Receptor-Meditated Endocytosis by Hyaluronic Acid@Superparamagnetic Nanovetor for Targeting of CD44-Overexpressing Tumor Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Synthesis and Surface Modification of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (SPIONs)
2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Analysis of Surface Modified SPIONs
2.3. Surface Charge by Zeta Potential
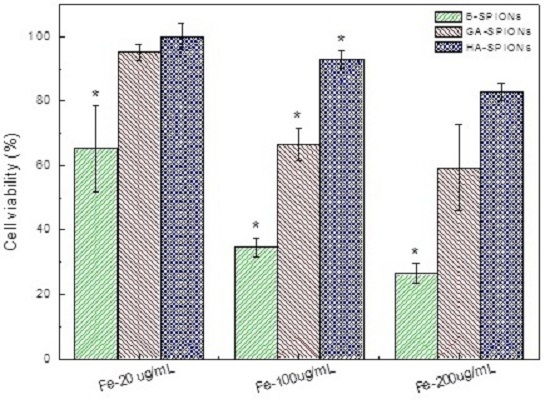
2.4. Intercellular Uptake
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Instrumentation
3.2. Peroxide Activation, Glutamic Acid (GA) Modification and Hyaluronan Sodium Salts (HA) Conjugation to Bare SPIONs (B-SPIONs)
3.3. Cytotoxicity by 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl Tetrazolium Bromide (MTT) Assays
3.4. Cytotoxicity by Live/Dead Two-Colored Cell Viability Assay
3.5. Cellular Internalization Study
3.6. Quantitative Analysis of Particle Cellular Internalization
3.7. Determination of Fe Content
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gorvin, C.M.; Wilmer, M.J.; Piret, S.E.; Harding, B.; van den Heuvel, L.P.; Wrong, O.; Jat, P.S.; Lippiat, J.D.; Levtchenko, E.N.; Thakker, R.V. Receptor-mediated endocytosis and endosomal acidification is impaired in proximal tubule epithelial cells of dent disease patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7014–7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.-M.; Ma, Y.-Q. Role of physicochemical properties of coating ligands in receptor-mediated endocytosis of nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5798–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Sze, R.; Zhang, M. Folic acid-peg conjugated superparamagnetic nanoparticles for targeted cellular uptake and detection by mri. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2006, 78, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraswati, T.E.; Ogino, A.; Nagatsu, M. Plasma-activated immobilization of biomolecules onto graphite-encapsulated magnetic nanoparticles. Carbon 2012, 50, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-T.; Ahmed, M.; Liu, Q.; Narain, R. Synthesis of cationic magnetic nanoparticles and evaluation of their gene delivery efficacy in hep g2 cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2012, 100, 2342–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Huang, J.; Guo, M.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.; Yan, H.; Liu, K. Biocompatible superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle dispersions stabilized with poly(ethylene glycol)-oligo(aspartic acid) hybrids. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2007, 80, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, S.; Singh, S.K.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Sinha, A.S.K.; Mandal, R.K.; Dash, D. Negative regulation of fibrin polymerization and clot formation by nanoparticles of silver. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 82, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, P.; Cardoso, R.; Correia, T.R.; Antunes, B.P.; Correia, I.J.; Ferreira, P. Surface modification of polyurethane films by plasma and ultraviolet light to improve haemocompatibility for artificial heart valves. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 113, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Lee, E.; Kim, D.K.; Jang, N.K.; Jeong, Y.Y.; Jon, S. Antibiofouling polymer-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as potential magnetic resonance contrast agents for in vivo cancer imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7383–7389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, C.-R.; Lin, C.-W.; Chou, C.-M.; Chung, C.-J.; He, J.-L. Surface modification of blood-contacting biomaterials by plasma-polymerized superhydrophobic films using hexamethyldisiloxane and tetrafluoromethane as precursors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 346, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Han, D.; Jiang, L. On improving blood compatibility: From bioinspired to synthetic design and fabrication of biointerfacial topography at micro/nano scales. Coll. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 85, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.K.; Dobson, J. Nanomedicine for targeted drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 6294–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arachchige, M.C.M.; Reshetnyak, Y.K.; Andreev, O.A. Advanced targeted nanomedicine. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 202, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Xu, K.; Gu, H.; Zheng, R.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Z.; Xu, B. Dopamine as a robust anchor to immobilize functional molecules on the iron oxide shell of magnetic nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9938–9939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Wang, B.; Sun, S. Dumbbell-like au-fe3o4 nanoparticles for target-specific platin delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4216–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Palma, R.; Peeters, S.; Van Bael, M.; van de Rul, H.; Bonroy, K.; Laureyn, W.; Mullens, J.; Borghs, G.; Maes, G. Silane ligand exchange to make hydrophobic superparamagnetic nanoparticles water-dispersible. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Y.W.; Lee, J.-H.; Cheon, J. Chemical desgin of nanoparticle probes for high-performance magnetic resonance imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 5122–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, M.H.; Rubin, J.C.; Sobrinho, P.G.; Tourinho, F.A. Biocompatible magnetic fluid precursors based on aspartic and glutamic acid modified maghemite nanostructures. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 225, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toole, B.P.; Wight, T.N.; Tammi, M.I. Hyaluronan-cell interaction in cancer and vascular disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 4593–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothenhöfer, M.; Grundmann, M.; Bernhardt, G.; Matysik, F.-M.; Buschauer, A. High performance anion exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection (hpaec-pad) for the sensitive determination of hyaluronan oligosaccharides. J. Chromatogr. B 2015, 988, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopoulos, T.A.; Papageorgakpoulou, N.; Theocharis, D.A.; Mastronikolis, N.S.; Papadas, T.A.; Vynios, D.H. Hyaluronidase and cd44 hyaluronan receptor expression in squamous cell laryngeal carcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2006, 1760, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marha, R.; Zoller, M. Cd44 in cancer progression: Adhesion, migration and growth regulation. J. Mol. Histol. 2004, 35, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-R.; Wheeler, M.A.; Wilson, C.M.; Iida, J.; Eng, D.; Simpson, M.A.; McCarthy, J.B.; Bullard, K.M. Hyaluronan facilitates invasion of colon carcinoma cells in vitro via interaction with cd44. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 4569–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMeo, C.; Panza, L.; Captitani, D.; Mannina, L.; Banzato, A.; Rondina, M.; Renier, D. Hyaluronan as carrier of carboranes for tumor targeting in boron neutron capture therapy. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, O.P.; Sun, W.; Hilborn, J.; Ossipov, D.A. In situ cross-linkable high molecular weight hyaluronan-bisphophonate conjugate for localized delivery and cell-specific targeting: A hydrogel linked prodrug approach. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8781–8783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.C.; Neslihan Alpay, S.; Klostergaard, J. Cd44: A validated target for improved delivery of cancer therapeutics. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morra, M. Engineering of biomaterials sruface by hyaluronan. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 1205–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitarresi, G.; Craparo, E.F.; Palumbo, F.S.; Carlisi, B.; Giammona, G. Composite nanoparticles based on hyaluronic acid chemically cross-linked with alpha,beta-polyaspartylhydrazide. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 1890–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouyani, T.; Prestwich, G.D. Functionalized derivatives of hyaluronic acid oligosaccharides: Drug carriers and novel biomaterials. Bioconjugate. Chem 1994, 5, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuang, S.C.; Neoh, K.G.; Kang, E.-T.; Pack, D.W.; Leckband, D.E. Polypyrrole nanospheres with magnetic and cell-targeting capabilities. Macromol. Rapid. Comm. 2007, 28, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhang, S.H.; Won, N.; Lee, T.-J.; Jin, H.; Nam, J.; Park, J.; Chung, H.; Park, H.-S.; Sung, Y.-E.; Hahn, S.W.; et al. Hyaluronic acid-quantum dot conjugates for in vivo lymphatic vessel imaging. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Z. Polysacchrides-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1650–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanson, G.T. Bioconjugate Techniques; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Rron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurences and Uses; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co.: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.M.; Li, S.; Kim, H.-H.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.B.; Muhammed, M.; Kim, D.K. Complete separation of magnetic nanoparticles via chemical cleavage of dextran by ethylenediamine for intracellular uptake. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereda, F.; de Vicente, J.; Hidalgo-Álvarez, R. Colloidal characterization of micron-sized rod-like magnetite particles. Coll. Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 319, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykhaylyk, O.; Antequera, Y.S.; Vlaskou, D.; Plank, C. Generation of magnetic nonviral gene tranfer agents and magnetofection in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2391–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, K.S.; Lin, M.M.; Lee, H.-J.; Tae, K.-S.; Kang, B.-S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, N.S.; Jeong, Y.G.; Han, S.-Y.; Kim, D.K. Receptor-Meditated Endocytosis by Hyaluronic Acid@Superparamagnetic Nanovetor for Targeting of CD44-Overexpressing Tumor Cells. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6080149
Yu KS, Lin MM, Lee H-J, Tae K-S, Kang B-S, Lee JH, Lee NS, Jeong YG, Han S-Y, Kim DK. Receptor-Meditated Endocytosis by Hyaluronic Acid@Superparamagnetic Nanovetor for Targeting of CD44-Overexpressing Tumor Cells. Nanomaterials. 2016; 6(8):149. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6080149
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Kwang Sik, Meng Meng Lin, Hyun-Ju Lee, Ki-Sik Tae, Bo-Sun Kang, Je Hun Lee, Nam Seob Lee, Young Gil Jeong, Seung-Yun Han, and Do Kyung Kim. 2016. "Receptor-Meditated Endocytosis by Hyaluronic Acid@Superparamagnetic Nanovetor for Targeting of CD44-Overexpressing Tumor Cells" Nanomaterials 6, no. 8: 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6080149
APA StyleYu, K. S., Lin, M. M., Lee, H.-J., Tae, K.-S., Kang, B.-S., Lee, J. H., Lee, N. S., Jeong, Y. G., Han, S.-Y., & Kim, D. K. (2016). Receptor-Meditated Endocytosis by Hyaluronic Acid@Superparamagnetic Nanovetor for Targeting of CD44-Overexpressing Tumor Cells. Nanomaterials, 6(8), 149. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6080149