Smart MXene Quantum Dot-Based Nanosystems for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
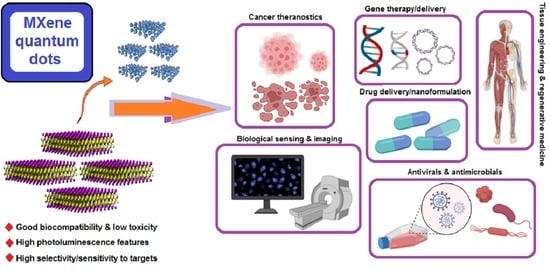
:1. Introduction
2. Biomedical Advancements
2.1. Biological Sensing and Imaging
2.2. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
2.3. Cancer Theranostics
2.4. Antioxidant Effects
3. Challenges and Future Perspectives
4. Conclusions and Future Outlooks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naguib, M.; Barsoum, M.W.; Gogotsi, Y. Ten Years of Progress in the Synthesis and Development of MXenes. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2103393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VahidMohammadi, A.; Rosen, J.; Gogotsi, Y. The world of two-dimensional carbides and nitrides (MXenes). Science 2021, 372, eabf1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogotsi, Y.; Huang, Q. MXenes: Two-Dimensional Building Blocks for Future Materials and Devices. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 5775–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, Y.; Mo, A. Multilayered Titanium Carbide MXene Film for Guided Bone Regeneration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 10091–10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. MXenes for Cancer Therapy and Diagnosis: Recent Advances and Current Challenges. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 1900–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Zeng, X.; Chen, H.; Li, Z.; Zeng, W.; Mei, L.; Zhao, Y. Versatile Polydopamine Platforms: Synthesis and Promising Applications for Surface Modification and Advanced Nanomedicine. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8537–8565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Luo, M.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Tao, W.; Lin, Y.; Ji, X.; Nie, L.; Mei, L. Polydopamine-Modified Black Phosphorous Nanocapsule with Enhanced Stability and Photothermal Performance for Tumor Multimodal Treatments. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, M.; Fan, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mei, L. 2D Black Phosphorus–Based Biomedical Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamalipour Soufi, G.; Iravani, S. Eco-friendly and sustainable synthesis of biocompatible nanomaterials for diagnostic imaging: Current challenges and future perspectives. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 2662–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Zhu, X.; Yu, X.; Zeng, X.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ji, X.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Black Phosphorus Nanosheets as a Robust Delivery Platform for Cancer Theranostics. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, B.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, G.; Wang, H.; Liang, Q.; He, Q.; Cheng, M.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, L.; Song, B. Two-dimensional transition metal carbide and nitride (MXene) derived quantum dots (QDs): Synthesis, properties, applications and prospects. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 7508–7535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Ding, L.X.; Chen, G.F.; Zhang, L.; Xue, J.; Wang, H. Molybdenum Carbide Nanodots Enable Efficient Electrocatalytic Nitrogen Fixation under Ambient Conditions. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1803694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Sun, X.; Xu, W.; Pan, G.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Bai, X.; Dong, B.; Song, H. Ratiometric photoluminescence sensing based on Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots as an intracellular pH sensor. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Chu, P.K.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S. Graphitic carbon nitride-based materials for photocatalytic antibacterial application. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2021, 145, 100610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; He, F.; Li, Q.; Zhong, L.; Zhao, R.; Che, H.; Gao, H.; Fang, B. Emerging graphitic carbon nitride-based materials for biomedical applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 112, 100666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.; Han, J.; Fang, Y.; Han, Y.; Niu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Sun, C.; Xu, Y. Rational Design of Hydroxyl-Rich Ti3C2Tx MXene Quantum Dots for High-Performance Electrochemical N2 Reduction. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Insights into 2D MXenes for Versatile Biomedical Applications: Current Advances and Challenges Ahead. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; Gao, S.; Dai, C.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. A two-dimensional biodegradable niobium carbide (MXene) for photothermal tumor eradication in NIR-I and NIR-II biowindows. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16235–16247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Two-Dimensional Ultrathin MXene Ceramic Nanosheets for Photothermal Conversion. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Theranostic 2D Tantalum Carbide (MXene). Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Guo, J.; Kang, N.; Ma, X.-L.; Cheng, H.-M.; Ren, W. Large-area high-quality 2D ultrathin Mo2C superconducting crystals. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Shah, S.; Chen, Y.; Tan, Z.; Gao, H.; Habib, T.; Radovic, M.; Green, M. Electrochemical etching of Ti2AlC to Ti2CTx (MXene) in low-concentration hydrochloric acid solution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 21663–21668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yao, L.; Liu, Q.; Gu, J.; Luo, R.; Li, J.; Yan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, P.; Chen, B. Fluorine-Free Synthesis of High-Purity Ti3C2Tx (T=OH, O) via Alkali Treatment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2018, 57, 6115–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Ting, L.R.L.; Molinari, V.; Giordano, C.; Yeo, B.S. Efficient hydrogen evolution reaction catalyzed by molybdenum carbide and molybdenum nitride nanocatalysts synthesized via the urea glass route. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 8361–8368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhao, J.; Yi, S.; Wan, X.; Tang, J. Biodegradable and photostable Nb2C MXene quantum dots as promising nanofluorophores for metal ions sensing and fluorescence imaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 309, 127735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Bai, Y.; He, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, J.; Song, G. Facile microwave-assisted synthesis of Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots for ratiometric fluorescence detection of hypochlorite. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Lu, W.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. MXene-Enabled Electrochemical Microfluidic Biosensor: Applications toward Multicomponent Continuous Monitoring in Whole Blood. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, O.; Mahmoud, K.A.; Pant, K.K.; Joshi, R.K. Introduction to MXenes: Synthesis and characteristics. Mater. Today Chem. 2019, 14, 100191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbankowski, P.; Anasori, B.; Makaryan, T.; Er, D.; Kota, S.; Walsh, P.L.; Zhao, M.; Shenoy, V.B.; Barsoum, M.W.; Gogotsi, Y. Synthesis of two-dimensional titanium nitride Ti4N3 (MXene). Nanoscale 2016, 8, 11385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, M.; Pei, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Deng, Q.; Zhou, J.; et al. Photoluminescent Ti3C2 MXene Quantum Dots for Multicolor Cellular Imaging. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Cai, X.; Cui, H.; Lee, S.-W.; Yu, X.-F.; Liu, B. Fluorine-free preparation of titanium carbide MXene quantum dots with high near-infrared photothermal performances for cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 17859–17864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, M.; Song, G. Microwave-assisted synthesis of nitrogen, phosphorus-doped Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots for colorimetric/fluorometric dual-modal nitrite assay with a portable smartphone platform. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 357, 131410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuck, C.E.; Ventura-Martinez, K.; Goad, A.; Uzun, S.; Shekhirev, M.; Gogotsi, Y. Safe Synthesis of MAX and MXene: Guidelines to Reduce Risk During Synthesis. ACS Chem. Health Saf. 2021, 28, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. MXenes and MXene-based materials for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: Recent advances. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 2906–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogotsi, Y.; Anasori, B. The Rise of MXenes. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8491–8494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamalipour Soufi, G.; Iravani, P.; Hekmatnia, A.; Mostafavi, E.; Khatami, M.; Iravani, S. MXenes and MXene-based Materials with Cancer Diagnostic Applications: Challenges and Opportunities. Comments Inorg. Chem. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, K.; Mahmoud, K.A.; Johnson, D.J.; Helal, M.; Berdiyorov, G.R.; Gogotsi, Y. Efficient Antibacterial Membrane based on Two-Dimensional Ti3C2Tx (MXene) Nanosheets. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Yu, J.; Lv, F.; Yan, L.; Zheng, L.R.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Functionalized Nano-MoS2 with Peroxidase Catalytic and Near-Infrared Photothermal Activities for Safe and Synergetic Wound Antibacterial Applications. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 11000–11011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, N.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Iravani, S. Green Synthesis of Silica and Silicon Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical and Catalytic Applications. Comments Inorg. Chem. 2021, 41, 317–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, G.P.; Soon, C.F.; Ma, N.L.; Morsin, M.; Nayan, N.; Ahmad, M.K.; Tee, K.S. Cytotoxicity of MXene-based nanomaterials for biomedical applications: A mini review. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafieerad, A.; Yan, W.; Sequiera, G.L.; Sareen, N.; Abu-El-Rub, E.; Moudgil, M.; Dhingra, S. Application of Ti3C2 MXene Quantum Dots for Immunomodulation and Regenerative Medicine. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, 1900569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Pan, G.; Xu, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, D.; Li, D.; Chen, C.; Lu, G.; Song, H. Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots/TiO2 inverse opal heterojunction electrode platform for superior photoelectrochemical biosensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 289, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Yu, Z.; Tong, P.; Tang, D. Ti3C2 MXene quantum dot-encapsulated liposomes for photothermal immunoassays using a portable near-infrared imaging camera on a smartphone. