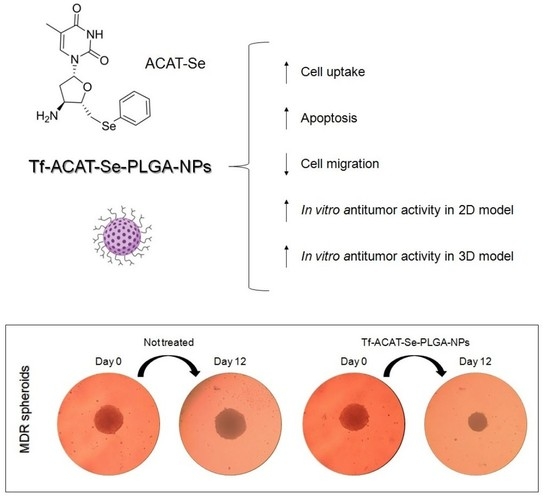
Transferrin-Decorated PLGA Nanoparticles Loaded with an Organoselenium Compound as an Innovative Approach to Sensitize MDR Tumor Cells: An In Vitro Study Using 2D and 3D Cell Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Nanoparticles
2.3. Characterization of Nanoparticles
2.4. In Vitro Release Studies
2.5. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity
2.6. Protein Corona Study
2.7. Biological Safety Profile of the NPs: In Vitro Biocompatibility Studies
2.8. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
2.9. In Vitro Antitumor Activity Screening Using 2D Cell Models
2.10. In Vitro Antitumor Activity Assays Using 3D Cell Models
2.11. Cell Migration
2.12. Cell Uptake Studies
2.13. Intracellular Retention
2.14. Determination of Apoptosis Rate
2.15. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.16. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Nanoparticles
3.2. In Vitro Release Studies
3.3. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity
3.4. Protein Corona Study
3.5. In Vitro Biocompatibility Studies
3.6. In Vitro Antitumor Activity Using 2D Cell Monolayer Assays
3.7. In Vitro Antitumor Activity Assays Using 3D Cell Models
3.8. Cell Migration
3.9. Cell Uptake Studies
3.10. Intracellular Retention
3.11. Determination of Apoptosis Rate
3.12. Cell Cycle Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bukowski, K.; Kciuk, M.; Kontek, R. Mechanisms of Multidrug Resistance in Cancer Chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, F.U.; Sufiyan Chhipa, A.; Mishra, V.; Gupta, V.K.; Rawat, S.G.; Kumar, A.; Pathak, C. Molecular and Cellular Paradigms of Multidrug Resistance in Cancer. Cancer Rep. 2022, 5, e1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallavalle, S.; Dobričić, V.; Lazzarato, L.; Gazzano, E.; Machuqueiro, M.; Pajeva, I.; Tsakovska, I.; Zidar, N.; Fruttero, R. Improvement of Conventional Anti-Cancer Drugs as New Tools against Multidrug Resistant Tumors. Drug Resist. Updat. 2020, 50, 100682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidinia, M.; Mirza-Aghazadeh-Attari, M.; Rahimi, M.; Mihanfar, A.; Karimian, A.; Safa, A.; Yousefi, B. Overcoming Multidrug Resistance in Cancer: Recent Progress in Nanotechnology and New Horizons. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 855–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Li, M.; Dey, R.; Chen, Y. Nanomaterials for Cancer Therapy: Current Progress and Perspectives. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Cheng, K.; Chen, K.; Xu, C.; Ma, P.; Dang, G.; Yang, Y.; Lei, Q.; Huang, H.; Yu, Y.; et al. Nanoparticle-Based Medicines in Clinical Cancer Therapy. Nano Today 2022, 45, 101512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzy, L.; Nasr, M.; Metwally, A.A.; Awad, G.A.S. Cancer Nanotheranostics: A Review of the Role of Conjugated Ligands for Overexpressed Receptors. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 104, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira-Librelotto, D.R.; Codevilla, C.F.; Farooqi, A.; Rolim, C.M.B. Transferrin-Conjugated Nanocarriers as Active-Targeted Drug Delivery Platforms for Cancer Therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandin, V.; Khalkar, P.; Braude, J.; Fernandes, A.P. Organic Selenium Compounds as Potential Chemotherapeutic Agents for Improved Cancer Treatment. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 127, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spengler, G.; Gajdács, M.; Marć, M.A.; Domínguez-Álvarez, E.; Sanmartín, C. Organoselenium Compounds as Novel Adjuvants of Chemotherapy Drugs—A Promising Approach to Fight Cancer Drug Resistance. Molecules 2019, 24, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Rosa, R.M.; Piccoli, B.C.; da Silva, F.D.; Dornelles, L.; Rocha, J.B.T.; Sonego, M.S.; Begnini, K.R.; Collares, T.; Seixas, F.K.; Rodrigues, O.E.D. Synthesis, Antioxidant and Antitumoral Activities of 5′-Arylchalcogeno-3-Aminothymidine (ACAT) Derivatives. Med. Chem. Commun. 2017, 8, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, L.B.; Nogueira-Librelotto, D.R.; Mathes, D.; de Vargas, J.M.; da Rosa, R.M.; Rodrigues, O.E.D.; Vinardell, M.P.; Mitjans, M.; Rolim, C.M.B. Overcoming MDR by Associating Doxorubicin and PH-Sensitive PLGA Nanoparticles Containing a Novel Organoselenium Compound—An In Vitro Study. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, M.; Chanda, N. Formulation of PLGA Nano-Carriers: Specialized Modification for Cancer Therapeutic Applications. