Sustainable Synthesis of Cadmium Sulfide, with Applicability in Photocatalysis, Hydrogen Production, and as an Antibacterial Agent, Using Two Mechanochemical Protocols
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
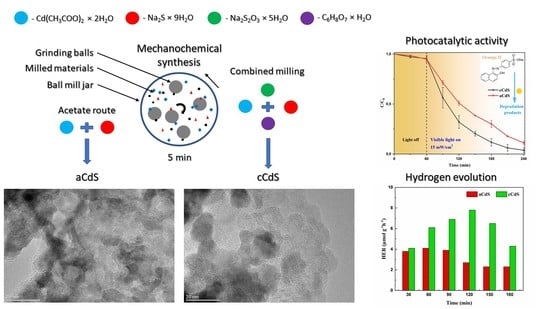
2.2. Mechanochemical Synthesis of CdS Nanoparticles
2.3. Characterization Methods and Techniques
2.4. Photocatalytic Measurements
2.5. Hydrogen Evolution
2.6. Antibacterial Activity
3. Results
3.1. XRD Results
3.2. Raman Spectroscopy Results
3.3. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Results
3.4. UV-Vis Spectroscopy Results
3.5. PL Spectroscopy Results
3.6. SEM Results
3.7. TEM Results
3.8. DLS Analysis Results
3.9. Photocatalysis Results
3.10. Hydrogen Evolution Results
3.11. Antimicrobial Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yadav, P.; Singh, J.; Srivastava, D.K.; Mishra, V. Environmental pollution and sustainability. In Environmental Sustainability and Economy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.-H.; Smith, S.M.; Wantala, K.; Kajitvichyanukul, P. Photocatalytic remediation of persistent organic pollutants (POPs): A review. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 8309–8337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.W.; Zhong, L.L.; Yuan, J.L.; Xiang, W.H.; Xin, X.; Liu, H.M.; Luo, H.Y.; Li, L.Y.; Chen, M.; Zhong, D.J.; et al. Photocatalytic optical fibers for degradation of organic pollutants in wastewater: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, R.; Varadharajan, K.; Jayaraman, V. Fabrication of tantalum doped CdS nanoparticles for enhanced photocatalytic degradation of organic dye under visible light exposure. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 580, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shume, W.M.; Murthy, H.C.A.; Zereffa, E.A. A Review on Synthesis and Characterization of Ag2O Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic Applications. J. Chem. 2020, 2020, 5039479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urakaev, F.K.; Khan, N.; Shalabaev, Z.S.; Tatykaev, B.; Nadirov, R.; Burkitbaev, M. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Properties of Silver Chloride/Silver Composite Colloidal Particles. Colloid J. 2020, 82, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadwal, A.S.; Tripathi, R.M.; Gupta, R.K.; Kumar, N.; Singh, R.P.; Shrivastav, A. Biogenic synthesis and photocatalytic activity of CdS nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 9484–9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afeesh, R.; Barakat, N.A.M.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Yousef, A.; Kim, H.Y. Nematic shaped cadmium sulfide doped electrospun nanofiber mat: Highly efficient, reusable, solar light photocatalyst. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 409, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harish, R.; Nisha, K.D.; Prabakaran, S.; Sridevi, B.; Harish, S.; Navaneethan, M.; Ponnusamy, S.; Hayakawa, Y.; Vinniee, C.; Ganesh, M.R. Cytotoxicity assessment of chitosan coated CdS nanoparticles for bioimaging applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 499, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, R.; Liu, X.H. Efficient visible light driven photocatalytic hydrogen production from water using attapulgite clay sensitized by CdS nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerathangam, K.; Pandian, M.S.; Ramasamy, P. Photovoltaic performance of Ag-doped CdS quantum dots for solar cell application. Mater. Res. Bull. 2017, 94, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldiya, M.; Narasimman, R.; Bhagat, D.; Vankhade, D.; Mukhopadhyay, I. Nanoparticulate CdS 2D array by chemical bath deposition: Characterization and optoelectronic study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 226, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckel, J.S.; Snee, P.; Coe-Sullivan, S.; Zimmer, J.R.; Halpert, J.E.; Anikeeva, P.; Kim, L.A.; Bulovic, V.; Bawendi, M.G. Color-saturated green-emitting QD-LEDs. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2006, 45, 5796–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonker, R.K.; Yadav, B.C.; Gupta, V.; Tomar, M. Synthesis of CdS nanoparticle by sol-gel method as low temperature NO2 sensor. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 239, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq Bhat, I.U.; Yi, Y.S. Green synthesis and antibacterial activity of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles (CdSNPs) using Panicum sarmentosum. Asian J. Green Chem. 2019, 3, 455–469. [Google Scholar]