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 15659–15667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X. A Semimetal-like Molybdenum Carbide Quantum Dots Photoacoustic Imaging and Photothermal Agent with High Photothermal Conversion Efficiency. Materials 2018, 11, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhang, K.; Meng, X.; Dai, W.; Wang, D.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X. Engineered Exosome-Mediated Near-Infrared-II Region V2C Quantum Dot Delivery for Nucleus-Target Low-Temperature Photothermal Therapy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhu, X.; Wang, S.; Lei, C.; Huang, Y.; Nie, Z.; Yao, S. Fluorescent Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots for an alkaline phosphatase assay and embryonic stem cell identification based on the inner filter effect. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 19579–19585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Nitrogen-Doped Ti2C MXene Quantum Dots as Antioxidants. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 12308–12315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhou, J.; He, Y.; Cai, Z.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, J.; Song, G. ε-Poly-L-lysine-protected Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots with high quantum yield for fluorometric determination of cytochrome c and trypsin. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Diao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, G.; Ma, B. Highly sensitive fluorescent sensing for intracellular glutathione based on Ti3C2 quantum dots. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2020, 31, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Ma, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, X.; Dong, X.; Fan, Y.; Cai, L.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Highly fluorescent Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots for macrophage labeling and Cu2+ ion sensing. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 14123–14133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Jia, Q.; Duan, F.; Hu, B.; Wang, M.; He, L.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Z. Multiwall carbon nanotubes loaded with MoS2 quantum dots and MXene quantum dots: Non–Pt bifunctional catalyst for the methanol oxidation and oxygen reduction reactions in alkaline solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 464, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, J.; Ouyang, X.; Cai, L.; Xu, Q. Two-dimensional quantum dots for biological applications. Nano Res. 2021, 14, 3820–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Dhanjai; Zhao, H.; Huang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, J.; Jain, R. MXene: An emerging material for sensing and biosensing. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatami, M.; Iravani, S. MXenes and MXene-based Materials for the Removal of Water Pollutants: Challenges and Opportunities. Comments Inorg. Chem. 2021, 41, 213–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Sun, J.; Wang, C.; Shang, C.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. MXenes: Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Applications in Ultrafast Photonics. Small 2021, 17, 2006054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verger, L.; Xu, C.; Natu, V.; Cheng, H.-M.; Ren, W.; Barsoum, M.W. Overview of the synthesis of MXenes and other ultrathin 2D transition metal carbides and nitrides. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2019, 23, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, K.; Zhang, T.; Shuck, C.E.; VahidMohammadi, A.; Gogotsi, Y. Guidelines for Synthesis and Processing of Chemically Stable Two-Dimensional V2CTx MXene. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, B.C.; Rosenkranz, A.; Anasori, B. 2D MXenes: Tunable Mechanical and Tribological Properties. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2007973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, K.; Kovářík, T.; Pasha, S.K. State of the art recent progress in two dimensional MXenes based gas sensors and biosensors: A comprehensive review. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 424, 213514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ge, Y.; Yin, T.; Guo, J.; Zhang, F.; Tang, X.; Qiu, M.; Liang, W.; Xu, N.; Wang, C.; et al. Ti3C2Tx MXene Quantum Dots with Enhanced Stability for Ultrafast Photonics. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 11850–11860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Biofactories: Engineered nanoparticles via genetically engineered organisms. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 4583–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Green synthesis, biomedical and biotechnological applications of carbon and graphene quantum dots. A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 703–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Ma, J.; Khan, W.; Zeng, X.; Li, N.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xu, M. Highly green fluorescent Nb2C MXene quantum dots. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 6648–6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Ding, L.; Wen, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhou, H.; Chen, X.; Street, J.; Zhou, A.; Ong, W.