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 837–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Huang, L. Nanoparticles Containing Insoluble Drug for Cancer Therapy. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheeren, L.E.; Nogueira-Librelotto, D.R.; Macedo, L.B.; de Vargas, J.M.; Mitjans, M.; Vinardell, M.P.; Rolim, C.M.B. Transferrin-Conjugated Doxorubicin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles with PH-Responsive Behavior: A Synergistic Approach for Cancer Therapy. J. Nanopart. Res. 2020, 22, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavano, L.; Muzzalupo, R.; Mauro, L.; Pellegrino, M.; Andò, S.; Picci, N. Transferrin-Conjugated Pluronic Niosomes as a New Drug Delivery System for Anticancer Therapy. Langmuir 2013, 29, 12638–12646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritger, P.L.; Peppas, N.A. A Simple Equation for Description of Solute Release I. Fickian and Non-Fickian Release from Non-Swellable Devices in the Form of Slabs, Spheres, Cylinders or Discs. J. Control. Release 1987, 5, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Sahlin, J.J. A Simple Equation for the Description of Solute Release. III. Coupling of Diffusion and Relaxation. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 57, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, O.P.; Bhat, T.K. DPPH Antioxidant Assay Revisited. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 1202–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant Activity Applying an Improved ABTS Radical Cation Decolorization Assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obst, K.; Yealland, G.; Balzus, B.; Miceli, E.; Dimde, M.; Weise, C.; Eravci, M.; Bodmeier, R.; Haag, R.; Calderón, M.; et al. Protein Corona Formation on Colloidal Polymeric Nanoparticles and Polymeric Nanogels: Impact on Cellular Uptake, Toxicity, Immunogenicity, and Drug Release Properties. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 1762–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira-Librelotto, D.R.; Scheeren, L.E.; Vinardell, M.P.; Mitjans, M.; Rolim, C.M.B. Chitosan-Tripolyphosphate Nanoparticles Functionalized with a PH-Responsive Amphiphile Improved the in Vitro Antineoplastic Effects of Doxorubicin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 147, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Q.; Si, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Han, F.; Huang, Z. Synergistic Effects of SAM and Selenium Compounds on Proliferation, Migration and Adhesion of HeLa Cells. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 4433–4441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, E.; Ali, A.; Fatima, M.T.; Nimisha; Apurva; Kumar, A.; Sumi, M.P.; Sattar, R.S.A.; Mahajan, B.; Saluja, S.S. Ligand Decorated Biodegradable Nanomedicine in the Treatment of Cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 167, 105544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheeren, L.E.; Nogueira-Librelotto, D.R.; Mathes, D.; Pillat, M.M.; Macedo, L.B.; Mitjans, M.; Vinardell, M.P.; Rolim, C.M.B. Multifunctional PLGA Nanoparticles Combining Transferrin-Targetability and PH-Stimuli Sensitivity Enhanced Doxorubicin Intracellular Delivery and in Vitro Antineoplastic Activity in MDR Tumor Cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2021, 75, 105192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.-J.; Xing, L.; Cui, P.-F.; Zhang, J.-L.; Zhu, Y.; Qiao, J.-B.; Lyu, J.-Y.; Zhang, M.; Luo, C.-Q.; Zhou, Y.-X.; et al. Transferrin-Inspired Vehicles Based on PH-Responsive Coordination Bond to Combat Multidrug-Resistant Breast Cancer. Biomaterials 2017, 113, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.; Cinu, T.A.; Sebastian, R.; Shoja, M.H.; Aleykutty, N.A.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Santini, A.; Souto, E.B. Transferrin-Conjugated Docetaxel–PLGA Nanoparticles for Tumor Targeting: Influence on MCF-7 Cell Cycle. Polymers 2019, 11, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bidkar, A.P.; Sanpui, P.; Ghosh, S.S. Transferrin-Conjugated Red Blood Cell Membrane-Coated Poly(Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid) Nanoparticles for the Delivery of Doxorubicin and Methylene Blue. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 3807–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, J.W.; Santos, J.L.; Williford, J.-M.; Mao, H.