- Sekar, P.V.; Parvathi, V.D.; Sumitha, R. Green nanotechnology in cadmium sulphide nanoparticles and understanding its toxicity and antimicrobial properties. Biomed. Res. 2019, 30, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shivashankarappa, A.; Sanjay, K.R. Escherichia coli-based synthesis of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles, characterization, antimicrobial and cytotoxicity studies. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2020, 51, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthrammel, M.A.; Ganesh, V.; Shkir, M.; Yahia, I.S.; Alfaify, S. Facile synthesis of La-doped CdS nanoparticles by microwave assisted co-precipitation technique for optoelectronic application. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S. Studies on the dielectric properties of CdS nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 2014, 4, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khushboo; Umar, A.; Kansal, S.K.; Mehta, S.K. Highly-sensitive and selective detection of hydrazine at gold electrode modified with PEG-coated CdS nanoparticles. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2013, 188, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, Q.R.; Tian, Y.P. 1-D coordination polymer template approach to CdS and HgS aligned-nanowire bundles. New J. Chem. 2003, 27, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routkevitch, D.; Bigioni, T.; Moskovits, M.; Xu, J.M. Electrochemical fabrication of CdS nanowire arrays in porous anodic aluminum oxide templates. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 14037–14047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, P.M.S.; Timmons, A.B.; Neves, M.C.; Dynarowicz, P.; Trindade, T. Langmuir-Blodgett manipulation of capped cadmium sulfide quantum dots. Thin Solid Films 2001, 389, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ren, Y.; Han, L.; Xie, G.; Zhong, B. Mixed-solvothermal synthesis of CdS micro/nanostructures with optical and ferromagnetic properties. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostructures 2017, 92, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loudhaief, N.; Labiadh, H.; Hannachi, E.; Zouaoui, M.; Salem, M.B. Synthesis of CdS nanoparticles by hydrothermal method and their effects on the electrical properties of Bi-based superconductors. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2018, 31, 2305–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranthatta, S.; Janardhanan, P.; Pilankatta, R.; Nair, S.S. Green Synthesis of Engineered CdS Nanoparticles with Reduced Cytotoxicity for Enhanced Bioimaging Application. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 8646–8655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, A.; Priyam, A.; Das, S.K.; Saha, A. Size tunable synthesis of cysteine-capped CdS nanoparticles by γ-irradiation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 294, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dameron, C.; Reese, R.; Mehra, R.; Kortan, A.; Carroll, P.; Steigerwald, M.; Brus, L.; Winge, D. Biosynthesis of cadmium sulphide quantum semiconductor crystallites. Nature 1989, 338, 596–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godočíková, E.; Baláž, P.; Gock, E.; Choi, W.S.; Kim, B.S. Mechanochemical synthesis of the nanocrystalline semiconductors in an industrial mill. Powder Technol. 2006, 164, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, T.; McCormick, P.G. Mechanochemical synthesis of metal sulphide nanoparticles. Nanostruct. Mater. 1999, 12, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, A.; Mingelgrin, U. Mechanochemistry: A review of surface reactions and environmental applications. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 67, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, D. Mechanochemistry: A Power Tool for Green Synthesis. In Advances in Green Synthesis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 23–39. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, D.; García, F. Main group mechanochemistry: From curiosity to established protocols. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2274–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balaz, M. Environmental Mechanochemistry: Recycling Waste into Materials Using High-Energy Ball Milling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Baláž, P.; Boldižárová, E.; Godočíková, E.; Briančin, J. Mechanochemical route for sulphide nanoparticles preparation. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 1585–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutková, E.; Baláž, P.; Pourghahramani, P. CdS nanoparticles mechanochemically synthesized in a high-energy mill. J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2009, 11, 2102–2107. [Google Scholar]
