Ionic Adsorption and Desorption of CNT Nanoropes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Molecular Dynamics Model of Nanoropes
3. Calculation of Adsorption of Metal and Negative Ions
4. Adsorption Capacity of Nanorope
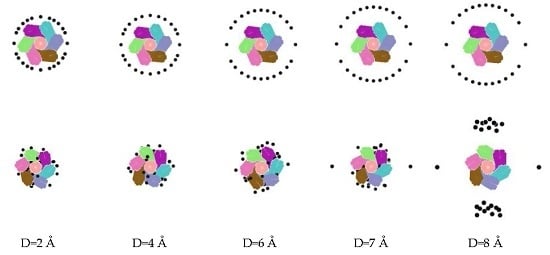
5. Desorption of Negative Ions
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Radbin, R.; Vahedi, F.; Chamani, J. The influence of drinking-water pollution with heavy metal on the expression of IL-4 and IFN-γ in mice by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Cytotechnology 2014, 66, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimori, T.; Takigami, H. Pollution distribution of heavy metals in surface soil at an informal electronic-waste recycling site. Environ. Geochem. Health 2014, 36, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrales, J.; Naja, G.M.; Rivero, R.G.; Miralles-Wilhelm, F.; Bhat, M.G. Water quality trading programs towards solving environmental pollution problems. Irrig. Drain. 2013, 622, 72–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgolo, S.; Petronella, F.; Ciannarella, R.; Comparelli, R.; Agostiano, A.; Curri, M.L.; Mascolo, G. UV and solar-based photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants by nano-sized TiO2 grown on carbon nanotubes. Catal. Today 2015, 240, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghipour, H.; Mosaferi, M.; Armanfar, F.; Gaemmagami, S.J. Heavy metals pollution in the soils of suburban areas in big cities: a case study. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Tavassoli, N.; Sadeghi, O.; Amini, M.M. Optimization of solid-phase extraction using artificial neural networks and response surface methodology in combination with experimental design for determination of gold by atomic absorption spectrometry in industrial wastewater samples. Talanta 2012, 97, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipeaiyeda, A.R.; Odola, A.J. Co-precipitation of Ni, Cr, Mn, Pb and Zn in industrial wastewater and sediment samples with copper(II) cyclo-hexylmethyldithiocarbamate for their flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.Y.; Luo, T.; Zhang, Y.X.; Jia, Y.; Zhu, B.J.; Fu, X.C.; Liu, J.H.; Huang, X.J. Adsorption of lead(II) on O2-plasma-oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes: thermodynamics, kinetics, and desorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2585–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samadi, N.; Hasanzadeh, R.; Rasad, M. Adsorption isotherms, kinetic, and desorption studies on removal of toxic metal ions from aqueous solutions by polymeric adsorbent. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Wang, S.G.; Wei, J.Q.; Zhang, X.F.; Xu, C.L.; Luan, Z.K.; Wu, D.H.; Wei, B.Q. Lead adsorption on carbon nanotubes. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2002, 357, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastos, M.; Camps, I. First-principles calculations of nickel, cadmium, and lead adsorption on a single-walled (10,0) carbon nanotube. J. Mol. Model. 2014, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, P.; Kitaura, R.; Nakanishi, R.; Shiozawa, H.; Ogawa, D.; Hoffmann, P.; Shinohara, H.; Pichler, T. Templating rare-earth hybridization via ultrahigh vacuum annealing of ErCl3 nanowires inside carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayan, P.M.; Iijima, S. Capillarity-induced filling of carbon nanotubes. Nature 1993, 361, 333–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Lieber, C.M. Nanotube nanotweezers. Science 1999, 286, 2148–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baughman, R.H.; Cui, C.X.; Zakhidov, A.A.; Iqbal, Z.; Barisci, J.N.; Spinks, G.M.; Wallace, G.G.; Mazzoldi, A.; De Rossi, D.; Rinzler, A.G.; et al. Carbon nanotube actuators. Science 1999, 284, 1340–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, S.; Mashl, R.J.; Jakobsson, E.; Aluru, N.R. Electrolytic transport in modified carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashl, R.J.; Joseph, S.; Aluru, N.R.; Jakobsson, E. Anomalously immobilized water: A new water phase induced by confinement in nanotubes. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, R.; Aluru, N.R. Atypical dependence of electroosmotic transport on surface charge in a single-wall carbon nanotube. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijani, H.; Beyki, M.H.; Shariatinia, Z.; Bayat, M.; Shemirani, F. A new approach for one step synthesis of magnetic carbon nanotubes/diatomite earth composite by chemical vapor deposition method: Application for removal of lead ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 253, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasis, D.; Tagmatarchis, N.; Bianco, A.; Prato, M. Chemistry of carbon nanotubes. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 1105–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.Y.; Xu, C.X. Comparative investigation on decorating carbon nanotubes with different transition metals. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 102, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, L.; Armentano, I.; Kenny, J.M. Electrically switchable carbon nanotubes hydrophobic surfaces. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2005, 14, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoreishi, S.R.; Davies, P.; Cartraud, P.; Messager, T. Analytical modeling of synthetic fiber ropes. Part II: A linear elastic model for 1+6 fibrous structures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2007, 44, 2943–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plimpton, S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular-dynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 1995, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, S.J.; Tutein, A.B.; Harrison, J.A. A reactive potential for hydrocarbons with intermolecular interactions. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 112, 6472–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, D.W.; Shenderova, O.A.; Harrison, J.A.; Stuart, S.J.; Ni, B.; Sinnott, S.B. A second-generation reactive empirical bond order (REBO) potential energy expression for hydrocarbons. J. Phys.-Condens. Matter 2002, 14, 783–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wei, N.; Fan, Z.; Jiang, J.W.; Rabczuk, T. The mechanical properties of three types of carbon allotropes. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 95702–95712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.H.; Yang, Q.S. Rotation, elongation and failure of CNT nanoropes induced by electric field. Comp. Mater. Sci. 2015, 98, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Chou, T.W. Charge-induced strains in single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 4624–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Chou, T. Theoretical studies on the charge-induced failure of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2007, 45, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Conditions | A+ | B− | C-atom | Ensemble | Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 28 | 0 | 6888 | NVT | 200 ps |
| 2 | 0 | 28 | 6888 | NVT | 200 ps |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, J.-J.; Yang, Q.-S.; Yan, X.-H.; He, X.-Q.; Liew, K.-M. Ionic Adsorption and Desorption of CNT Nanoropes. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6100177
Shang J-J, Yang Q-S, Yan X-H, He X-Q, Liew K-M. Ionic Adsorption and Desorption of CNT Nanoropes. Nanomaterials. 2016; 6(10):177. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6100177
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Jun-Jun, Qing-Sheng Yang, Xiao-Hui Yan, Xiao-Qiao He, and Kim-Meow Liew. 2016. "Ionic Adsorption and Desorption of CNT Nanoropes" Nanomaterials 6, no. 10: 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6100177
APA StyleShang, J. -J., Yang, Q. -S., Yan, X. -H., He, X. -Q., & Liew, K. -M. (2016). Ionic Adsorption and Desorption of CNT Nanoropes. Nanomaterials, 6(10), 177. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6100177