-J.; Li, N. High photoluminescence quantum yield of 18.7% by using nitrogen-doped Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 6360–6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Dai, Z.; Yan, X.; Ma, J.; Niu, Y.; Lan, W.; Wang, X.; Xu, Q. Comparison of toxicity of Ti3C2 and Nb2C Mxene quantum dots (QDs) to human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2021, 41, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafari, M.; Soroush, M. Surface functionalization of MXenes. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 7277–7307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Lou, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, L.; Han, W.; Jiang, K.; Shen, G. Biomimetic, biocompatible and robust silk Fibroin-MXene film with sTable 3D cross-link structure for flexible pressure sensors. Nano Energy 2020, 78, 105252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Duais, M.A.; Mohammedsaleh, Z.M.; Al-Shehri, H.S.; Al-Awthan, Y.S.; Bani-Atta, S.A.; Keshk, A.A.; Mustafa, S.K.; Althaqafy, A.D.; Al-Tweher, J.N.; Al-Aoh, H.A.; et al. Bovine serum albumin functionalized blue emitting Ti3C2 MXene Quantum Dots as a sensitive fluorescence probe for Fe3+ ions detection and its toxicity analysis. Luminescence 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Sui, L.; Liu, Y.; Yong, X.; Xiao, G.; Yuan, K.; Liu, Z.; Liu, B.; Zou, B.; Yang, B. White Photoluminescent Ti3C2 MXene Quantum Dots with Two-Photon Fluorescence. Advaced Sci. 2019, 6, 1801470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rafieerad, A.; Yan, W.; Amiri, A.; Dhingra, S. Bioactive and trackable MXene quantum dots for subcellular nanomedicine applications. Mater. Des. 2020, 196, 109091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhou, F.; Deng, Q.; Peng, C. Solvothermal synthesis of in situ nitrogen-doped Ti3C2 MXene fluorescent quantum dots for selective Cu2+ detection. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 8320–8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, F.; Fu, C.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Yan, X.; Zheng, X. Amino-Functionalized Ti3C2 MXene Quantum Dots as Photoluminescent Sensors for Diagnosing Histidine in Human Serum. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 8192–8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Du, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Shen, G. MXene quantum dot within natural 3D watermelon peel matrix for biocompatible flexible sensing platform. Nano Res. 2021, 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Kan, L.; Duan, F.; He, L.; Wang, M.; Cui, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Surface plasmon resonance aptasensor based on niobium carbide MXene quantum dots for nucleocapsid of SARS-CoV-2 detection. Mikrochim. Acta 2021, 188, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, G. Nitrogen, boron-doped Ti3C2 MXene quantum dot-based ratiometric fluorescence sensing platform for point-of-care testing of tetracycline using an enhanced antenna effect by Eu3+. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafieerad, A.; Yan, W.; Alagarsamy, K.N.; Srivastava, A.; Sareen, N.; Arora, R.C.; Dhingra, S. Fabrication of Smart Tantalum Carbide MXene Quantum Dots with Intrinsic Immunomodulatory Properties for Treatment of Allograft Vasculopathy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2106786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Ganguly, S.; Margel, S.; Gedanken, A. Tailor made magnetic nanolights: Fabrication to cancer theranostics applications. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 6762–6796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.R.; Kumar, S.; Ortega, G.A.; Srinivasan, S.; Rajabzadeh, A.R. Target specific aptamer-induced self-assembly of fluorescent graphene quantum dots on palladium nanoparticles for sensitive detection of tetracycline in raw milk. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Ganguly, S.; Saha, A.; Noked, M.; Margel, S.; Gedanken, A. Carbon-Dots-Initiated Photopolymerization: An In Situ Synthetic Approach for MXene/Poly(norepinephrine)/Copper Hybrid and its Application for Mitigating Water Pollution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 31038–31050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.R.; Sherazee, M.; Srinivasan, S.; Rajabzadeh, A.R. Nanozymatic detection of thiocyanate through accelerating the growth of ultra-small gold nanoparticles/graphene quantum dots hybrids. Food Chem. 2022, 379, 132152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, F.; Huang, D.; Xue, N.; Dang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, L.; et al. Nonoxidized MXene Quantum Dots Prepared by Microexplosion Method for Cancer Catalytic Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, C.; Lin, J.; Huang, P. Biodegradable titanium nitride MXene quantum dots for cancer phototheranostics in NIR-I/II biowindows. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 126009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Hu, N.; Shi, W. Nitrogen-doped Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots as novel high-efficiency electrochemiluminescent emitters for sensitive mucin 1 detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 350, 130891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Kong, W.; Gou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.