- Kristl, M.; Ban, I.; Gyergyek, S. Preparation of nanosized copper and cadmium chalcogenides by mechanochemical synthesis. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2013, 28, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalabayev, Z.; Baláz, M.; Daneu, N.; Dutková, E.; Bujnáková, Z.; Kanuchová, M.; Danková, Z.; Balázová, L.; Urakaev, F.; Tkáciková, L. Sulfur-mediated mechanochemical synthesis of spherical and needle-like copper sulfide nanocrystals with antibacterial activity. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 12897–12909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuschek, E.; Brown, D.F.J.; Kahlmeter, G. Development of the EUCAST disk diffusion antimicrobial susceptibility testing method and its implementation in routine microbiology laboratories. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O255–O266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, P.; Saxena, N.; Chandra, R.; Gupta, V.; Agarwal, A.; Kanjilal, D. Nanotwinning and structural phase transition in CdS quantum dots. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devi, R.A.; Latha, M.; Velumani, S.; Oza, G.; Reyes-Figueroa, P.; Rohini, M.; Becerril-Juarez, I.; Lee, J.-H.; Yi, J. Synthesis and characterization of cadmium sulfide nanoparticles by chemical precipitation method. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 8434–8439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chava, R.K.; Son, N.; Kim, Y.S.; Kang, M. Controlled growth and bandstructure properties of one dimensional cadmium sulfide nanorods for visible photocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Maliki, H.; Bernede, J.C.; Marsillac, S.; Pinel, J.; Castel, X.; Pouzet, J. Study of the influence of annealing on the properties of CBD-CdS thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2003, 205, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedoseeva, Y.V.; Bulusheva, L.G.; Asanov, I.P.; Kurenya, A.G.; Gusel’nikov, A.V.; Maksimovskiy, E.A.; Gulyaev, D.V.; Zhuravlev, K.S.; Gutakovskii, A.K.; Okotrub, A.V. Electrically activated chemical bath deposition of CdS on carbon nanotube arrays. Synth. Met. 2021, 273, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, U.; Eich, D.; Chen, Z.H.; Fink, R.; Kulkarni, S.K.; Umbach, E. Detailed investigation of CdS nanoparticle surfaces by high-resolution photoelectron spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1999, 306, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enriguez, J.P.; Mathew, X. Influence of the thickness on structural, optical and electrical properties of chemical bath deposited CdS thin films. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2003, 76, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, P.C.; Das, R. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange dye on interaction with synthesized ligand free CdS nanocrystals under visible light illumination. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 231, 118122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamble, M.M.; Rondiya, S.R.; Bade, B.R.; Kore, K.B.; Nasane, M.P.; Dzade, N.Y.; Funde, A.M.; Jadkar, S.R. Optical, structural and morphological study of CdS nanoparticles: Role of sulfur source. Nanomater. Energy 2020, 9, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, M.M.; Christy, R.S.; Benitta, T.A.; Kumaran, J.T.T. Phase transitions in cadmium sulfide nanoparticles. AIP Adv. 2021, 11, 085129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, A.; Gomez, H.; Marotti, R.E.; Riveros, G.; Dalchiele, E.A. Grain size dependence of the bandgap in chemical bath deposited CdS thin films. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2004, 82, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, H.; Fatima, K.; Akhter, Z.; Nadeem, M.A.; Siddiq, M.; Iqbal, A. Fluorescence modulation of cadmium sulfide quantum dots by azobenzene photochromic switches. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 472, 20150692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, A.; Lakouraj, M.M.; Tashakkorian, H. Study of the effect of band gap and photoluminescence on biological properties of polyaniline/CdS QD nanocomposites based on natural polymer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.Z.