworks-Modified Diatomite for Efficient Separation of Bisphenol A from Water in a Convenient Column Mode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 298, 121611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachfule, P.; Kandmabeth, S.; Mallick, A.; Banerjee, R. Hollow Tubular Porous Covalent Organic Framework (COF) Nanostructures. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 11717–11720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sun, Z.; Yue, Q.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Deng, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhao, D. An Interface-Directed Coassembly Approach to Synthesize Uniform Large-Pore Mesoporous Silica Spheres. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1884–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Xu, L.L.; Jiang, J.G.; Calin, N.; Lam, K.F.; Zhang, S.J.; Wu, H.H.; Wu, G.D.; Albela, B.; Bonneviot, L.; et al. Facile Large-Scale Synthesis of Monodisperse Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres with Tunable Pore Structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2427–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.Y.; Zhao, Y.K.; Yan, X.; Hua, Y.Q.; Meng, Z.Q. Flower-Like Composite Material Delivery of Co-Packaged Lenvatinib and Bufalin Prevents the Migration and Invasion of Cholangiocarcinoma. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Abbaraju, P.L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Xiang, G.; Yu, C. Multi-shelled Dendritic Mesoporous Organosilica Hollow Spheres: Roles of Composition and Architecture in Cancer Immunotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 8446–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, M.; Fang, Y.; Deng, C.; Shen, H.H.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y. Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Hollow Spheres for Nano-Bioreactor Application. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Guo, R.R.; Jiao, Y.F.; Sun, Y.F.; Shen, S.; Wang, Y.J.; Lu, D.R.; Jiang, X.G.; Yang, W.L. Redox Stimuli-Responsive Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanocarriers for Targeted Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Nanoscale Horiz. 2016, 1, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.L.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.H.; Song, J.Y.; Tang, Y.; Caruso, F.; Wang, Y.J. Synthesis of Chemically Asymmetric Silica Nanobottles and Their Application for Cargo Loading and as Nanoreactors and Nanomotors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 14733–14737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.; Cattoen, X.; Man, M.W.; Gallud, A.; Raehm, L.; Trens, P.; Maynadier, M.; Durand, J.O. Biodegradable Ethylene-Bis(propyl)disulfide-Based Periodic Mesoporous Organosilica Nanorods and Nanospheres for Efficient In-Vitro Drug Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6174–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Trewyn, B.G.; Stellmaker, M.P.; Lin, V.S.Y. Stimuli-Responsive Controlled-Release Delivery System Based on Mesoporous Silica Nanorods Capped with Magnetic Nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. 2005, 117, 5166–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, X.; Lin, R.; Chen, L.; Sun, C.; Chen, Q.; Hung, C.T.; Zhou, Q.; Lan, K.; Wang, W.; et al. Surface-Confined Winding Assembly of Mesoporous Nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 20359–20367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, A. Amine-Impregnated Mesoporous Silica Nanotube as an Emerging Nanocomposite for CO2 Capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17312–17320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, C.; Zhou, F.; Yang, W.; Yi, D.; Wang, X.; Tang, Y.; Caruso, F.; Wang, Y. Template-Free Synthesis of Chemically Asymmetric Silica Nanotubes for Selective Cargo Loading and Sustained Drug Release. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 4291–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lei, C.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C.Z. Dendritic Mesoporous Nanoparticles: Structure, Synthesis and Properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202112752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhou, F.Z.; Wu, M.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yi, D.L.; Yuan, W.; Wang, Y.J. Engineering of Dendritic Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Efficient Delivery of Water-Insoluble Paclitaxel in Cancer Therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 593, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Meng, W.; Li, L.; Xu, G.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, M.; Lin, J.; Zhao, R. Facile Room-Temperature Synthesis of a Spherical Mesoporous Covalent Organic Framework for Ultrasensitive Solid-Phase Microextraction of Phenols Prior to Gas Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Gao, J.; Jiang, D. Stable, Crystalline, Porous, Covalent Organic Frameworks as a Platform for Chiral Organocatalysts. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, T.; Kumari, S.S.; Sathiyanarayanan, S. Dendrimer Like Mesoporous Silica Nano Container (DMSN) Based Smart Self Healing Coating for Corrosion Protection Performance. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 154, 106201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Yang, S.; Yang, X.; Ye, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, W.; Guo, Y.; Mi, L.; Wu, Z.; Soutis, C.; et al. Conjugated Covalent Organic Frameworks as Platinum Nanoparticle Supports for Catalyzing the Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 9747–9752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Yuan, J.Y. Schiff’s Base as a Stimuli-Responsive Linker in Polymer Chemistry. Polym. Chem. 2012, 3, 3045–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, Y.Y.; Han, X.D.; Liu, G.; Jia, Q.M.; Shan, S.Y. Schiff Base-Containing Dextran Nanogel as PH-Sensitive Drug Delivery System of Doxorubicin: Synthesis and Characterization. J. Biomater. Appl. 2018, 33, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.W.; Chan, J.M.; Farokhzad, O.C. PH-Responsive Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Kumar, A.; Tan, A.; Jin, S.; Mozhi, A.; Liang, X.J. PH-Sensitive Nano-Systems for Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 693–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barenholz, Y.; Amselem, S.; Goren, D.; Cohen, R.; Gelvan, D.; Samuni, A.; Golden, E.B.; Gabizon, A. Stability of Liposomal Doxorubicin Formulations-Problems and Prospects. Med. Res. Rev. 1993, 13, 449–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Hosta-Rigau, L.; Lomas, H.; Caruso, F. Nanostructured Polymer Assemblies formed at interfaces: Applications From Immobilization and Encapsulation to Stimuli-Responsive release. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 4782–4801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Sample | DMSN | DMSN@COF | COF HP | Bulk COF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface area (m2/g) | 276.3 | 544.1 | 720.7 | 608.2 |
| Micropore volume (cm3/g) | - | 0.266 | 0.523 | 0.371 |
| DOX loading (w/w, %) | 15.2 | 29.1 | 46.8 | 32.1 |
| Sample | COF HP-0.1 | COF HP-0.3 | COF HP-0.5 | COF HP-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Particle size (nm) | 127 ± 14 | 197 ± 10 | 317 ± 23 | 466 ± 28 |
| Zeta potential (mV) | +15.2 | +15.8 | +15.5 | +14.7 |
| DOX loading (w/w, %) | 46.8 | 44.5 | 41.7 | 40.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, F.; Fang, Y.; Deng, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, M.; Shen, H.-H.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y. Templated Assembly of pH-Labile Covalent Organic Framework Hierarchical Particles for Intracellular Drug Delivery. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12173055
Zhou F, Fang Y, Deng C, Zhang Q, Wu M, Shen H-H, Tang Y, Wang Y. Templated Assembly of pH-Labile Covalent Organic Framework Hierarchical Particles for Intracellular Drug Delivery. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(17):3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12173055
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Fangzhou, Yuanyuan Fang, Chao Deng, Qian Zhang, Minying Wu, Hsin-Hui Shen, Yi Tang, and Yajun Wang. 2022. "Templated Assembly of pH-Labile Covalent Organic Framework Hierarchical Particles for Intracellular Drug Delivery" Nanomaterials 12, no. 17: 3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12173055
APA StyleZhou, F., Fang, Y., Deng, C., Zhang, Q., Wu, M., Shen, H. -H., Tang, Y., & Wang, Y. (2022). Templated Assembly of pH-Labile Covalent Organic Framework Hierarchical Particles for Intracellular Drug Delivery. Nanomaterials, 12(17), 3055. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12173055