-Q. Control of Polymeric Nanoparticle Size to Improve Therapeutic Delivery. J. Control. Release 2015, 219, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalyane, D.; Raval, N.; Maheshwari, R.; Tambe, V.; Kalia, K.; Tekade, R.K. Employment of Enhanced Permeability and Retention Effect (EPR): Nanoparticle-Based Precision Tools for Targeting of Therapeutic and Diagnostic Agent in Cancer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 1252–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mao, H.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G. Insight into the Interactions between Nanoparticles and Cells. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.I.; Samad, N.A.; Fang, L.; Lim, V. Cytotoxicity of Targeted PLGA Nanoparticles: A Systematic Review. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 9433–9449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrintaj, P.; Ramsey, J.D.; Samadi, A.; Atoufi, Z.; Yazdi, M.K.; Ganjali, M.R.; Amirabad, L.M.; Zangene, E.; Farokhi, M.; Formela, K.; et al. Poloxamer: A Versatile Tri-Block Copolymer for Biomedical Applications. Acta Biomater. 2020, 110, 37–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, H.; Hernández-Parra, H.; Bernal-Chávez, S.A.; Del Prado-Audelo, M.L.; Caballero-Florán, I.H.; Borbolla-Jiménez, F.V.; González-Torres, M.; Magaña, J.J.; Leyva-Gómez, G. Non-Ionic Surfactants for Stabilization of Polymeric Nanoparticles for Biomedical Uses. Materials 2021, 14, 3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaaban, S.; Ashmawy, A.M.; Negm, A.; Wessjohann, L.A. Synthesis and Biochemical Studies of Novel Organic Selenides with Increased Selectivity for Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Breast Adenocarcinoma. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 179, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sak, M.; Al-Faiyz, Y.S.; Elsawy, H.; Shaaban, S. Novel Organoselenium Redox Modulators with Potential Anticancer, Antimicrobial, and Antioxidant Activities. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrecoso, G.; Crecente-Campo, J.; Alonso, M.J. Unveiling the Pitfalls of the Protein Corona of Polymeric Drug Nanocarriers. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 730–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, A.; Giuliano, E.; Venkateswararao, E.; Fresta, M.; Bulotta, S.; Awasthi, V.; Cosco, D. Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery to Solid Tumors. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, B.; Barick, K.C.; Hassan, P.A. Recent Advances in Active Targeting of Nanomaterials for Anticancer Drug Delivery. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 296, 102509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, S.M.; Rao, C.M.; Ahmad, M.F. Nanoparticle-Protein Interaction: The Significance and Role of Protein Corona. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1048, 175–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Decarli, M.C.; Amaral, R.; dos Santos, D.P.; Tofani, L.B.; Katayama, E.; Rezende, R.A.; da Silva, J.V.L.; Swiech, K.; Suazo, C.A.T.; Mota, C.; et al. Cell Spheroids as a Versatile Research Platform: Formation Mechanisms, High Throughput Production, Characterization and Applications. Biofabrication 2021, 13, 032002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yedgar, S.; Barshtein, G.; Gural, A. Hemolytic Activity of Nanoparticles as a Marker of Their Hemocompatibility. Micromachines 2022, 13, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesus, S.; Schmutz, M.; Som, C.; Borchard, G.; Wick, P.; Borges, O. Hazard Assessment of Polymeric Nanobiomaterials for Drug Delivery: What Can We Learn From Literature So Far. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jo, Y.; Choi, N.; Kim, K.; Koo, H.-J.; Choi, J.; Kim, H.N. Chemoresistance of Cancer Cells: Requirements of Tumor Microenvironment-Mimicking In Vitro Models in Anti-Cancer Drug Development. Theranostics 2018, 8, 5259–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorella, S.; Karagiannis, T.C. Transferrin Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis: A Useful Target for Cancer Therapy. J. Membr. Biol. 2014, 247, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Decker, C.C.; Zechner, L.; Krstin, S.; Wink, M. In Vitro Wound Healing of Tumor Cells: Inhibition of Cell Migration by Selected Cytotoxic Alkaloids. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arya, G.; Das, M.; Sahoo, S.K. Evaluation of Curcumin Loaded Chitosan/PEG Blended PLGA Nanoparticles for Effective Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soe, Z.C.; Kwon, J.B.; Thapa, R.K.; Ou, W.; Nguyen, H.T.; Gautam, M.; Oh, K.T.; Choi, H.