-N.; Yu, G.; Zhang, P.; Cheng, H.; et al. Mechanism of Nitrogen-Doped Ti3C2 Quantum Dots for Free-Radical Scavenging and the Ultrasensitive H2O2 Detection Performance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 42442–42450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Qi, Z.; Ge, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.Z. Designed synthesis of chlorine and nitrogen co-doped Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots and their outstanding hydroxyl radical scavenging properties. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 78, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Ge, Q.; Zhang, J.Z. Scavenging activity and reaction mechanism of Ti3C2Tx MXene as a novel free radical scavenger. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 16555–16561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, L.-Y.; Li, J.-M.; Peng, L.-M.; Tang, C.-Y.; Zha, X.-J.; Ke, K.; Yang, M.-B.; Su, B.-H.; Yang, W. Redox-Mediated Artificial Non-Enzymatic Antioxidant MXene Nanoplatforms for Acute Kidney Injury Alleviation. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2101498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamhuri, A.; Lim, G.P.; Ma, N.L.; Tee, K.S.; Soon, C.F. MXene in the lens of biomedical engineering: Synthesis, applications and future outlook. BioMed. Eng. OnLine 2021, 20, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; An, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Feng, W.; Qiu, S.; Wang, Q.; Sun, C. A DFT study of Ti3C2O2 MXenes quantum dots supported on single layer graphene: Electronic structure an hydrogen evolution performance. Front. Phys. 2021, 16, 53506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, S.K.; Singh, H.; Khatri, M.; Kim, K.-H.; Bhardwaj, N. Advances in MXenes-based optical biosensors: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 202, 113995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Gu, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; He, L.; Wang, M.; Huang, X.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, Z. Ti3C2Tx MXene and polyoxometalate nanohybrid embedded with polypyrrole: Ultra-sensitive platform for the detection of osteopontin. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 498, 143889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, A.; Charlier, J.-C. Physical properties of 2D MXenes: From a theoretical perspective. J. Phys. Mater. 2021, 3, 032006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, N.; Dhand, C.; Kumar, P.; Srivastava, A.K. Emergent 2D materials for combating infectious diseases: The potential of MXenes and MXene–graphene composites to fight against pandemics. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 2892–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wei, S.; Wu, J.; Jia, G.; Fang, X.; Chen, F.; et al. A 2D transition metal carbide MXene-based SPR biosensor for ultrasensitive carcinoembryonic antigen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 144, 111697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadniaei, M.; Koyappayil, A.; Sun, Y.; Min, J.; Lee, M.-H. Gold nanoparticle/MXene for multiple and sensitive detection of oncomiRs based on synergetic signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 159, 112208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| MXene QDs | Synthesis Methods | Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti3C2 | Hydrothermal synthesis | Immunomodulation | [41] |
| Ti3C2 | Hydrothermal synthesis | Glutathione detection and photoelectrochemical biosensing | [42] |
| Ti3C2 | Intercalation-ultrasound sysnthesis | Prostate-specific antigen detection | [43] |
| Mo2C | Ultrasound-assisted synthesis | (Bio)imaging and photothermal therapy | [44] |
| Mo2C | Molten salt (molybdenum acetylacetonate, NaCl, 800 °C for 2 h) | Nitrogen reduction reaction | [12] |
| V2C | Hydrothermal synthesis | (Bio)imaging, photothermal therapy, and tumor destruction | [45] |
| Ti3C2 | Hydrothermal synthesis | Multicolor cellular imaging and Zn2+ detection | [30] |
| Ti3C2 | Ultrasound-assisted synthesis; fluorine-free preparation | (Bio)imaging and photothermal therapy | [31] |
| Ti3C2 | Hydrothermal synthesis | (Bio)imaging and pH sensor | [13] |
| Ti3C2 | Hydrothermal synthesis | Enzyme assay and cell identification | [46] |
| Ti2C | Hydrothermal synthesis | Antioxidant effects | [47] |
| Ti3C2 | Hydrothermal synthesis | Cytochrome c and trypsin detection | [48] |
| Ti3C2 | Reflux technique | Glutathione detection | [49] |
| Ti3C2 | Hydrothermal synthesis | Bioimaging, macrophage labeling, and Cu2+ detection | [50] |
| MoS2 | Hydrothermal synthesis | Methanol oxidation reaction and oxygen reduction reaction | [51] |
| Ti3C2 | Microwave-assisted technique | Detection of curcumin and hypochlorite (ClO−) | [26] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iravani, S.; Varma, R.S. Smart MXene Quantum Dot-Based Nanosystems for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12071200
Iravani S, Varma RS. Smart MXene Quantum Dot-Based Nanosystems for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(7):1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12071200
Chicago/Turabian StyleIravani, Siavash, and Rajender S. Varma. 2022. "Smart MXene Quantum Dot-Based Nanosystems for Biomedical Applications" Nanomaterials 12, no. 7: 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12071200
APA StyleIravani, S., & Varma, R. S. (2022). Smart MXene Quantum Dot-Based Nanosystems for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials, 12(7), 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12071200