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.F.; Chen, Y.B.; Liu, M.C. Photocatalytic Activities of Copper Doped Cadmium Sulfide Microspheres Prepared by a Facile Ultrasonic Spray-Pyrolysis Method. Molecules 2016, 21, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Sharma, S.K. Low-temperature synthesis and characterization of cadmium sulfide nanowires grown using simple chemical reaction through the pores in an alumina template. Phys. Scr. 2010, 82, 025801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhage, S.R.; Colorado, H.A.; Hahn, T. Morphological variations in cadmium sulfide nanocrystals without phase transformation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baláž, P.; Baláž, M.; Achimovičová, M.; Bujňáková, Z.; Dutková, E. Chalcogenide mechanochemistry in materials science: Insight into synthesis and applications (a review). J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 11851–11890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senasu, T.; Hemavibool, K.; Nanan, S. Hydrothermally grown CdS nanoparticles for photodegradation of anionic azo dyes under UV-visible light irradiation. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 22592–22605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez-Rodriguez, E.; Loeza-Poot, M.; Riech, I.; Rejon, V.; Pena, J.L. A comparative study of CdS:F and CdS:O thin films deposited by reactive RF-sputtering technique for window layer application in solar cells. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Pal, A.; Ghosh, D.; Ghosh, A.B.; Nandi, M.; Biswas, P. Improved photocurrent response, photostability and photocatalytic hydrogen generation ability of CdS nanoparticles in presence of mesoporous carbon. Materials Research Bulletin 2021, 134, 111085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, D.D.; Guo, P.; Leckie, J.O. One-step fabrication and high photocatalytic activity of porous TiO2 hollow aggregates by using a low-temperature hydrothermal method without templates. Chem. A Eur. J. 2007, 13, 1851–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Biswal, N.; Martha, S.; Parida, K. Solar-light induced photodegradation of organic pollutants over CdS-pillared zirconium–titanium phosphate (ZTP). J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2011, 349, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, C.; Wang, X.; Xi, Y. Photocatalytic activity of CdS nanoparticles synthesized by a facile composite molten salt method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 4370–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Tan, L.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Fu, Y.; Qian, L. Photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of CdS nanoparticles prepared by solvothermal method. NIScPR Online Period. Repos. 2013, 52, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Cao, Y.; Jia, D.; Niu, X. Facile synthesis of CdS nanoparticles photocatalyst with high performance. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, J. Preparation of popcorn-shaped CdS nanoparticles by hydrothermal method and their potent photocatalytic degradation efficiency. Mater. Lett. 2015, 158, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayodhya, D.; Venkatesham, M.; Bhagavanth Reddy, G.; Veerabhadram, G. One-pot sonochemical synthesis of CdS nanoparticles: Photocatalytic and electrical properties. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2015, 6, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, F.; Zuo, Y.; Fan, C.; Xu, S.; Yang, S.; Gu, F. Immobilisation of CdS nanoparticles on chitosan microspheres via a photochemical method with enhanced photocatalytic activity in the decolourisation of methyl orange. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2014, 156, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chai, T.; Guo, J. Synthesis and photochemical performance of CdS nanoparticles photocatalysts for photodegradation of organic dye. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 7609–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatykayev, B.; Chouchene, B.; Balan, L.; Gries, T.; Medjahdi, G.; Girot, E.; Uralbekov, B.; Schneider, R. Heterostructured g-CN/TiO2 photocatalysts prepared by thermolysis of g-CN/MIL-125 (Ti) composites for efficient pollutant degradation and hydrogen production. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, P.; Augustyniak, A.; Cendrowski, K.; Nawrotek, P.; Mijowska, E. Antimicrobial Activity of Al2O3, CuO, Fe3O4, and ZnO Nanoparticles in Scope of Their Further Application in Cement-Based Building Materials. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanpui, P.