-G.; Ku, S.K.; Yong, C.S.; et al. Transferrin-Conjugated Polymeric Nanoparticle for Receptor-Mediated Delivery of Doxorubicin in Doxorubicin-Resistant Breast Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frasco, M.F.; Almeida, G.M.; Santos-Silva, F.; Pereira, M.d.C.; Coelho, M.A.N. Transferrin Surface-Modified PLGA Nanoparticles-Mediated Delivery of a Proteasome Inhibitor to Human Pancreatic Cancer Cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2015, 103, 1476–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, M.J.; Bravo, M.; Loureiro, J.A.; Lima, J.; Pereira, M.C. Transferrin-Modified Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of Asiatic Acid to Glioblastoma Cells. Life Sci. 2022, 296, 120435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Guo, J.; Tian, Z.; Chen, J.; Gou, G.; Niu, Y.; Li, L.; Yang, J. Piperine-Loaded Glycyrrhizic Acid- and PLGA-Based Nanoparticles Modified with Transferrin for Antitumor. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsesmetzis, N.; Paulin, C.; Rudd, S.; Herold, N. Nucleobase and Nucleoside Analogues: Resistance and Re-Sensitisation at the Level of Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics and Metabolism. Cancers 2018, 10, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Icard, P.; Fournel, L.; Wu, Z.; Alifano, M.; Lincet, H. Interconnection between Metabolism and Cell Cycle in Cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-M.; Chiu, C.-C.; Wu, P.-F.; Chen, C.-Y. Subamolide E from Cinnamomum Subavenium Induces Sub-G1 Cell-Cycle Arrest and Caspase-Dependent Apoptosis and Reduces the Migration Ability of Human Melanoma Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8187–8192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecker, A.; Ledur, P.C.; da Silva, R.S.; Leal, D.B.R.; Rodrigues, O.E.D.; Ardisson-Araújo, D.; Waczuk, E.P.; da Rocha, J.B.T.; Barbosa, N.V. Chalcogenozidovudine Derivatives with Antitumor Activity: Comparative Toxicities in Cultured Human Mononuclear Cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 160, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, A.; Huang, P.; Matsuda, A.; Plunkett, W. 2′-C-Cyano-2′-Deoxy-1-β-D-Arabino-Pentofuranosylcytosine: A Novel Anticancer Nucleoside Analog That Causes Both DNA Strand Breaks and G2 Arrest. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Tf-ACAT-Se-PLGA-NPs | ||
|---|---|---|
| IC50 | SI | |
| A375 | 14.38 | 4.17 |
| HeLa | 31.64 | 1.90 |
| MCF-7 | 14.40 | 4.17 |
| U-87 | 27.04 | 2.22 |
| NCI/ADR-RES | 31.48 | 1.91 |
| PBMCs | 60.02 * | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Macedo, L.B.; Nogueira-Librelotto, D.R.; Mathes, D.; Pieta, T.B.; Mainardi Pillat, M.; Rosa, R.M.d.; Rodrigues, O.E.D.; Vinardell, M.P.; Rolim, C.M.B. Transferrin-Decorated PLGA Nanoparticles Loaded with an Organoselenium Compound as an Innovative Approach to Sensitize MDR Tumor Cells: An In Vitro Study Using 2D and 3D Cell Models. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2306. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13162306
Macedo LB, Nogueira-Librelotto DR, Mathes D, Pieta TB, Mainardi Pillat M, Rosa RMd, Rodrigues OED, Vinardell MP, Rolim CMB. Transferrin-Decorated PLGA Nanoparticles Loaded with an Organoselenium Compound as an Innovative Approach to Sensitize MDR Tumor Cells: An In Vitro Study Using 2D and 3D Cell Models. Nanomaterials. 2023; 13(16):2306. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13162306
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacedo, Letícia Bueno, Daniele Rubert Nogueira-Librelotto, Daniela Mathes, Taís Baldissera Pieta, Micheli Mainardi Pillat, Raquel Mello da Rosa, Oscar Endrigo Dorneles Rodrigues, Maria Pilar Vinardell, and Clarice Madalena Bueno Rolim. 2023. "Transferrin-Decorated PLGA Nanoparticles Loaded with an Organoselenium Compound as an Innovative Approach to Sensitize MDR Tumor Cells: An In Vitro Study Using 2D and 3D Cell Models" Nanomaterials 13, no. 16: 2306. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13162306
APA StyleMacedo, L. B., Nogueira-Librelotto, D. R., Mathes, D., Pieta, T. B., Mainardi Pillat, M., Rosa, R. M. d., Rodrigues, O. E. D., Vinardell, M. P., & Rolim, C. M. B. (2023). Transferrin-Decorated PLGA Nanoparticles Loaded with an Organoselenium Compound as an Innovative Approach to Sensitize MDR Tumor Cells: An In Vitro Study Using 2D and 3D Cell Models. Nanomaterials, 13(16), 2306. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13162306