Investigation of the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Graphene Nanoplatelet-Cement Composite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Dispersibility of GNPs in Aqueous Solution
2.1.1. UV-Vis Absorbency Analysis of GNP Suspension
2.1.2. Optical Microscope and TEM Analysis of GNP Suspension
2.2. Workability
2.3. Mechanical Properties of GNP–Cement Composite
2.4. XRD Analysis
2.5. Thermal (TG/DTG) Analysis
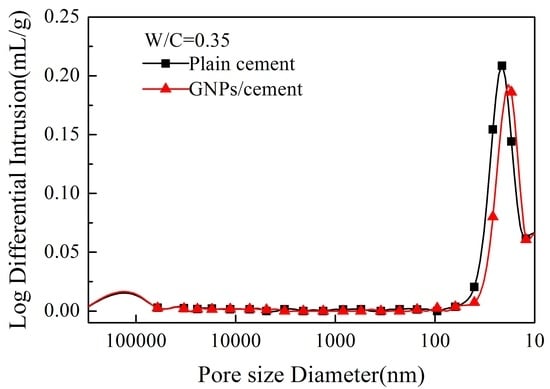
2.6. Porosity and Pore Size Distribution
2.7. Microstructure
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of GNP Suspensions
4.3. GNP–Cement Composite Processing
4.4. Test Methods
4.4.1. Characterizing the Dispersibility of GNP Suspensions
4.4.2. Slump Flow Test
4.4.3. Mechanical Property Tests
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reis, J.M.L. Fracture and flexural characterization of natural fiber-reinforced polymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2006, 20, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holschemacher, K.; Mueller, T.; Ribakov, Y. Effect of steel fibers on mechanical properties of high-strength concrete. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 2604–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Liu, A.; Sou, H.; Chouw, N. Mechanical and dynamic properties of coconut fiber reinforced concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, B.W.; Kim, C.H.; Tae, G.; Park, J.B. Characteristics of cement mortar with nano-SiO2 particles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 1351–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidou, M.; Papayianni, I. Influence of nano-SiO2 on the Portland cement pastes. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 2706–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Han, Y.; Liu, S. Effect of highly dispersed carbon nanotubes on the flexural toughness of cement-based composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 46, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, R.; Mehta, A. Effect of carbon nanotubes on properties of cement mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, C.; Brown, L.; Sanchez, F. Quantification of the re-agglomeration of carbon nanofiber aqueous dispersion in cement pastes and effect on the early age flexural response. Carbon 2016, 107, 482–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gdoutos, E.E.; Konsta-Gdoutos, M.S.; Danoglidis, P.A. Portland cement mortar nanocomposites at low carbon nanotube and carbon nanofiber content: A fracture mechanics experimental study. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2016, 70, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoller, M.D.; Park, S.; Zhu, Y.; An, J.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene-based ultracapacitors. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3498–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.G.; Wei, X.D.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the Elastic Properties and Intrinsic Strength of Monolayer Graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Murali, S.; Cai, W.; Li, X.; Suk, J.W.; Potts, J.R.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene and Graphene Oxide: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 3906–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Istrate, O.M.; Paton, K.R.; Khan, U.; O’Neill, A.; Bell, A.P.; Coleman, J.N. Reinforcement in melt-processed polymer–graphene composites at extremely low graphene loading level. Carbon 2014, 78, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Oh, H.S.; Shon, I.J. The effect of graphene reinforcement on the mechanical properties of Al2O3 ceramics rapidly sintered by high-frequency induction heating. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2015, 48, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, B.; Kim, S.; Arepalli, S.; Nah, C. A study of graphene oxide-reinforced rubber nanocomposite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Pan, Z.; Korayem, A.H.; Qiu, L.; Li, D.; Collins, F.; Wang, C.M.; Duan, W.H. Reinforcing Effects of Graphene Oxide on Portland Cement Paste. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2014, 27, A4014010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saafi, M.; Tang, L.; Fung, J.; Rahman, M.; Liggat, J. Enhanced properties of graphene/fly ash geopolymeric composite cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 67, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Ma, Y.; Qiu, C.; Sun, T.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q. Effect of graphene oxide nanosheets of microstructure and mechanical properties of cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; He, L.; Qiu, L.; Korayem, A.H.; Li, G.; Zhu, J.W.; Collins, F.; Li, D.; Duan, W.H.; Wang, M.C. Mechanical properties and microstructure of a graphene oxide–cement composite. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2015, 58, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, I.; Kim, Y.A.; Shin, G.O.; Kim, J.H.; Muramatsu, H. Compressive strength sensitivity of cement mortar using rice husk-derived graphene with a high specific surface area. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.; Li, W.; Dong, H. Role of graphene waviness on the thermal conductivity of graphene composites. Appl. Phys. A-Mater. 2013, 111, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Fukushima, H.; Drzal, L.T. Mechanical and electrical property enhancement in exfoliated graphene nanoplatelet/liquid crystalline polymer nanocomposites. Compos. Part A 2011, 42, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wei, S.; Ryu, J.; Sun, L.; Guo, Z. Poly(propylene)/graphene nanoplatelet nanocomposites: Melt rheological behavior and thermal, electrical, and electronic properties. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2011, 212, 1951–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Dichiara, A.; Bai, J. Carbon nanotube–graphene nanoplatelet hybrids as high-performance multifunctional reinforcements in epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2013, 74, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yan, H.; Jiang, K. Mechanical properties of graphene platelet-reinforced alumina ceramic composites. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 6215–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, N.; Mehrali, M.; Mehrali, M.; Alengaram, U.J.; Jumaat, M.Z. Graphene nanoplatelet-fly ash based geopolymer composites. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 76, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyvandi, A.; Soroushian, P.; Abdol, N.; Balachandra, A.M. Surface-modified graphite nanomaterials for improved reinforcement efficiency in cementitious paste. Carbon 2013, 63, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghat, A.; Ram, M.K.; Zayed, A.; Kamal, R.; Shanahan, N. Investigation of physical properties of graphene-cement composite for structural applications. Open J. Compos. Mater. 2014, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Pang, S.D. Enhancement of barrier properties of cement mortar with graphene nanoplatelet. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 76, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Wang, K.; Lu, H.; Yang, Y.; Nutt, S. Covalent polymer functionaliazation of graphene nanosheets and mechanical properties of composites. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 7098–7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Hawkins, S.C.; Huynh, C.P.; Su, S. Carbon nanotube modified carbon composite monoliths as superior adsorbents for carbon dioxide capture. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2591–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhari, F.; Banthia, N. Cement-based sensors with carbon fibers and carbon nanotubes for piezoresistive sensing. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2012, 34, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.Q.; Han, Y.; Ma, H.N. Dispersion of carbon nanofibers in aqueous solution. Nano 2012, 7, 1250052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, F.; Lambert, J.; Duan, W.H. The influences of admixtures on the dispersion, workability, and strength of carbon nanotube–OPC paste mixtures. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2012, 34, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, M.A.; Rafiee, J.; Srivastava, I.; Wang, Z.; Song, H.; Yu, Z.Z.; Koratkar, N. Fracture and fatigue in graphene nanocomposites. Small 2010, 6, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Yazdani, B.; Zhu, Y. Recent Advances on Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Reinforced Ceramics Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 90–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Yan, H.; Reece, M.J.; Jiang, K. Toughening of zirconia/alumina composites by the addition of graphene platelets. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 32, 4185–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothiyal, N.C.; Sharma, S.; Mahajan, S.; Sethi, S. Characterization of reactive graphene oxide synthesized from ball–milled graphite: Its enhanced reinforcing effects on cement nanocomposites. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2016, 30, 915–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez de Ibarra, Y.; Gaitero, J.J.; Erkizia, E.; Campillo, I. Atomic force microscopy and nanoindentation of cement pastes with nanotube dispersions. Phys. Status Solidi A 2006, 203, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhateb, H.; Al-Ostaz, A.; Cheng, A.H.D.; Li, X. Materials genome for graphene-cement nanocomposites. J. Nanomech. Micromech. 2013, 3, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horszczaruk, E.; Mijowska, E.; Kalenczuk, R.J.; Aleksandrzak, M.; Mijowska, S. Nanocomposite of cement/graphene oxide–Impact on hydration kinetics and Young’s modulus. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 78, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradaran, S.; Moghaddam, E.; Basirun, W.J.; Mehrali, M.; Sookhakian, M.; Hamdi, M.; Nakhaei Moghaddam, M.R.; Alias, Y. Mechanical properties and biomedical applications of a nanotube hydroxyapatite-reduced graphene oxide composite. Carbon 2014, 69, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Sample | Plain Cement | GNP/Cement |
|---|---|---|
| Mean Spread Diameter (mm) | 89 ± 3 | 68 ± 2 |
| Sample | Total Intrusion Volume/(mL/g) | Total Pore Area/(m2/g) | Median Pore Diameter (Volume)/nm | Median Pore Diameter (Area)/nm | Average Pore Diameter/nm | Porosity/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plain cement | 0.0981 | 21.26 | 22 | 13 | 18 | 18.35 |
| GNP/cement | 0.0887 | 21 | 19 | 12 | 16 | 17.01 |
| CaO | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | SO3 | MgO | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 61.13 | 21.45 | 5.24 | 2.89 | 2.50 | 2.08 | 0.77 |
| Loss on Ignition/% | Setting Time/min | Special Surface Area/m2·kg−1 | Compressive Strength/MPa | Flexural Strength/MPa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Setting | Final Setting | 3 days | 28 days | 3 days | 28 days | ||
| 3.50 | 175 | 235 | 346 | 6.0 | 8.5 | 30.0 | 53.5 |
| Products | Particle Diameters/μm | Thickness/nm | Purity/% | Electrical Conductivity/(S/m) | Special Surface Area/m2·g−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x-GnP-M25 | 25 | 6–8 | ˃99.5 | 107 | 120–150 |
| Sample | Water-Cement Ratio | Mix Proportion (wt %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GNPs | MC | TBP | SP | ||
| Plain cement | 0.35 | 0 | 0 | 0.15 | 0.1 |
| GNP/cement | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.1 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, B.; Jiang, R.; Wu, Z. Investigation of the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Graphene Nanoplatelet-Cement Composite. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6110200
Wang B, Jiang R, Wu Z. Investigation of the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Graphene Nanoplatelet-Cement Composite. Nanomaterials. 2016; 6(11):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6110200
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Baomin, Ruishuang Jiang, and Zhenlin Wu. 2016. "Investigation of the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Graphene Nanoplatelet-Cement Composite" Nanomaterials 6, no. 11: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6110200
APA StyleWang, B., Jiang, R., & Wu, Z. (2016). Investigation of the Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Graphene Nanoplatelet-Cement Composite. Nanomaterials, 6(11), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6110200