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Ghosh, S.S. Induction of Apoptosis in Cancer Cells at Low Silver Nanoparticle Concentrations using Chitosan Nanocarrier. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivask, A.; Kurvet, I.; Kasemets, K.; Blinova, I.; Aruoja, V.; Suppi, S.; Vija, H.; Käkinen, A.; Titma, T.; Heinlaan, M. Size-dependent toxicity of silver nanoparticles to bacteria, yeast, algae, crustaceans and mammalian cells in vitro. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleifer, K.H.; Bell, J.A. Staphylococcus. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Sheutz, F.; Strockbine, N. Escherichia. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematics of Archaea and Bacteria; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Augustyniak, A.; Jablonska, J.; Cendrowski, K.; Głowacka, A.; Stephan, D.; Mijowska, E.; Sikora, P. Investigating the release of ZnO nanoparticles from cement mortars on microbiological models. Appl. Nanosci. 2021, 12, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustyniak, A.; Cendrowski, K.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Jabłońska, J.; Nawrotek, P.; Trukawka, M.; Mijowska, E.; Popowska, M. The response of pseudomonas aeruginosa pao1 to uv-activated titanium dioxide/silica nanotubes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]















| The Sample | k, min−1 | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| aCdS | 0.012 | 0.98 |
| cCdS | 0.018 | 0.98 |
| № | Synthetic Method | Experimental Conditions | Precursors | Degraded Dye, Concentration | Photocatalytic Efficiency | Rate Constant (min−1) | [Ref] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Temperature (°C) | |||||||
| 1 | Composite-molten-salt (CMS) | 24–72 h | 160–220 | Cd(NO3)2·4H2O, Na2S·9H2O, LiNO3, KNO3 | MB, 4 mg/L | 76.3%@140 min | - | [62] |
| RhB, 8 mg/L | 94.9%@140 min | - | ||||||
| 2 | Solvothermal | 6 h | 180 | CdCl2·5H2O, CS(NH2)2 | MB, 6 mg/L | 95%@80 min | 0.0365 | [63] |
| 3 | One-step solid-state reaction | 30 min | - | Cd(CH3COO)2·2H2O, Na2S2O3·5H2O | RhB, 10 mg/L | 95%@80 min | 0.0429 | [64] |
| 4 | Biogenic synthesis | 72 h | 28 | Strain of T. Harzianum, CdCl2, Na2S | MB, 10 mg/L | 37.15%@60 min | 0.0076 | [59] |
| 5 | Hydrothermal | 24 h | - | Cd(Ac)2·2H2O, PVP-K30, CS(NH2)2 | MO, 20 mg/L | 93.3%@240 min | - | [65] |
| 6 | Sonochemical | 1 h | RT | Cd(CH3COO)2, Na2S, tryptophan | MO, 5 × 10−6 M | 75.33%@240 min | 0.0062 | [66] |
| 7 | Photochemical | 24 h | - | CdSO4, Na2S2O3 | MO, 8 × 10−6 M | 26.3%@70 min | 0.0058 | [67] |
| 8 | Commercial CdS | - | - | - | MO, 10 mg/L | 78%@90 min | - | [68] |
| 9 | Mechanochemical | 5 min | RT | Cd(CH3COO)2·2H2O, Na2S·9H2O, Na2S2O3·5H2O, C6H8O7 | Orange II, 10 mg/L | 93%@180 min | 0.018 | this work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shalabayev, Z.; Baláž, M.; Khan, N.; Nurlan, Y.; Augustyniak, A.; Daneu, N.; Tatykayev, B.; Dutková, E.; Burashev, G.; Casas-Luna, M.; et al. Sustainable Synthesis of Cadmium Sulfide, with Applicability in Photocatalysis, Hydrogen Production, and as an Antibacterial Agent, Using Two Mechanochemical Protocols. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12081250
Shalabayev Z, Baláž M, Khan N, Nurlan Y, Augustyniak A, Daneu N, Tatykayev B, Dutková E, Burashev G, Casas-Luna M, et al. Sustainable Synthesis of Cadmium Sulfide, with Applicability in Photocatalysis, Hydrogen Production, and as an Antibacterial Agent, Using Two Mechanochemical Protocols. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(8):1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12081250
Chicago/Turabian StyleShalabayev, Zhandos, Matej Baláž, Natalya Khan, Yelmira Nurlan, Adrian Augustyniak, Nina Daneu, Batukhan Tatykayev, Erika Dutková, Gairat Burashev, Mariano Casas-Luna, and et al. 2022. "Sustainable Synthesis of Cadmium Sulfide, with Applicability in Photocatalysis, Hydrogen Production, and as an Antibacterial Agent, Using Two Mechanochemical Protocols" Nanomaterials 12, no. 8: 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12081250
APA StyleShalabayev, Z., Baláž, M., Khan, N., Nurlan, Y., Augustyniak, A., Daneu, N., Tatykayev, B., Dutková, E., Burashev, G., Casas-Luna, M., Džunda, R., Bureš, R., Čelko, L., Ilin, A., & Burkitbayev, M. (2022). Sustainable Synthesis of Cadmium Sulfide, with Applicability in Photocatalysis, Hydrogen Production, and as an Antibacterial Agent, Using Two Mechanochemical Protocols. Nanomaterials, 12(8), 1250. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12081250